Concerns: Consistency, reduction of complexity, impact of change, flexibility
Purpose: Designing, deciding, informing
Scope: Multiple layer/Multiple aspect
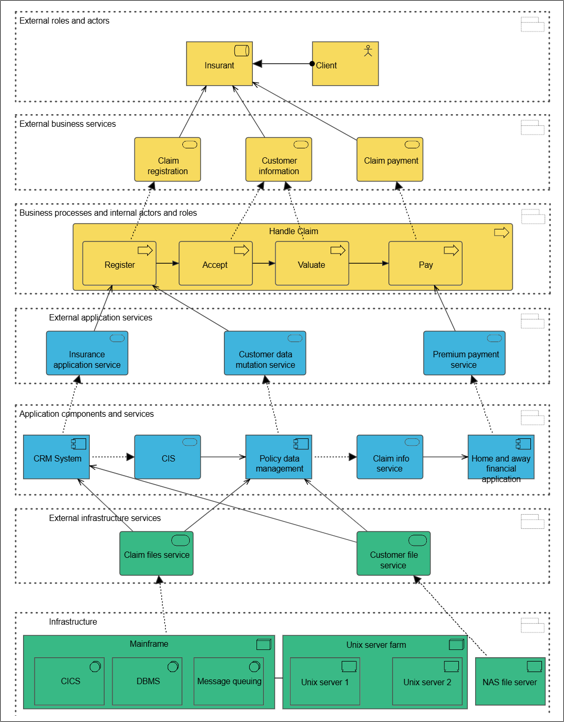
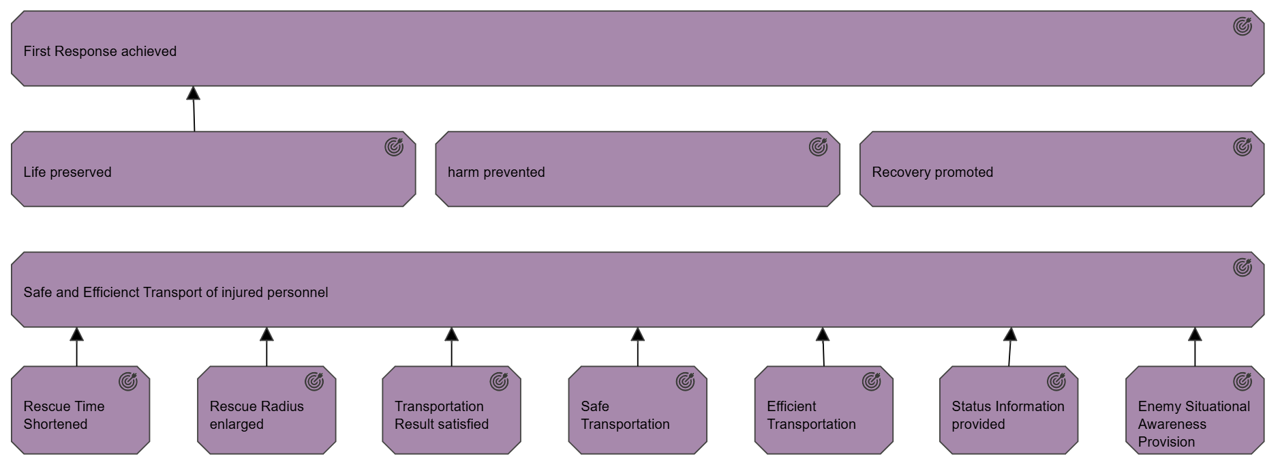
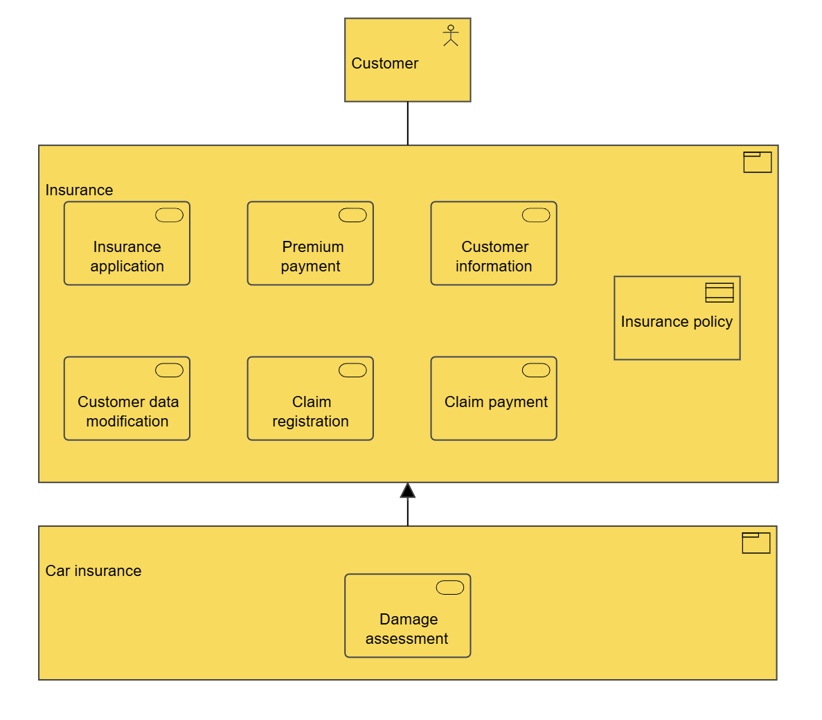
The layered viewpoint pictures several layers and aspects of an Enterprise Architecture in one diagram. There are two categories of layers, namely dedicated layers and service layers. The layers are the result of the use of the “grouping” relationship for a natural partitioning of the entire set of objects and relationships that belong to a model. The technology, application, process, and actor/role layers belong to the first category. The structural principle behind a fully layered viewpoint is that each dedicated layer exposes, by means of the “realization” relationship, a layer of services, which are further on “serving” the next dedicated layer. Thus, we can easily separate the internal structure and organization of a dedicated layer from its externally observable behavior expressed as the service layer that the dedicated layer realizes. The order, number, or nature of these layers are not fixed, but in general a (more or less) complete and natural layering of an ArchiMate model should contain the succession of layers depicted in the example given below. However, this example is by no means intended to be prescriptive. The main goal of the layered viewpoint is to provide an overview in one diagram. Furthermore, this viewpoint can be used as support for impact of change analysis and performance analysis or for extending the service portfolio.
All core elements and all relationships are permitted in this viewpoint.