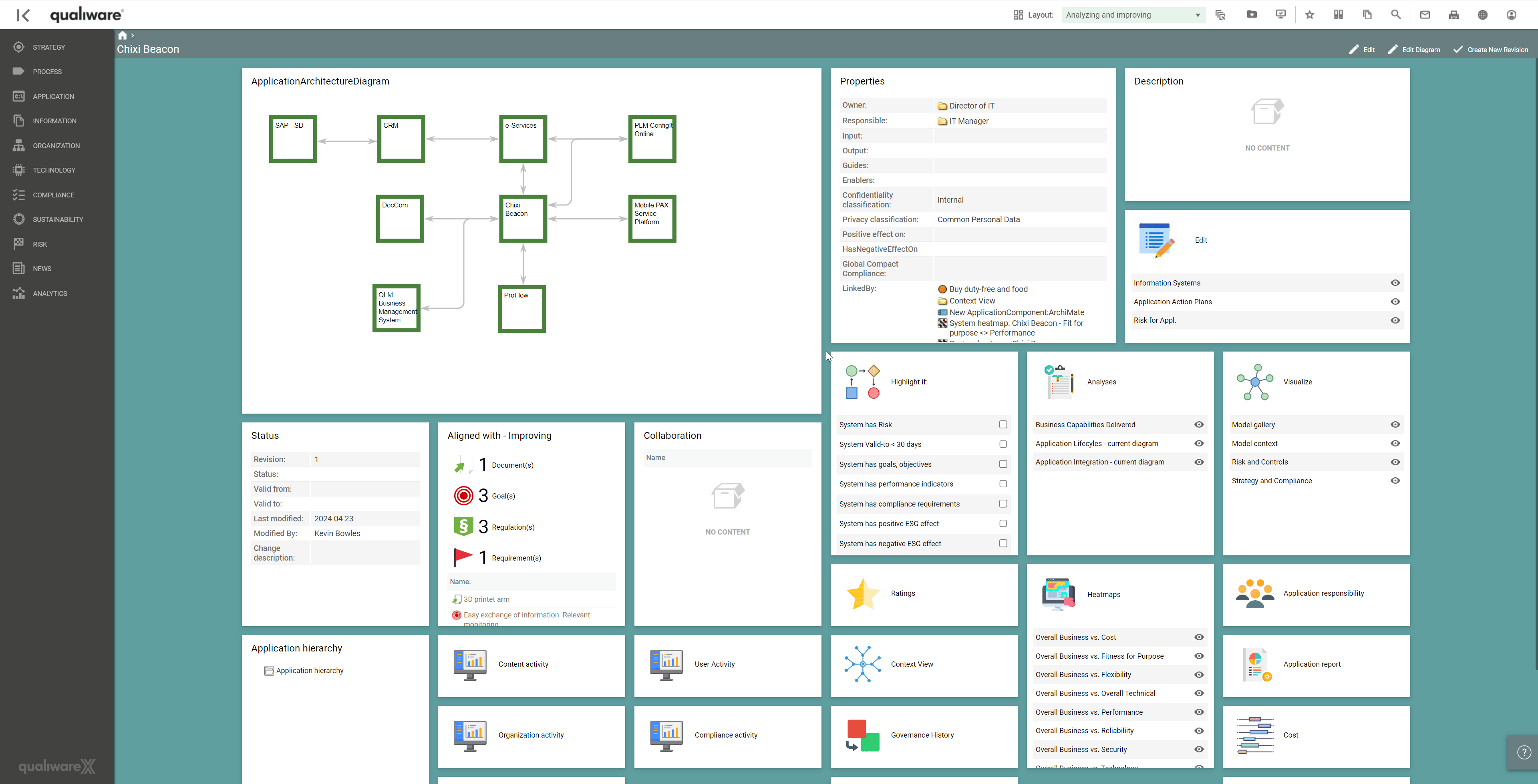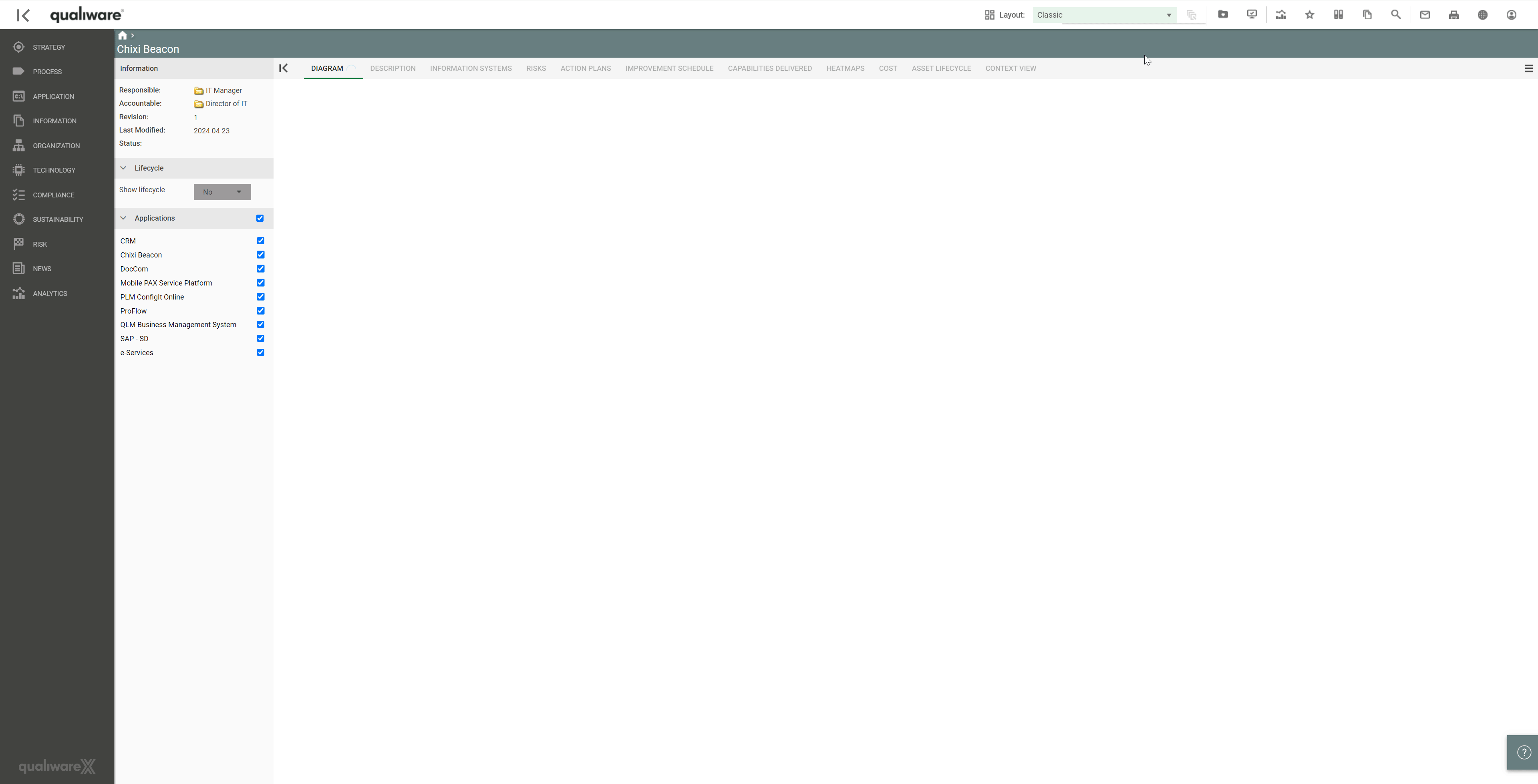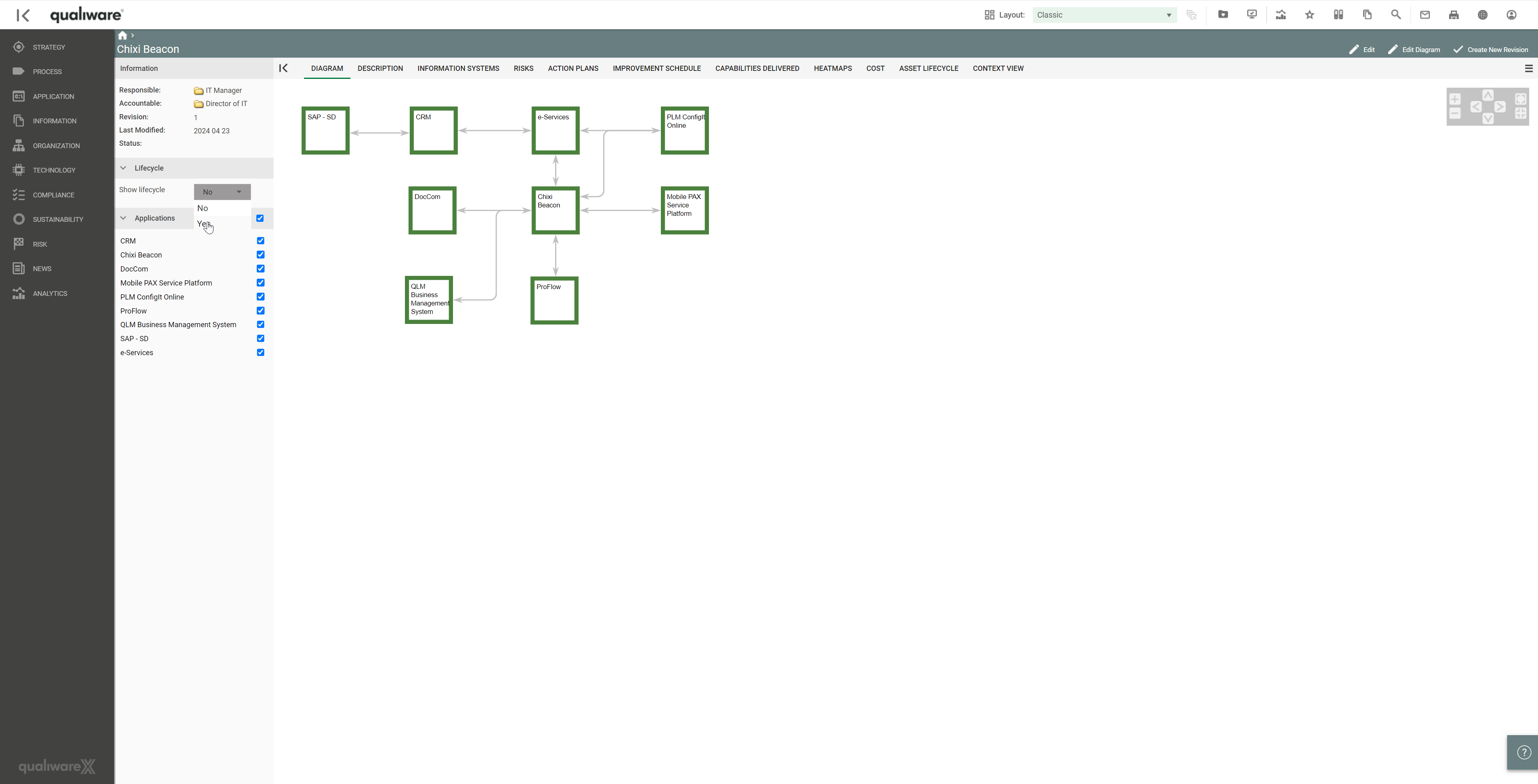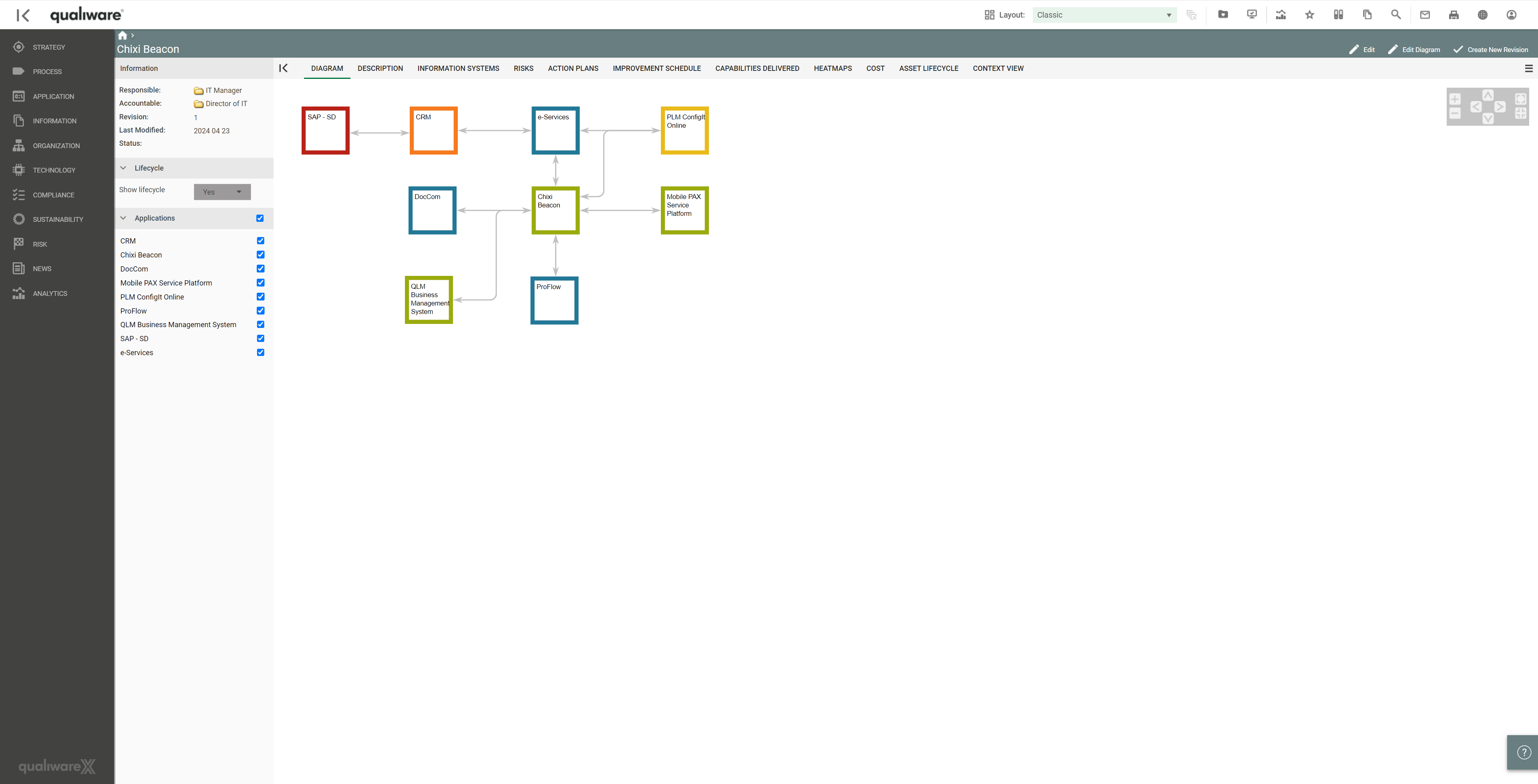
Architects should evaluate potential redundancies among applications and eliminate duplicate functionality wherever possible. Duplicate functionality across applications is representative of wasted expenditure and is a good candidate for rationalisation. Applications with similar functionality should be consolidated to reduce complexity and costs.
Identifying application redundancies is one of the strengths of APM. By allocating applications with assessments of lifecycle, strategic delivery, process impact, dependencies, functionality, and several other performance indicators, it is possible to realise inefficiencies, redundancies or overlapping functions within an organisation’s application portfolio. All these properties are essential for the Enterprise Architect to document and update continuously to ensure an efficient application portfolio.
In QualiWare, it is possible to update and maintain all aspects of the application within the landscape when it transitions into a transformation and optimisation phase.
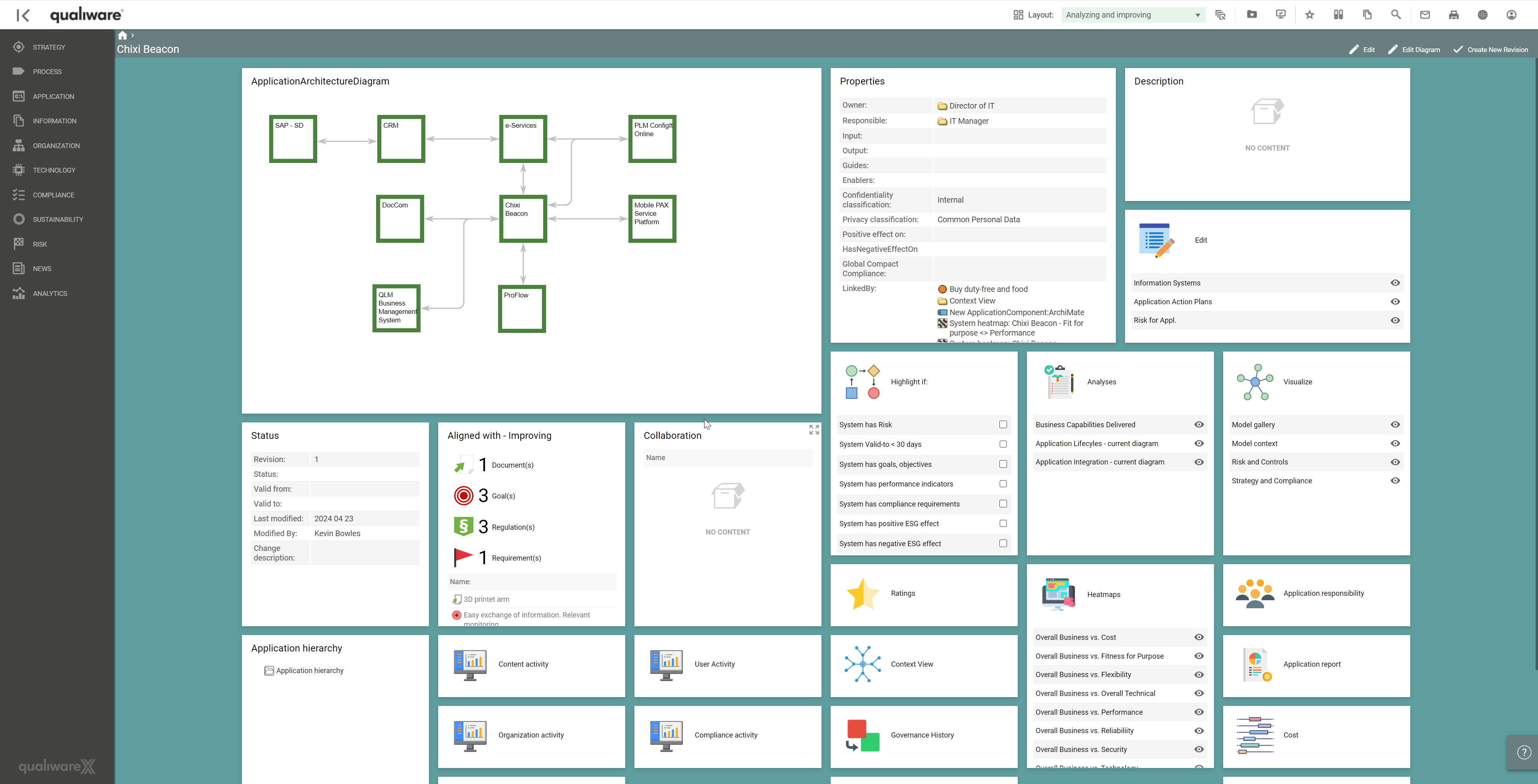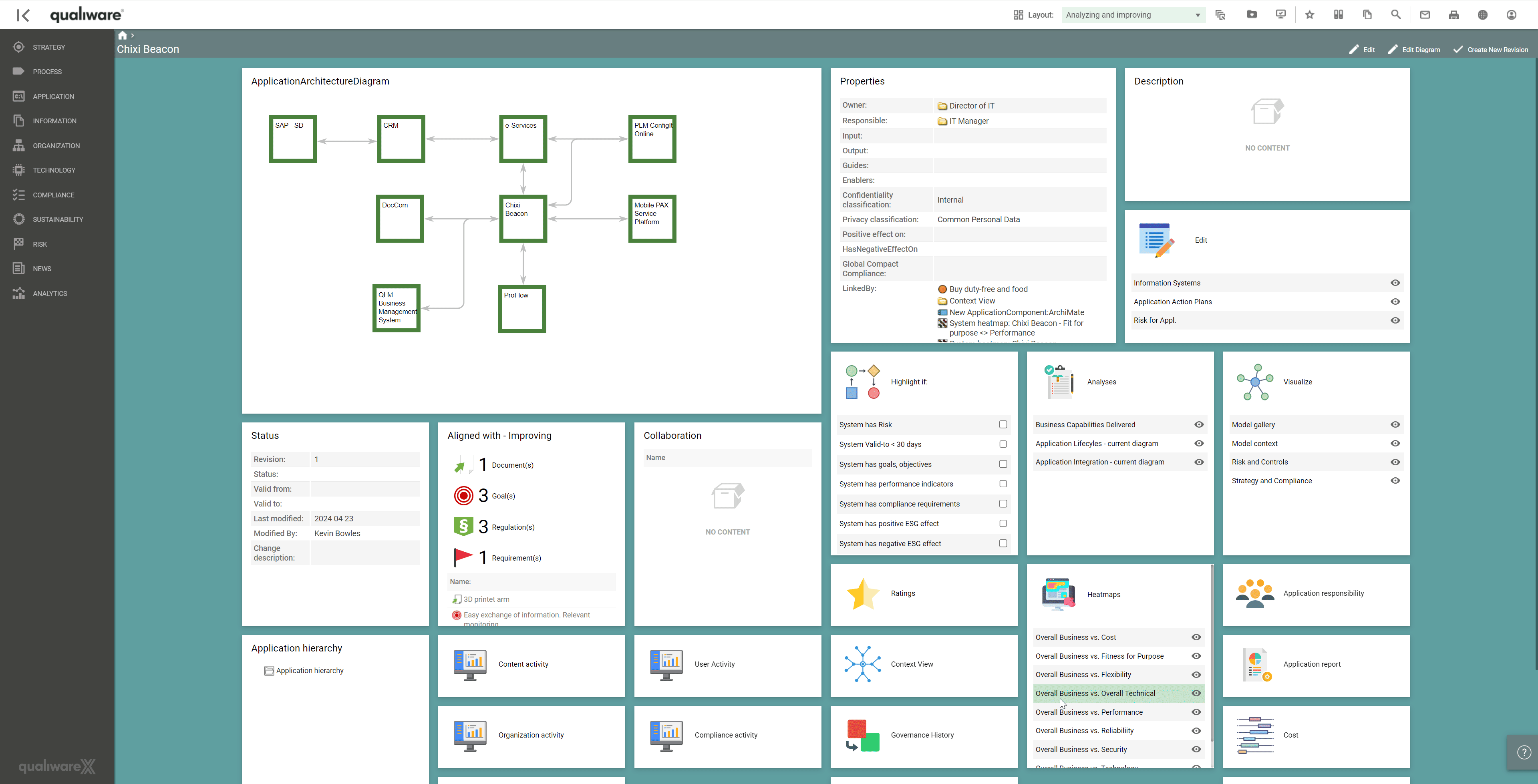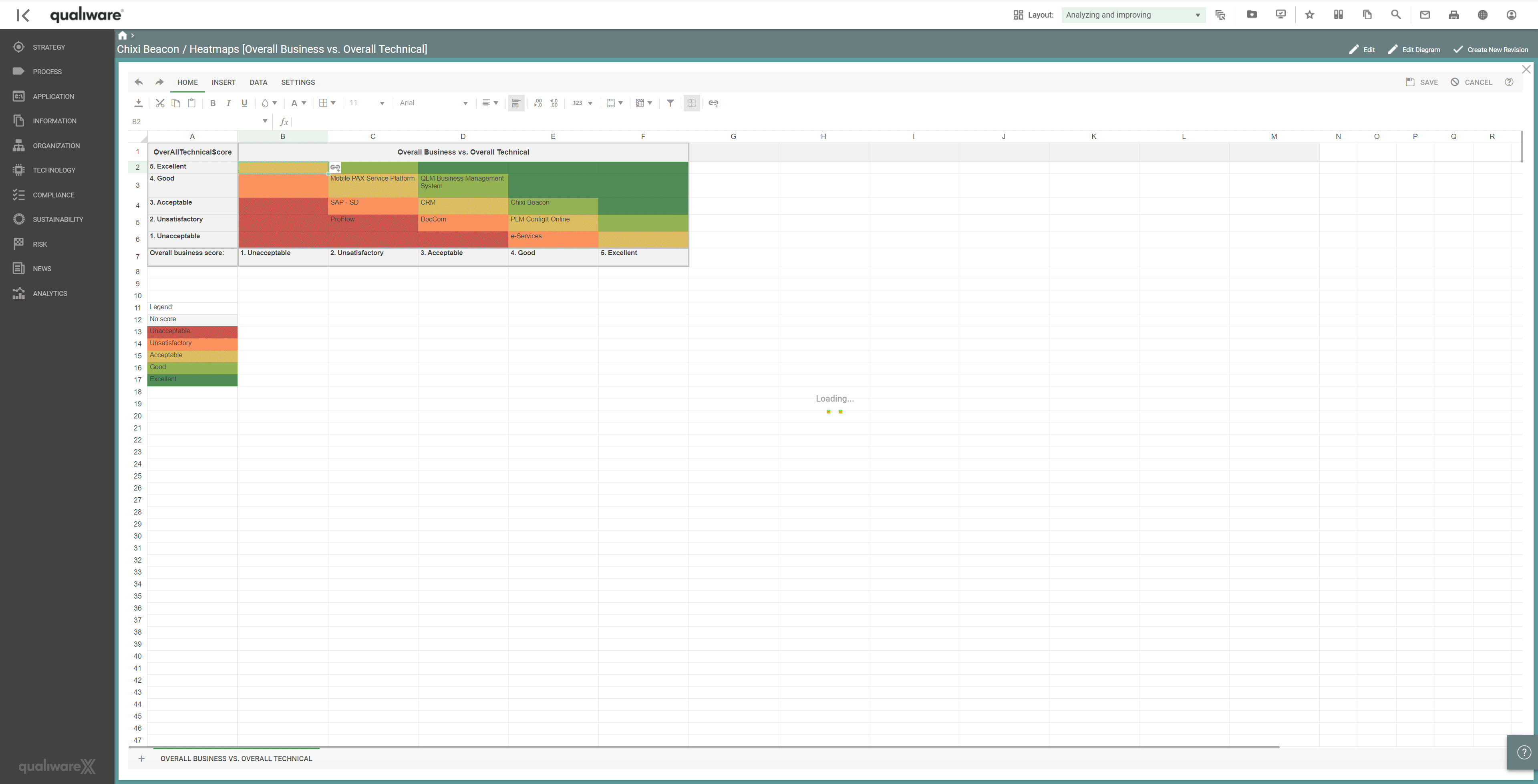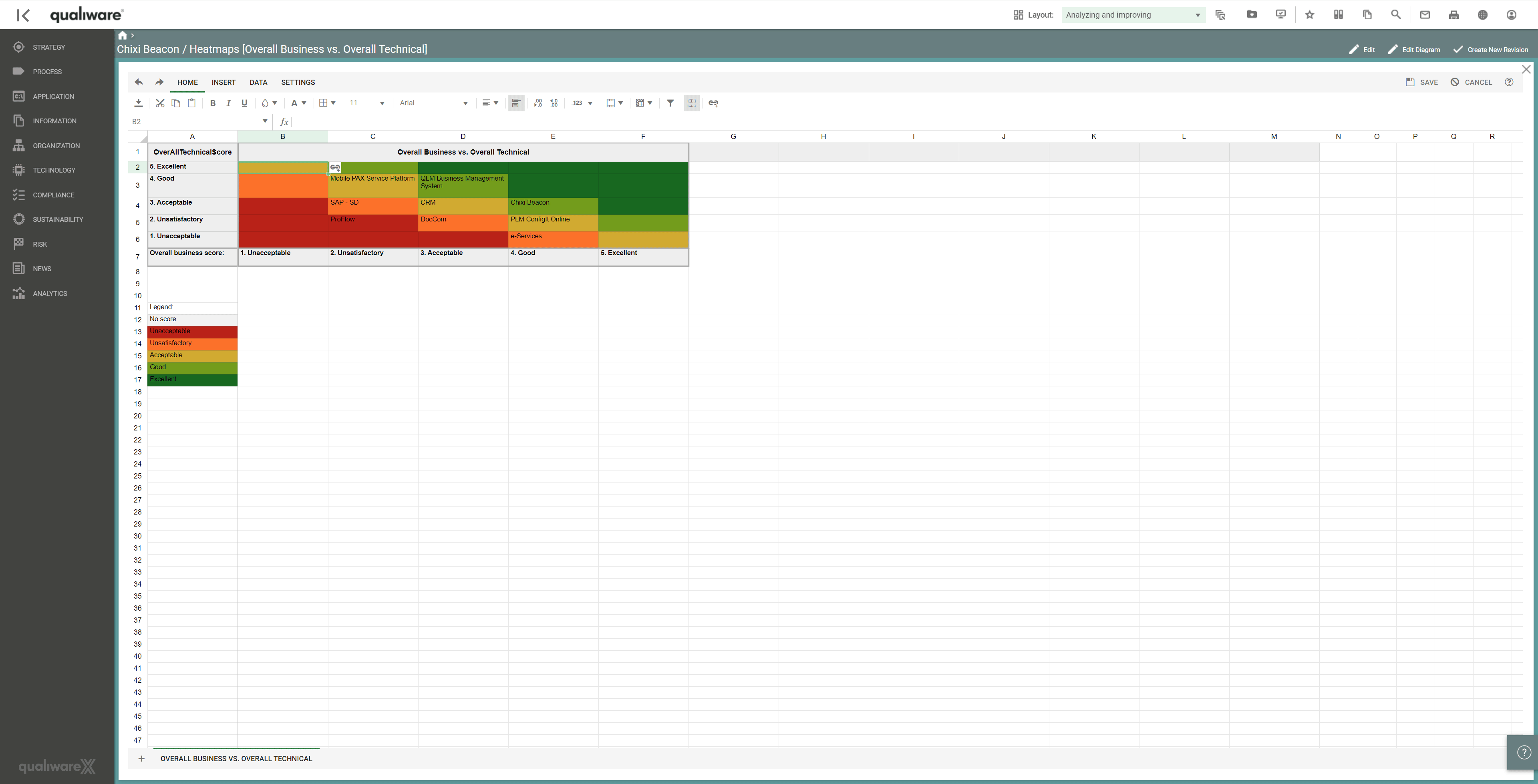
Using QualiWare to analyse and visualise capabilities delivered by applications, the analysis of changing, discontinuing or improving applications can be achieved via a series of heatmaps.
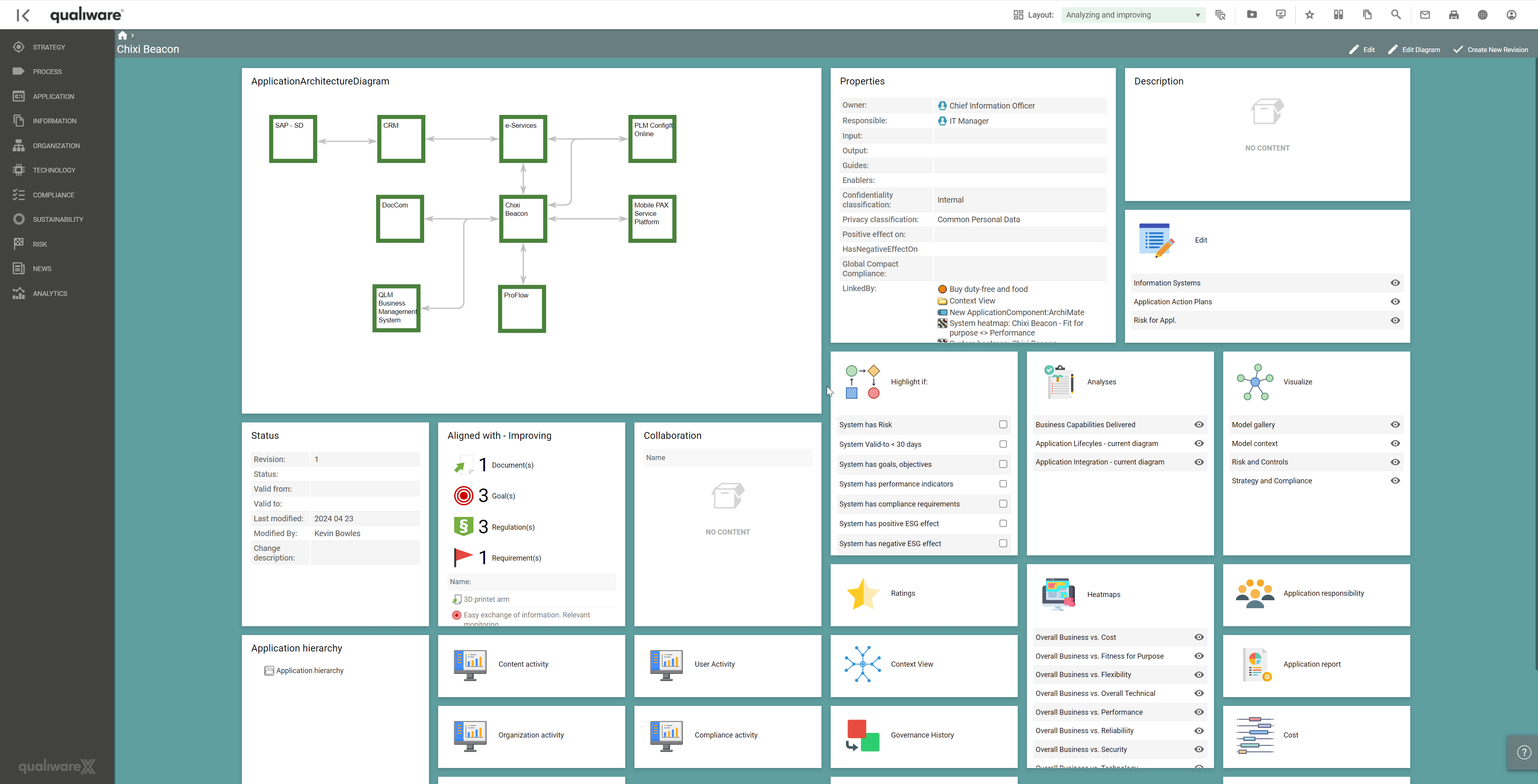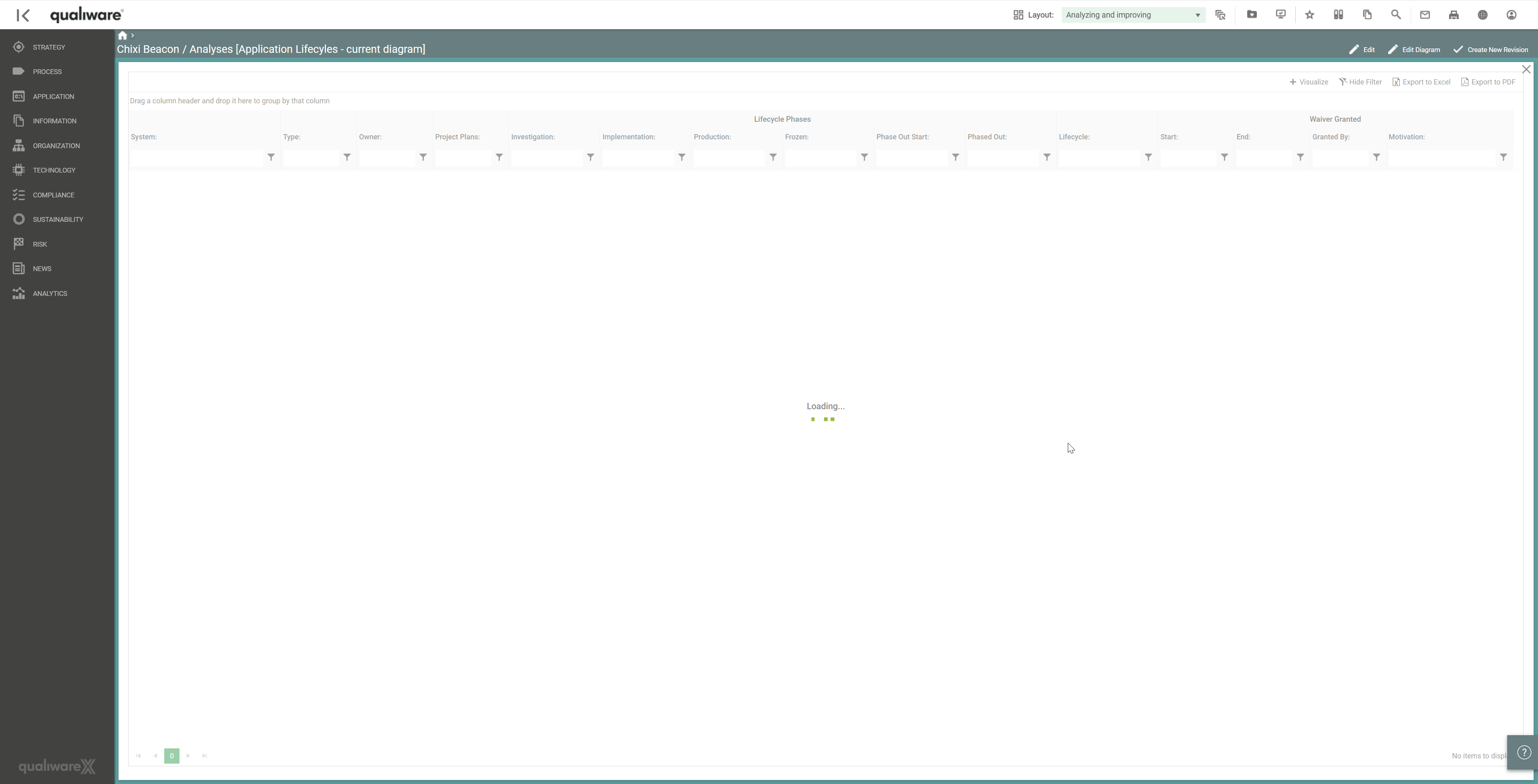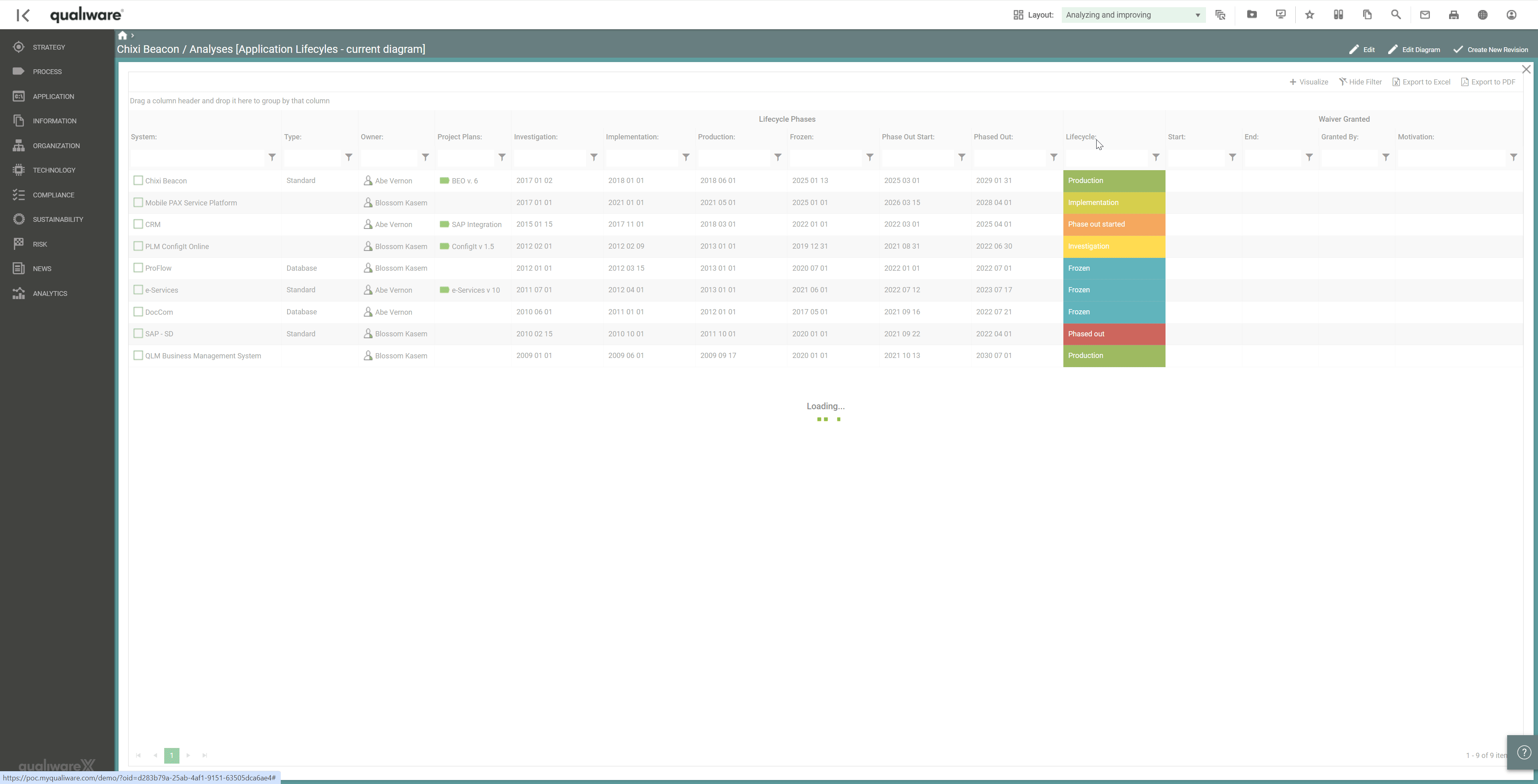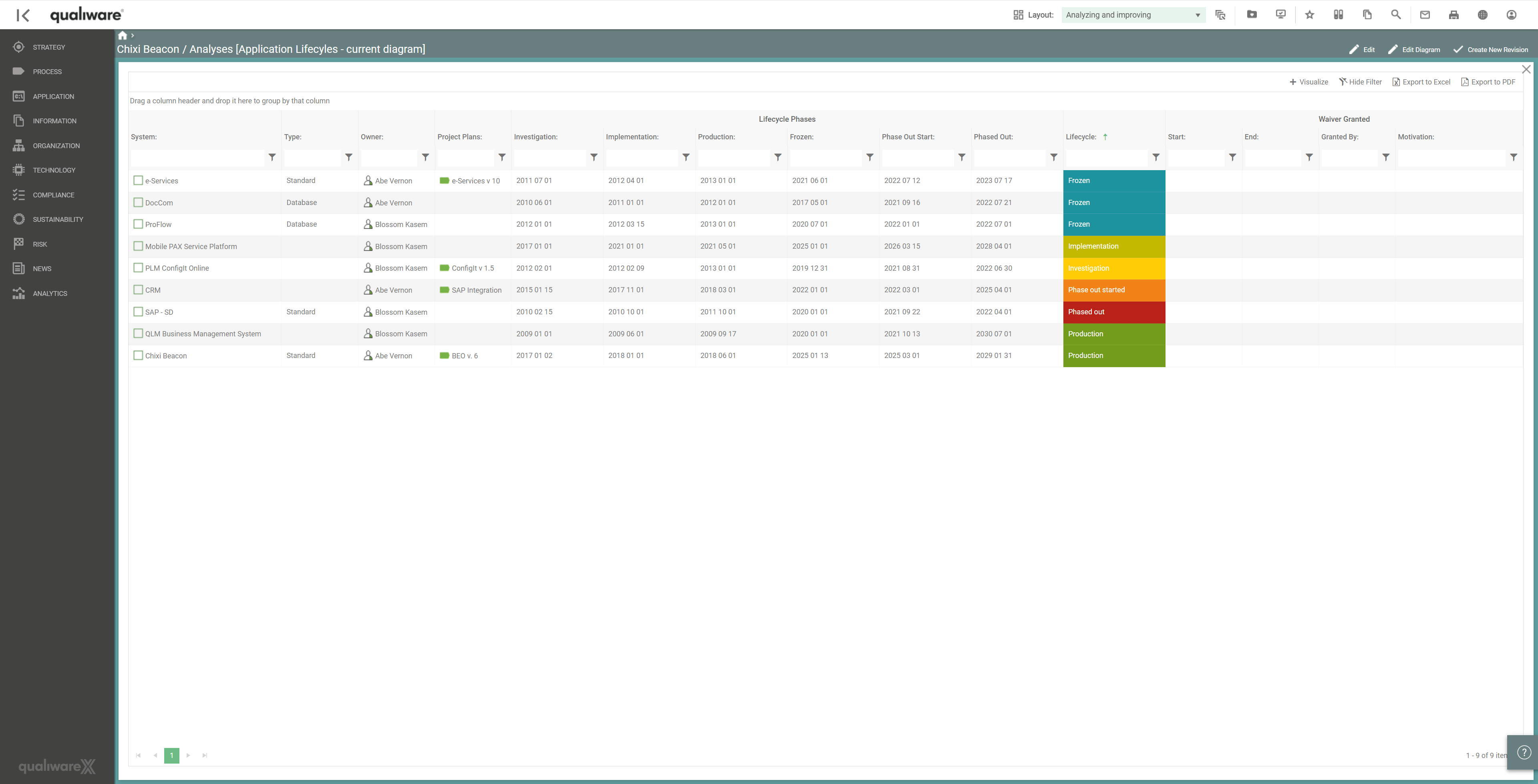
Furthermore, a lifecycle assessment makes it possible to see where the organisation is in the application landscape and when some applications may be phased out.
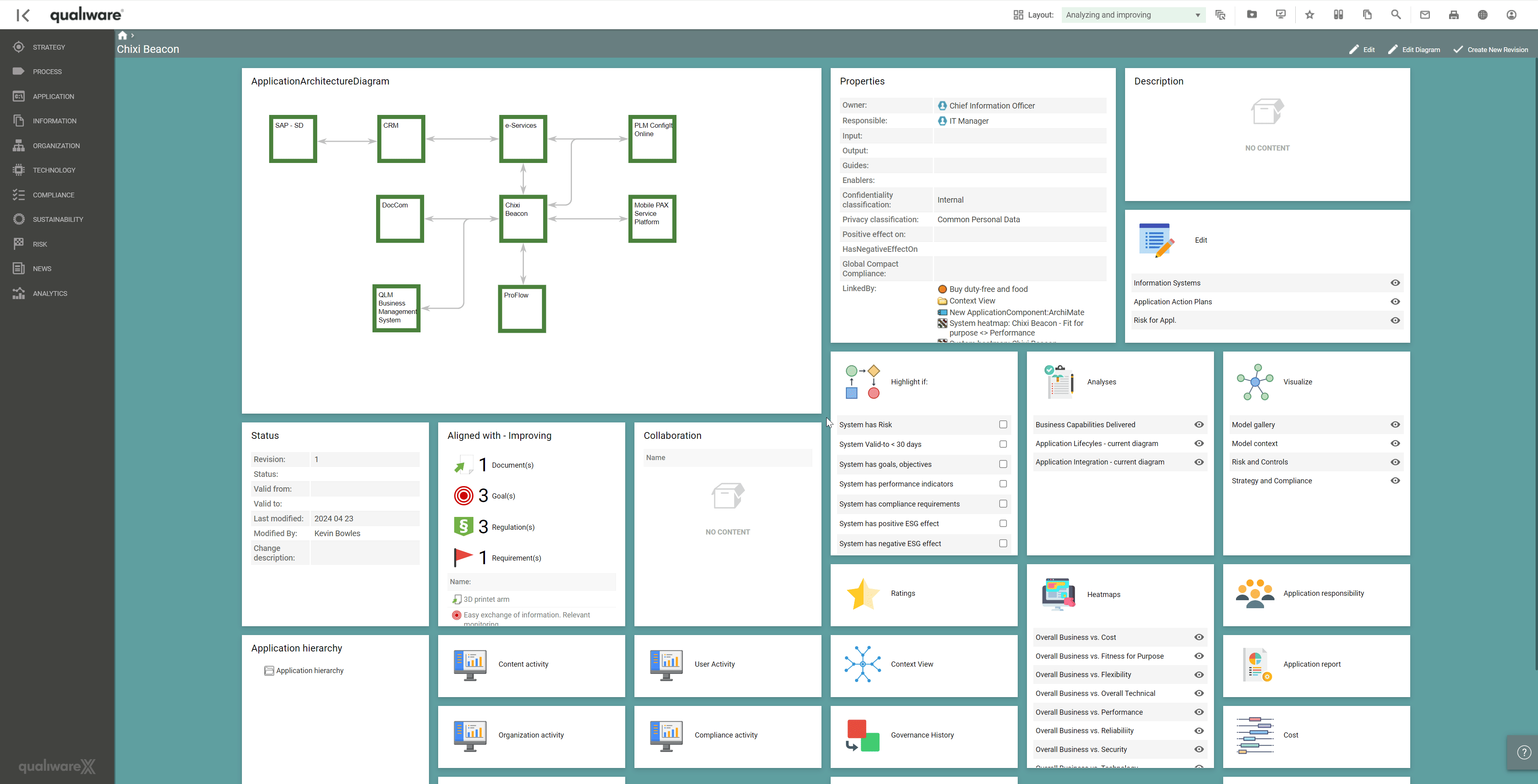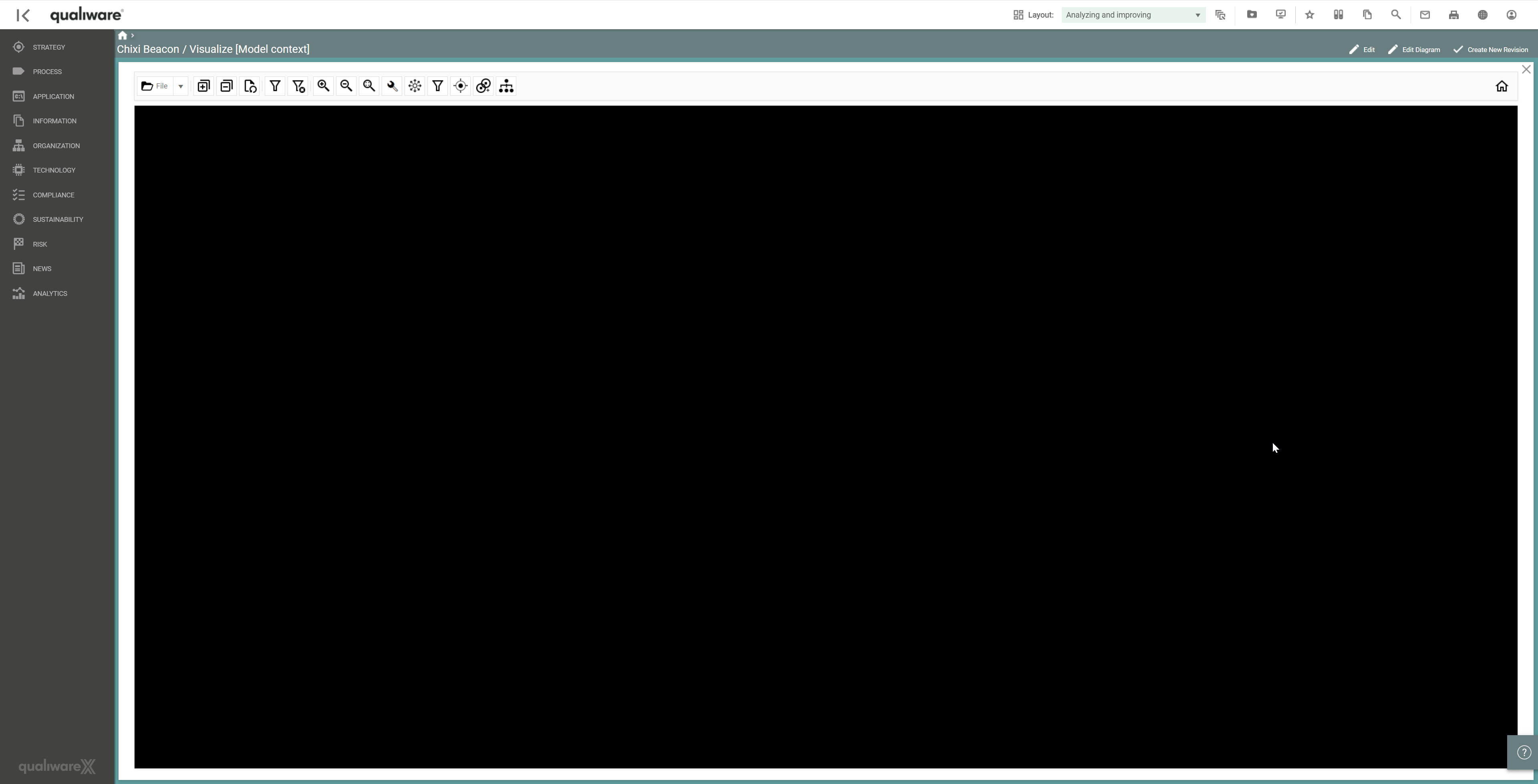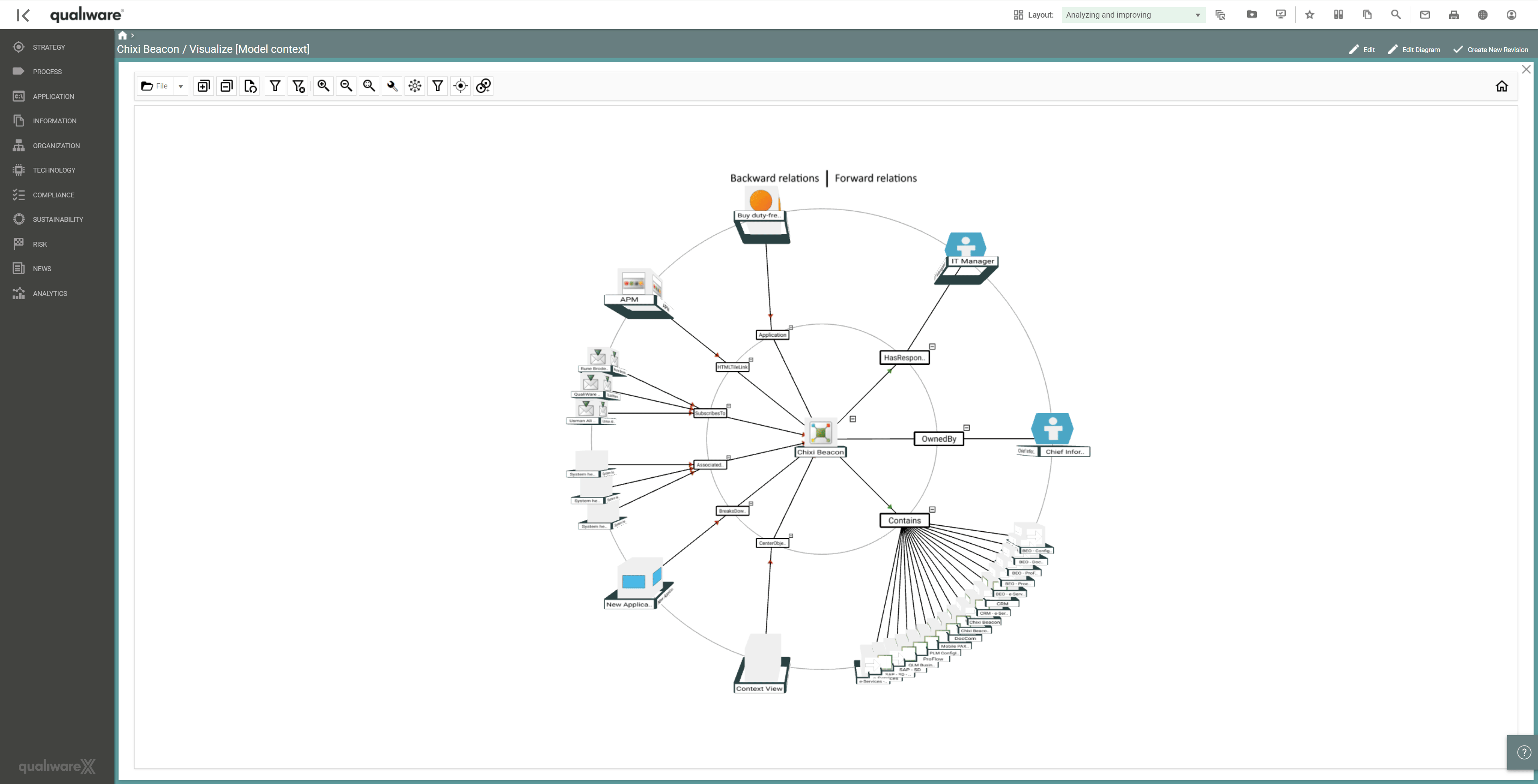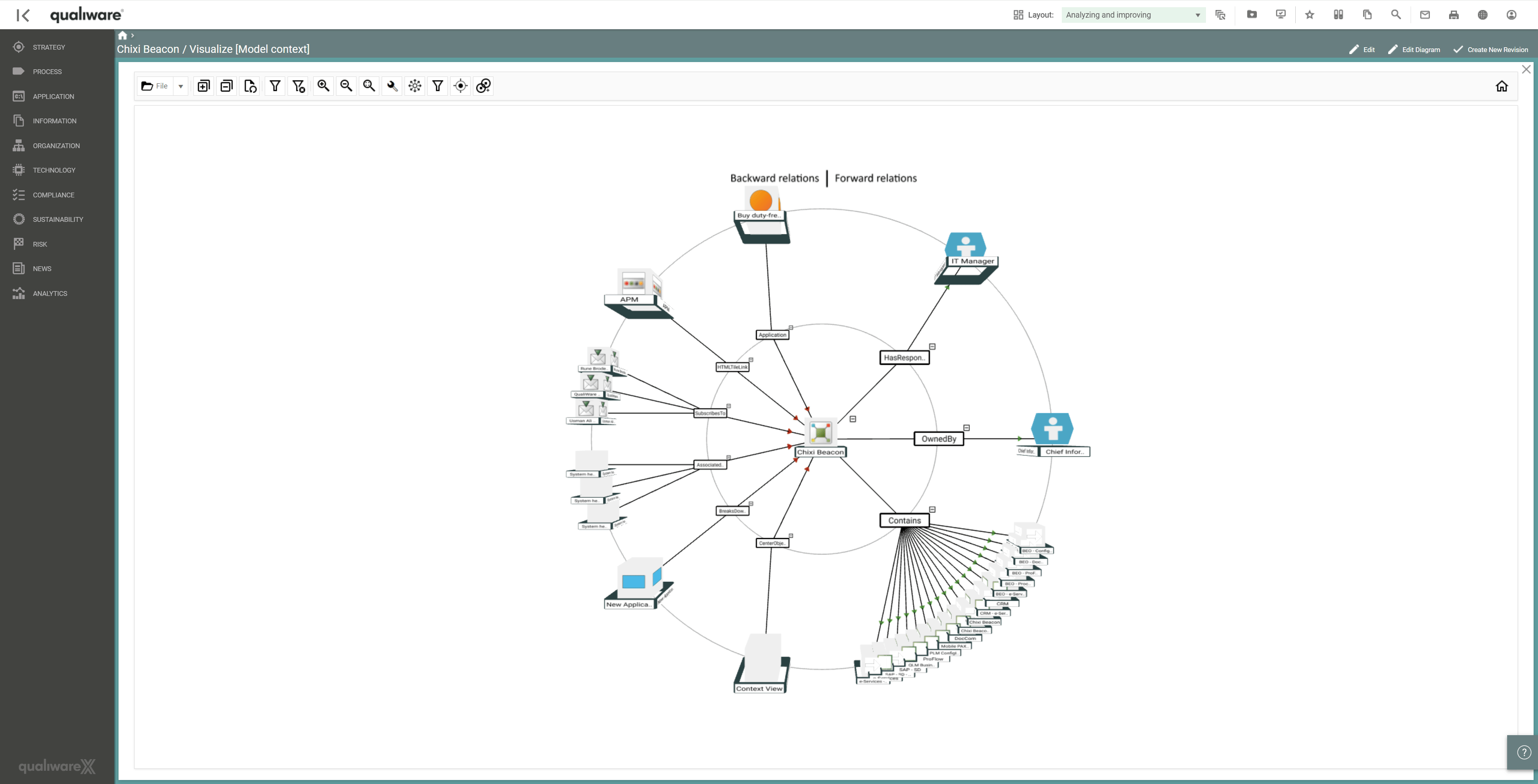
Another pivotal aspect that can be captured using QualiWare is assessing dependencies, integrations, and shared data between applications to proactively understand the impact of removing or supporting the applications in the portfolio. These can easily be viewed by accessing the 3D visualiser, which can be used to explore the forward and reverse relationships for the applications and associated technologies, processes, and services.