Purpose: Designing, deciding
Concerns: Dependencies between business processes, consistency and completeness, responsibilities
Scope: Multiple layer/Multiple aspect
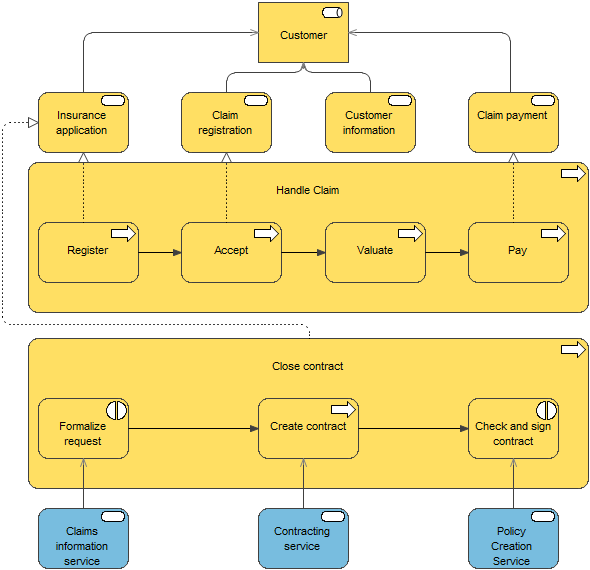
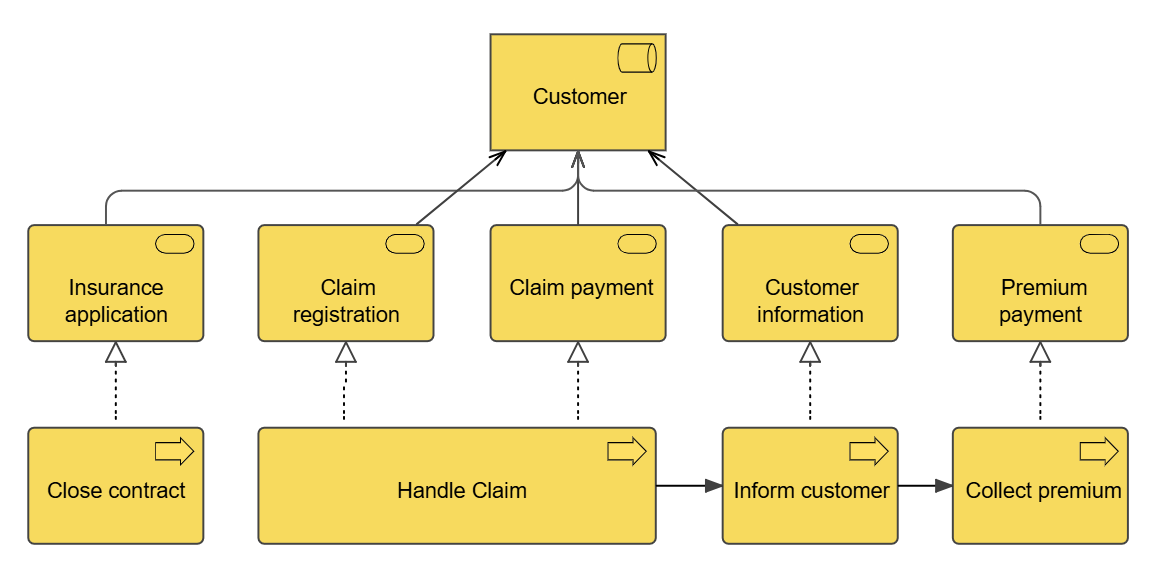
The business process cooperation viewpoint is used to show the relationships of one or more business processes with each other and/or with their environment. It can be used both to create a high-level design of business processes within their context and to provide an operational manager responsible for one or more such processes with insight into their dependencies. Important aspects of business process cooperation are:
- Causal relationships between the main business processes of the enterprise
- Mapping of business processes onto business functions
- Realization of services by business processes
- Use of shared data
Each of these can be regarded as a “sub-viewpoint” of the business process cooperation viewpoint.