A workcenter can be a part of a Production Site, used to graphically contain production assets such as ProductionLines, Equipments, FixedInstallations.
Additionally it is possible to describe the workcenter from a economic point of view.

A workcenter can be a part of a Production Site, used to graphically contain production assets such as ProductionLines, Equipments, FixedInstallations.
Additionally it is possible to describe the workcenter from a economic point of view.

A weakness refers to a negative aspect of a process, workflow, or journey that hinders its success. It is a characteristic or attribute that creates obstacles and challenges that need to be addressed. For example, in a customer journey map, a weakness might refer to the poor navigation of a website or the long wait times for customer service. In a process map, a weakness might refer to the inefficiency or unreliability of a particular stage in the process.
Produces a value based on a specification, such as a constant or expression.
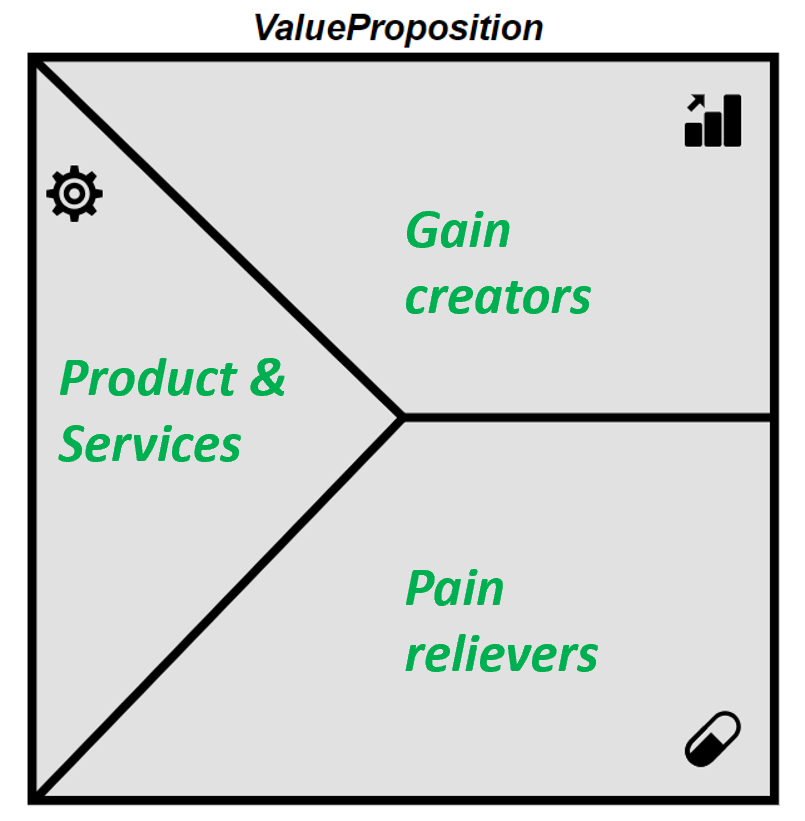
A value proposition stands as a promise by a company to a customer or market segment.
The proposition is an easy-to-understand reason why a customer should buy a product or service from that particular business.
A value propostion can be shown as a symbol in a ValueStream

In a ValuePropostionCanvas a ValueProposition can be shown as a “canvas” where Gains and Pains can be mapped together with the Products & Services for a ValueProposition.
Holds a constant value used by an action, often for configuration or control.
In a workflow diagram, the user interface symbol represents the point at which a user interacts with a system or application. It indicates the point where a user inputs data or makes a selection, and where the system displays information or results back to the user. The user interface symbol is typically represented by a rectangle with rounded corners, and may include labels to indicate the specific type of interface, such as a button or text box. It is an important symbol in workflow diagrams as it helps to identify the different touchpoints where users interact with the system, and can be used to guide the design of the user interface for optimal usability and efficiency.
A use case represents an example of how the system could be used.
A use case is modelled in a use case diagram.
A touchpoint refers to any interaction or point of contact that a customer has with a company during their journey. Touchpoints can occur at various stages of the customer journey, from initial awareness of a company’s products or services, to post-purchase support and beyond.
Touchpoints can be physical (such as visiting a store or interacting with a sales representative) or digital (such as using a company’s website, mobile app, or social media channels). They can also be proactive (such as a sales call or promotional email) or reactive (such as a customer service call or complaint).
Each touchpoint represents an opportunity for a company to engage with its customers and make a positive impact on their experience. Touchpoints can influence a customer’s perceptions of a company, and if handled well, can lead to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
When mapping the customer journey, it is important to consider all of the different touchpoints that a customer may encounter, and to design them to be as positive and seamless as possible. This can help to create a more consistent and enjoyable customer experience and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In a Strategic Roadmap, the symbol Timeframe is used to represent a specific period of time or a range of time during which a project, initiative, or objective will be executed. It usually appears as a horizontal bar or a line on the roadmap, and its length or position can indicate the duration or start/end date of the associated activity.
For example, in a Strategic Roadmap for a software development company, the Timeframe symbol might represent a six-month period during which the company plans to release a new product. The length and position of the symbol on the roadmap would indicate the start and end dates of the development, testing, and launch phases of the project. By including the Timeframe symbol on the roadmap, stakeholders can quickly understand the timing and duration of the company’s initiatives and plan their own activities accordingly.
A threat refers to a negative external factor that can impact a process, workflow, or journey. It is a potential risk or challenge that needs to be recognized and addressed. For example, in a customer journey map, a threat might refer to a new competitor or a change in regulations that can impact the business.