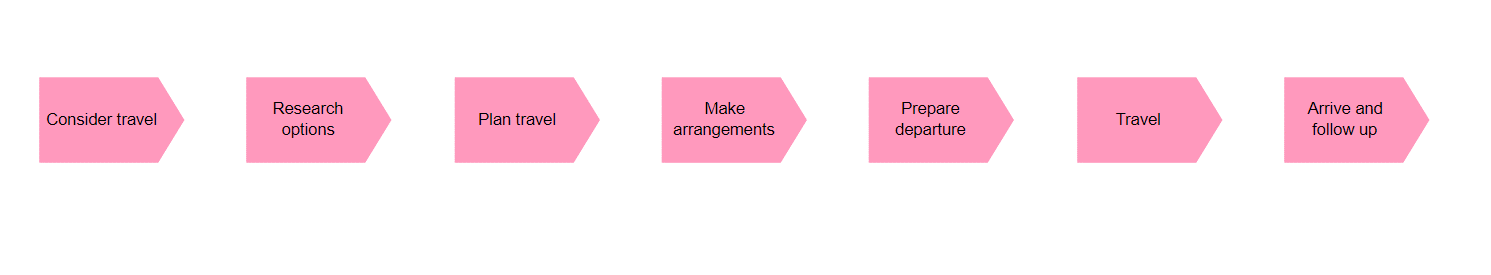
Purpose: The Business Function Viewpoint in ArchiMate aims to model the capabilities and functionalities of an enterprise, and how they are organized and executed to achieve business goals and objectives. This helps to provide a clear understanding of how the enterprise operates and how different functions and processes are interdependent.
Core Concerns: The core concerns of the Business Function Viewpoint include modeling the business functions and processes, their dependencies, inputs and outputs, and how they are organized to achieve business goals. By focusing on these core concerns, the Business Function Viewpoint can help identify opportunities for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and creating value for the organization. It can also facilitate communication and collaboration among stakeholders, providing a common understanding of the enterprise’s functional architecture and how it supports business objectives.
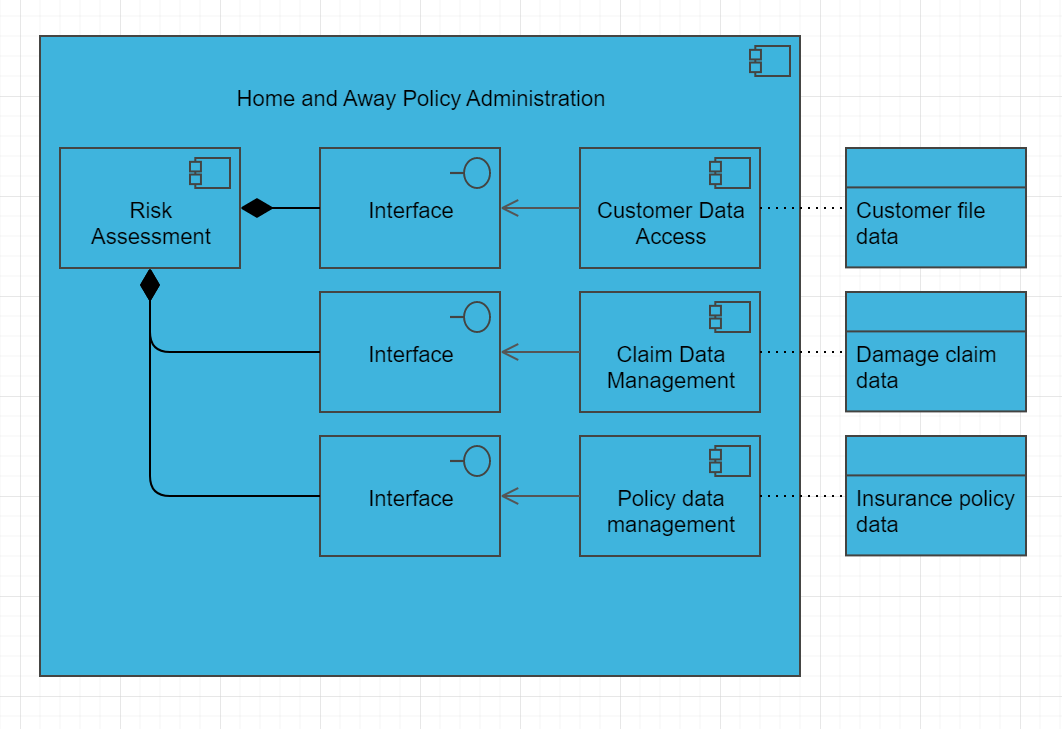
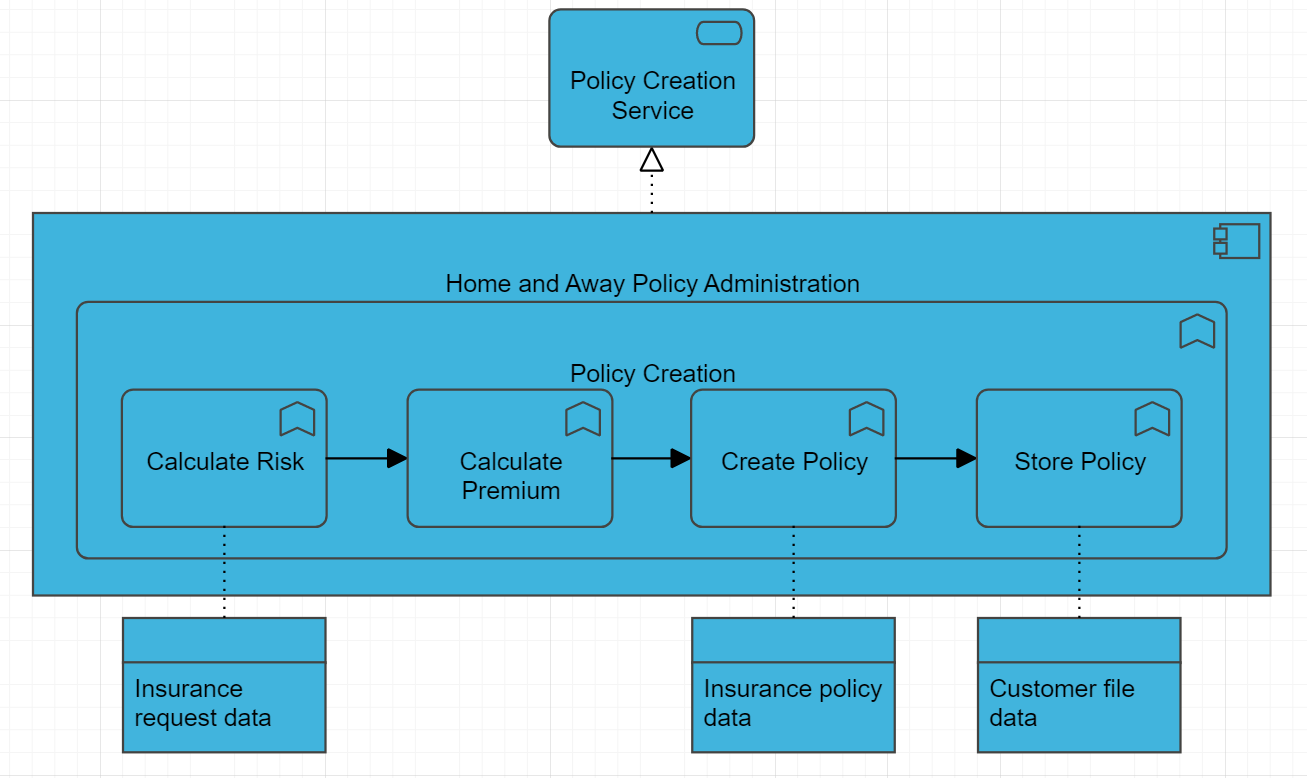
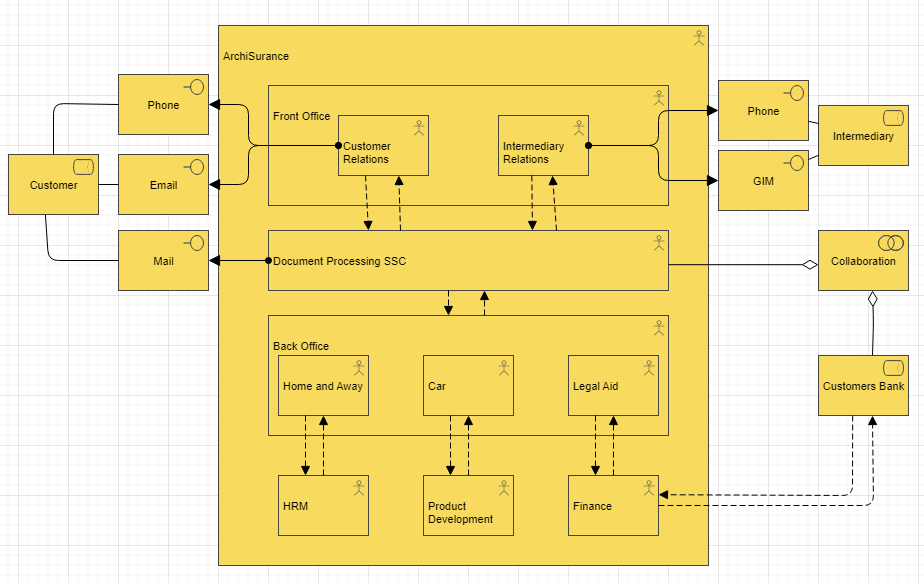
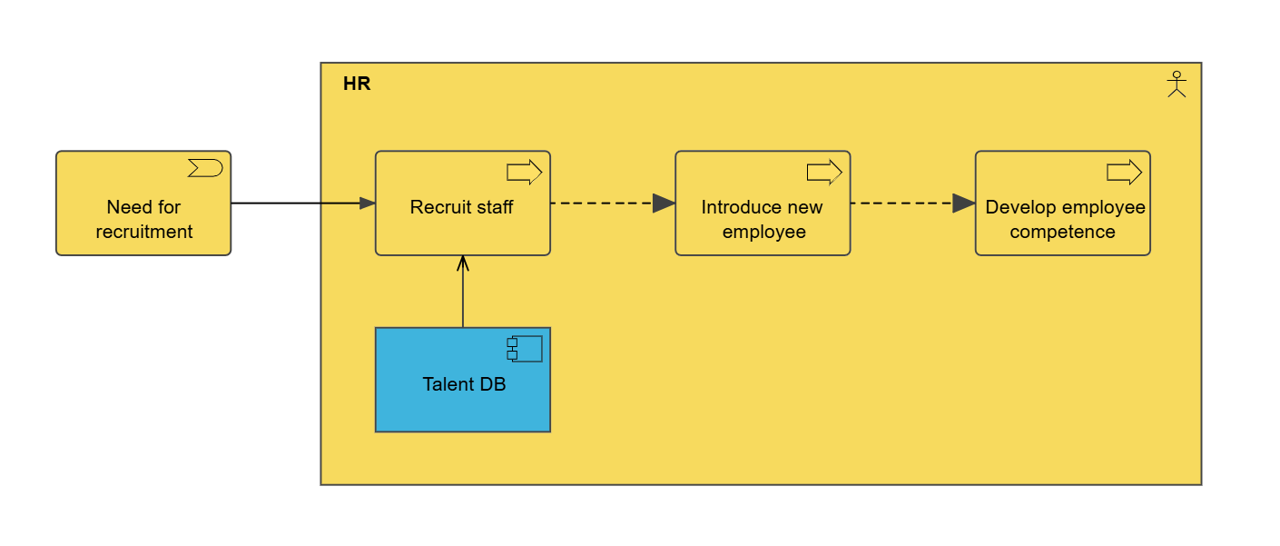
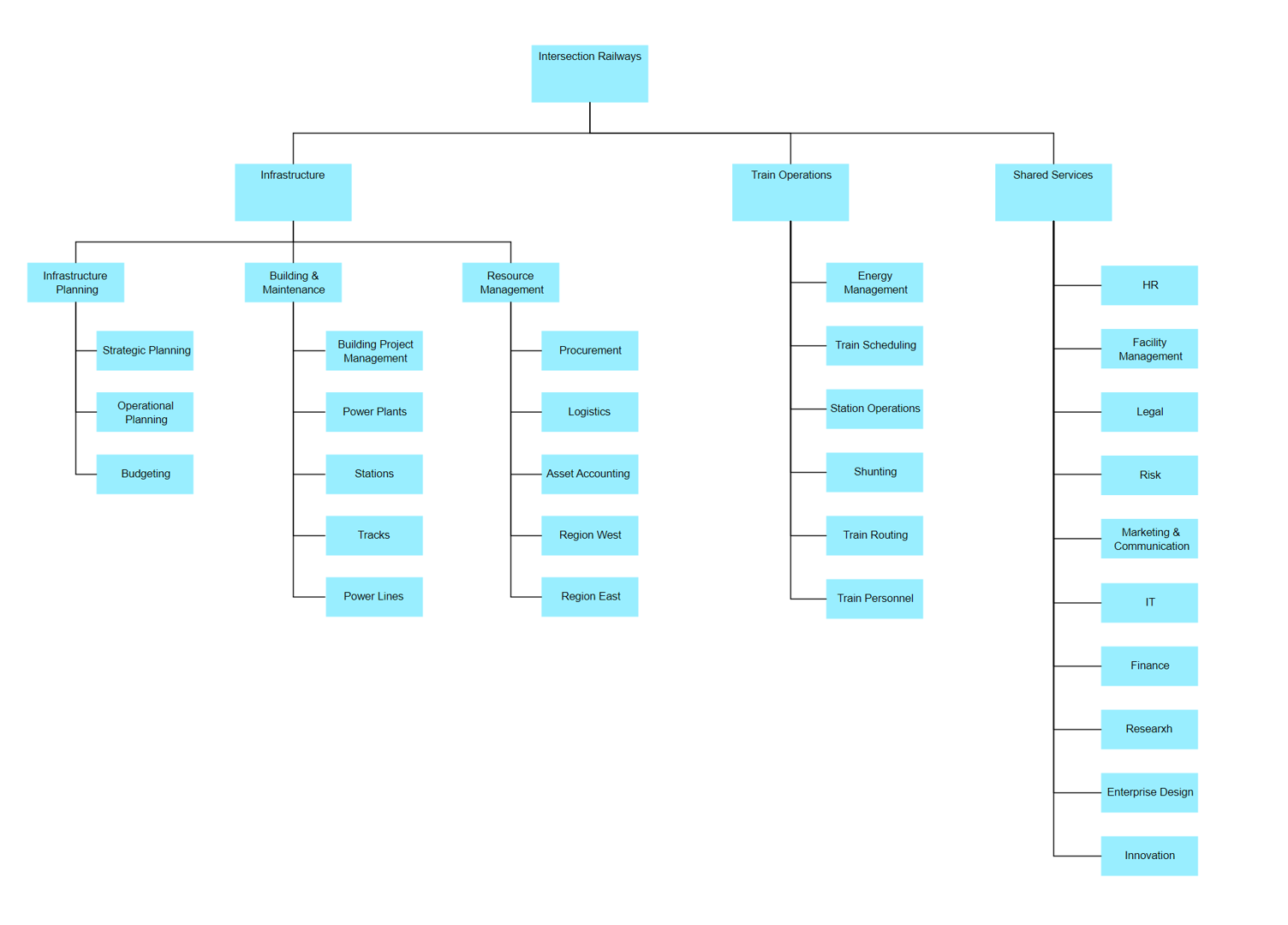
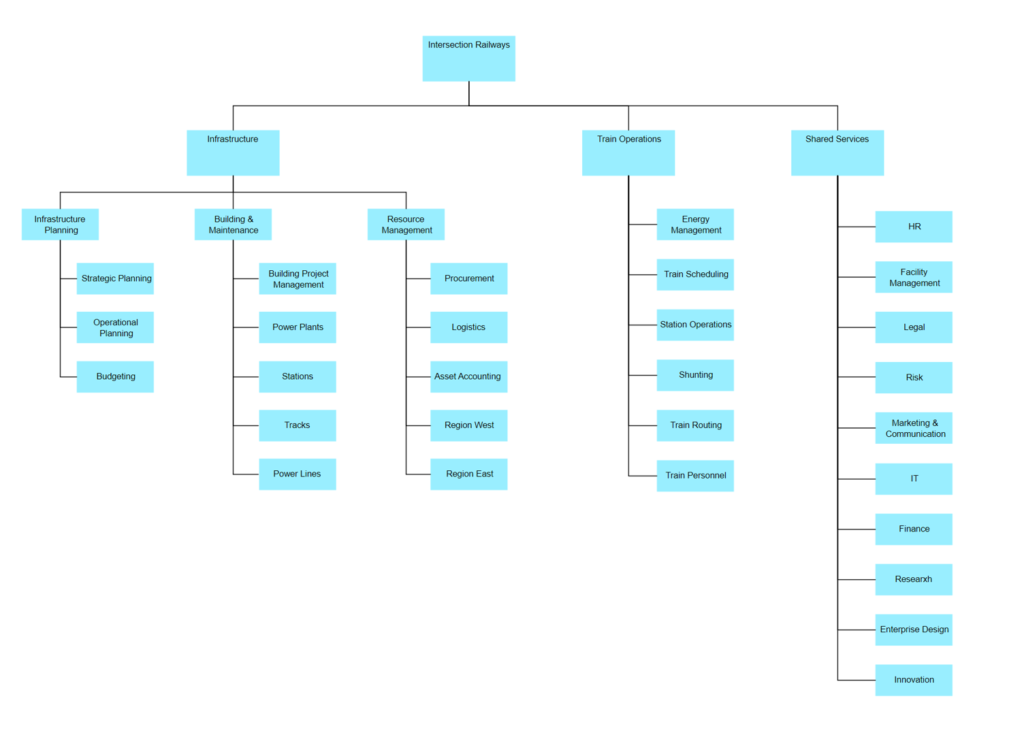
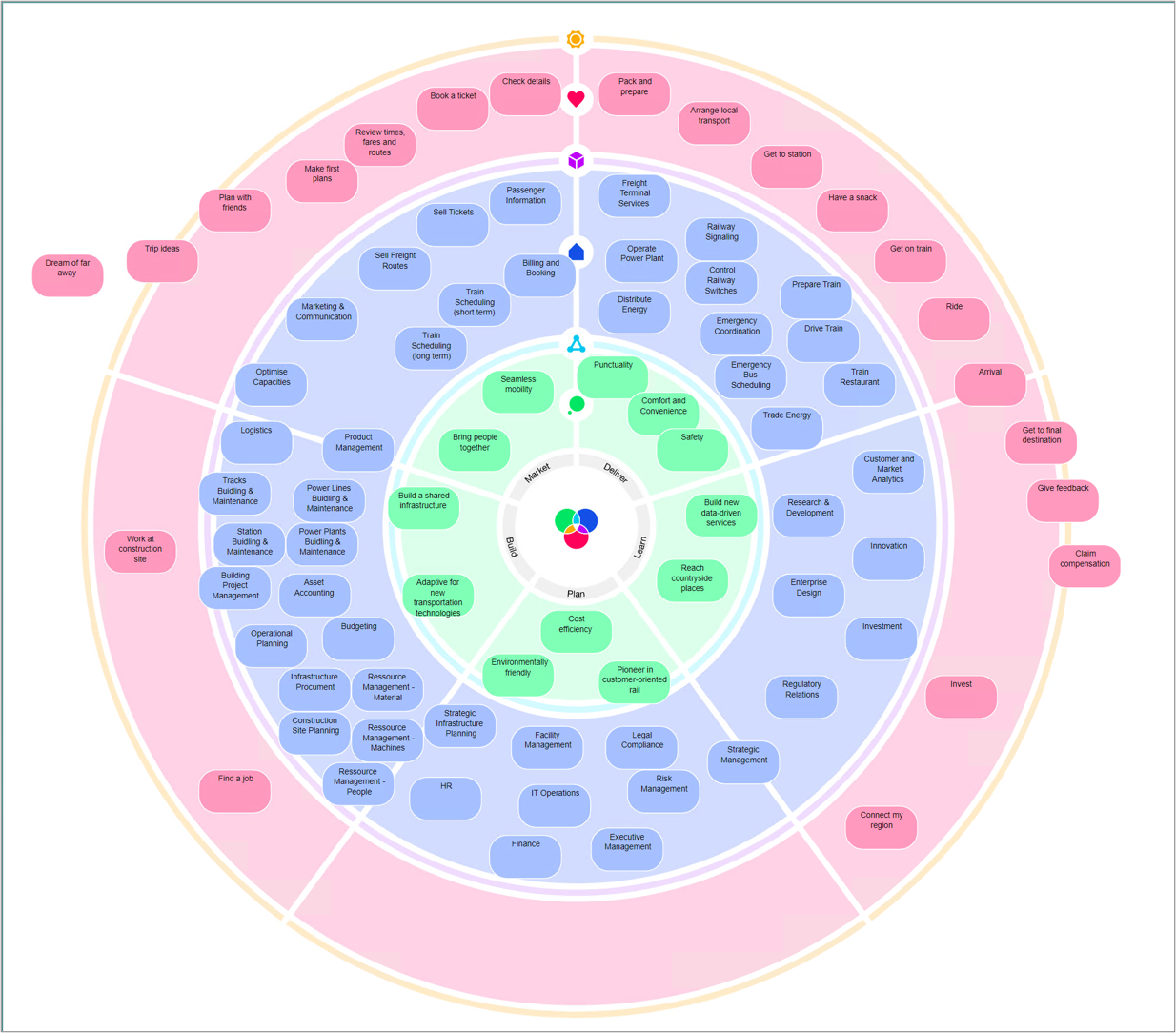
Example:
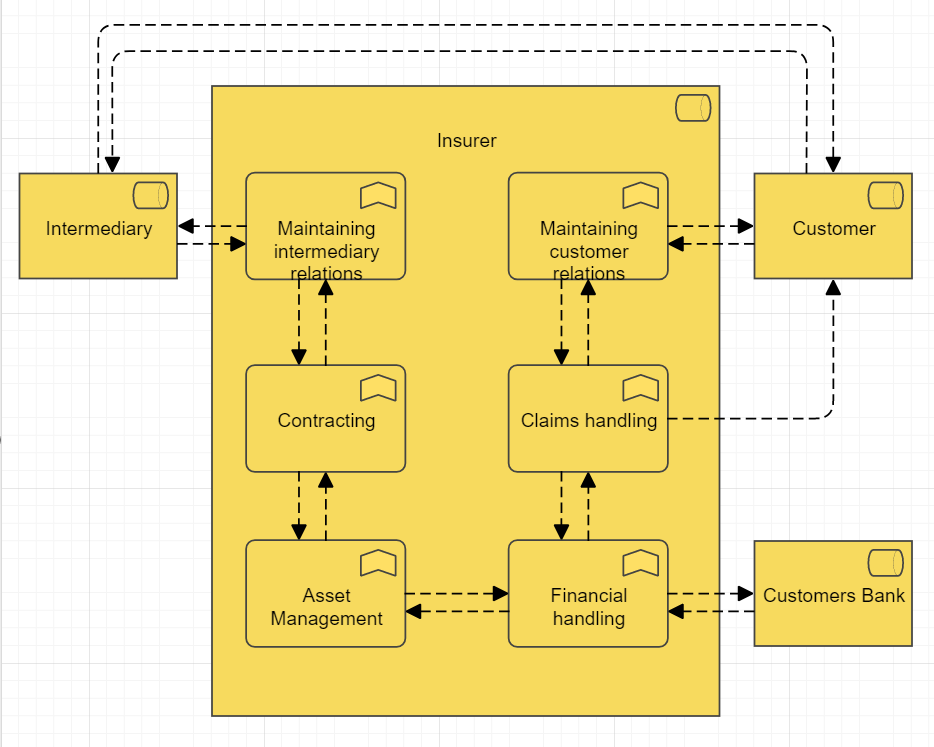
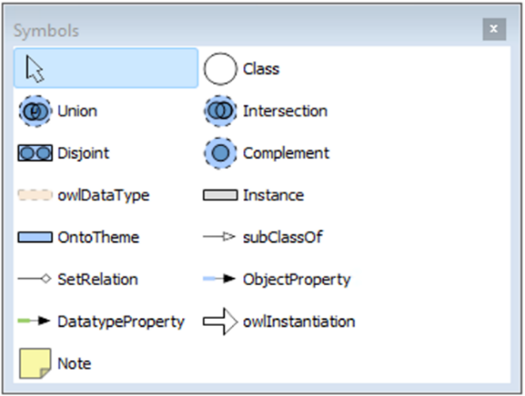
Overview: The Business Function Viewpoint is a perspective in the ArchiMate enterprise architecture modeling language that focuses on the business functions and processes of an enterprise. It provides a high-level overview of the enterprise’s functional architecture and how it supports business objectives. In the Business Function Viewpoint, business functions are represented as rectangles with labels that describe their purpose, while processes are represented as rounded rectangles with labels that describe their activities.
The Business Function Viewpoint includes several concepts for modeling different aspects of business functions, including:
- Business Functions: A business function is a capability or set of capabilities that performs a specific business activity. Business functions can be modeled to show their dependencies, inputs and outputs, and how they are organized to achieve business goals.
- Processes: A process is a series of activities that transforms inputs into outputs. Processes can be modeled to show their inputs and outputs, and how they are related to other processes and business functions.
- Dependencies: Dependencies represent the relationships between different business functions and processes. Dependencies can be modeled to show how different functions and processes are interdependent and how changes in one area can affect other areas.
- Inputs and Outputs: Inputs and outputs represent the data, information, and materials that are exchanged between different business functions and processes. Inputs and outputs can be modeled to show how they are related to different functions and processes and how they support business objectives.
Overall, the Business Function Viewpoint is useful for modeling the functional architecture of an enterprise and understanding how different functions and processes are interdependent and support business objectives. It can also help identify opportunities for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and creating value for the organization.