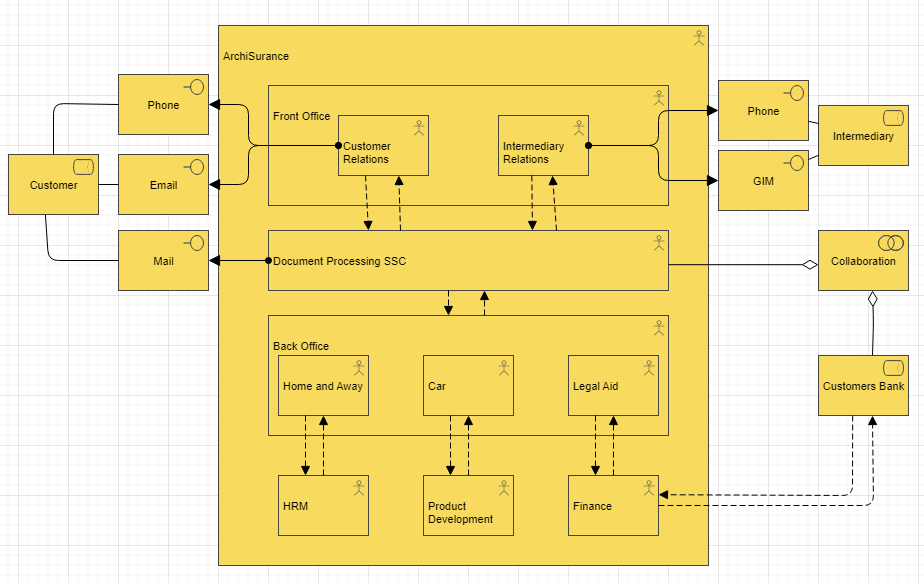
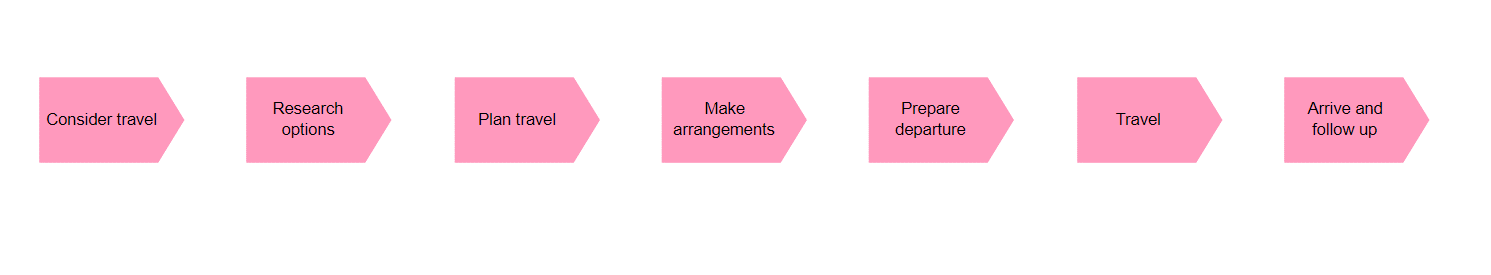
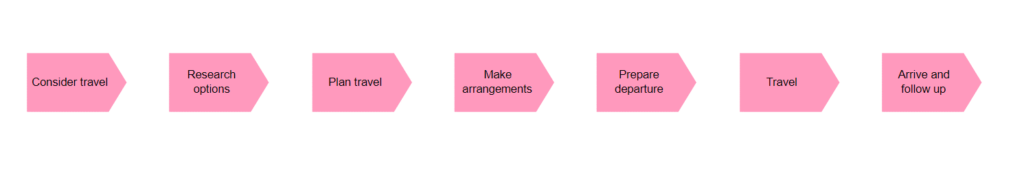
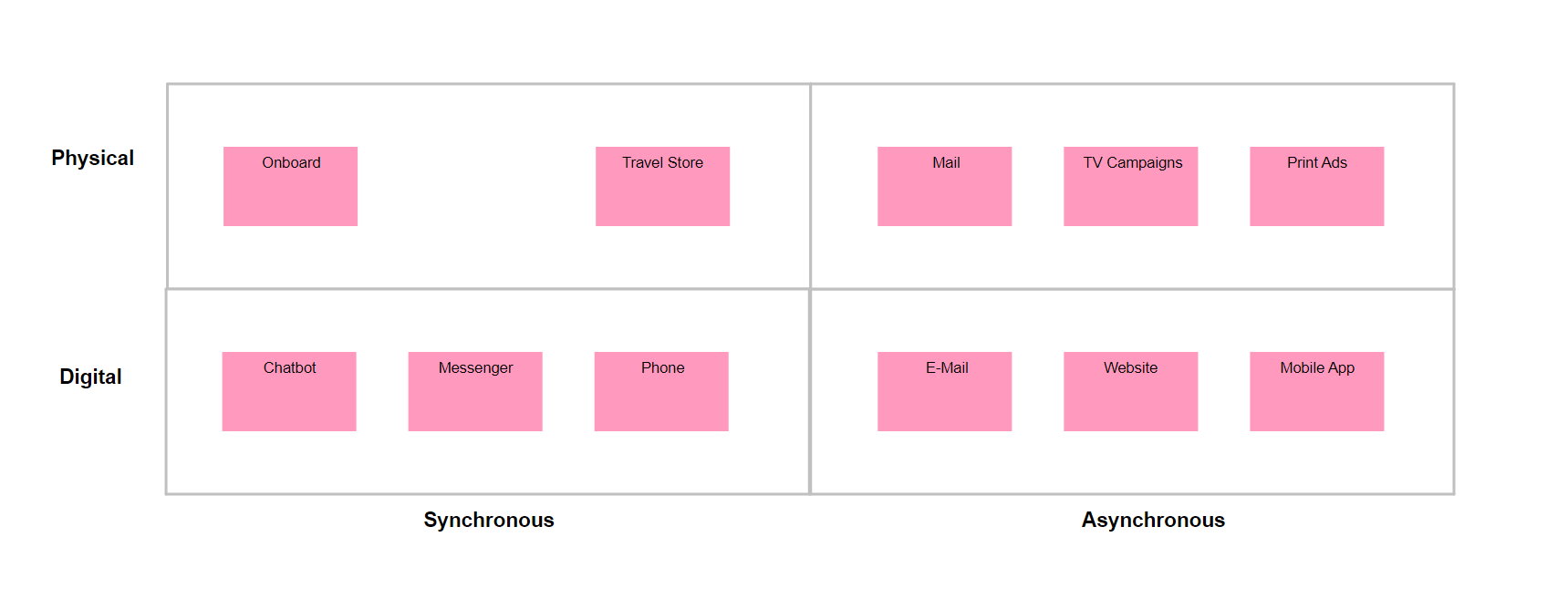
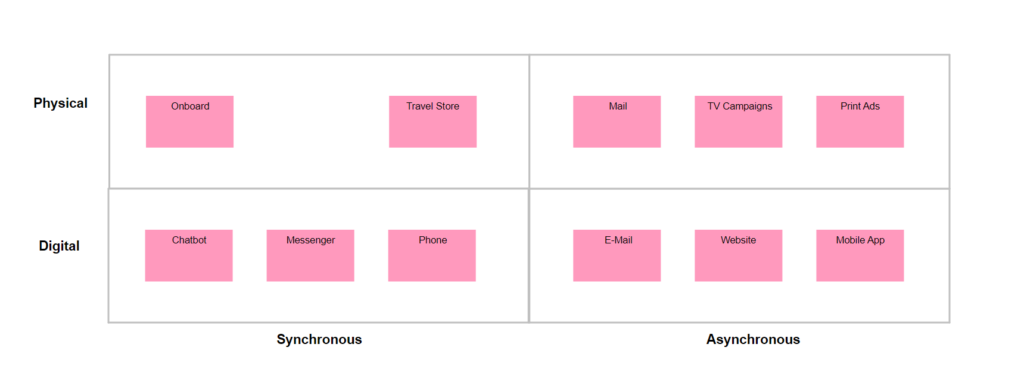
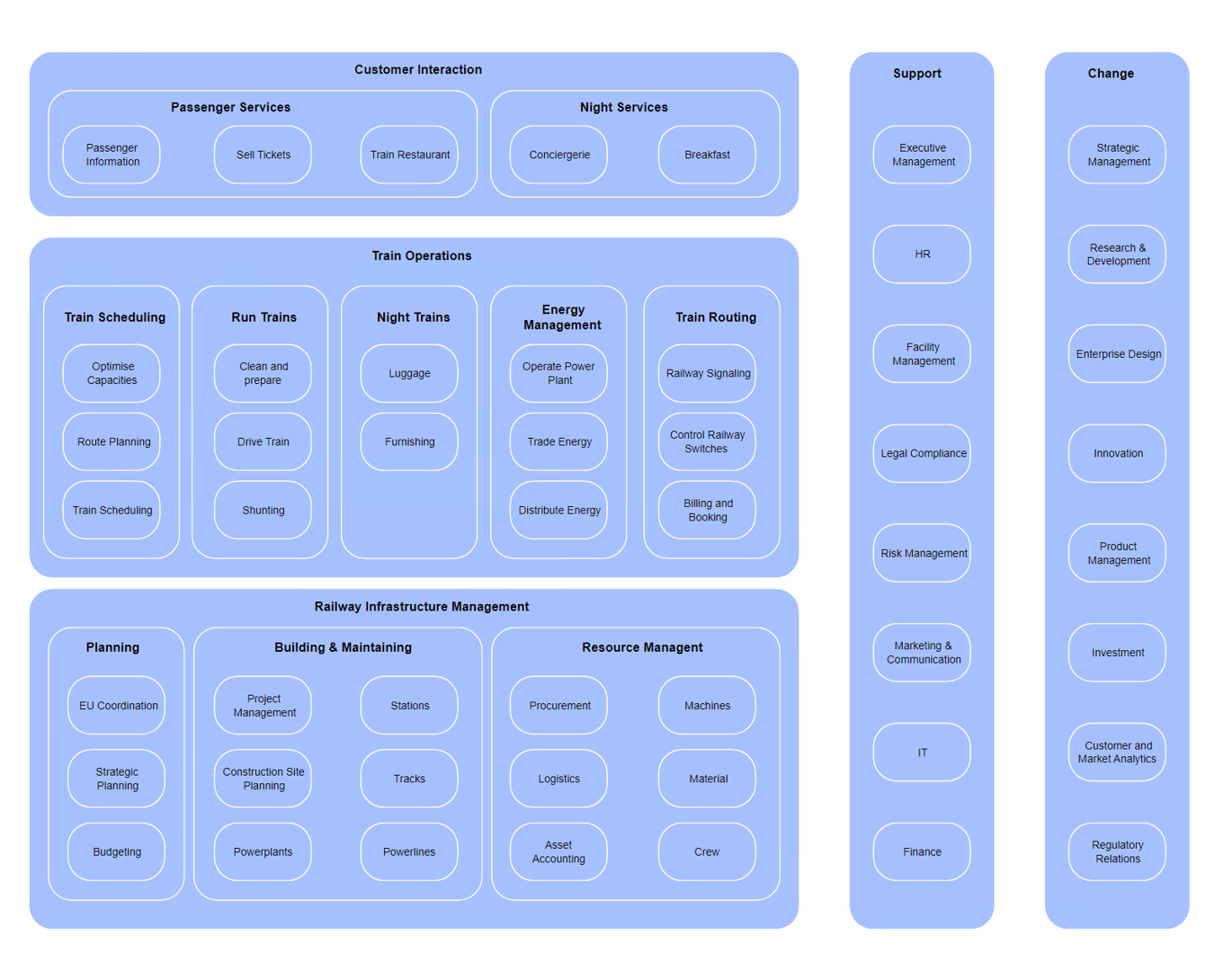
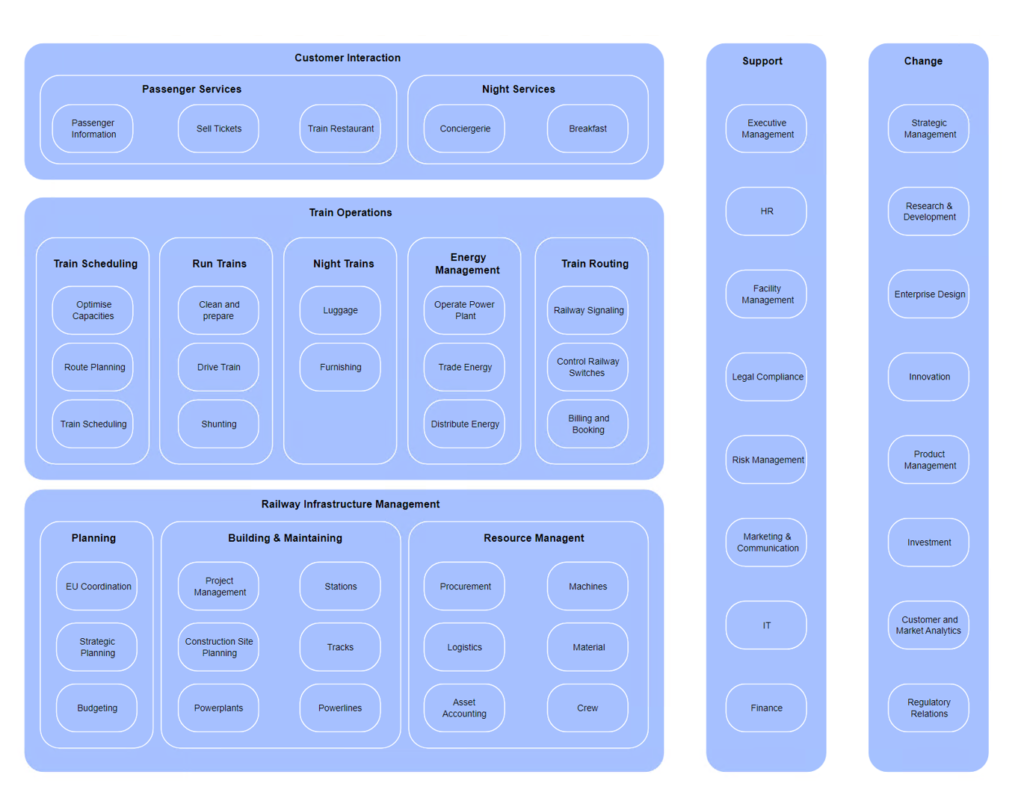
Purpose: The Application Behavior Viewpoint in ArchiMate aims to model the behavior and interactions of applications within an enterprise, providing a high-level view of how applications support business processes and goals. This helps to identify opportunities for optimizing application behavior, improving performance, and reducing costs.
Core Concerns: The core concerns of the Application Behavior Viewpoint include modeling the behavior of applications, the services they provide, and the interactions between applications and other components within the enterprise architecture. By focusing on these core concerns, the Application Behavior Viewpoint can help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement and provide a clear understanding of how applications contribute to the overall functioning of the enterprise.
Example:
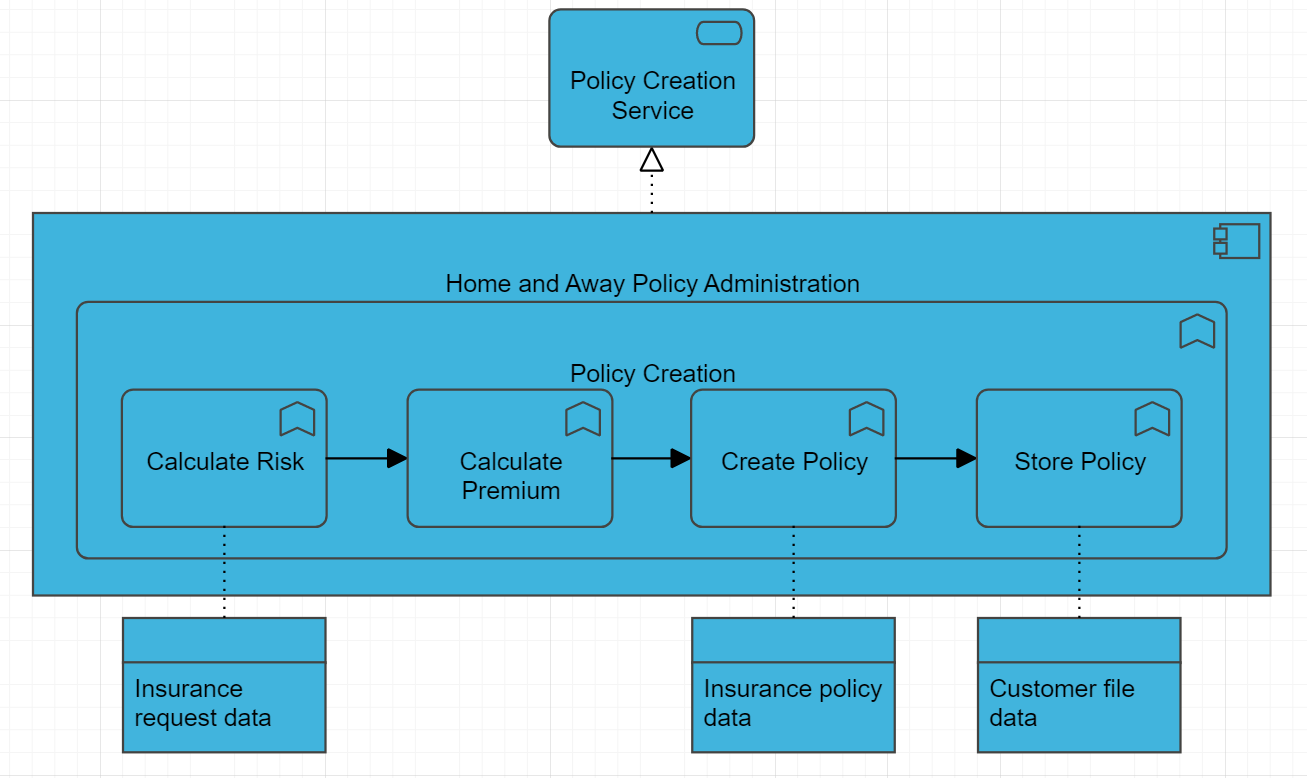
The Application Behavior Viewpoint includes several concepts for modeling different aspects of application behavior, including:
- Application Component: An application component represents a unit of functionality provided by an application. Application components can be modeled to show the services they provide and the interfaces through which they interact with other components.
- Application Service: An application service is a unit of functionality provided by an application component. Application services can be modeled to show the behavior and capabilities of an application component.
- Application Interface: An application interface represents a point of interaction between application components, or between an application component and other components within the enterprise architecture. Application interfaces can be modeled to show the data and functionality exchanged between components.
- Application Interaction: An application interaction represents the exchange of data and functionality between application components, or between an application component and other components within the enterprise architecture. Application interactions can be modeled to show the sequence and timing of events.
Overall, the Application Behavior Viewpoint is useful for modeling the behavior and interactions of applications within an enterprise, providing a high-level view of how applications support business processes and goals. By focusing on the core concerns of application behavior, the Application Behavior Viewpoint can help identify areas for improvement and optimization and provide a clear understanding of how applications contribute to the overall functioning of the enterprise architecture.