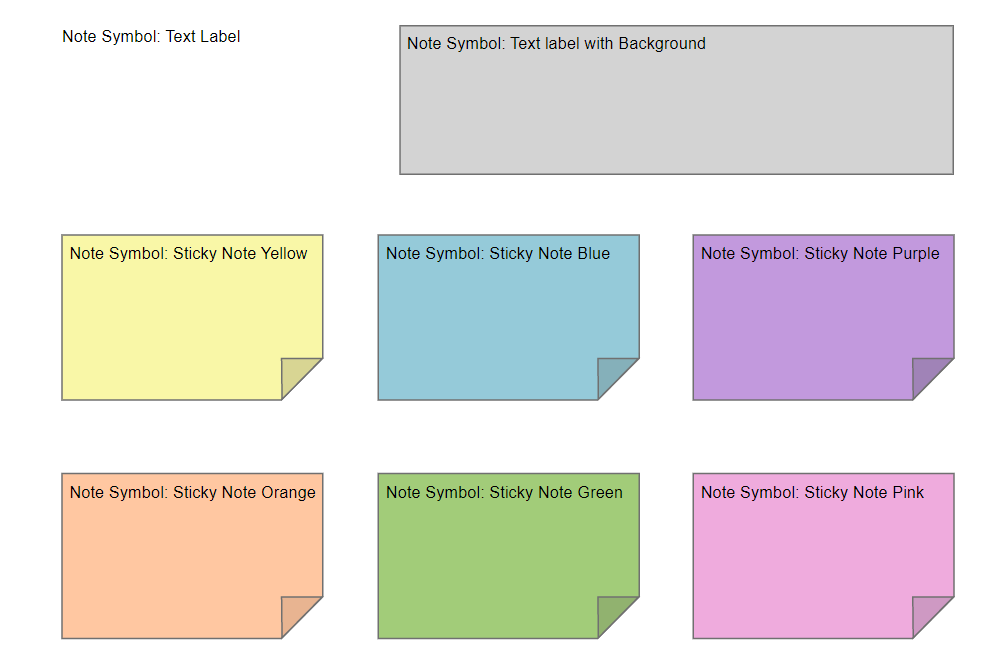
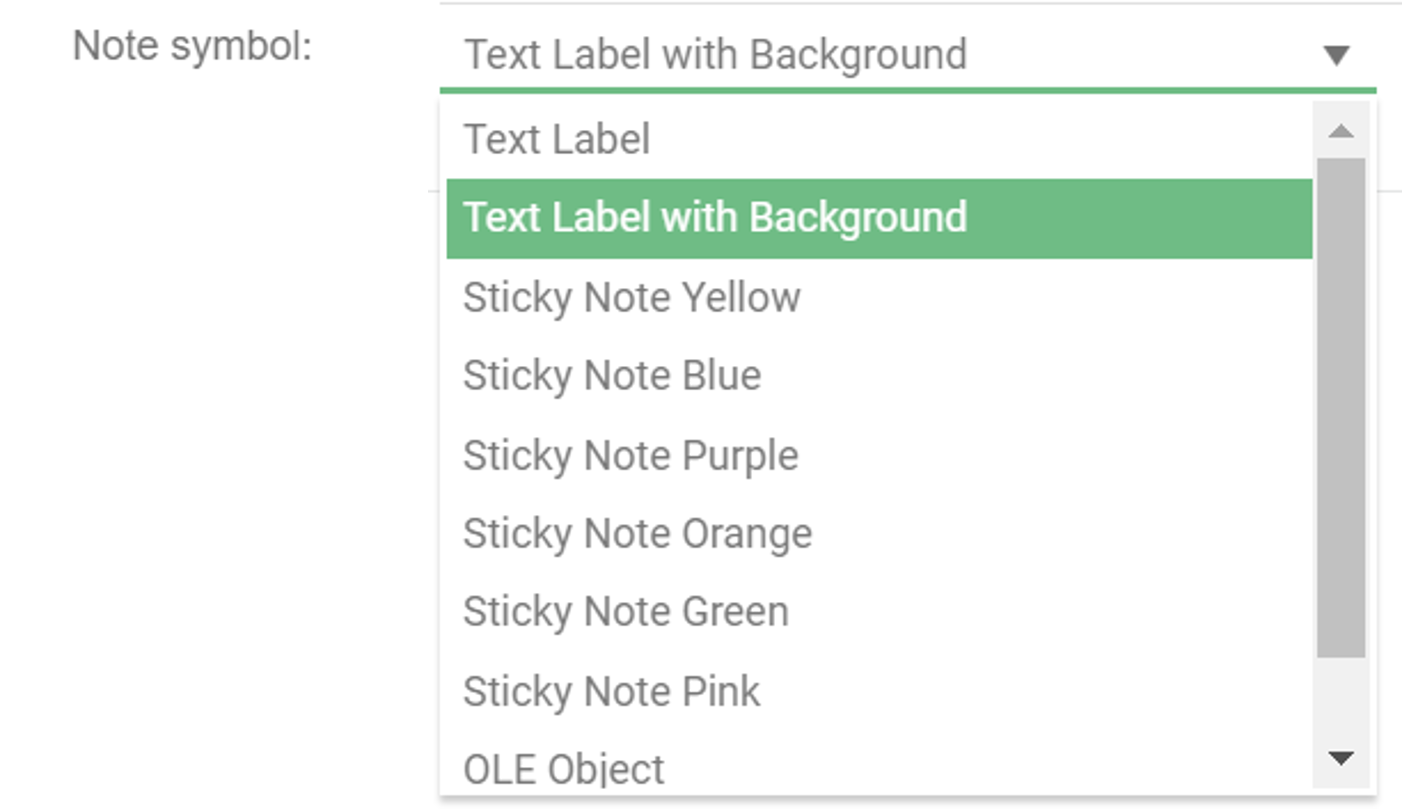
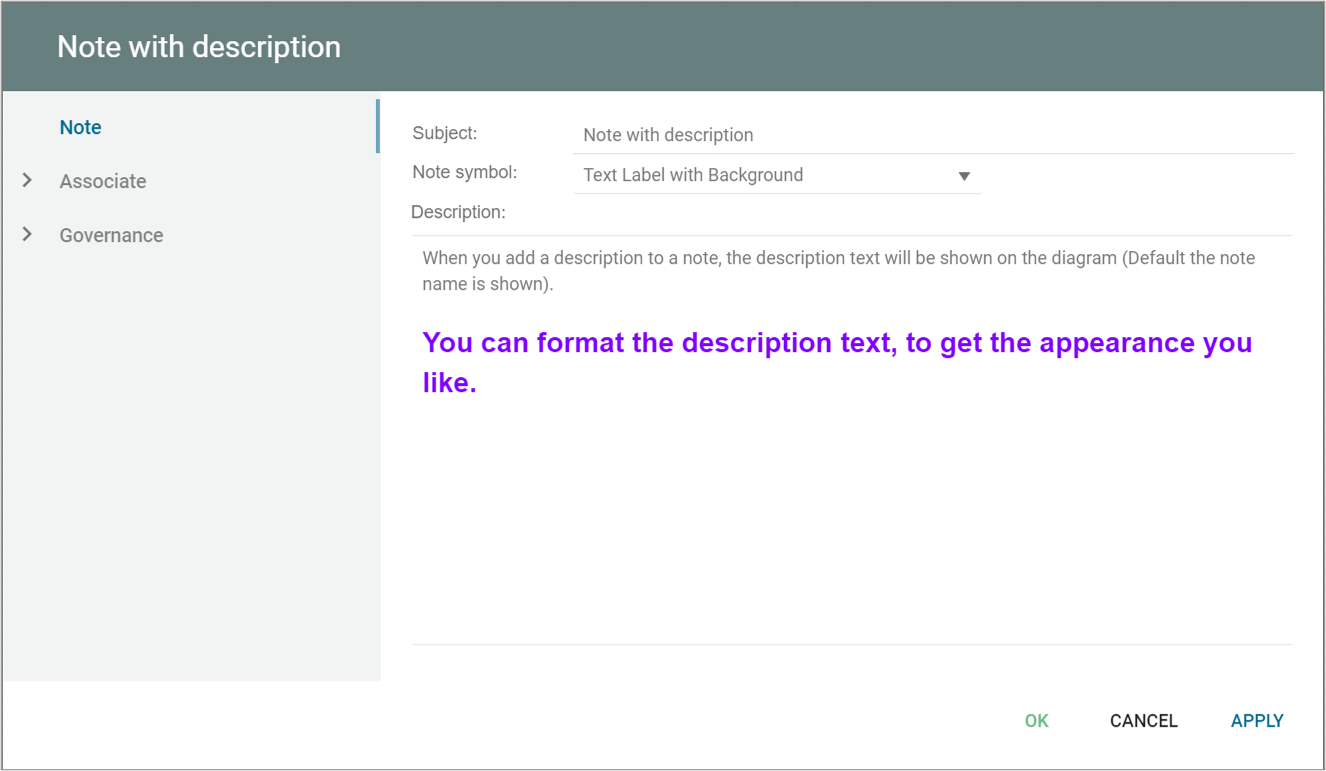
A DataEntity represent a logical group of information – a category of information.
In the early phases of a system analysis or even a business analysis a DataEntity is used to describe physical objects like ‘Customer’, ‘Order’ or ‘Product’. Or it is used to describe important concepts in the modelled system or its surroundings.
In a later phase a DataEntity will represent a smaller normalized informationgroup.
One of the most important characteristics of a DataEntity is, that it can be uniquely identified using a relation to a Key, and that it has got non-key Attribute describing its information content.
In QualiWare Lifecycle Manager the concept of a DataEntity includes a description of the operations performed on the DataEntity during its lifecycle – i.e. from it is created for the first time in the system, until it is deleted. This is accomplished by letting the user relate a DataEntity to a series of operations – here called Methods. This object oriented approach makes it possible for the designer to separate into small reusable groups related information and functions.
When a DataEntity is created it is good practice to give it a primary key. When this is done and the OK-button on the DataEntity dialog is pressed, the key attributes is automatically transferred to the attribute link list.