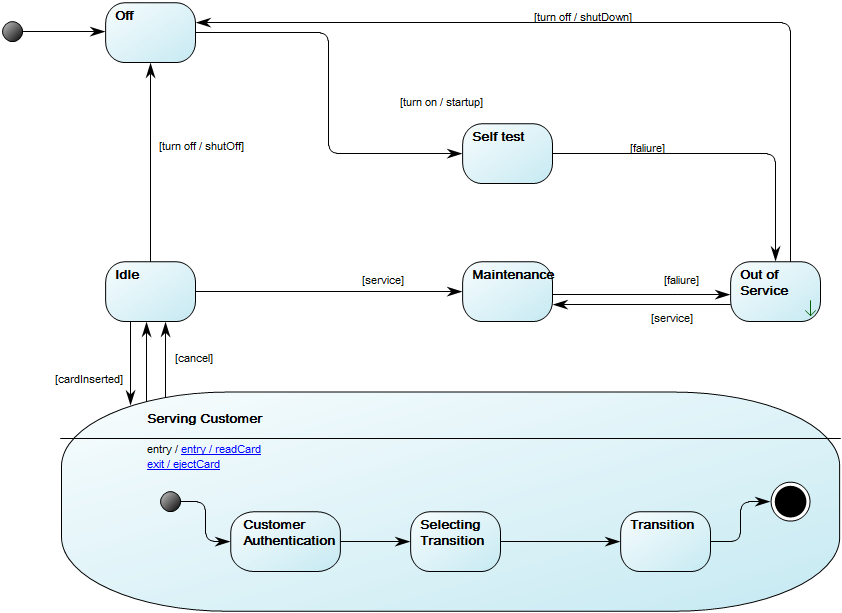
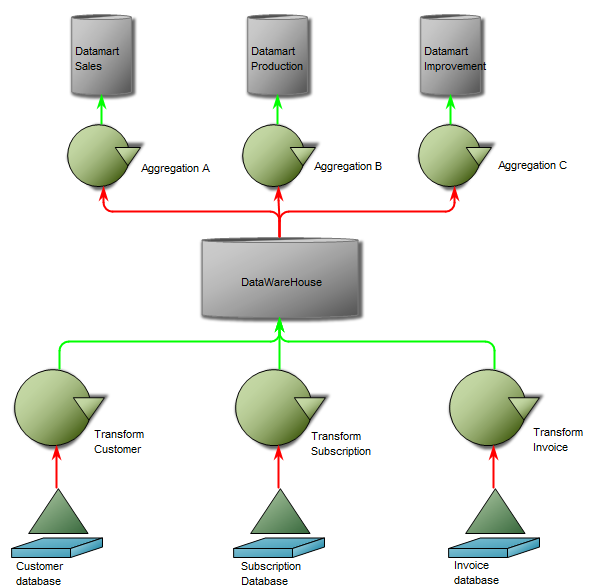
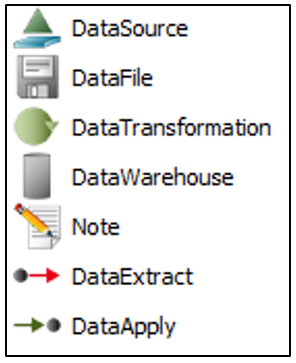
Purpose: The purpose of the Package Diagram is to group elements of a large system and illustrate the dependencies between them.
Core concerns: The Package Diagram can be used to organize a system’s parts and enables you to model Packages, Profiles and Annotations. These can be connected using Dependency, Profile Application, Package Merge, Package Import and Containment.
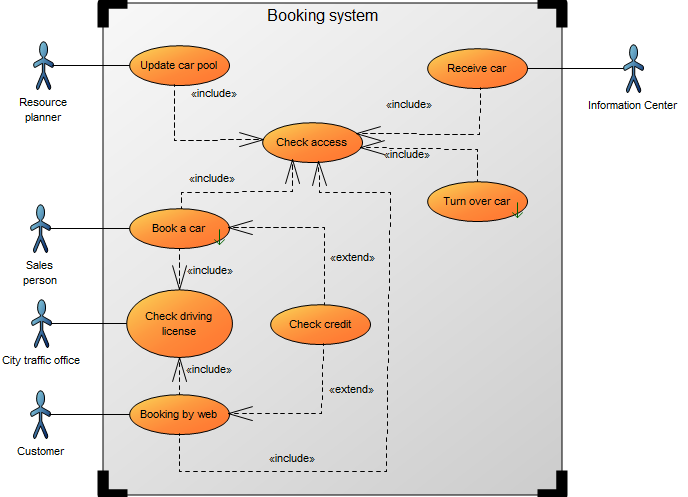
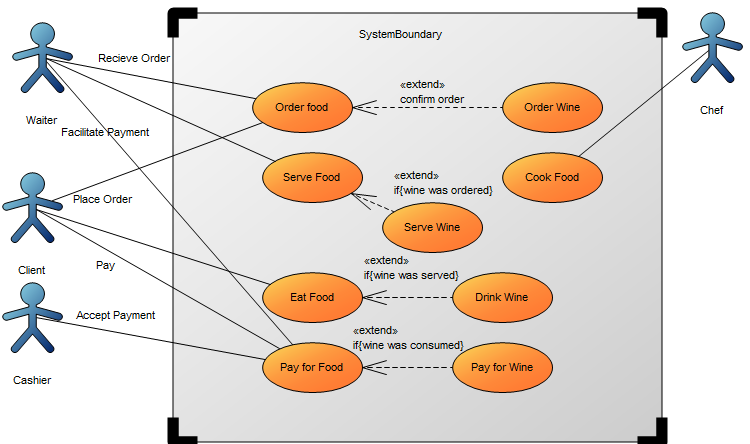
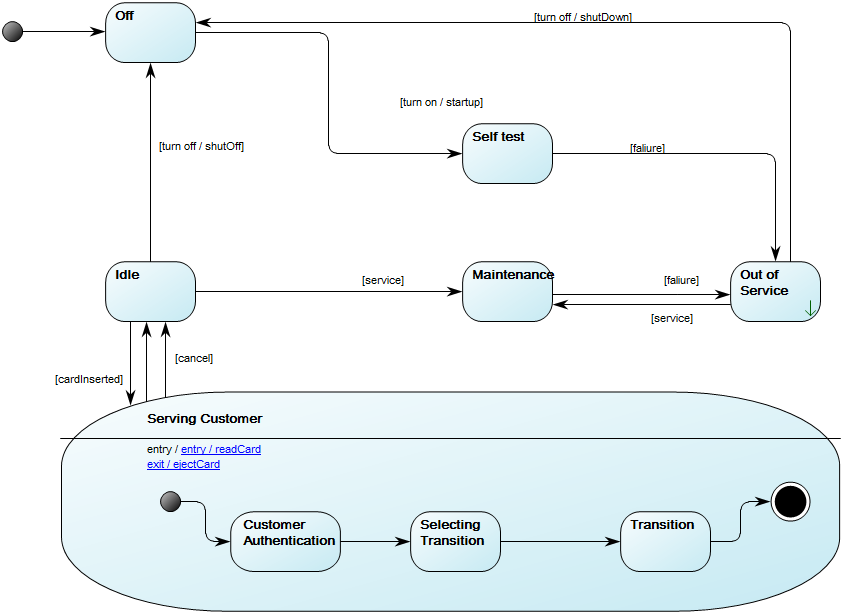
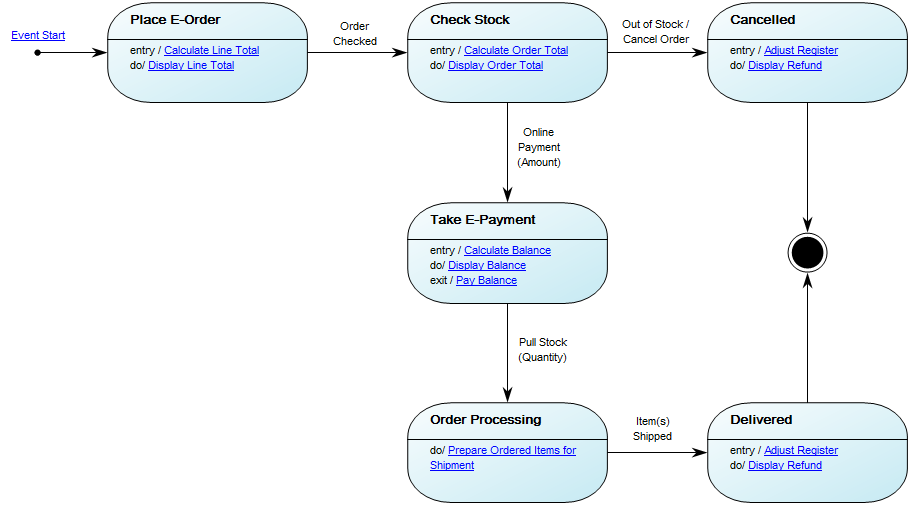
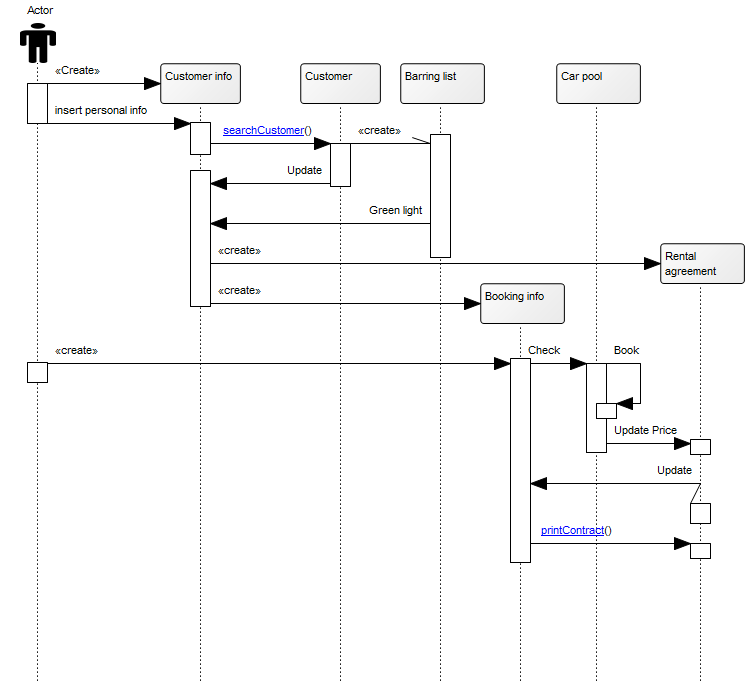
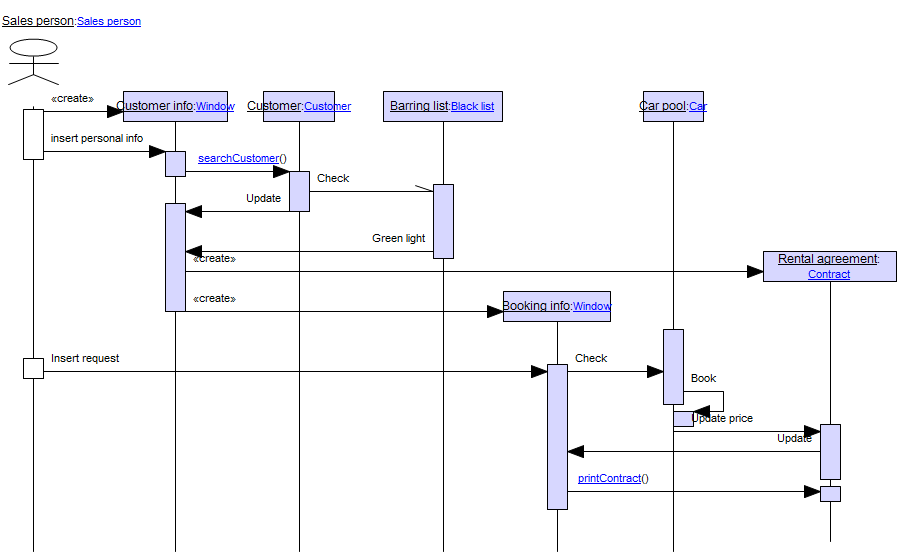
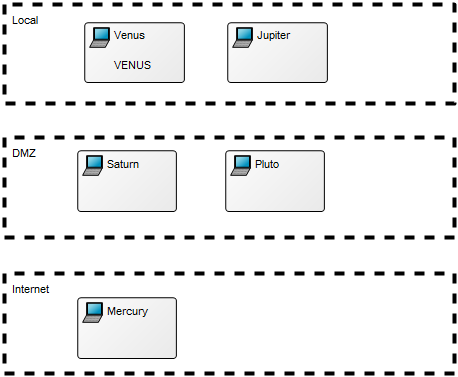
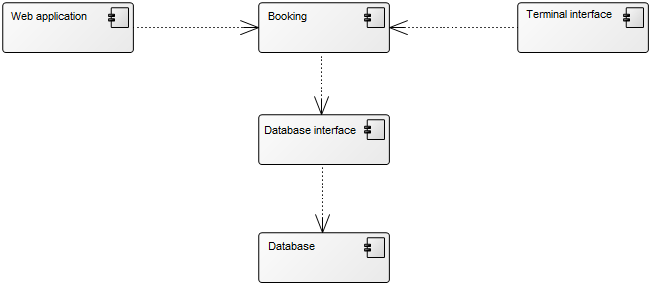
Below, you can see an example of a Package Diagram for a booking system for a car rental service:
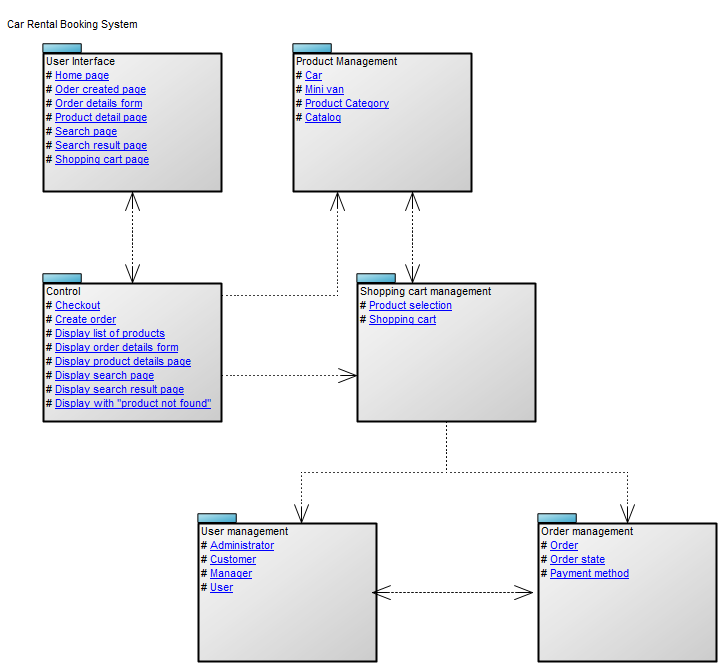
Relation to other templates: The Package diagram offers a simplified view of for example a Class Diagram, grouping classes into packages. It should be used when a class diagram becomes too large and complex to easily read.
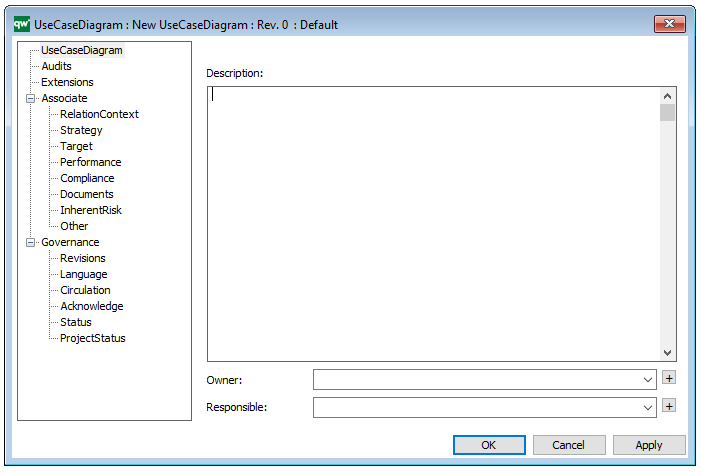
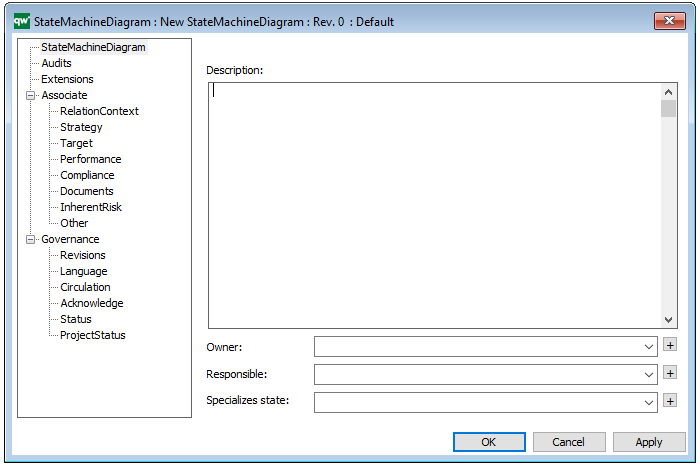
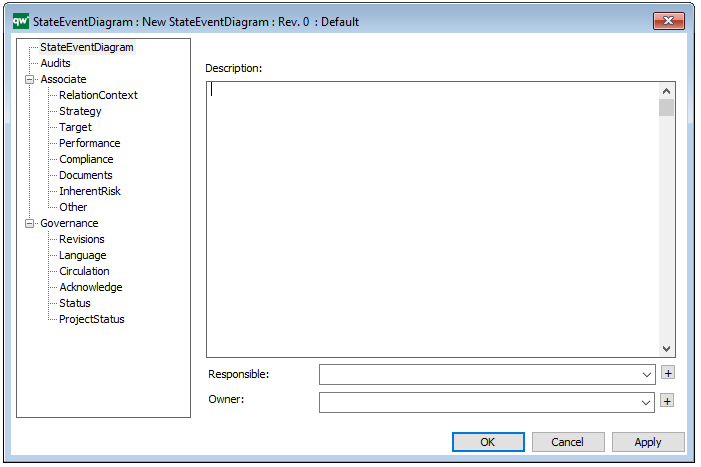
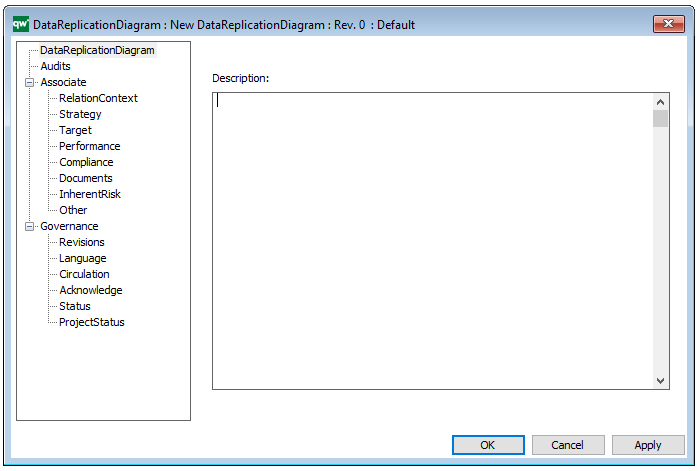
Properties and metadata: The Package Diagram template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
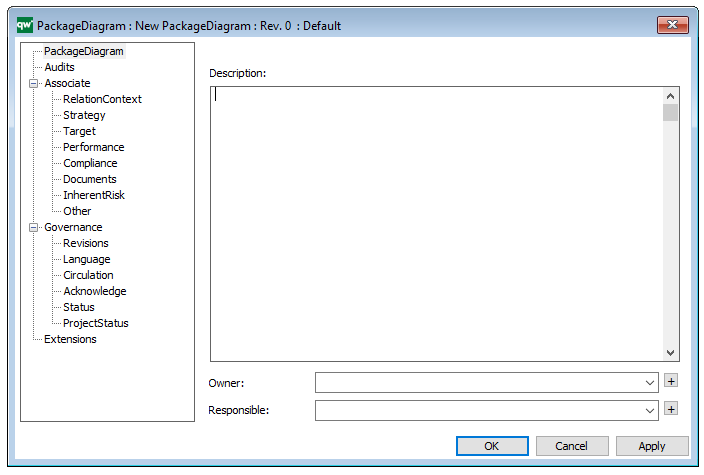
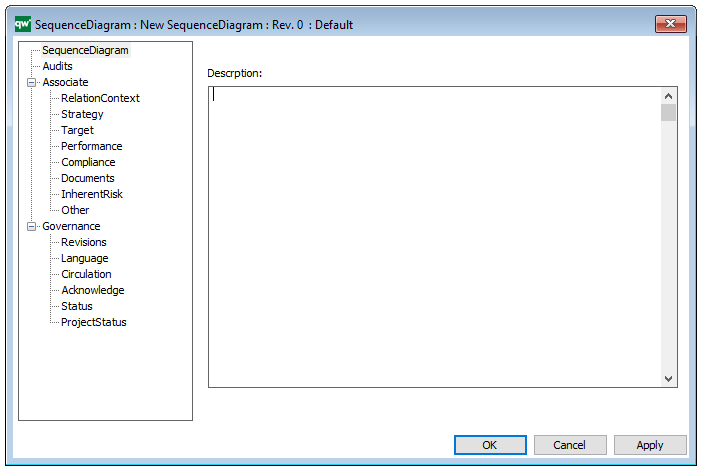
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Package Diagram template, where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.