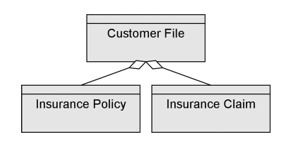
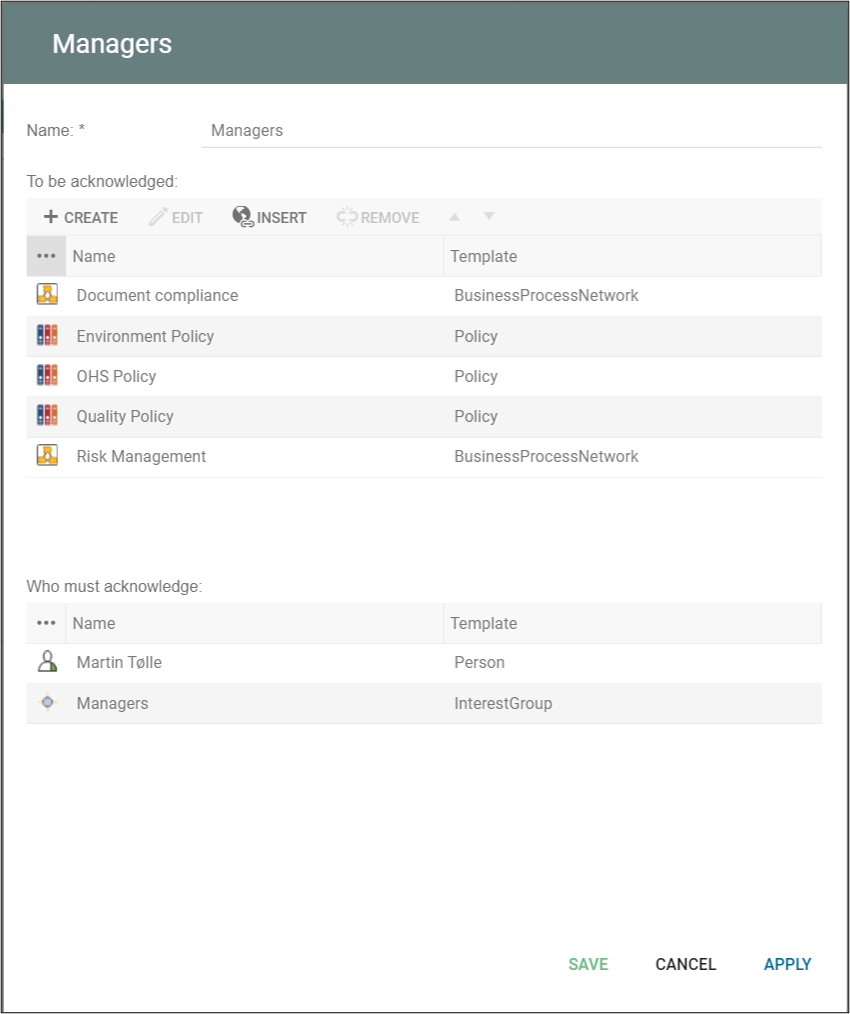
Access ArchiMate is one out of three ‘Dependency Relationships’ from the ArchiMate metamodel. IT represents a data dependency and is denoted by a dashed line.
Dependency relationships describe how elements support or are used by other elements. Three types of dependency relationship are distinguished:
- The servingrelationship represents a control dependency, denoted by a solid line.
- The accessrelationship represents a data dependency, denoted by a dashed line.
- The influencerelationship is the weakest type of dependency, used to model how motivation elements are influenced by other elements.
Note that, although the notation of these relationships resembles the notation of the dependency relationship in UML, these relationships have distinct meanings in ArchiMate notation and (usually) point in the opposite direction. One advantage of this is that it yields models with directionality, where most of the arrows that represent such supporting, influencing, serving, or realizing dependencies point ‘upwards’ towards the client/user/business. Another reason for this direction, in particular for the serving relationship, is that it abstracts from the ‘caller’ or ‘initiator’, since a service may be delivered proactively or reactively. The direction of delivery is always the same, but the starting point for the interaction can be on either end. UML’s dependency is often used to denote the latter, showing that the caller depends on some operation that is called. However, for modelling this type of initiative, the ArchiMate language provides the triggering relationship, which can be interpreted as a dynamic (i.e., temporal) dependency. Similarly, the flow relationship is used to model how something (usually information) is transferred from one element to another, which is also a dynamic kind of dependency.
If you want to learn more about the ArchiMate language, you can find the specification here