Command language commands executed at time of start up.
Archives: Templates
Templates and model types in the QualiWare platform.
Realization
The sender realizes an interface used by the receiver.
Realization:Archimate
The realization relationship indicates that more abstract entities (“what” or “logical”) are realized by means of more tangible entities (“how” or “physical”). The realization relationship is used to model run-time realization; for example, that a business process realizes a business service, and that a data object realizes a business object, an artifact realizes an application component, or a core element realizes a motivation element.
The usual interpretation of a realization relationship is that the whole or part of the source element realizes the whole of the target element. This means that if, for example, two internal behavior elements have a realization relationship to the same service, either of them can realize the complete service. If both internal behavior elements are needed to realize, the grouping element or a junction can be used. For weaker types of contribution to the realization of an element, the influence relationship should be used.
Recycling
Flow of reusable material.
Regulation
A Regulation contains a reference to a specific paragraph in the legislation controlling the business. It can also contain a reference in a specific relevant standard i.e. ISO or ANSI.
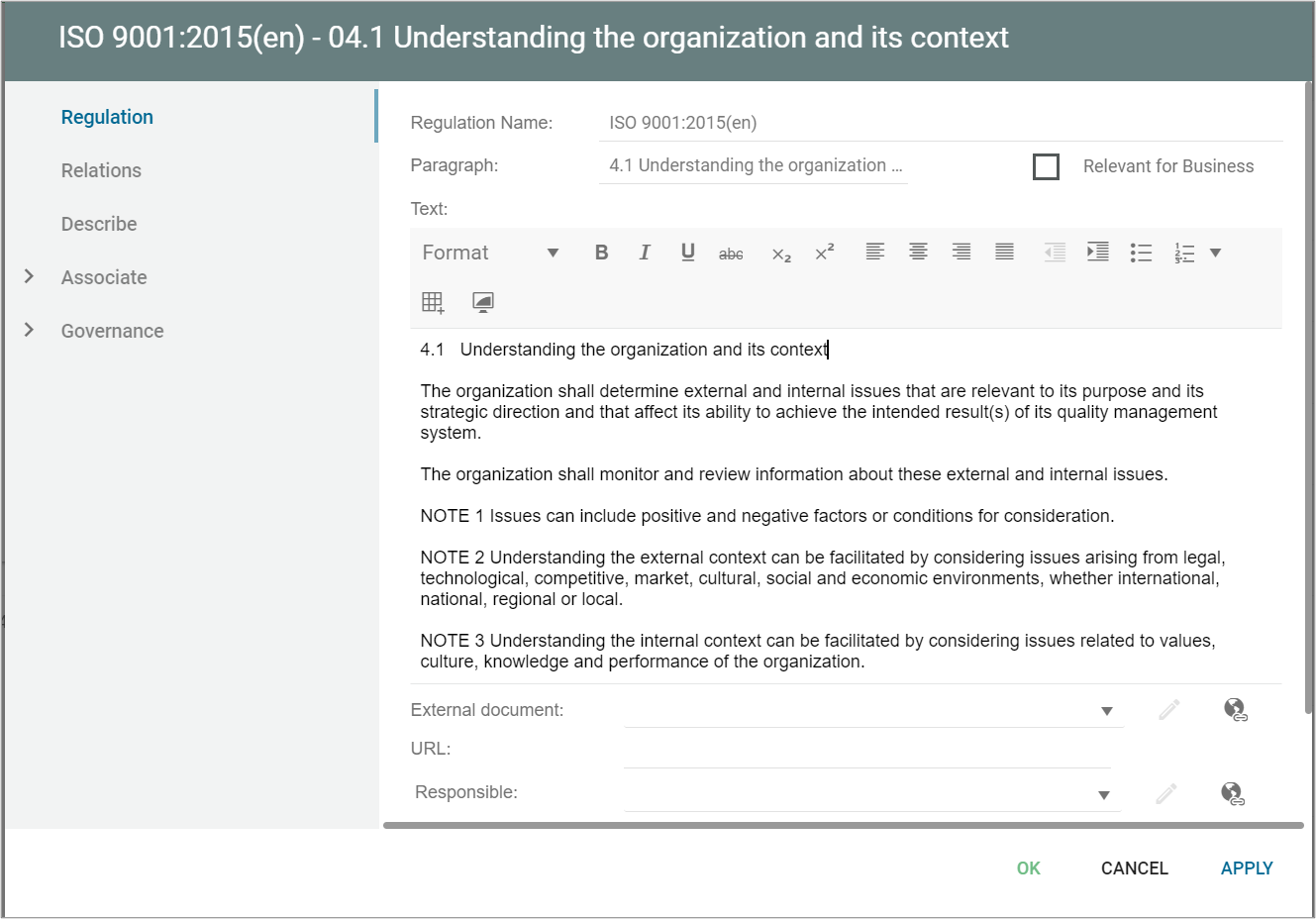
A regulation is used to relate an object (e.g. a Process) to a relevant Regulation. This relation is made with the “ComplianceWith” relation available on the complying object (e.g. a process). This will enable the user to trace the conformance to a specific Regulation in the Repository.
A regulation can be a part of a RegulationDiagram, and used document Compliance, e.g. in a Compliance Matrix.
Relationship Constraint
A constraint between two associations such as exclusive or (xor).
Report
A report executed from a Document Fragment.
Report Field
Description of a field on a ReportLayout.
Report Page
The border for a page in a report layout
Requirement
A Requirement is a prioritized demand placed on the project by one of its interested parties. Often it is the buyer the user or the management that have Requirements to the scope or results of the projects. But it can also technical requirements that appears because of constraints in the physical equipment or the algorithmic solutions chosen.
It is recommended to build a Requirement hierarchy by relating one Requirement to the sub requirements that composes it.
Requirement can be modelled in a Requirement Model.
