A connection point can be either a physical socket or a logical connection point.
QLM Users
Concept Relation
A concept relation is a connection on a ConceptualDataModel. It is used to relate InformationConcepts and defining the roles and cardinality of such relations.
A relation between two information concepts
Quality Control
A quality control is used to describe how a Result is to be validated/controlled in the case of reviews, inspections or any other kind of quality controlling activities. The quality control is used to describe the acceptance criteria, the questions to be asked, the roles of the parties involved etc.
QualityControl properties
The QualityControl tab
| Property | Metamodel name | Description |
| Short Description | ShortDescription | A short verbal description |
| Acceptance Criteria | AcceptanceCriteria | Description of criterias that must be met so acceptance can be granted. |
| Audit Roles | AuditRoles | This field is used to describe the roles of the different parites involved in the quality control activities. This includes f.ex. the external auditor, the customer or even the internal quality department. |
The Techniques tab
| Property | Metamodel name | Description |
| Use technique | UseTechnique | Links to technique instructions Links to: Document, ExternalDocument, Technique. |
| Tool | Tool | Link to tool-specifications for this result Links to: ExternalDocument, InformationSystem. |
| Good Practice examples | GoodPractice | Link to files showing good examples Links to: All templates. |
The Action tab
| Property | Metamodel name | Description |
| Macro | Macro | This field is used to create a command language program that can be executed when the user double clicks on the symbol. |
| Execute on Double-click | ExecuteOnDoubleClick | Macro is always executed when double clicking on the symbol. Initial value is off. |
Qualiware Setup
Command language commands executed at time of start up.
Realization
The sender realizes an interface used by the receiver.
Realization:Archimate
The realization relationship indicates that more abstract entities (“what” or “logical”) are realized by means of more tangible entities (“how” or “physical”). The realization relationship is used to model run-time realization; for example, that a business process realizes a business service, and that a data object realizes a business object, an artifact realizes an application component, or a core element realizes a motivation element.
The usual interpretation of a realization relationship is that the whole or part of the source element realizes the whole of the target element. This means that if, for example, two internal behavior elements have a realization relationship to the same service, either of them can realize the complete service. If both internal behavior elements are needed to realize, the grouping element or a junction can be used. For weaker types of contribution to the realization of an element, the influence relationship should be used.
Recycling
Flow of reusable material.
Regulation
A Regulation contains a reference to a specific paragraph in the legislation controlling the business. It can also contain a reference in a specific relevant standard i.e. ISO or ANSI.
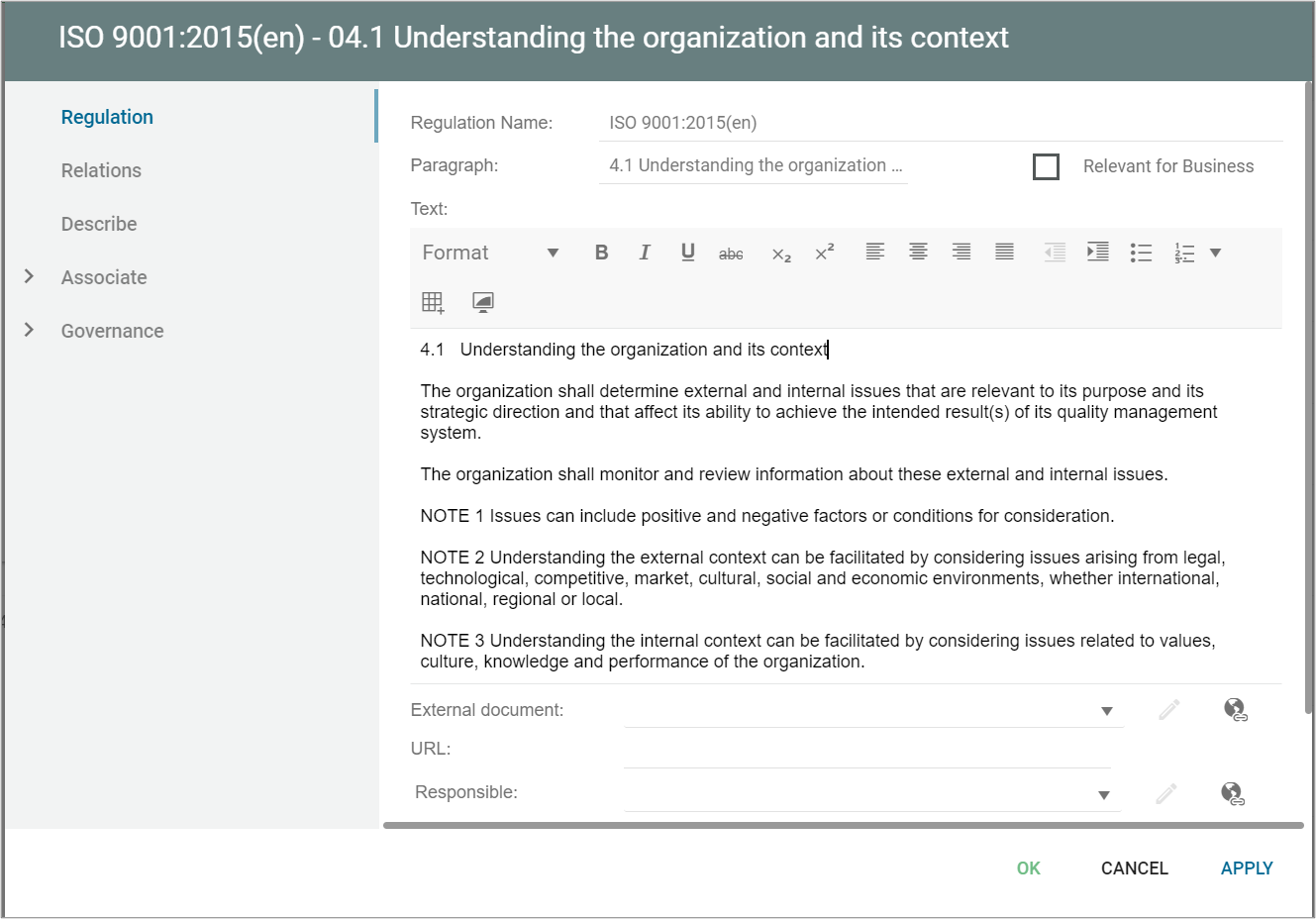
A regulation is used to relate an object (e.g. a Process) to a relevant Regulation. This relation is made with the “ComplianceWith” relation available on the complying object (e.g. a process). This will enable the user to trace the conformance to a specific Regulation in the Repository.
A regulation can be a part of a RegulationDiagram, and used document Compliance, e.g. in a Compliance Matrix.
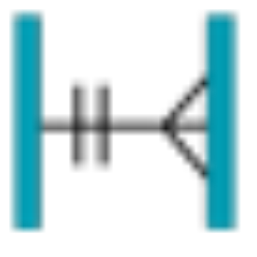
Relationship Constraint
A constraint between two associations such as exclusive or (xor).