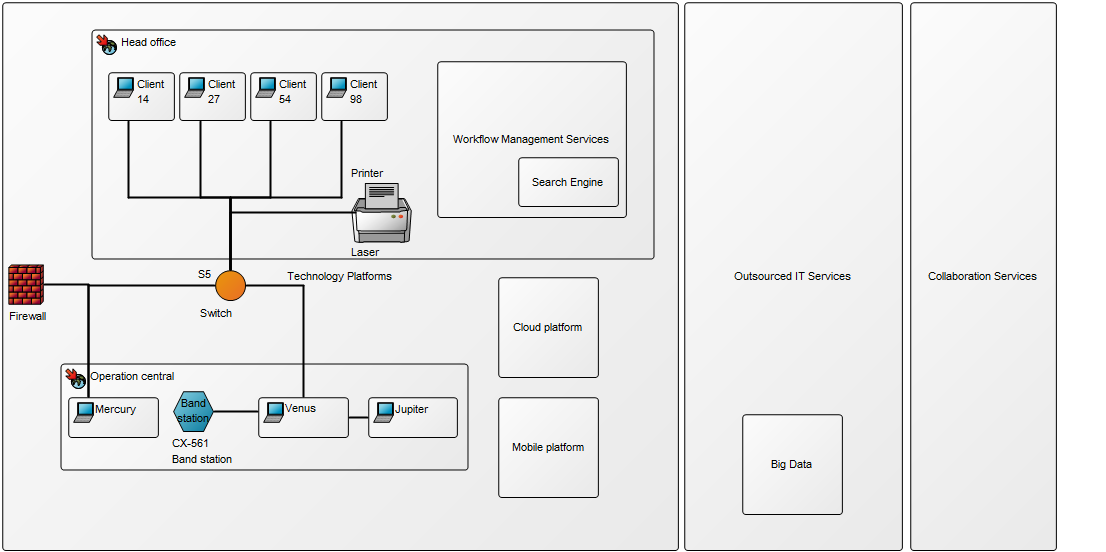
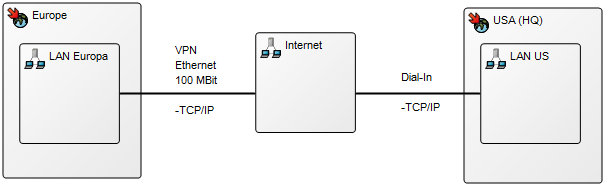
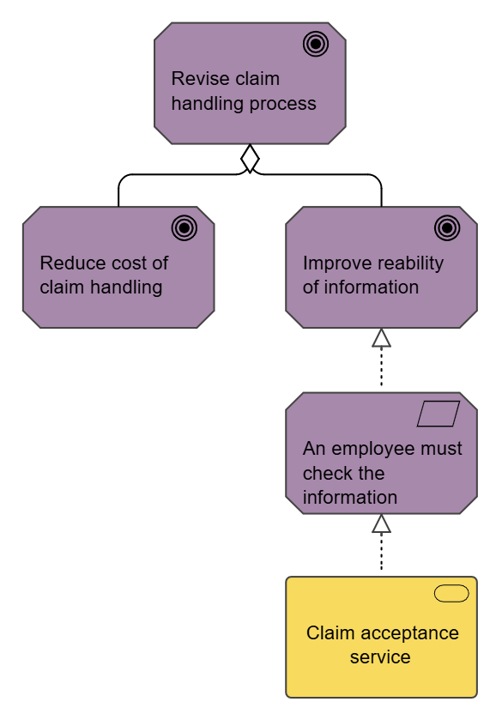
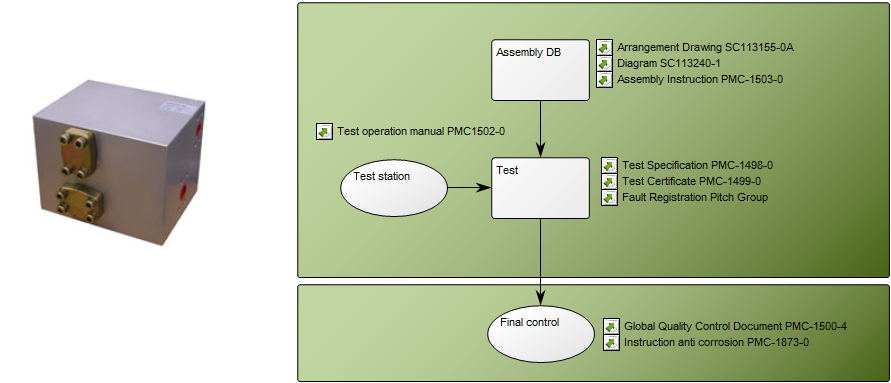
Purpose: The purpose of the Manufacturing Routing Network is to specify the steps used in manufacturing a product. Below is an example of a Manufacturing Routing Network of an Item including Assembly, test and final control. At the right-hand side, you can see that different specifications have been attached as well:
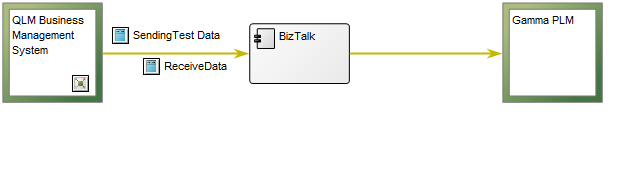
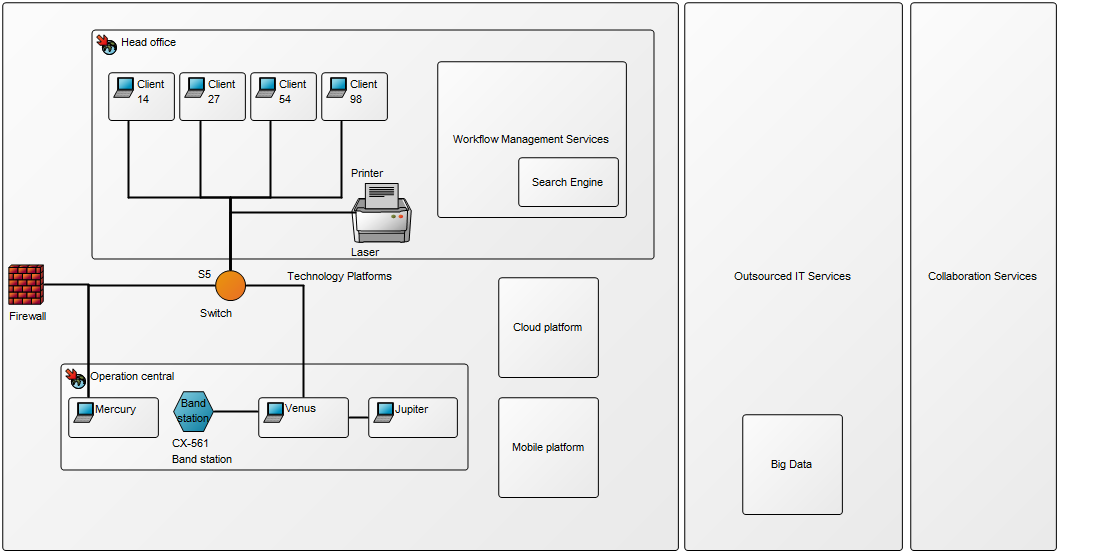
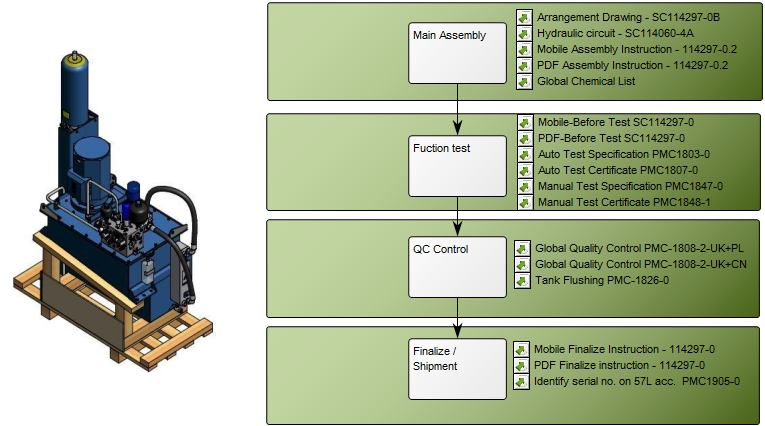
Core concerns: The Manufacturing Routing Network template enables you to model Work Operations, Products, Business Objects, General Concepts, and Production Lines. You are also able to distinguish between Activity Paths, Assembly Flows and Transport Systems. If you wish to attach External Documents, they should be attached to the Work Operations they pertain to. Below is another example of a Manufacturing Routing Network that describes the process from assembly to shipping:
Relation to other templates: The Manufacturing Routing Network template is related to the various different models for products such as the Product Viewpoint template, the Product Variant Master template, the Product Rule Table, the Product Roadmap and the Product Canvas. Each template offers a different viewpoint of the product in various stages of its lifecycle.
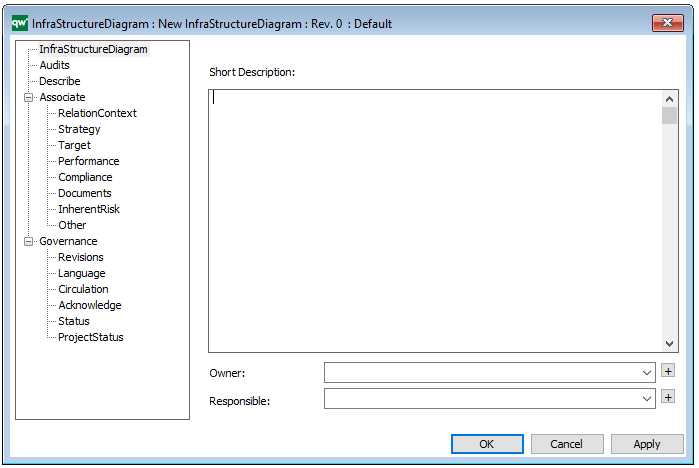
Properties and metadata: The Manufacturing Routing Network template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the accuracy of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
- Project status: information about budgeted and actual man-hours spent, percentage completed and the latest milestone, result and quality control of a change process.
In the picture below you can see the Manufacturing Routing Network’s properties dialogue window, where the properties can be viewed and edited: