Purpose: The purpose of the Application Functionality Context template is to document the in which Activities and/or Business Processes a given Application Functionality is used.
Core concerns: The Application Functionality Context template can be used to create graphical views showing where Application Functionalities are used. The template enables you to model Application Functionalities, Activities and Business Processes. The Business Processes and Activities are connected to Application Functionalities using Functionality Usage.
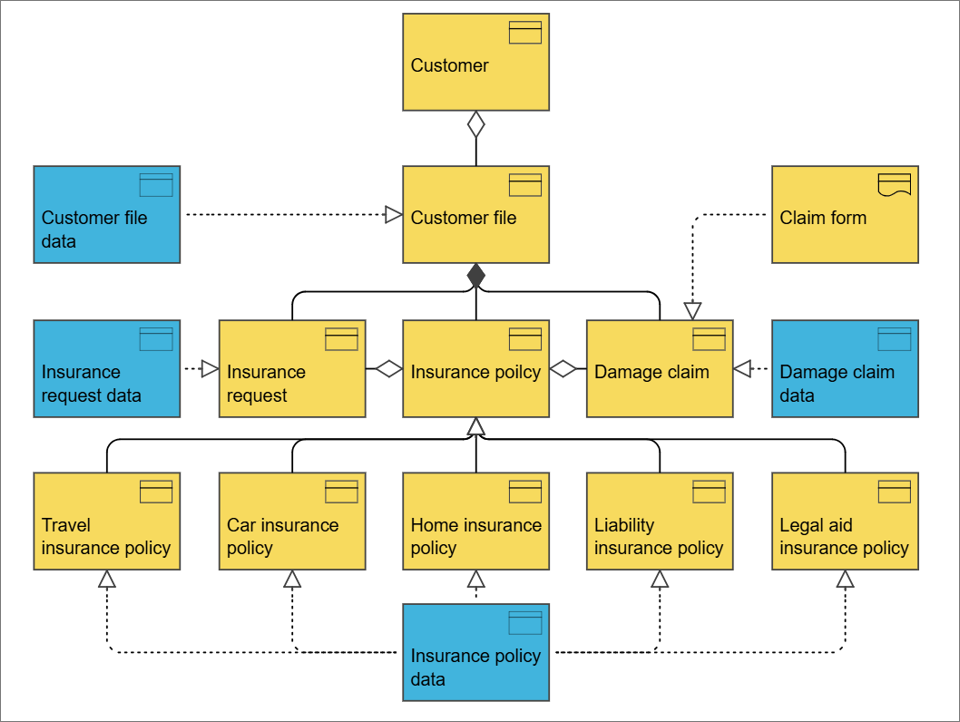
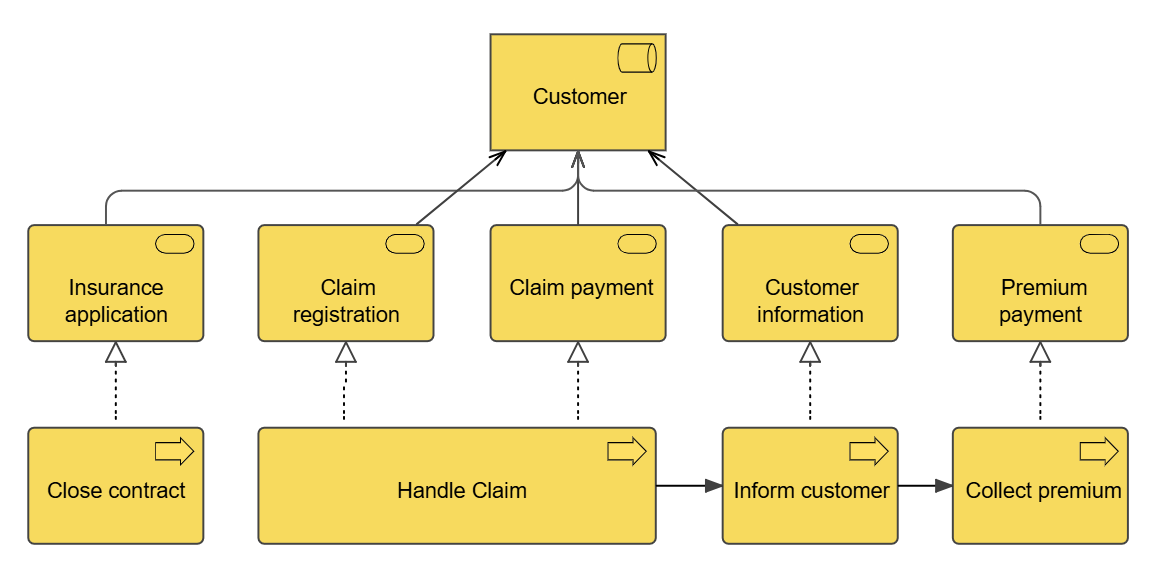
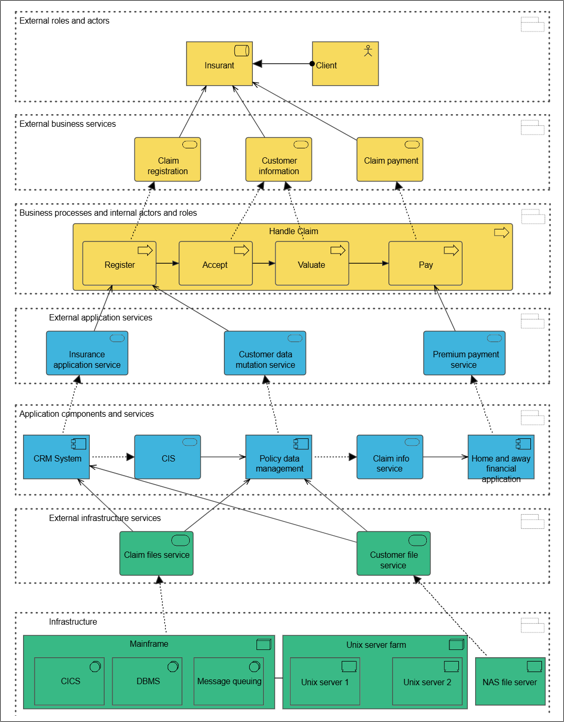
Below, you can see an example of an Application functionality contest diagram, where the context for the DocCom – Create and Store Document functionality is shown:
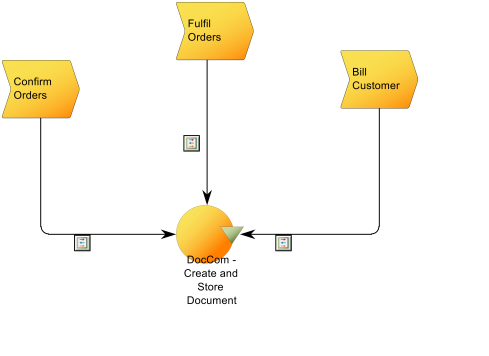
The diagram shows which Business Processes use the Application Functionality as well as which Information System delivers it.
Relation to other templates: To map applications hardware, the Application Architecture Diagram or Infrastructure Diagram template should be used. The Application Functionality Context template graphically connects functionalities of Information Systems to the Processes and Activities in which they are used. It offers an additional view to Application Architecture Diagrams, Workflow Diagrams, Business Process Diagrams and Business Process Networks.
Properties and metadata: The Application Functionality Context template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Application Functionality Context template where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.