Purpose: Designing, deciding
Concerns: Consistency and completeness, reduction of complexity
Scope: Multiple layer/Multiple aspect
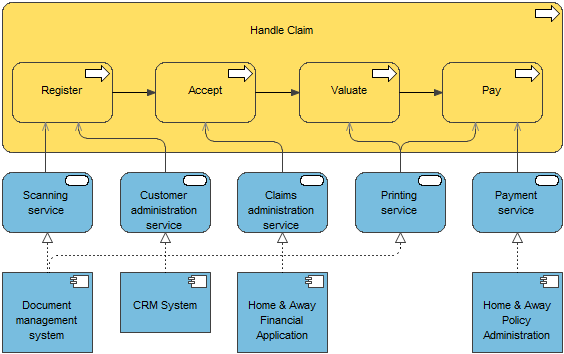
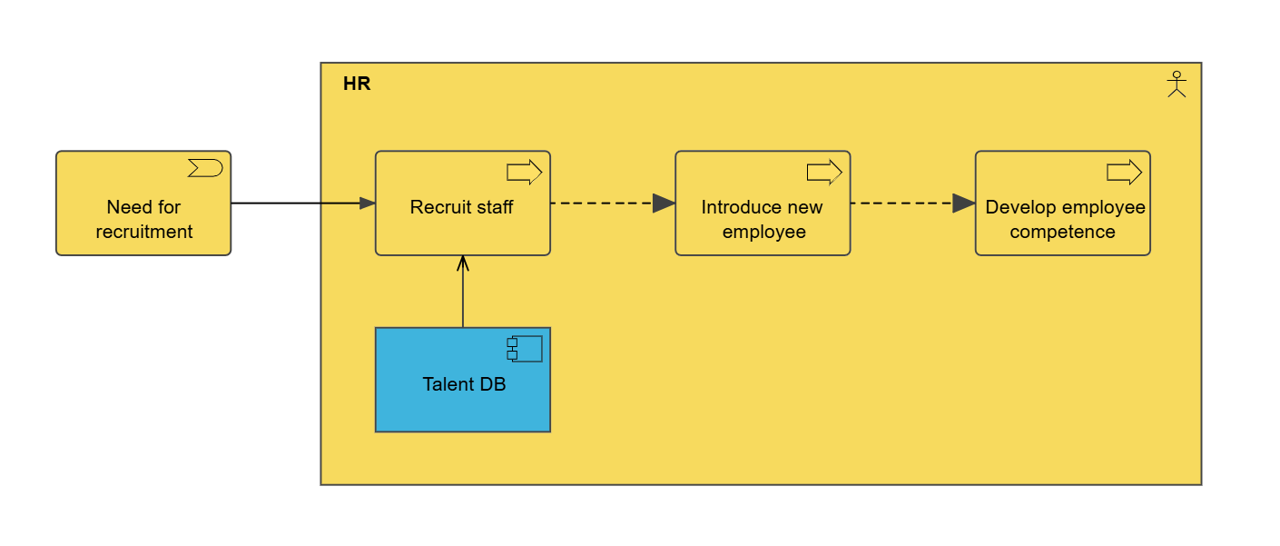
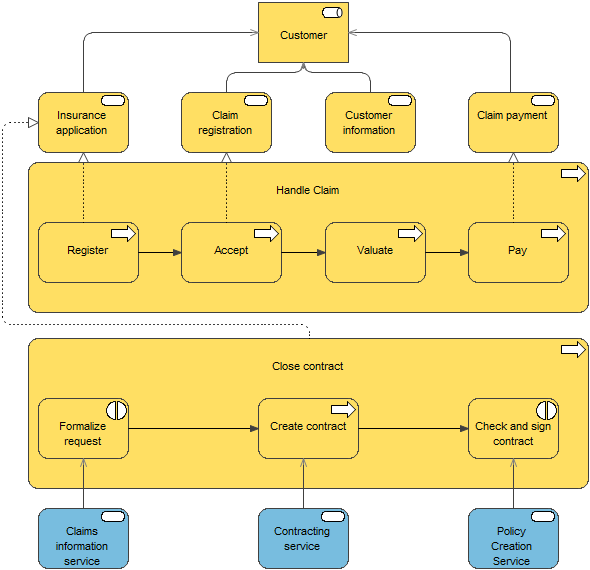
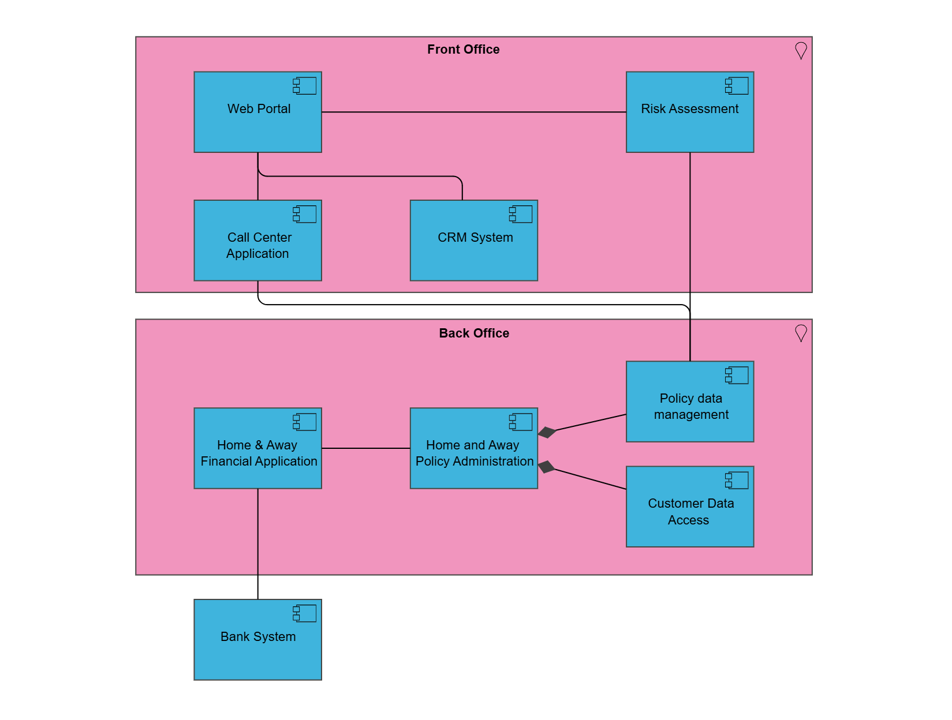
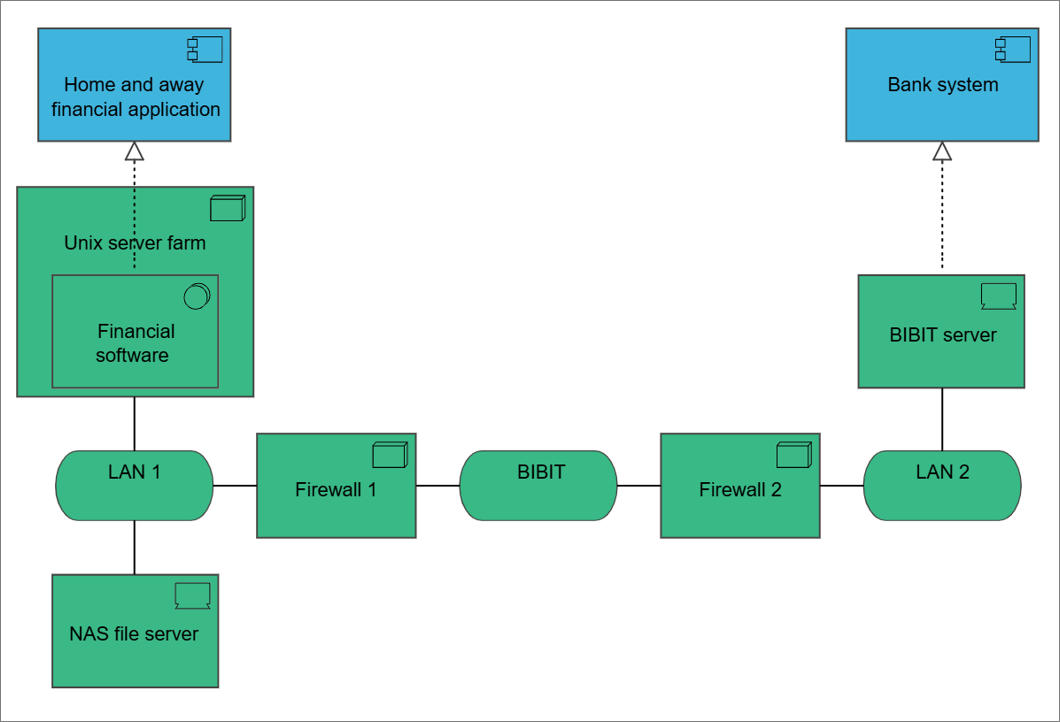
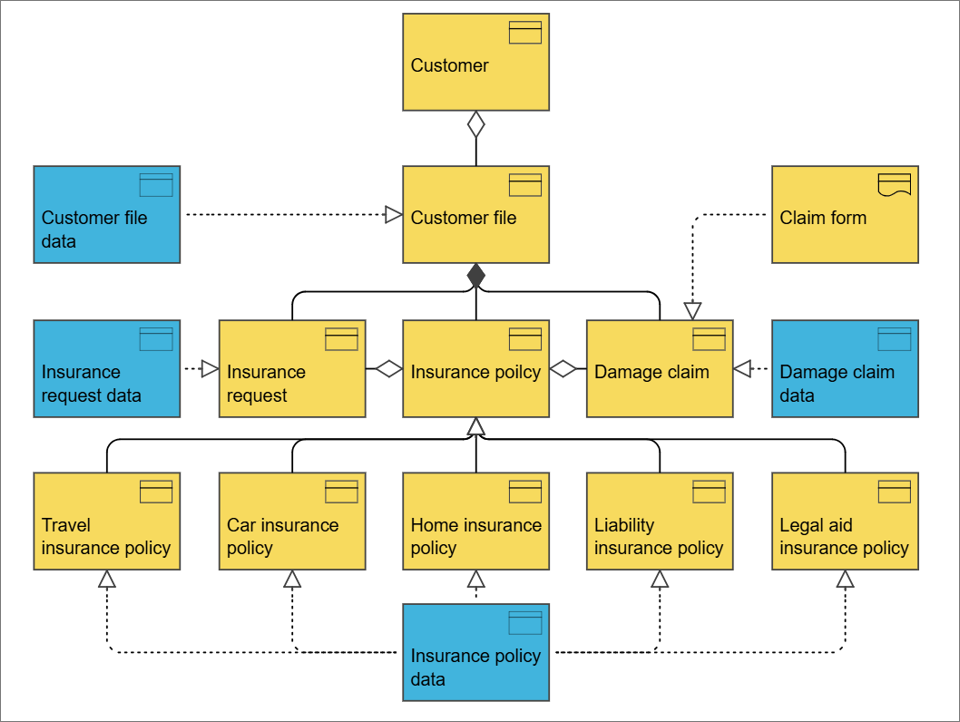
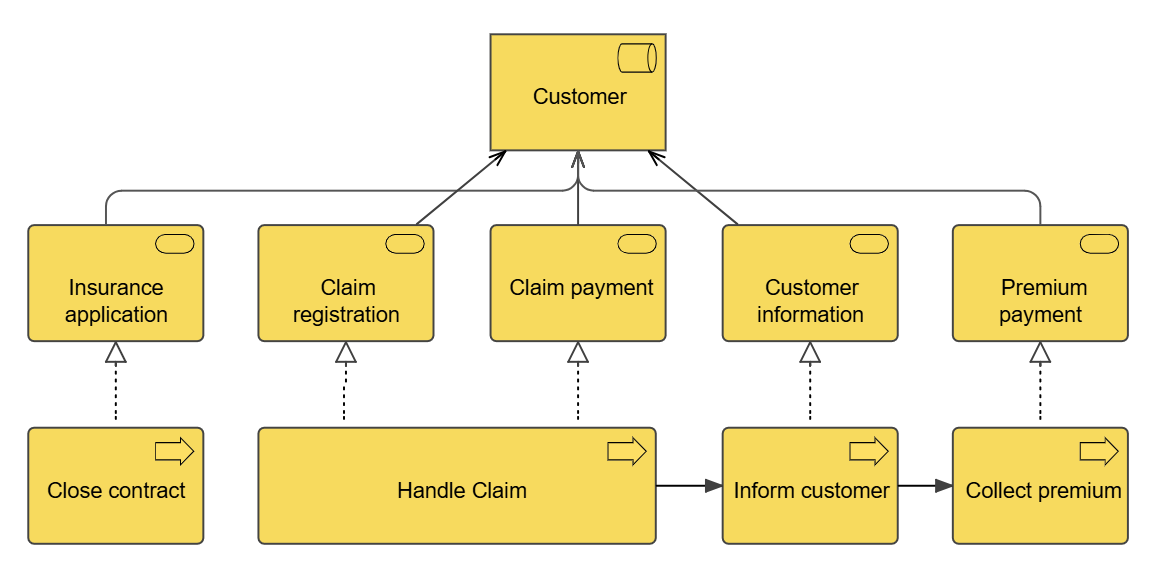
The application usage viewpoint describes how applications are used to support one or more business processes, and how they are used by other applications. It can be used in designing an application by identifying the services needed by business processes and other applications, or in designing business processes by describing the services that are available. Furthermore, since it identifies the dependencies of business processes upon applications, it may be useful to operational managers responsible for these processes.
Abstraction Level
Coherence
Layer
Business and application layers
Aspects
Behavior, active structure, passive structure