Questions are used in a survey.
It it possible to create text answers or answers with options, where the respondent choice among predefined options.
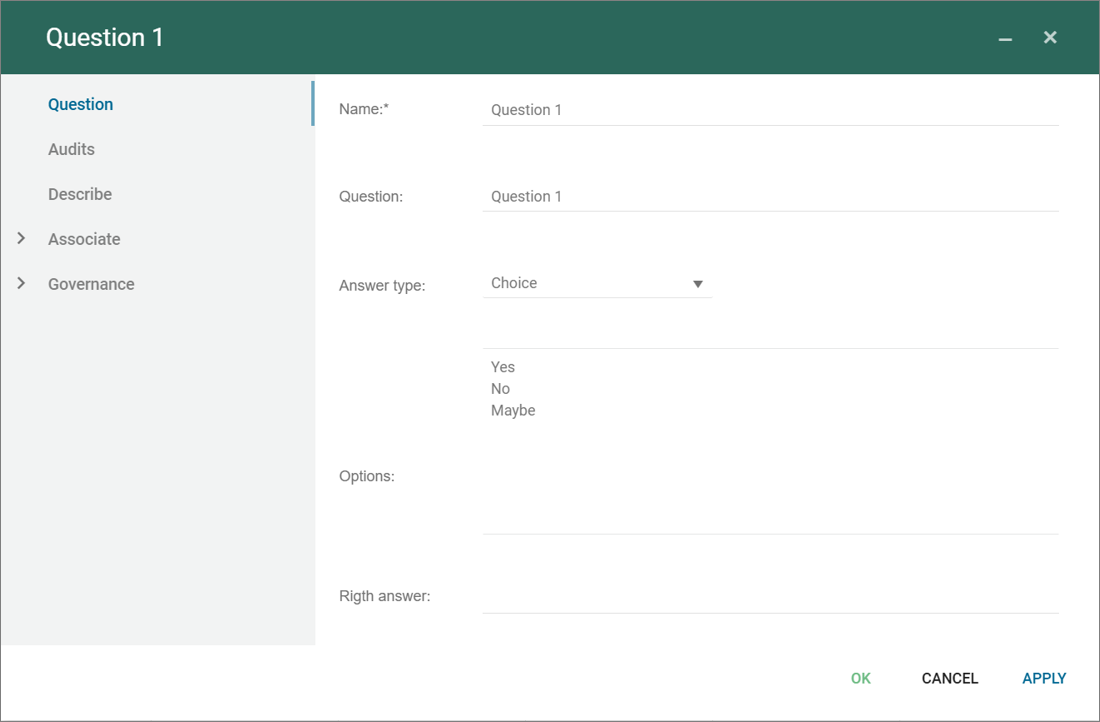
Questions are collected in Questiongroup as part of a questionnaire.
Read more about surveys here.
Templates and model types in the QualiWare platform.
Questions are used in a survey.
It it possible to create text answers or answers with options, where the respondent choice among predefined options.

Questions are collected in Questiongroup as part of a questionnaire.
Read more about surveys here.
The survey template is used to collect all relevant elements related to manage a survey, from designing the questionnaire, simulating it, inviting participants, and analyse the results.
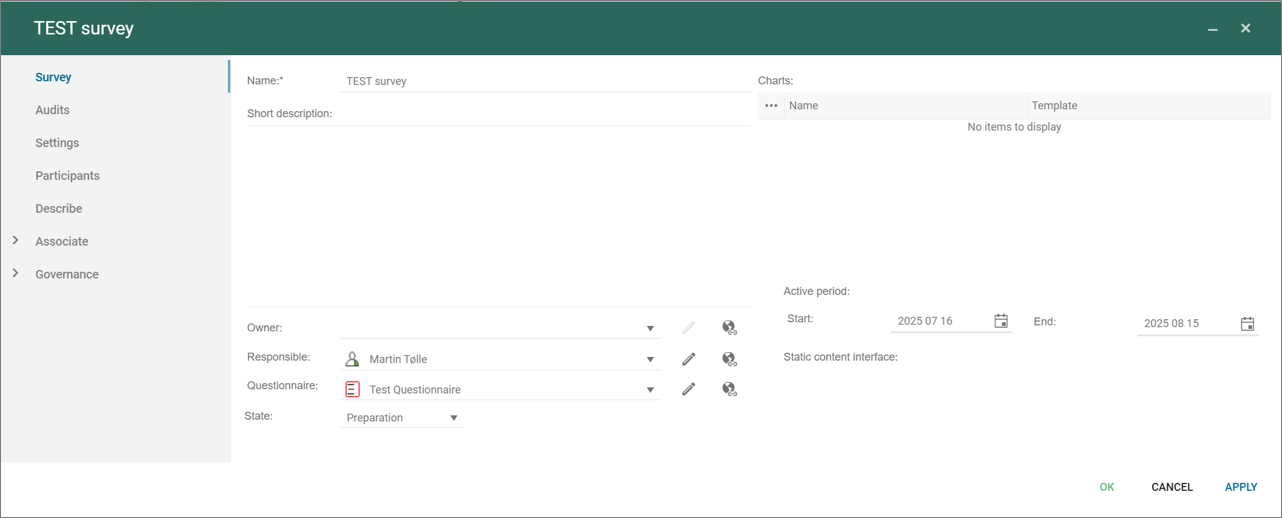
An essential part of the survey is the questionnaire that is linked to the survey.
The questionnaire can contain one or more questionsgroups and each questiongroup can contain one or more questions.
Read more about survey here.
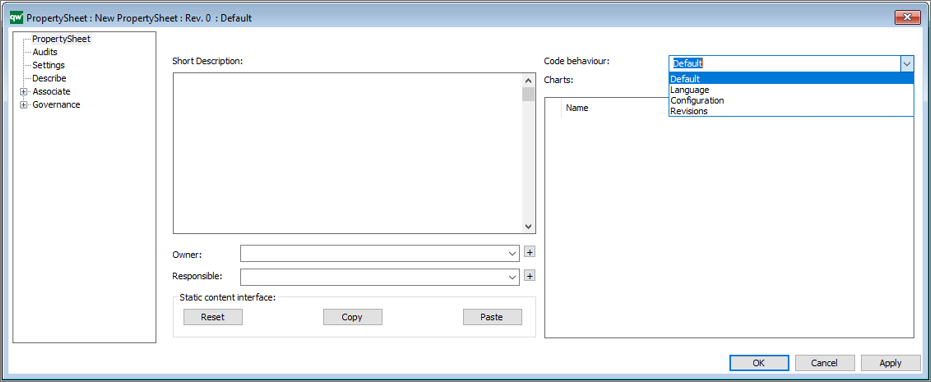
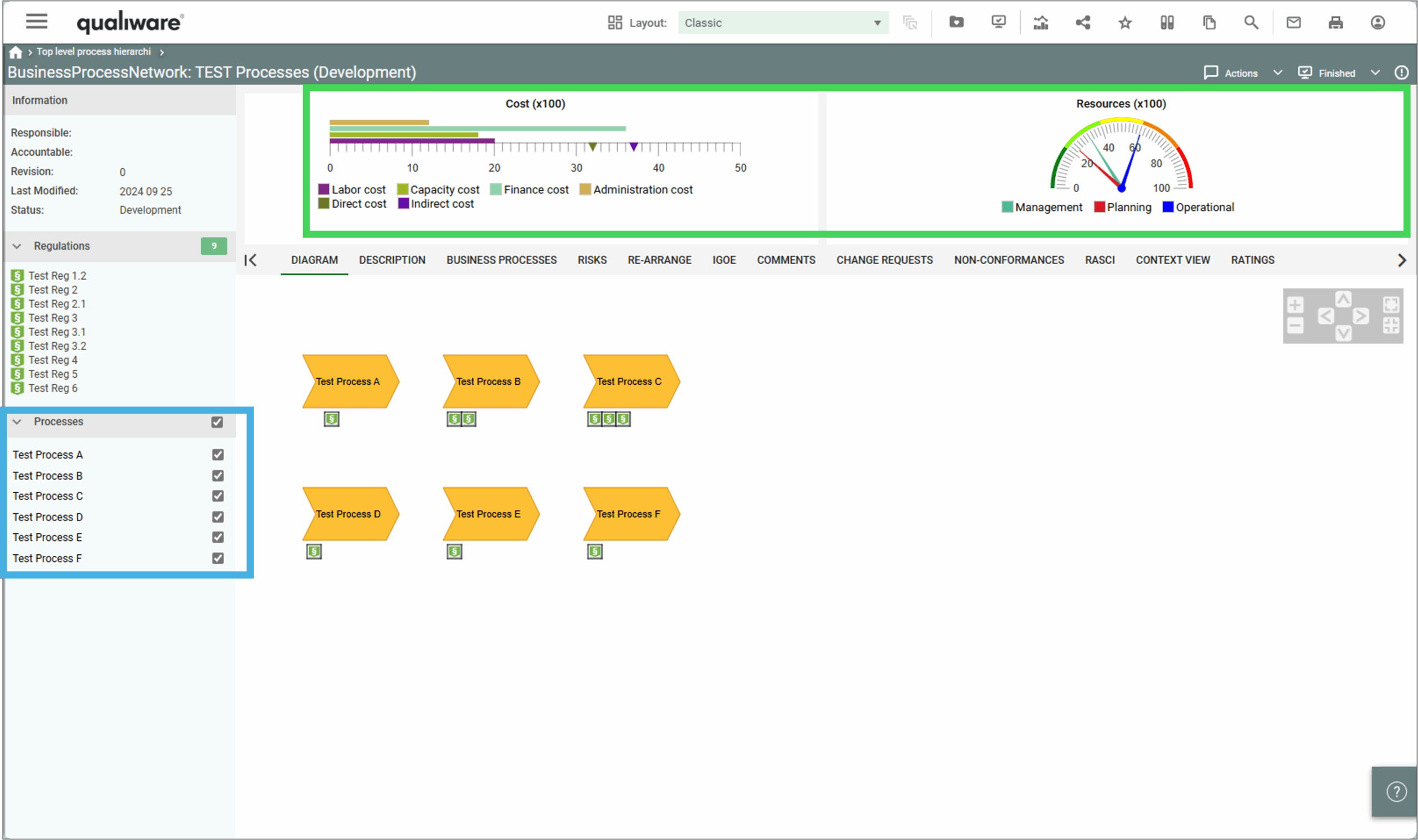
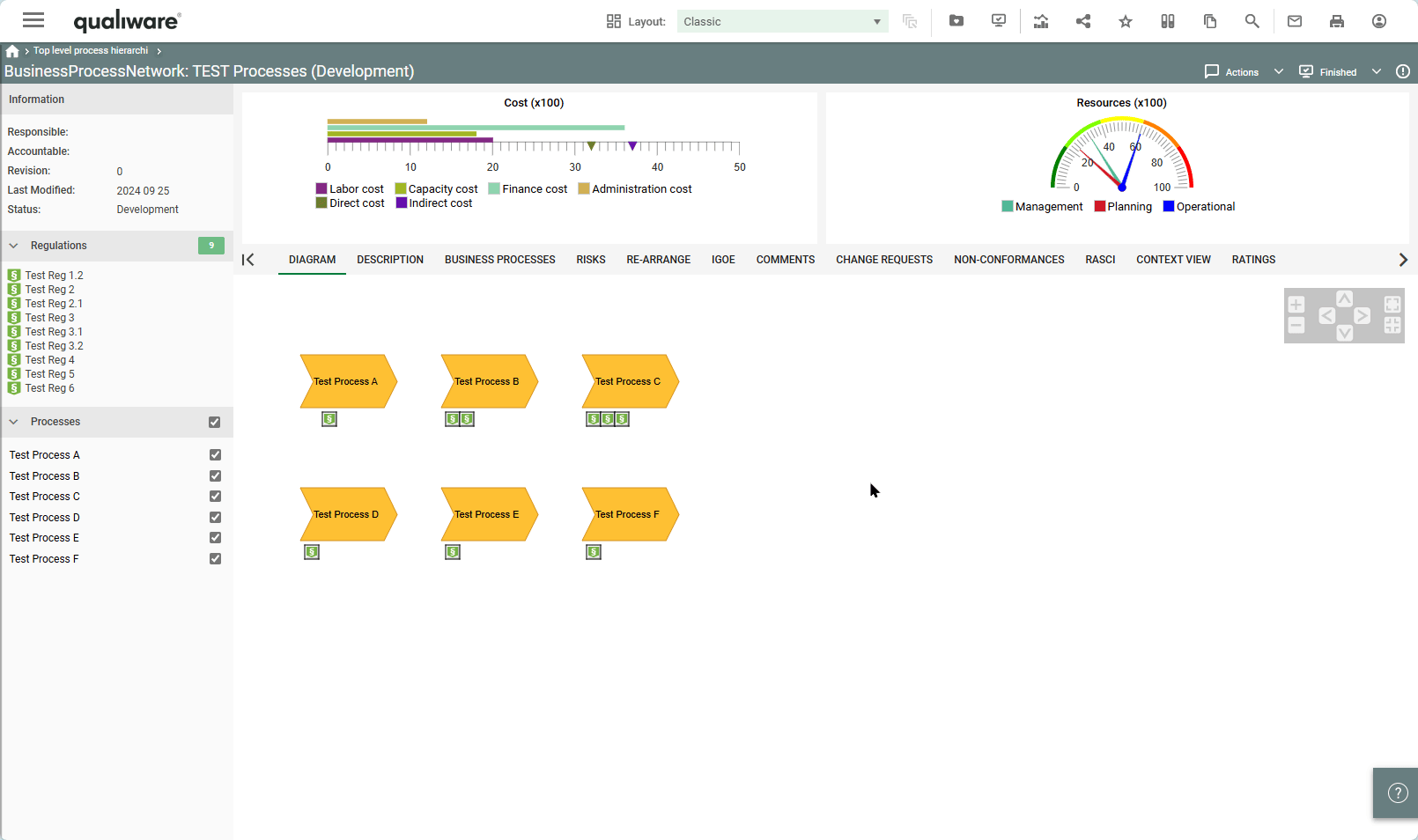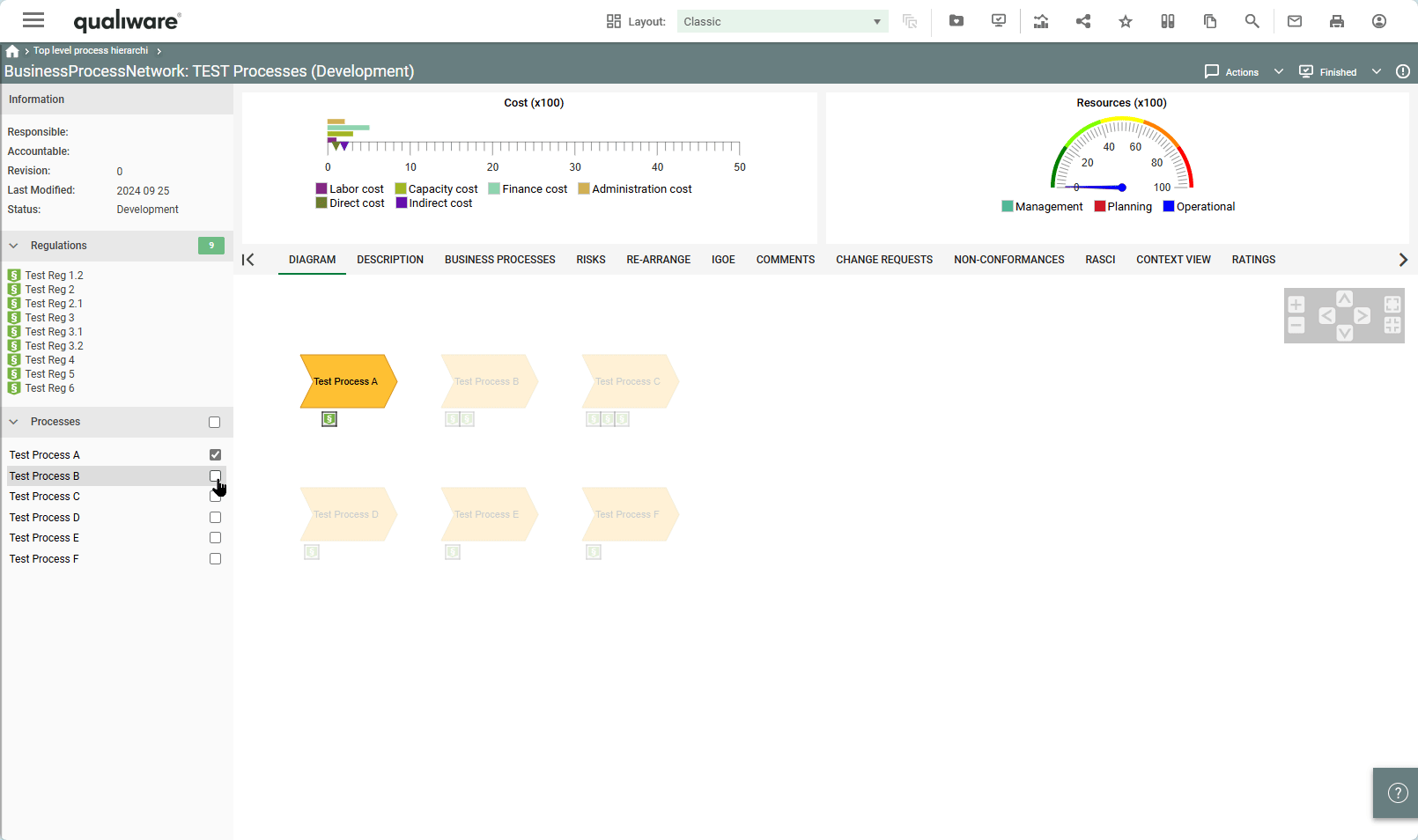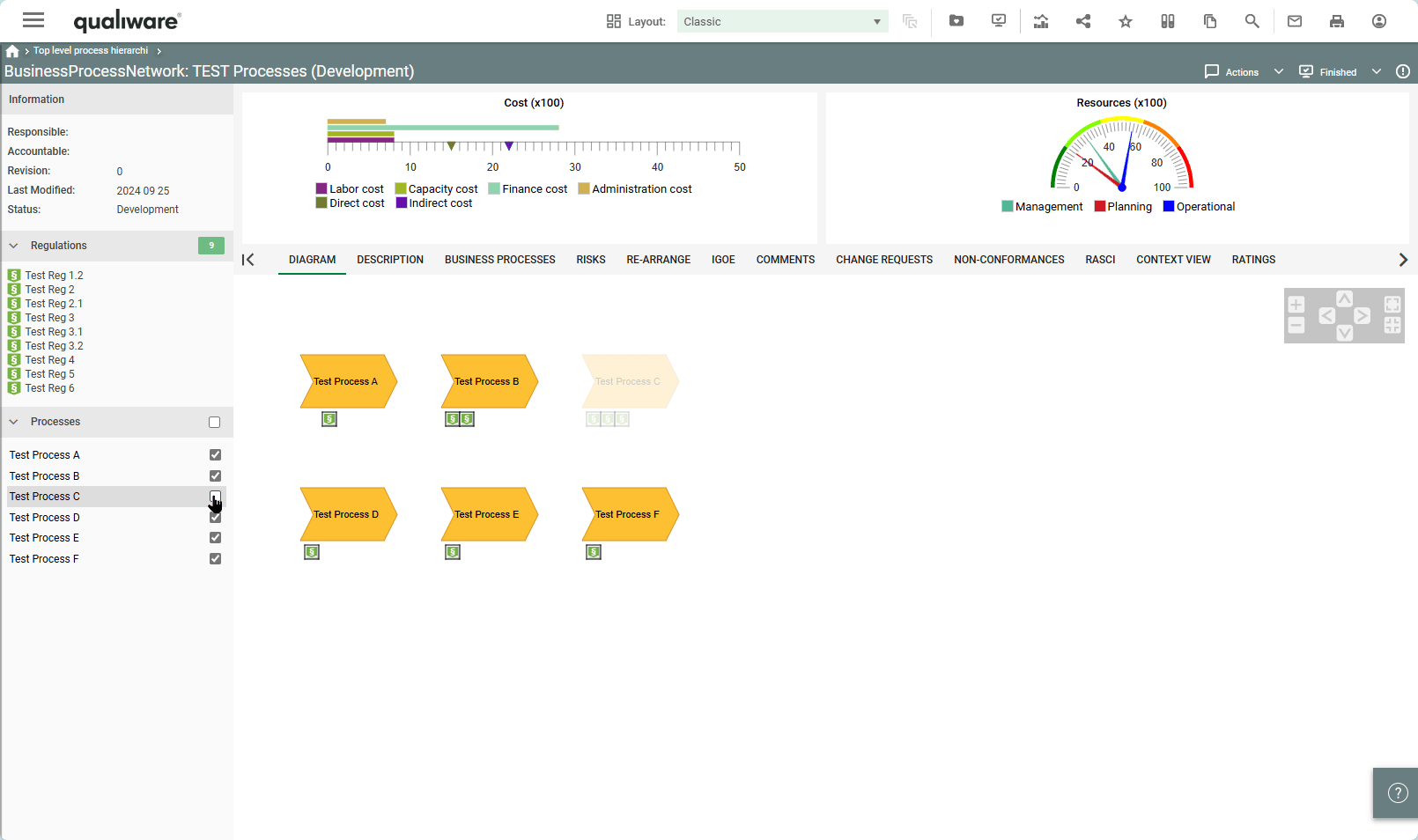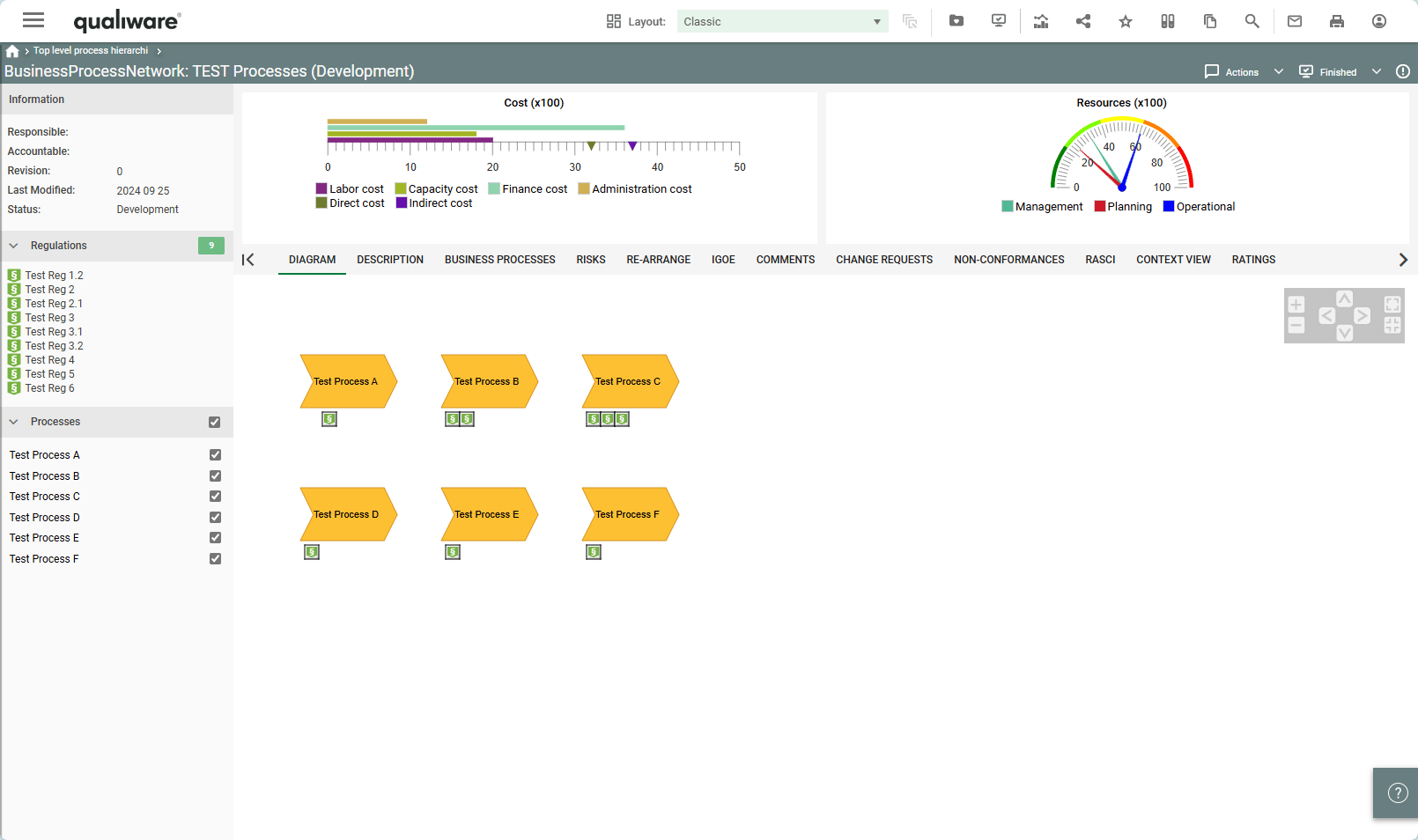
QualiWare 10.10 introduces a new propertysheet template, that enables to get a spreadsheet view of:
This enables the user to easily explore and modify properties of different variants of the same objects.
The behavior of the propertysheet can be selected from the list under code behaviour.
On the Settings tab it is possible to right click in the window and “Add standard parameters”.
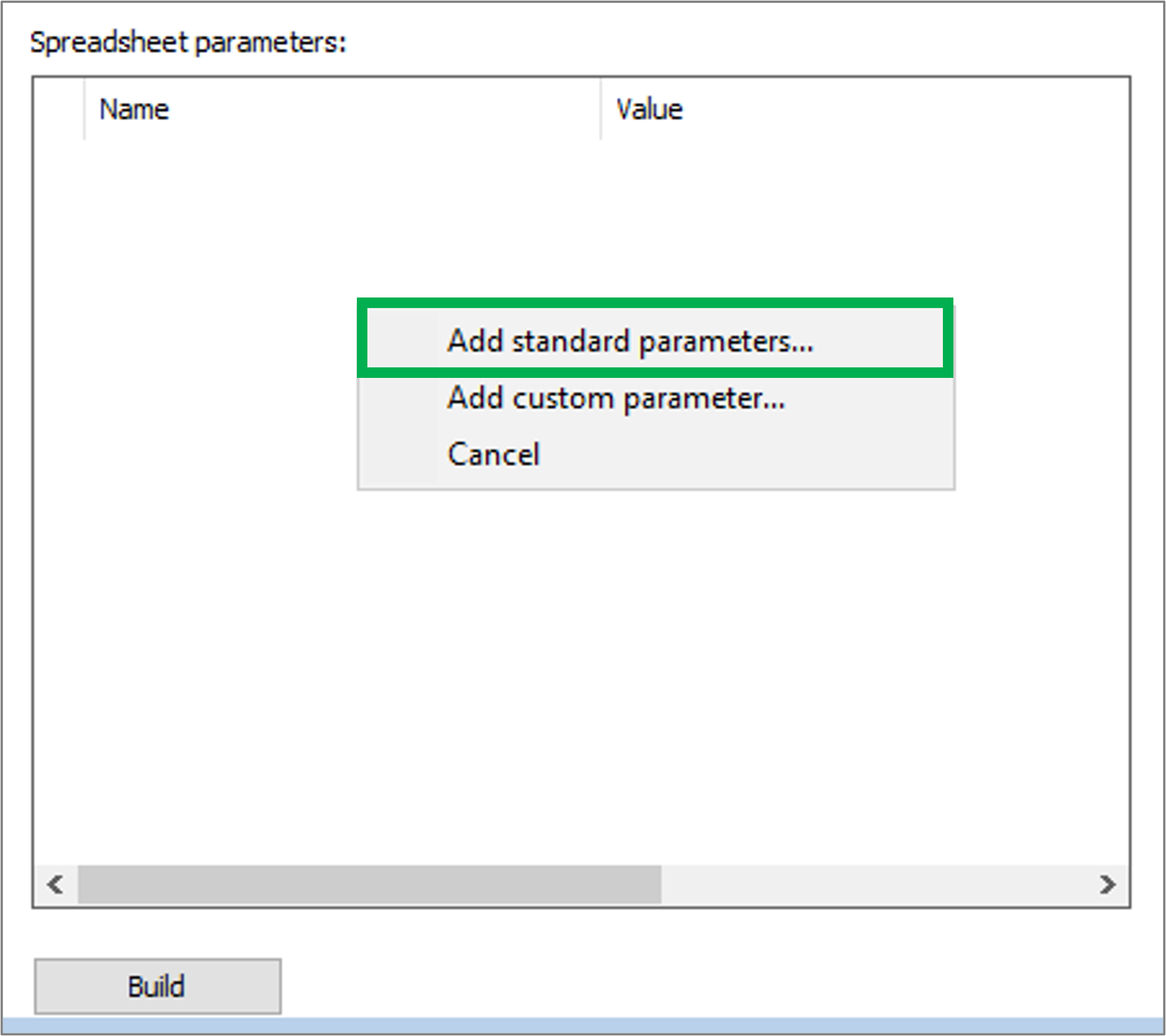
As a part of these settings, it is possible to specify the behavior of the spreadsheet.
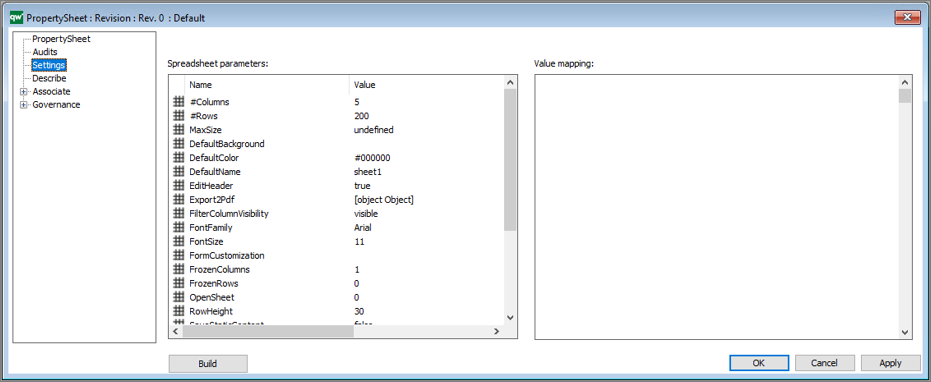
In the setting you can specify how many colums should be included in the spreadsheet. If more revisions are available the sheet will show the following coloum:
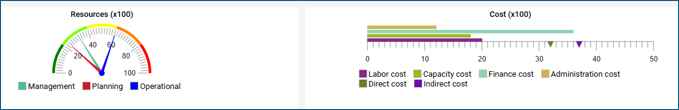
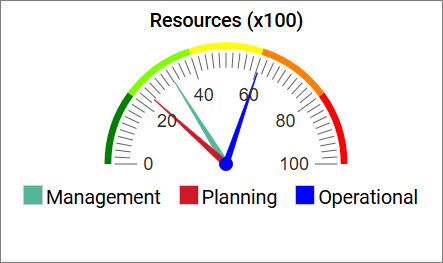
Gauges are a form of charts that can be used to in the web solution.
When used in relation to a contextbox with a checklist they aggregate based upon the checked selection.
Business Gauges can be used in the center top content of the HTMLTemplateDefinition.
Concerns: Here you link to an object of the type which data you would like to display (in the example above an InformationSystem)
Value:
For the gauge chart to display anything, it needs some values. Values are provided by either using URL parameters or by setting up a checklist in a HTMLContentBox left or right panel. When using a checklist, the attributes, defined in Value, will be taken from the selected objects and used in the gauge chart.
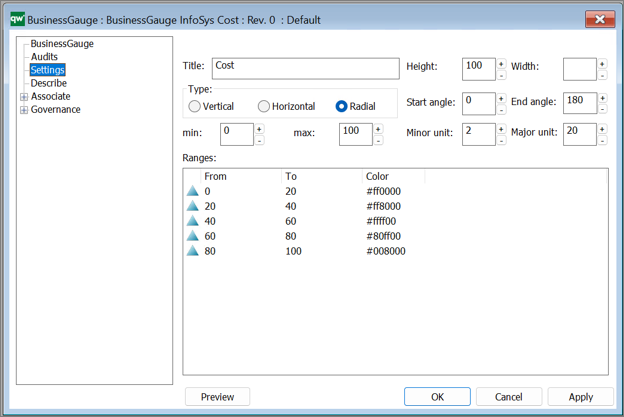
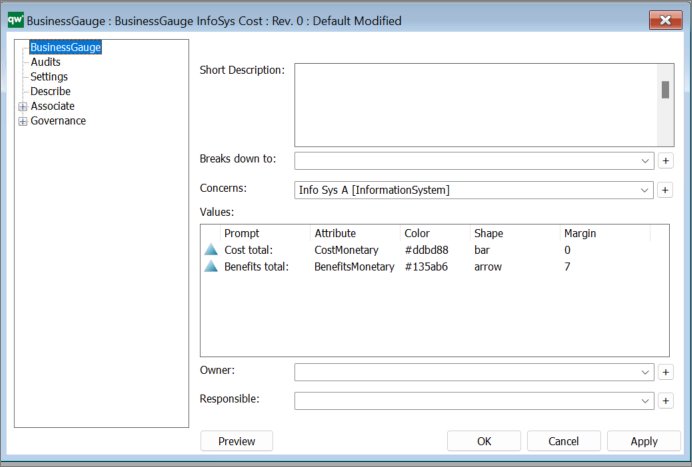
Title: The title will be shown in the top of the gauge chart on web.
Type:
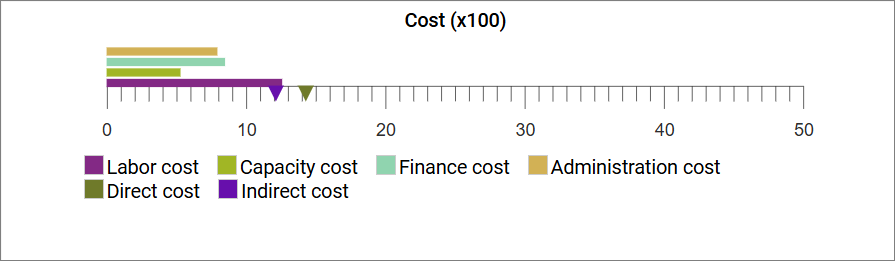
Miscellaneous display settings:
These are a mix of settings that each has an impact on how the final chart is displayed.
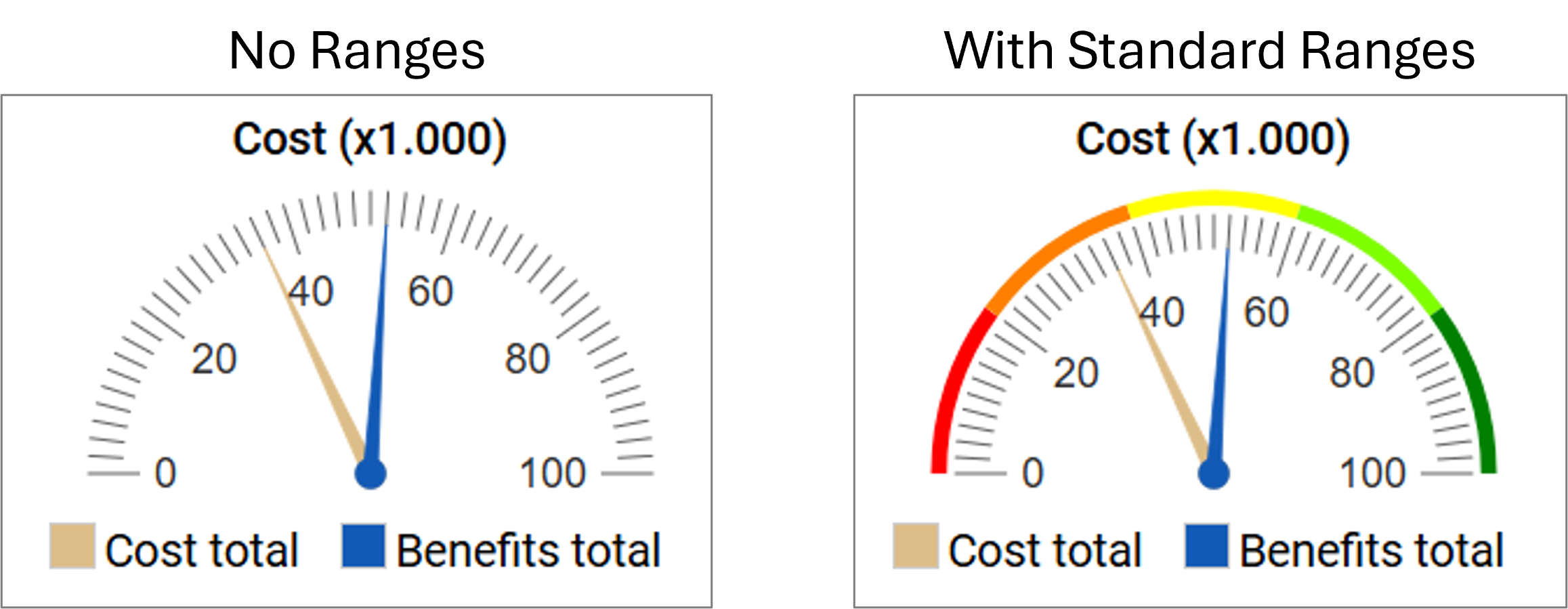
Ranges:
Ranges can be used to define if a range should be shown in a specific color. This can be used to enable a user to quickly see if any values are outside of normal values or in other ways concerning.
The Introductory Viewpoint is a legacy viewpoint from ArchiMate 2.0.
The Introductory Viewpoint in ArchiMate is designed to provide a simplified overview of an architecture, typically used at the beginning of a design process. This viewpoint uses a subset of the full ArchiMate language with a simplified notation, making it easier to understand and communicate the initial ideas without overwhelming stakeholders with too much detail.
The Landscape Map Viewpoint is a legacy viewpoint introduced in ArchiMate 2.0.
This viewpoint helps in visualizing the relationships and dependencies between different architectural elements across various layers, providing a comprehensive overview of the architecture landscape.
A ValueStream is a step in a ValueStreamModel, representing a step in a stream.
A ValueStream has inherited a set of the properties from the BusinessProcess, enabling to describe it:
Purpose: The purpose of a Value Stream Model is to model a value stream end-to-end from the perspective of one stakeholder and one value proposition.
Core concerns: The Value Stream Model template enables you to model the value stream stages, triggering stakeholder, and the value proposition. The value stream represents a formal description of how stakeholder value is delivered.
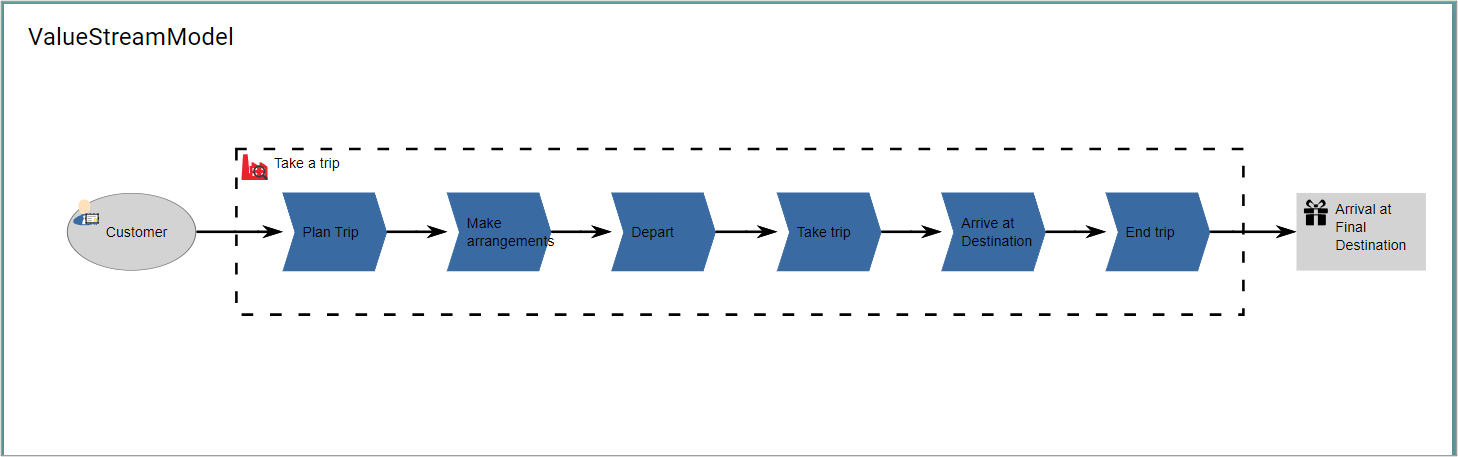
A sequence of activities that create an overall result for a customer, stakeholder, or end user.
A value stream describes how an enterprise organizes its activities to create value. A key principle of value streams is that value is always defined from the perspective of the stakeholder – the customer, end user, or recipient of the product, service, or deliverable produced by the work.
Value streams are typically realized by business processes and possibly other core behavior elements. The stages in a value stream provide a framework for organizing and defining business processes, but different parts of the organization may have their own implementations of business processes that realize the same value stream stage. Conversely, one business process may realize multiple stages in a value stream.
It is recommended that the name of a value stream be expressed using a verb-noun construct in the active tense; e.g., “Acquire Insurance Product”.

The role of an individual, team, or organization (or classes thereof) that represents their interests in the effects of the architecture. In order to direct efforts to their interests and concerns, stakeholders change, set, and emphasize goals. Stakeholders may also influence each other. Examples of stakeholders are executives and key managers in an organization, the board of directors, shareholders, customers, business and application architects, and external partners and regulators. The name of a stakeholder should preferably be a noun.