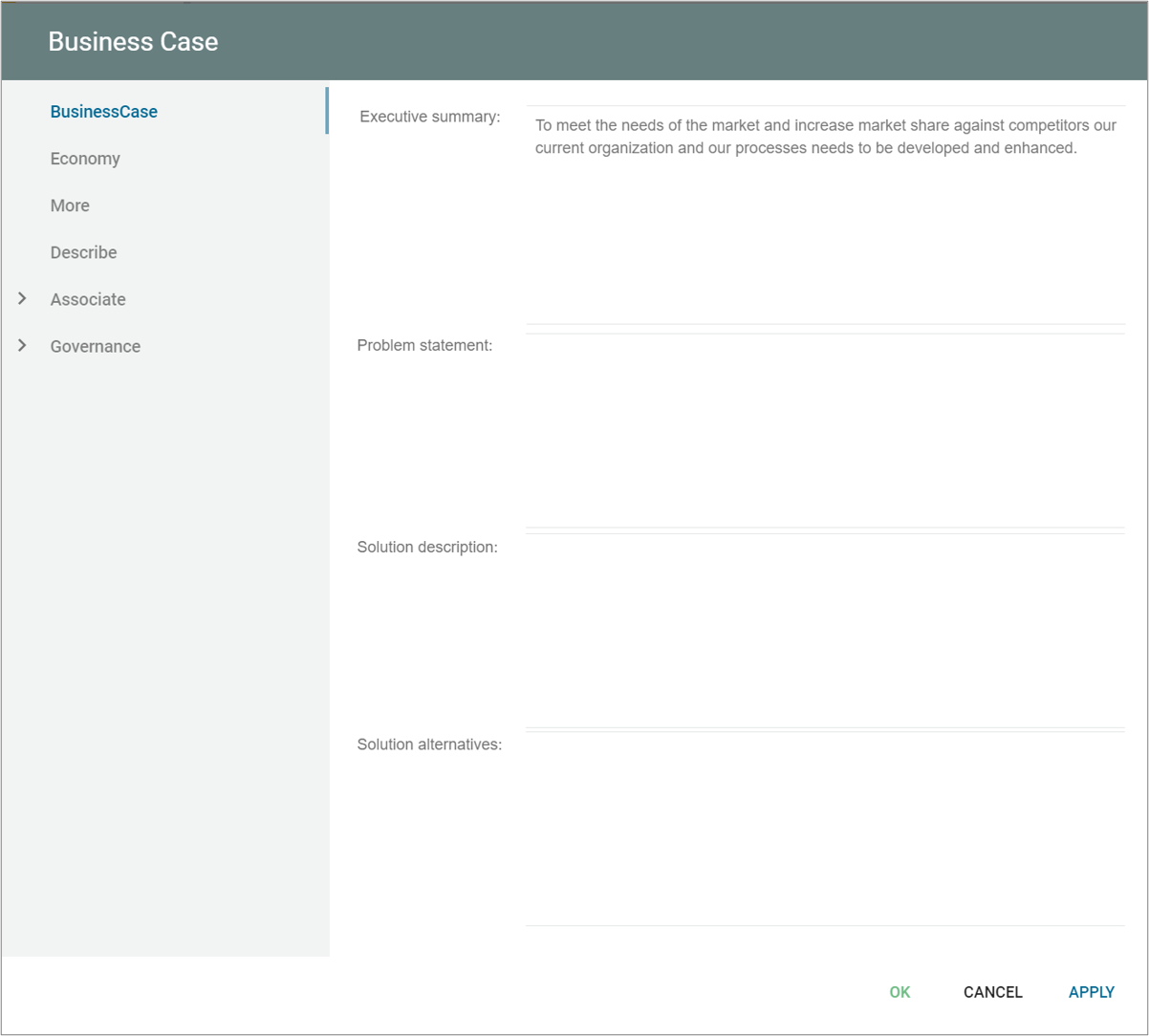
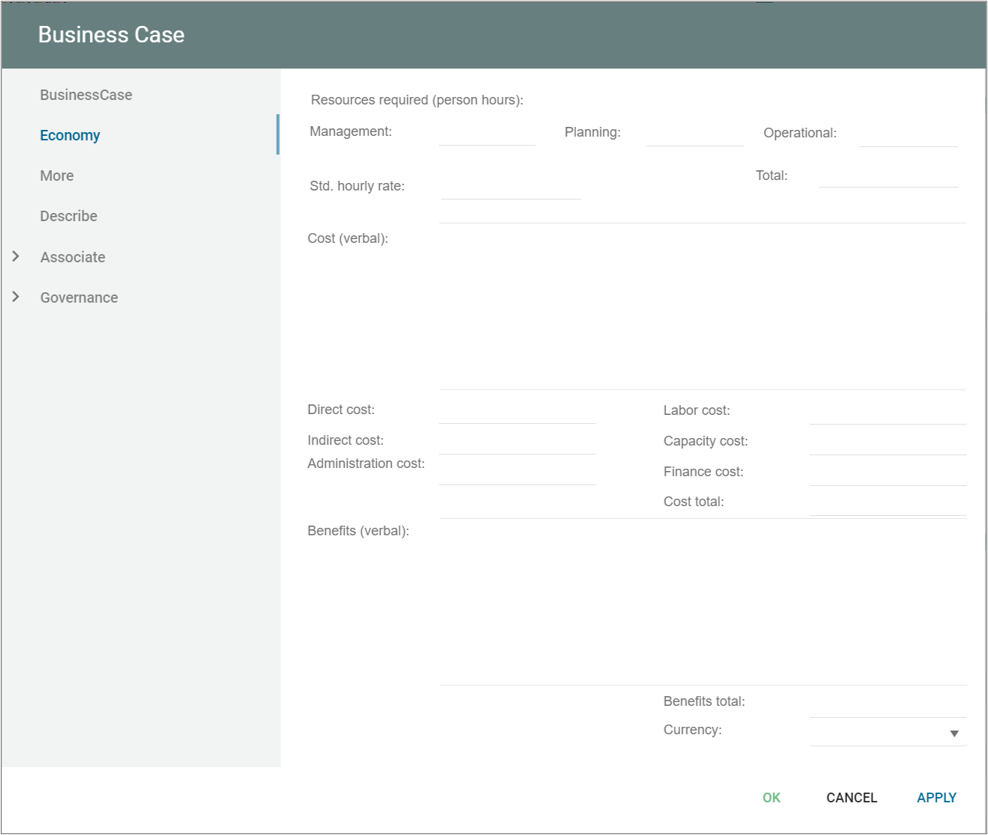
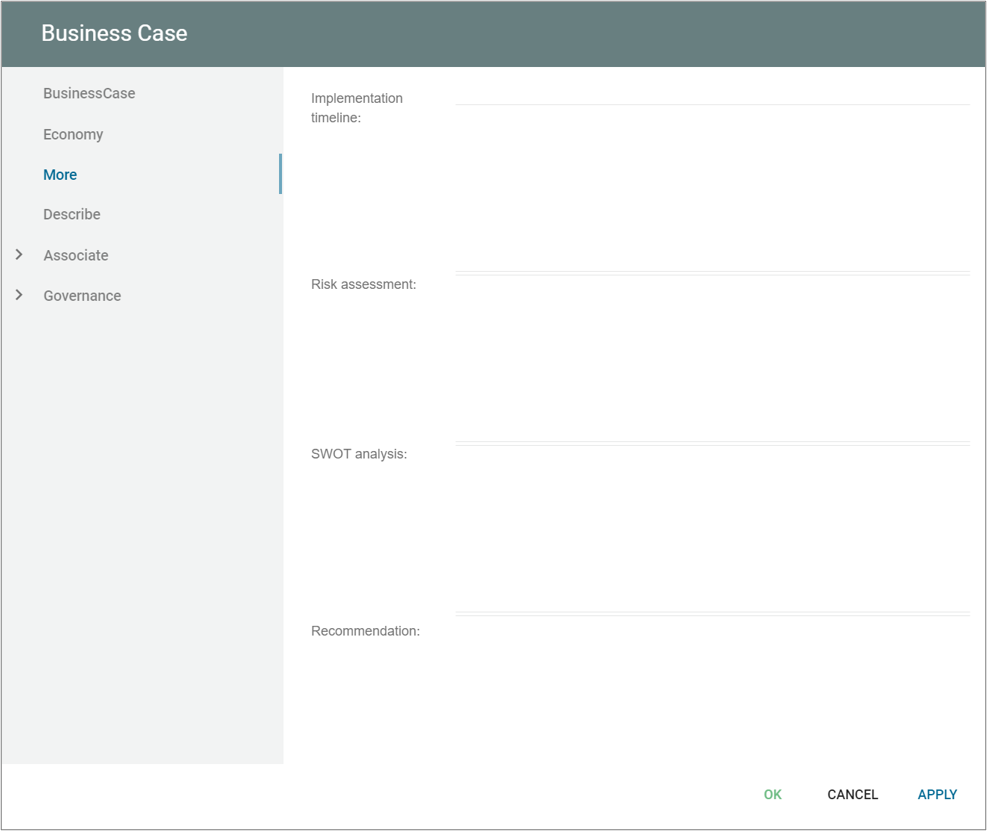
Business Knowledge Model (BKM) is a structured representation of the knowledge and business rules that are used to inform decisions. It is a part of the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) and is used to define the business concepts, rules, and constraints that are relevant to the decision-making process.
A BKM is typically used to describe the business logic and rules that govern a particular decision or process. It is a way to capture and organize the knowledge and expertise of a business domain expert and make it accessible to others involved in the decision-making process.
BKMs are designed to be modular and reusable, allowing them to be easily integrated into other business processes and decision-making models. They can be used in conjunction with decision tables, decision trees, and other decision-making elements to provide the information and rules necessary to make informed decisions.