Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity
Version 1.0
National Institute of Standards and Technology
February 12, 2014
Executive Summary
The national and economic security of the United States depends on the reliable functioning of critical infrastructure. Cybersecurity threats exploit the increased complexity and connectivity of critical infrastructure systems, placing the Nation’s security, economy, and public safety and health at risk. Similar to financial and reputational risk, cybersecurity risk affects a company’s bottom line. It can drive up costs and impact revenue. It can harm an organization’s ability to innovate and to gain and maintain customers.To better address these risks, the President issued Executive Order 13636, “Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity,” on February 12, 2013, which established that “[i]t is the Policy of the United States to enhance the security and resilience of the Nation’s critical infrastructure and to maintain a cyber environment that encourages efficiency, innovation, and economic prosperity while promoting safety, security, business confidentiality, privacy, and civil liberties.” In enacting this policy, the Executive Order calls for the development of a voluntary risk-based Cybersecurity Framework – a set of industry standards and best practices to help organizations manage cybersecurity risks. The resulting Framework, created through collaboration between government and the private sector, uses a common language to address and manage cybersecurity risk in a cost-effective way based on business needs without placing additional regulatory requirements on businesses.
The Framework focuses on using business drivers to guide cybersecurity activities and considering cybersecurity risks as part of the organization’s risk management processes. The Framework consists of three parts: the Framework Core, the Framework Profile, and the Framework Implementation Tiers. The Framework Core is a set of cybersecurity activities, outcomes, and informative references that are common across critical infrastructure sectors, providing the detailed guidance for developing individual organizational Profiles. Through use of the Profiles, the Framework will help the organization align its cybersecurity activities with its business requirements, risk tolerances, and resources. The Tiers provide a mechanism for organizations to view and understand the characteristics of their approach to managing cybersecurity risk.
The Executive Order also requires that the Framework include a methodology to protect individual privacy and civil liberties when critical infrastructure organizations conduct cybersecurity activities. While processes and existing needs will differ, the Framework can assist organizations in incorporating privacy and civil liberties as part of a comprehensive cybersecurity program.
The Framework enables organizations – regardless of size, degree of cybersecurity risk, or cybersecurity sophistication – to apply the principles and best practices of risk management to improving the security and resilience of critical infrastructure. The Framework provides organization and structure to today’s multiple approaches to cybersecurity by assembling standards, guidelines, and practices that are working effectively in industry today. Moreover, because it references globally recognized standards for cybersecurity, the Framework can also be used by organizations located outside the United States and can serve as a model for international cooperation on strengthening critical infrastructure cybersecurity.
The Framework is not a one-size-fits-all approach to managing cybersecurity risk for critical infrastructure. Organizations will continue to have unique risks – different threats, different vulnerabilities, different risk tolerances – and how they implement the practices in the Framework will vary. Organizations can determine activities that are important to critical service delivery and can prioritize investments to maximize the impact of each dollar spent. Ultimately, the Framework is aimed at reducing and better managing cybersecurity risks.
The Framework is a living document and will continue to be updated and improved as industry provides feedback on implementation. As the Framework is put into practice, lessons learned will be integrated into future versions. This will ensure it is meeting the needs of critical infrastructure owners and operators in a dynamic and challenging environment of new threats, risks, and solutions.
Use of this voluntary Framework is the next step to improve the cybersecurity of our Nation’s critical infrastructure – providing guidance for individual organizations, while increasing the cybersecurity posture of the Nation’s critical infrastructure as a whole.
Section 2
Framework Basics
The Framework provides a common language for understanding, managing, and expressing cybersecurity risk both internally and externally. It can be used to help identify and prioritize actions for reducing cybersecurity risk, and it is a tool for aligning policy, business, and technological approaches to managing that risk. It can be used to manage cybersecurity risk across entire organizations or it can be focused on the delivery of critical services within an organization. Different types of entities – including sector coordinating structures, associations, and organizations – can use the Framework for different purposes, including the creation of common Profiles.
The Framework Core (download Excel) provides a set of activities to achieve specific cybersecurity outcomes, and references examples of guidance to achieve those outcomes. The Core is not a checklist of actions to perform. It presents key cybersecurity outcomes identified by industry as helpful in managing cybersecurity risk. The Core comprises four elements: Functions, Categories, Subcategories, and Informative References, depicted in Figure 1:
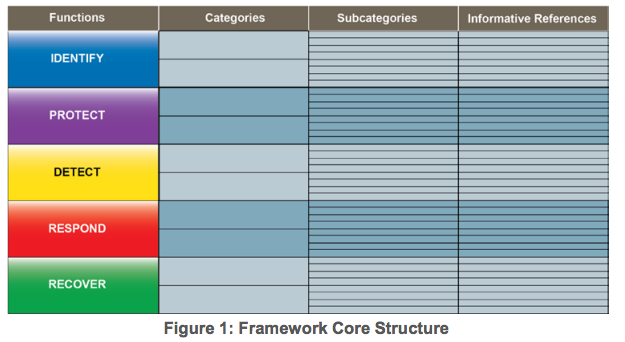
The Framework Core elements work together as follows:
- Functions organize basic cybersecurity activities at their highest level. These Functions are Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. They aid an organization in expressing its management of cybersecurity risk by organizing information, enabling risk management decisions, addressing threats, and improving by learning from previous activities. The Functions also align with existing methodologies for incident management and help show the impact of investments in cybersecurity. For example, investments in planning and exercises support timely response and recovery actions, resulting in reduced impact to the delivery of services.
- Categories are the subdivisions of a Function into groups of cybersecurity outcomes closely tied to programmatic needs and particular activities. Examples of Categories include Asset Management, Access Control, and Detection Processes.
- Subcategories further divide a Category into specific outcomes of technical and/or management activities. They provide a set of results that, while not exhaustive, help support achievement of the outcomes in each Category. Examples of Subcategories include External information systems are catalogued, Data-at-rest is protected, and Notifications from detection systems are investigated.
- Informative References are specific sections of standards, guidelines, and practices common among critical infrastructure sectors that illustrate a method to achieve the outcomes associated with each Subcategory. The Informative References presented in the Framework Core are illustrative and not exhaustive. They are based upon cross-sector guidance most frequently referenced during the Framework development process. NIST developed a Compendium of informative references gathered from the Request for Information (RFI) input, Cybersecurity Framework workshops, and stakeholder engagement during the Framework development process. The Compendium includes standards, guidelines, and practices to assist with implementation. The Compendium is not intended to be an exhaustive list, but rather a starting point based on initial stakeholder input.
The five Framework Core Functions are defined below. These Functions are not intended to form a serial path, or lead to a static desired end state. Rather, the Functions can be performed concurrently and continuously to form an operational culture that addresses the dynamic cybersecurity risk. See Appendix A for the complete Framework Core listing.
- Identify – Develop the organizational understanding to manage cybersecurity risk to systems, assets, data, and capabilities. The activities in the Identify Function are foundational for effective use of the Framework. Understanding the business context, the resources that support critical functions, and the related cybersecurity risks enables an organization to focus and prioritize its efforts, consistent with its risk management strategy and business needs. Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include: Asset Management; Business Environment; Governance; Risk Assessment; and Risk Management Strategy.
- Protect – Develop and implement the appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical infrastructure services. The Protect Function supports the ability to limit or contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event. Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include: Access Control; Awareness and Training; Data Security; Information Protection Processes and Procedures; Maintenance; and Protective Technology.
- Detect – Develop and implement the appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event. The Detect Function enables timely discovery of cybersecurity events. Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include: Anomalies and Events; Security Continuous Monitoring; and Detection Processes.
- Respond – Develop and implement the appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity event. The Respond Function supports the ability to contain the impact of a potential cybersecurity event. Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include: Response Planning; Communications; Analysis; Mitigation; and Improvements.
- Recover – Develop and implement the appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity event. The Recover Function supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact from a cybersecurity event. Examples of outcome Categories within this Function include: Recovery Planning; Improvements; and Communications.
Framework Implementation Tiers
The Framework Implementation Tiers (“Tiers”) provide context on how an organization views cybersecurity risk and the processes in place to manage that risk. The Tiers range from Partial (Tier 1) to Adaptive (Tier 4) and describe an increasing degree of rigor and sophistication in cybersecurity risk management practices and the extent to which cybersecurity risk management is informed by business needs and is integrated into an organization’s overall risk management practices. Risk management considerations include many aspects of cybersecurity, including the degree to which privacy and civil liberties considerations are integrated into an organization’s management of cybersecurity risk and potential risk responses.
The Tier selection process considers an organization’s current risk management practices, threat environment, legal and regulatory requirements, business/mission objectives, and organizational constraints. Organizations should determine the desired Tier, ensuring that the selected level meets the organizational goals, is feasible to implement, and reduces cybersecurity risk to critical assets and resources to levels acceptable to the organization. Organizations should consider leveraging external guidance obtained from Federal government departments and agencies, Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs), existing maturity models, or other sources to assist in determining their desired tier.
While organizations identified as Tier 1 (Partial) are encouraged to consider moving toward Tier 2 or greater, Tiers do not represent maturity levels. Progression to higher Tiers is encouraged when such a change would reduce cybersecurity risk and be cost effective. Successful implementation of the Framework is based upon achievement of the outcomes described in the organization’s Target Profile(s) and not upon Tier determination.
The Tier definitions are as follows:
Tier 1: Partial
• Risk Management Process – Organizational cybersecurity risk management practices are not formalized, and risk is managed in an ad hoc and sometimes reactive manner. Prioritization of cybersecurity activities may not be directly informed by organizational risk objectives, the threat environment, or business/mission requirements.
• Integrated Risk Management Program – There is limited awareness of cybersecurity risk at the organizational level and an organization-wide approach to managing cybersecurity risk has not been established. The organization implements cybersecurity risk management on an irregular, case-by-case basis due to varied experience or information gained from outside sources. The organization may not have processes that enable cybersecurity information to be shared within the organization.
• External Participation – An organization may not have the processes in place to participate in coordination or collaboration with other entities.
Tier 2: Risk Informed
• Risk Management Process – Risk management practices are approved by management but may not be established as organizational-wide policy. Prioritization of cybersecurity activities is directly informed by organizational risk objectives, the threat environment, or business/mission requirements.
• Integrated Risk Management Program – There is an awareness of cybersecurity risk at the organizational level but an organization-wide approach to managing cybersecurity risk has not been established. Risk-informed, management-approved processes and procedures are defined and implemented, and staff has adequate resources to perform their cybersecurity duties. Cybersecurity information is shared within the organization on an informal basis.
• External Participation – The organization knows its role in the larger ecosystem, but has not formalized its capabilities to interact and share information externally.
Tier 3: Repeatable
• Risk Management Process – The organization’s risk management practices are formally approved and expressed as policy. Organizational cybersecurity practices are regularly updated based on the application of risk management processes to changes in business/mission requirements and a changing threat and technology landscape.
• Integrated Risk Management Program – There is an organization-wide approach to manage cybersecurity risk. Risk-informed policies, processes, and procedures are defined, implemented as intended, and reviewed. Consistent methods are in place to respond effectively to changes in risk. Personnel possess the knowledge and skills to perform their appointed roles and responsibilities.
• External Participation – The organization understands its dependencies and partners and receives information from these partners that enables collaboration and risk-based management decisions within the organization in response to events.
Tier 4: Adaptive
• Risk Management Process – The organization adapts its cybersecurity practices based on lessons learned and predictive indicators derived from previous and current cybersecurity activities. Through a process of continuous improvement incorporating advanced cybersecurity technologies and practices, the organization actively adapts to a changing cybersecurity landscape and responds to evolving and sophisticated threats in a timely manner.
• Integrated Risk Management Program – There is an organization-wide approach to managing cybersecurity risk that uses risk-informed policies, processes, and procedures to address potential cybersecurity events. Cybersecurity risk management is part of the organizational culture and evolves from an awareness of previous activities, information shared by other sources, and continuous awareness of activities on their systems and networks.
• External Participation – The organization manages risk and actively shares information with partners to ensure that accurate, current information is being distributed and consumed to improve cybersecurity before a cybersecurity event occurs.
Framework Profile
The Framework Profile (“Profile”) is the alignment of the Functions, Categories, and Subcategories with the business requirements, risk tolerance, and resources of the organization. A Profile enables organizations to establish a roadmap for reducing cybersecurity risk that is well aligned with organizational and sector goals, considers legal/regulatory requirements and industry best practices, and reflects risk management priorities. Given the complexity of many organizations, they may choose to have multiple profiles, aligned with particular components and recognizing their individual needs.
Framework Profiles can be used to describe the current state or the desired target state of specific cybersecurity activities. The Current Profile indicates the cybersecurity outcomes that are currently being achieved. The Target Profile indicates the outcomes needed to achieve the desired cybersecurity risk management goals. Profiles support business/mission requirements and aid in the communication of risk within and between organizations. This Framework document does not prescribe Profile templates, allowing for flexibility in implementation.
Comparison of Profiles (e.g., the Current Profile and Target Profile) may reveal gaps to be addressed to meet cybersecurity risk management objectives. An action plan to address these gaps can contribute to the roadmap described above. Prioritization of gap mitigation is driven by the organization’s business needs and risk management processes. This risk-based approach enables an organization to gauge resource estimates (e.g., staffing, funding) to achieve cybersecurity goals in a cost-effective, prioritized manner.
Coordination of Framework Implementation
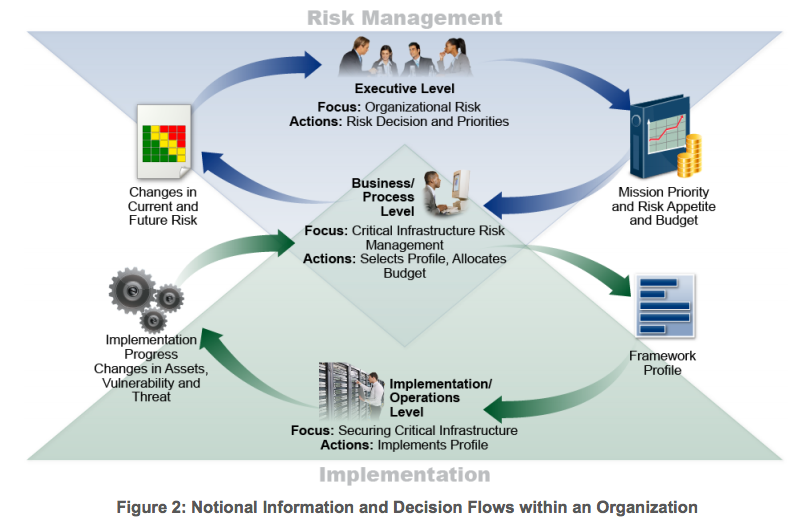
Figure 2 describes a common flow of information and decisions at the following levels within an organization: • Executive • Business/Process • Implementation/Operations The executive level communicates the mission priorities, available resources, and overall risk tolerance to the business/process level. The business/process level uses the information as inputs into the risk management process, and then collaborates with the implementation/operations level to communicate business needs and create a Profile. The implementation/operations level communicates the Profile implementation progress to the business/process level. The business/process level uses this information to perform an impact assessment. Business/process level management reports the outcomes of that impact assessment to the executive level to inform the organization’s overall risk management process and to the implementation/operations level for awareness of business impact.
Secions 3 and onwards, see PDF.