Concerns: Architecture mission and strategy, motivation
Purpose: Designing, deciding, informing
Scope: Motivation
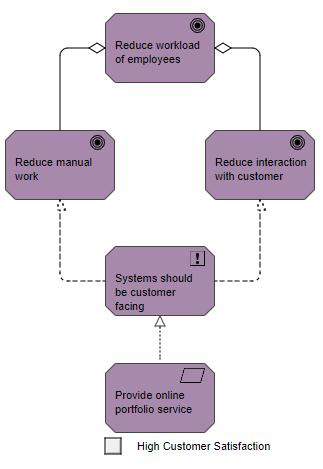
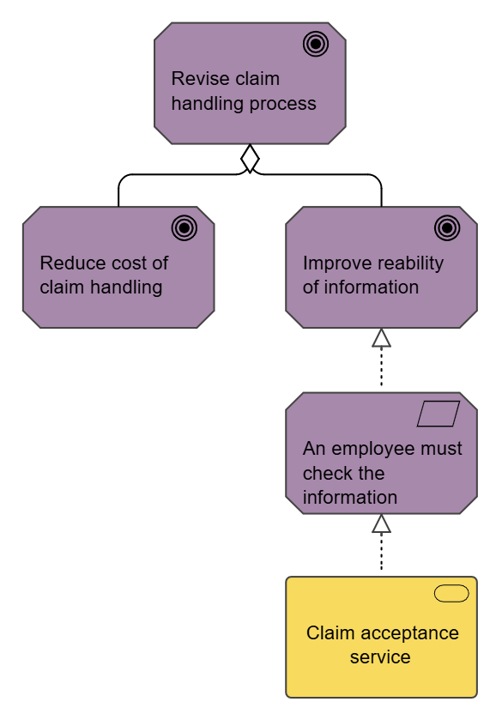
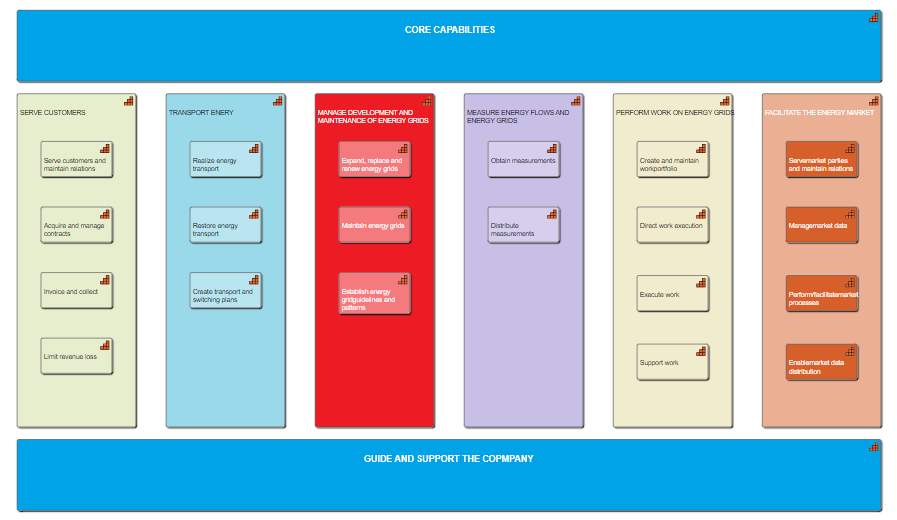
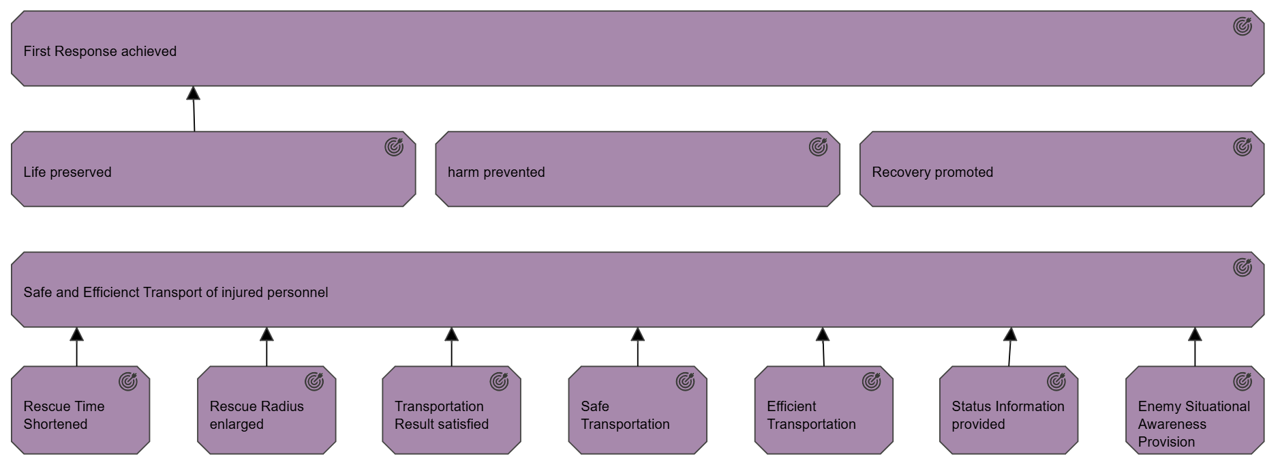
The stakeholder viewpoint allows the analyst to model the stakeholders, the internal and external drivers for change, and the assessments (in terms of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) of these drivers. Also, the links to the initial (high-level) goals that address these concerns and assessments may be described. These goals form the basis for the requirements engineering process, including goal refinement, contribution and conflict analysis, and the derivation of requirements that realize the goals.