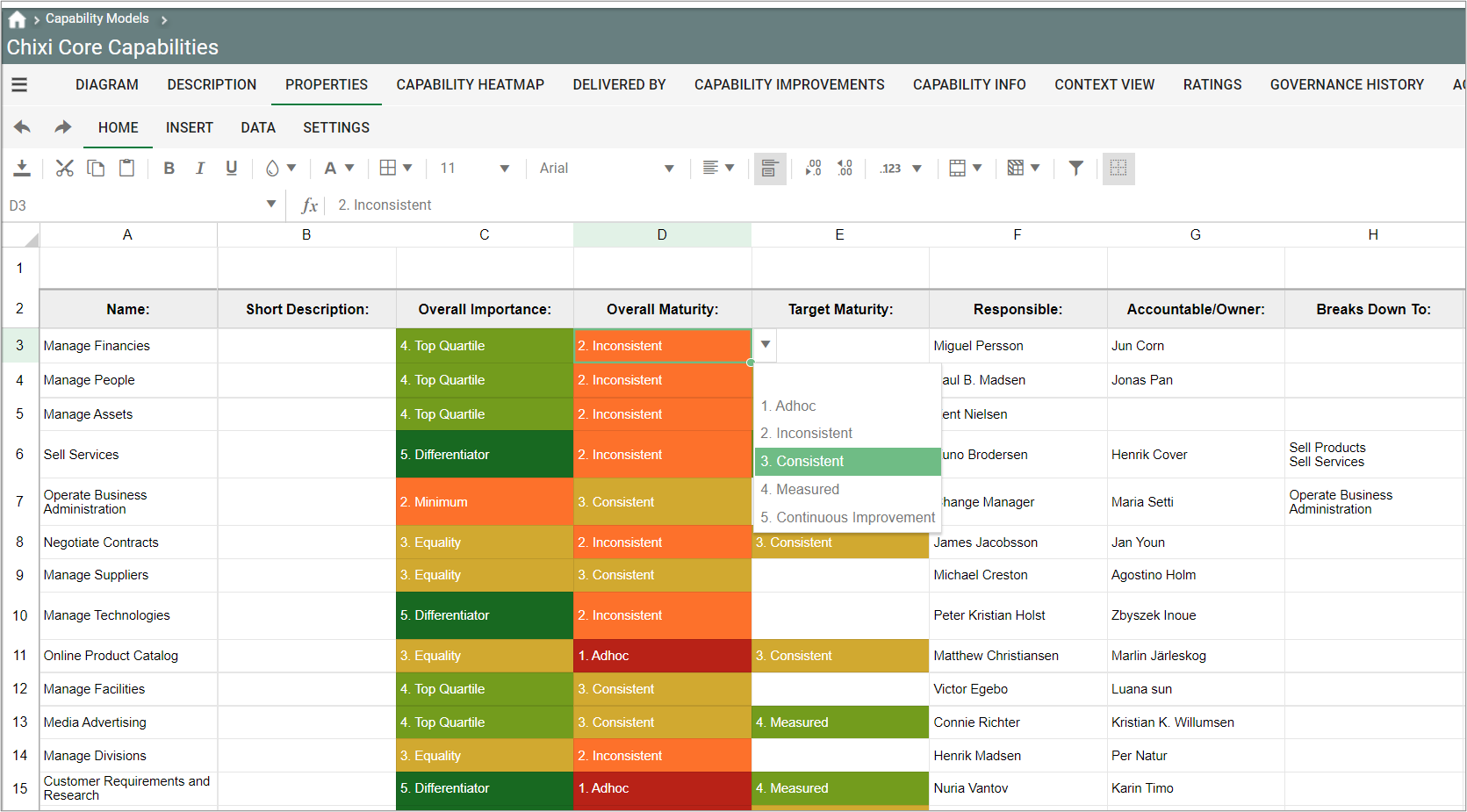
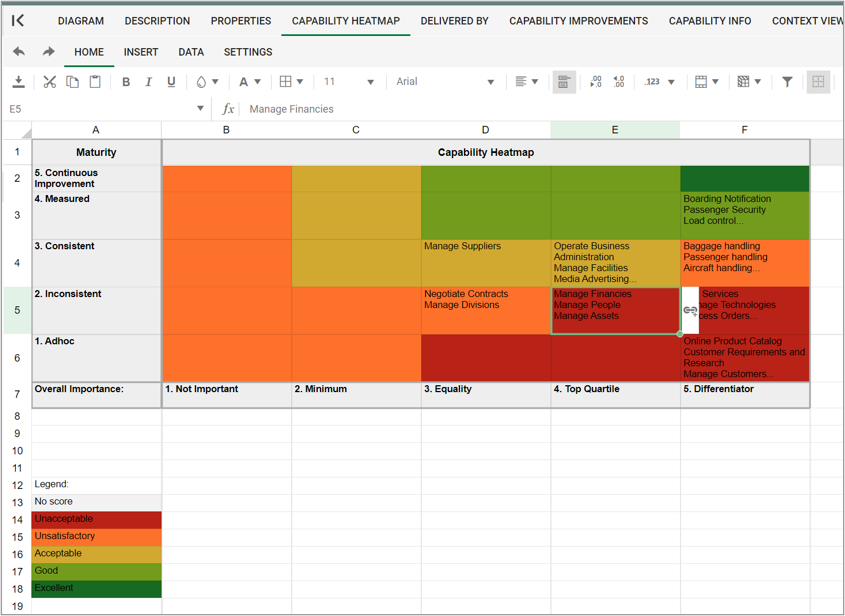
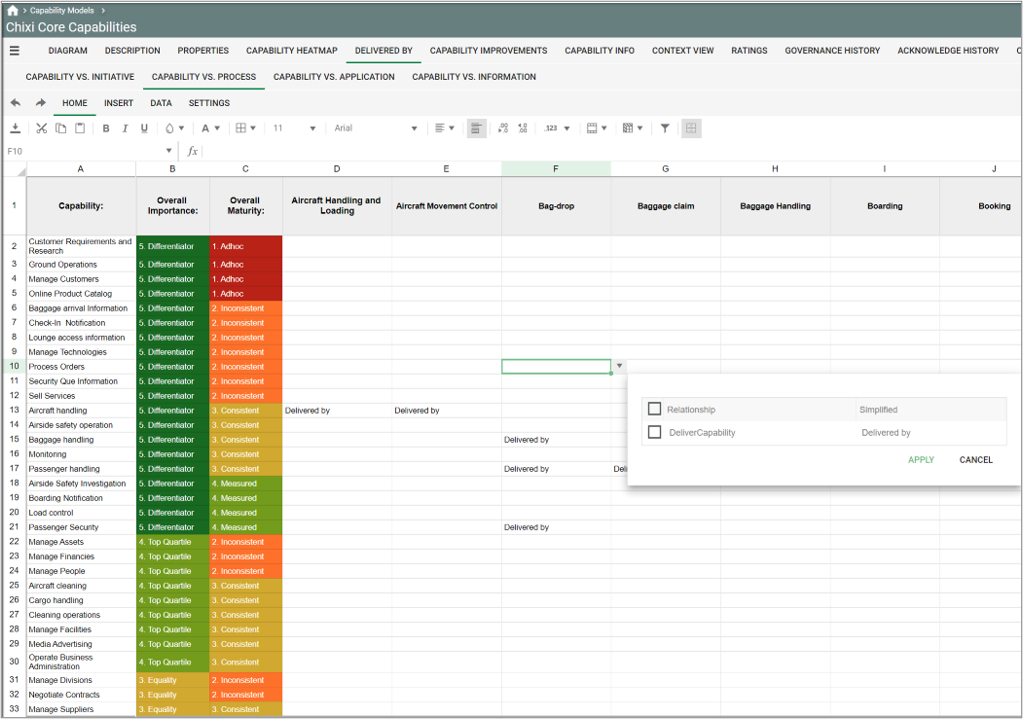
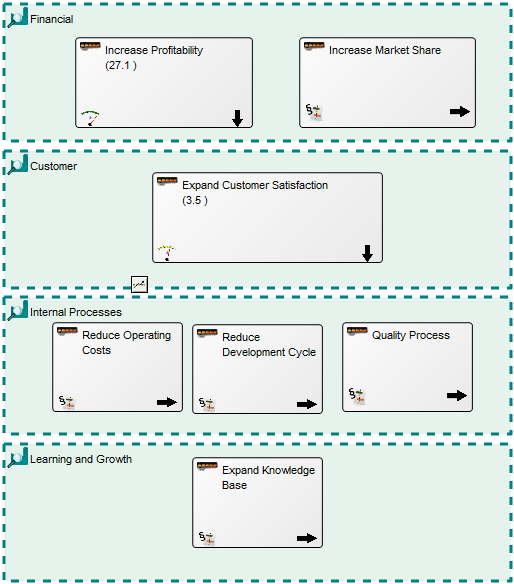
Purpose: The primary objective of the Class Diagram template is to visually represent and document the structural components of a system utilizing the Unified Modeling Language (UML). Displayed below is an example of a straightforward Class Diagram:
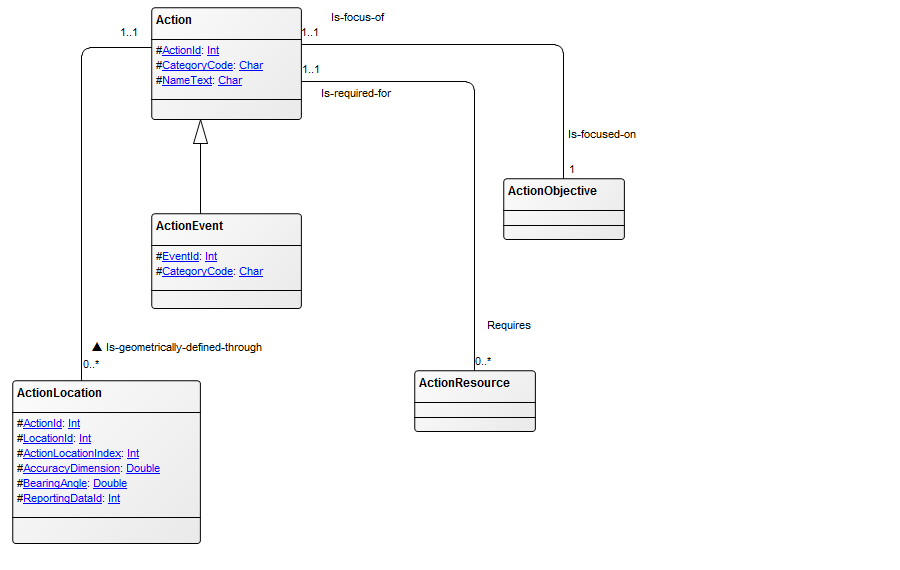
Core concerns: The Class Diagram effectively captures the various classes within a system, their attributes, operations, and the relationships between classes and other objects, such as packages. This comprehensive representation enables a clear understanding of the system’s structure, promoting efficient communication among stakeholders and facilitating system design and maintenance.
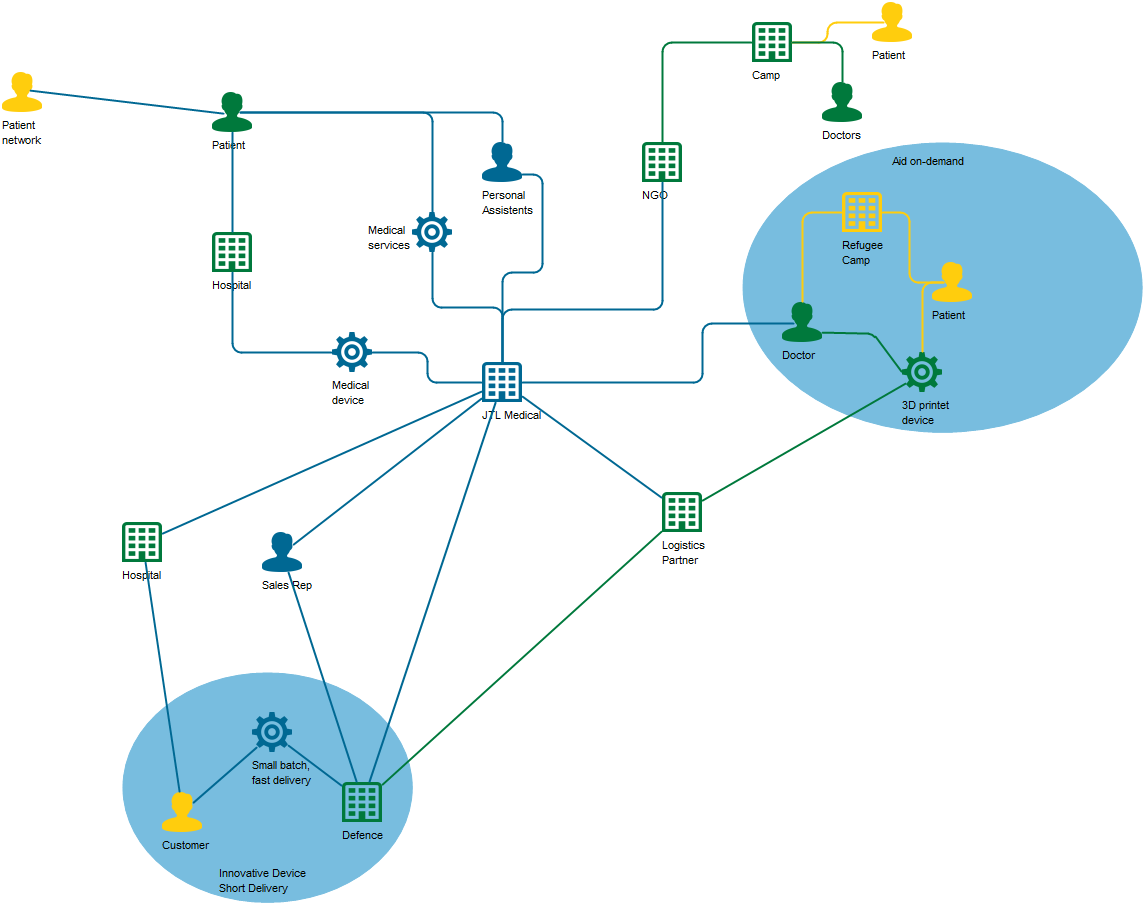
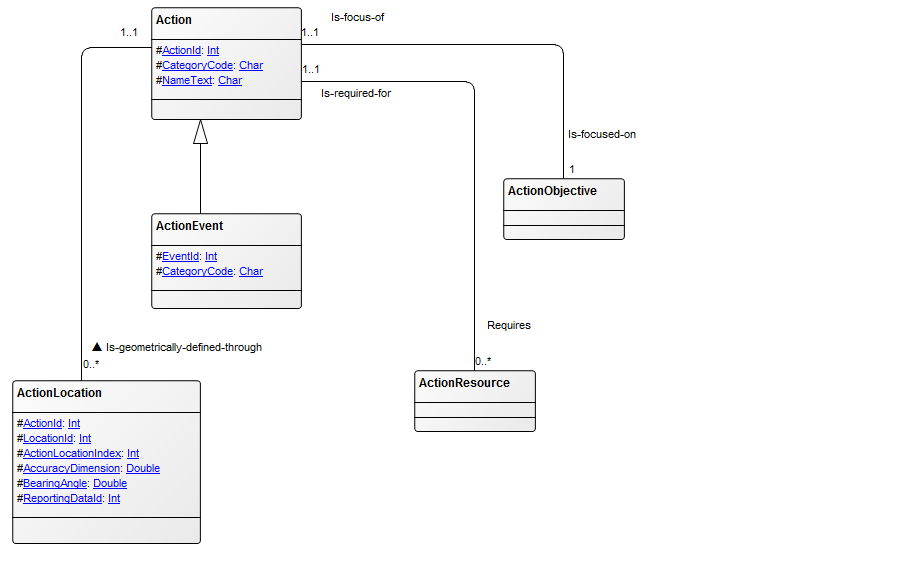
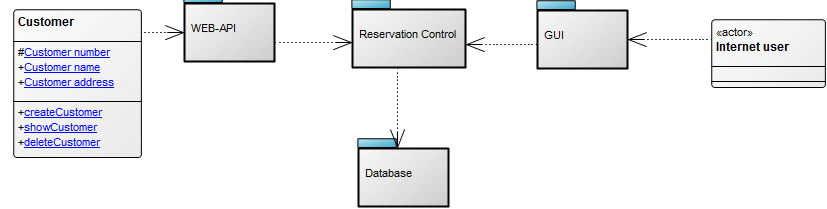
Example: In the Class Diagram below, the relationships between the classes “Customer” and “Internet User” and the packages “WEB-API”, “Reservation Control”, “GUI” (Graphical User Interface), and “Database” are illustrated. This example highlights the connections among different components and provides a visual overview of how they interact within the system:
Relation to other templates: The Class Diagram presents a detailed structural view of information. It can for example be a decomposition of an Information System which typically is presented in an Application Architecture Diagram. If a Class Diagram becomes too complex or large, a Package Diagram, where the classes are grouped into Packages, could be modelled instead.
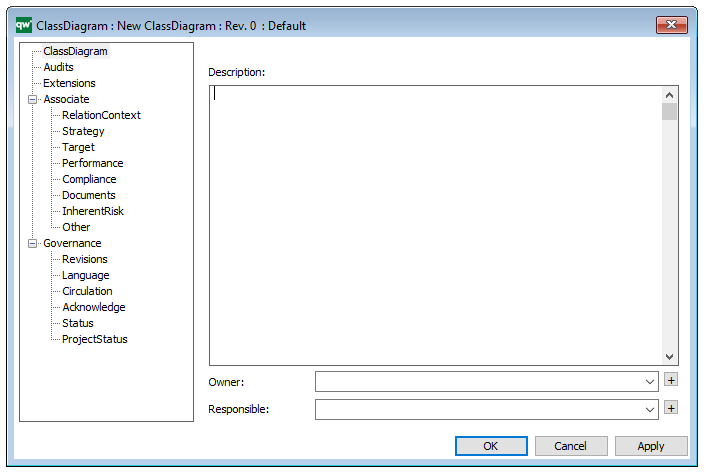
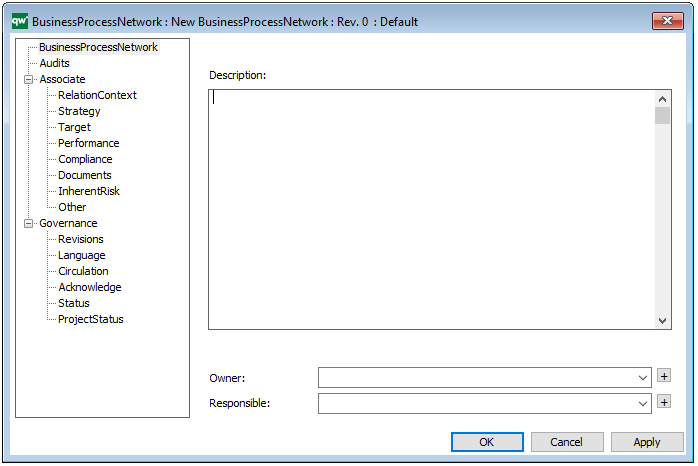
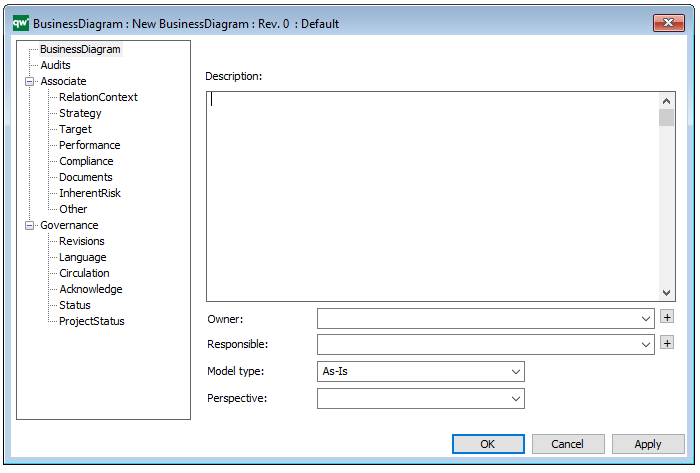
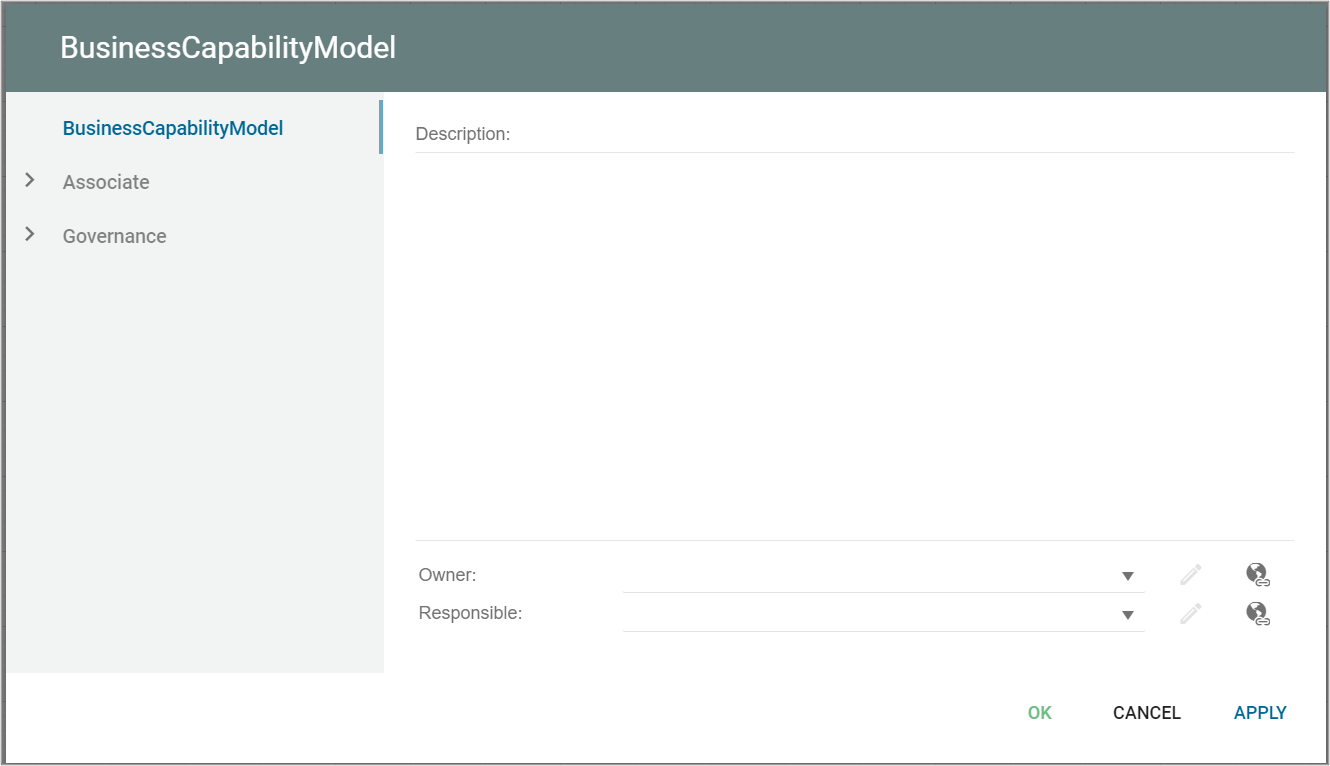
Properties and metadata: The Class Diagram can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Extensions regarding constraints and tagged values
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
In the picture below you can see the Class Diagrams properties dialogue window, where the information can be viewed and edited: