Capabilities can be described using the Capability template.
A capability can be described and rated in accordance with the business importance, current maturity and target maturity.
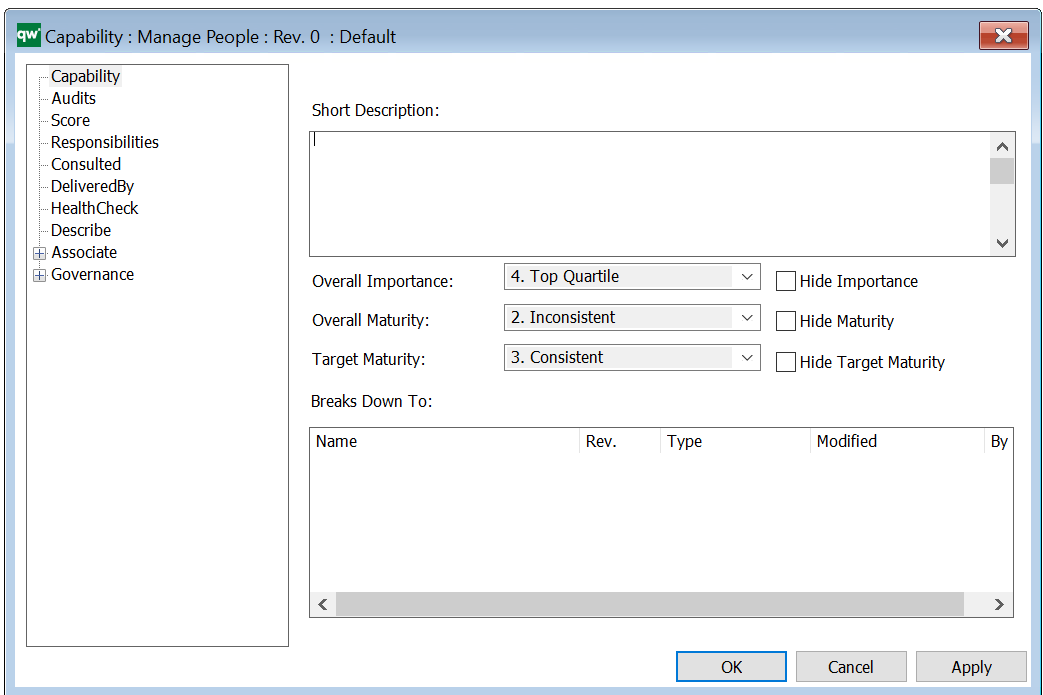
The capability rating can be illustrated on the object. The stripe on the left side represents the Business Importance and two dots represent the Business Maturity and Target Maturity.

On the Score tab, additional scoring possibilities are available:
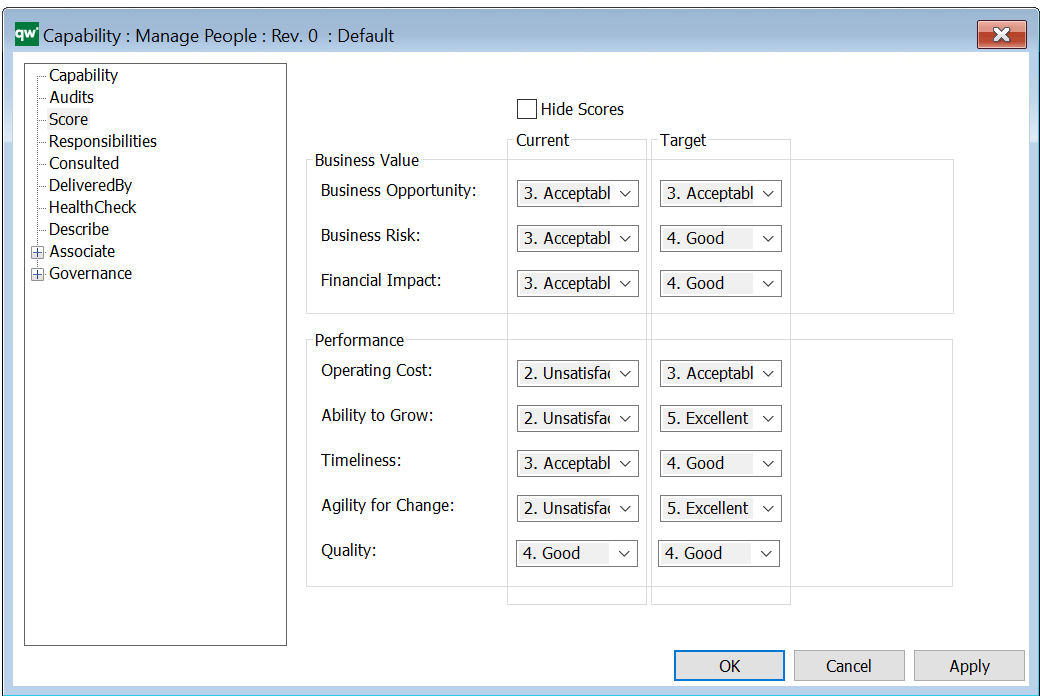
These scoring can also be shown on the object:
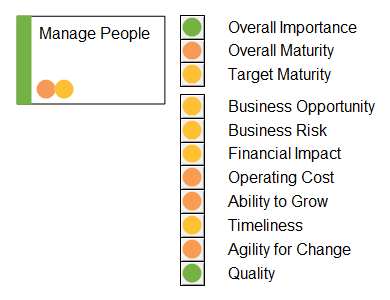
Capabilities are modelled in BusinessCapabilityModel-diagrams.