 EA3 artifact A-1: Application Interface Diagram
EA3 artifact A-1: Application Interface Diagram
The Application Interface Diagram shows the logical and/or physical interfaces between the enterprise’s systems for information, production, etc. where information and/or other resources are exchanged.
EA3 artifact D-10: The Object Library
GEM: Generic Enterprise Model
A GEM is an object library that defines the classes of objects that are generic across a type of enterprise, such as manufacturing or banking, and can be used (instantiated) in defining a specific enterprise.
A GEM is composed of the following:
Mark S. Fox and Michael Gruninger: Enterprise Modeling. AI Magazine Volume 19 Number 3 (1998)
EA3 artifact D-9: The Data Dictionary
The Data Dictionary provides a comprehensive listing of the data entities that are collected and maintained by the enterprise, including standards for the attribute fields, keys, and relationships. The Data Dictionary may also include a ‘library’ of re-useable Data Objects that use UML methods.
Examples
Daily use
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Description | Key | Sample |
| CustomerName | String | 15 | Name of Customer/Supplier | Thompson, Bob | |
| CustomerPhone | String | 15 | Phone of Customer/Supplier | (509) 555-1298 | |
| CustomerAddress | String | 45 | Address of Customer/Supplier | 1698 Mellowbrook Road | |
| CustomerState | String | 15 | State of Customer/Supplier | WA | |
| CustomerZip | Int | 9 | Zip of Customer/Supplier | 980045890 | |
| CustomerInventory | Int | 15 | Customer Inventory in Queue | 16 | |
| CustomerID | Int | 10 | Customer Primary Key | PK | 948920 |
| ProductName | String | 15 | Product Name | Hammer | |
| ProductCategory | String | 15 | Category of Product | Tools | |
| ProductID | Int | 30 | Primary Key for Product | FK | 5432 |
| ProductInventory | Int | 6 | Product Inventory in Warehouse | 32 | |
| CustomerAcct | Int | 15 | Customer Account Number | FK | 84392795 |
| PurchaseDate | Datetime | 8 | Date of Customer Purchase | FK | 12121986 |
| ShipDate | Datetime | 8 | Date of Customer Product Ship | FK | 12121986 |
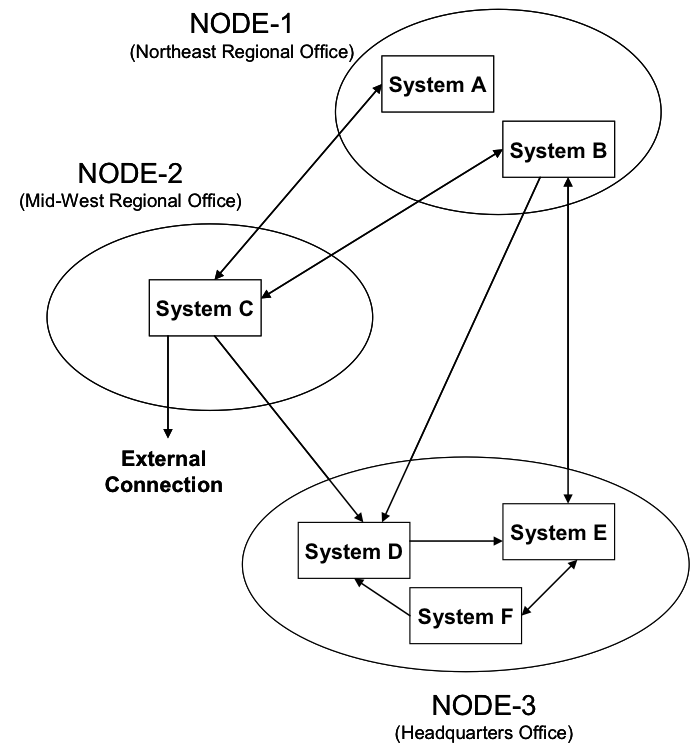
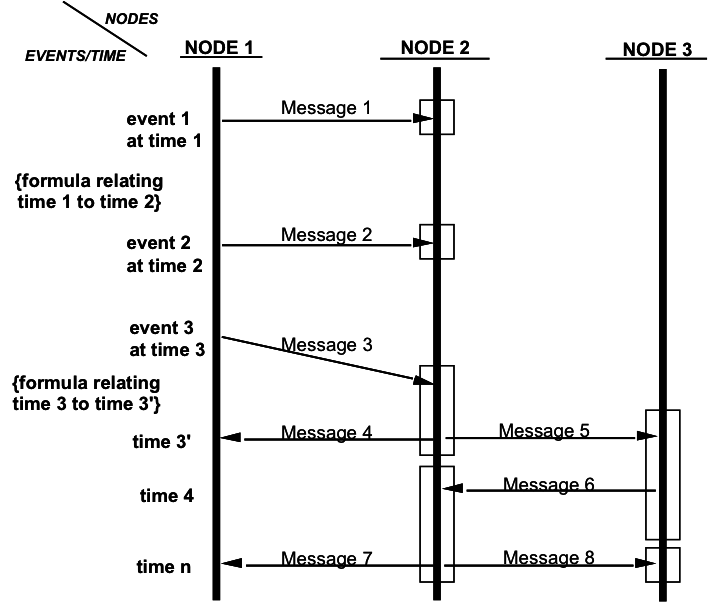
EA3 artifact D-8: The Event-Trace Diagram
The Event-Trace Diagram allows the tracking of actions in a set of scenarios or operational threads. Each diagram should focus on a critical sequence of events and a description of the event scenario should be provided.
With time proceeding from the top of the diagram to the bottom, a specific diagram lays out the sequence of information exchanges that occur between business nodes for a given scenario. These information exchanges are associated with events and actions (see Information Exchange Matrix). The direction of the event arrows shows flow of control, in terms of the business process, from node to no.
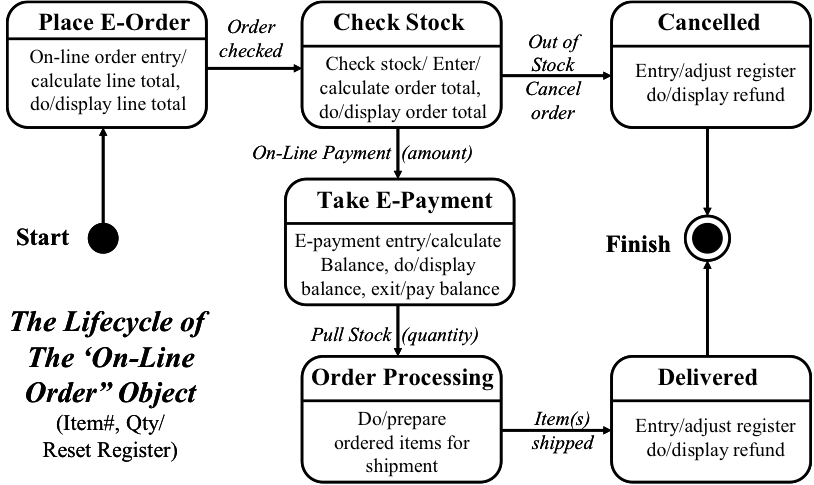
EA3 artifact D-7: The State Transition Diagram
The State Transition Diagram uses the notation from the Unified Modeling Language (UML) to show how the lifecycle of a specific data object. This diagram shows changes to attributes, links, and/or behavior(s) of the “On-Line Order” object that are a result of internal or external system events which trigger changes in state.
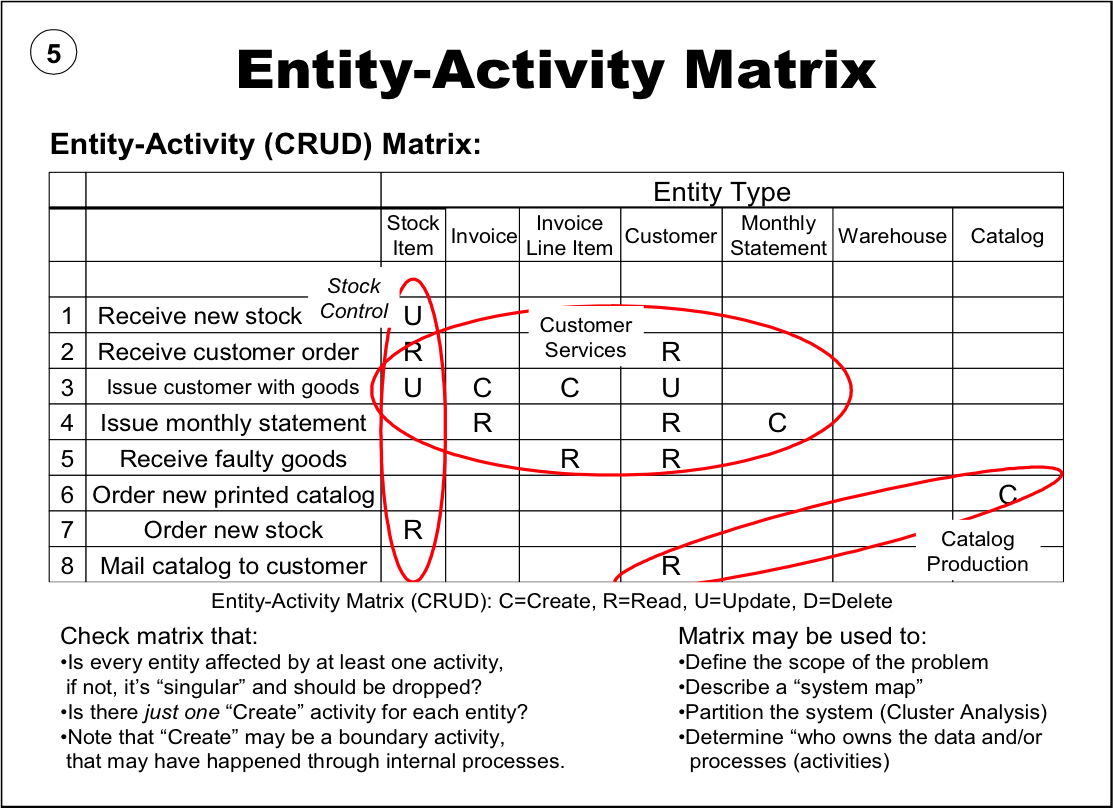
EA3 artifact D-6: The Activity/Entity Matrix
An Activity/Entity Matrix is developed by mapping which data entities are affected by related line of business activities. Often called a ‘CRUD’ matrix because it identifies the basic types of transformations that are performed on data (Create, Read, Update, Delete) through a process.
EA3 artifact D-5: Physical Data Model
The Physical Data Model (PDM) is used to describe how the information represented in the Logical Data Model is actually implemented in an information system. There should be a mapping from a given Logical Data Model to the PDM. The PDM is a composite model whose components can vary greatly, as shown in the template below. For some purposes, an entity-relationship style diagram of the physical database design will suffice. The Data Definition Language may also be used in the cases where shared databases are used to integrate systems.
Physical Data Model Provides
Message Format:
File Structure:
Physical Schema:
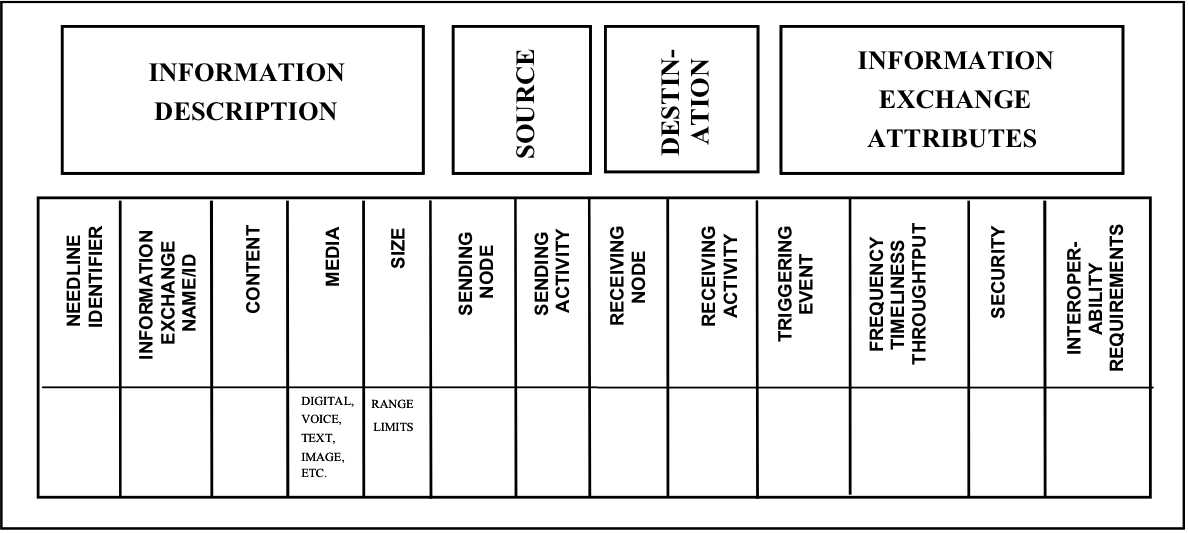
EA3 artifact D1.1 / D-2a: The Information Exchange Matrix
The Information Exchange Matrix describes relevant attributes of data exchanges between systems. These attributes include size, logical specification of the information i.e., media, timeliness required, and the security classification and properties of the information.
Information exchanges express the relationships across four important aspects of the architecture (information, activities, locations, and times) with a focus on the specific aspects of the information flow. Information exchanges identify which business nodes exchange what information during the performance of what activities and in response to which events. Additional information on who is performing the activity can be added, if needed for security analysis. The detailed information in the Information Exchange Matrix may be hard to collect but it is necessary to fully understand the information flow in the enterprise and its security aspects.
The matrix also identifies the event that triggers the information exchange (e.g., set schedule or citizen request). The matrix keys the exchange to the producing and using activities and nodes and to the needline (from the Node Connectivity Diagram) the exchange satisfies. The Information Exchange Matrix partitions each high-level needline into its component parts, i.e., into distinct information exchanges between business nodes. An example format for this artifact is provided below. Additional characteristics may be added to the D-1 matrix based on the purpose or goals of the enterprise.

EA3 artifact D-3: Data Quality Plan
The Data Quality Plan addresses the processes and internal controls implemented over spending information, including data quality control procedures.
A Data Quality Plan is mandatory in the US Federal government to support the Open Government objective of creating and sustaining transparency across Government over data related to Federal spending information and improving the quality and integrity of such information.