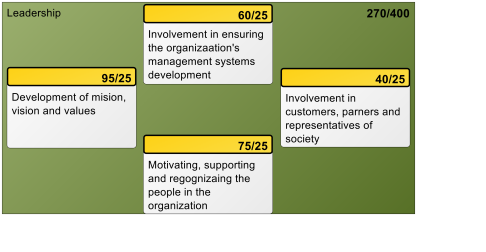
Purpose: The purpose of the Business Process Diagram template is to enable workflow modelling using the industry standard BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation).
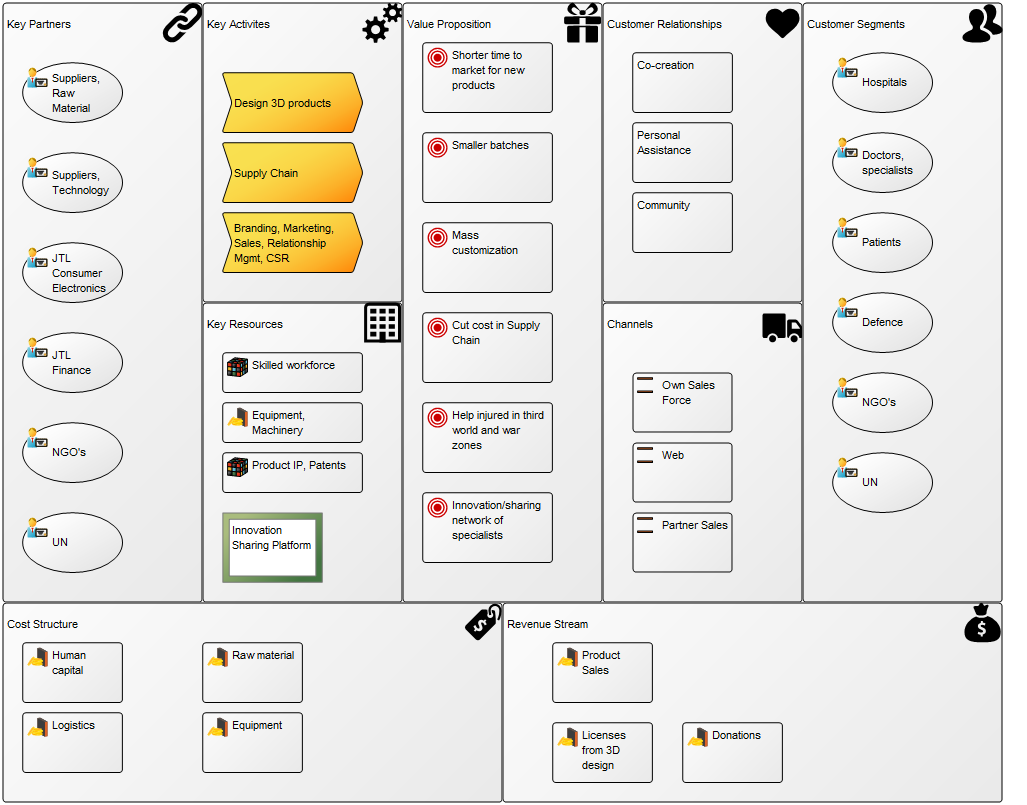
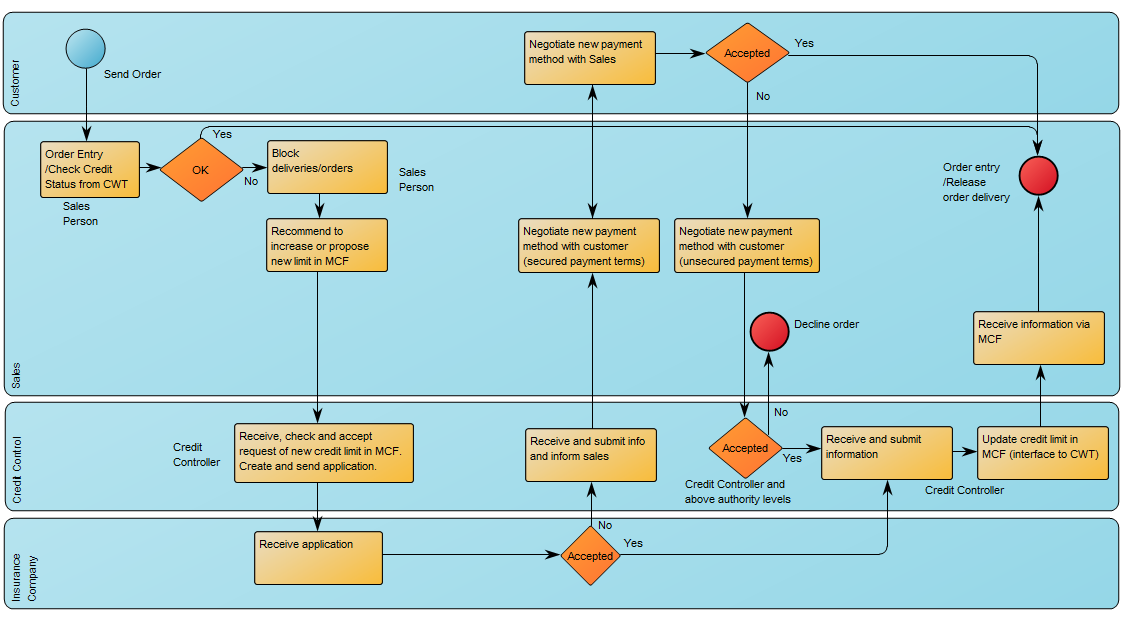
Core concerns: The Business Process Diagram template supply you with the BPMN icons that enable you to draw a workflow diagram. These icons include different types of events, activities, gateways, connectors, as well as pools, lanes and artifacts such as data objects and messages. The Business Process Diagram is typically used to illustrate business processes and software processes used in requirement documentation. Below is an example of a classic BPMN diagram with swimlanes:
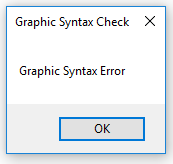
To ensure the right BPMN syntax, the Business Process Diagram template will continuously perform Graphic Syntax Checks while you model. When a graphic syntax error occurs, you will be met with an error message like the one shown below:
Other functionalities: The Business Process Diagram can enable the execution and automation of a process when the diagram is converted into XML type files.
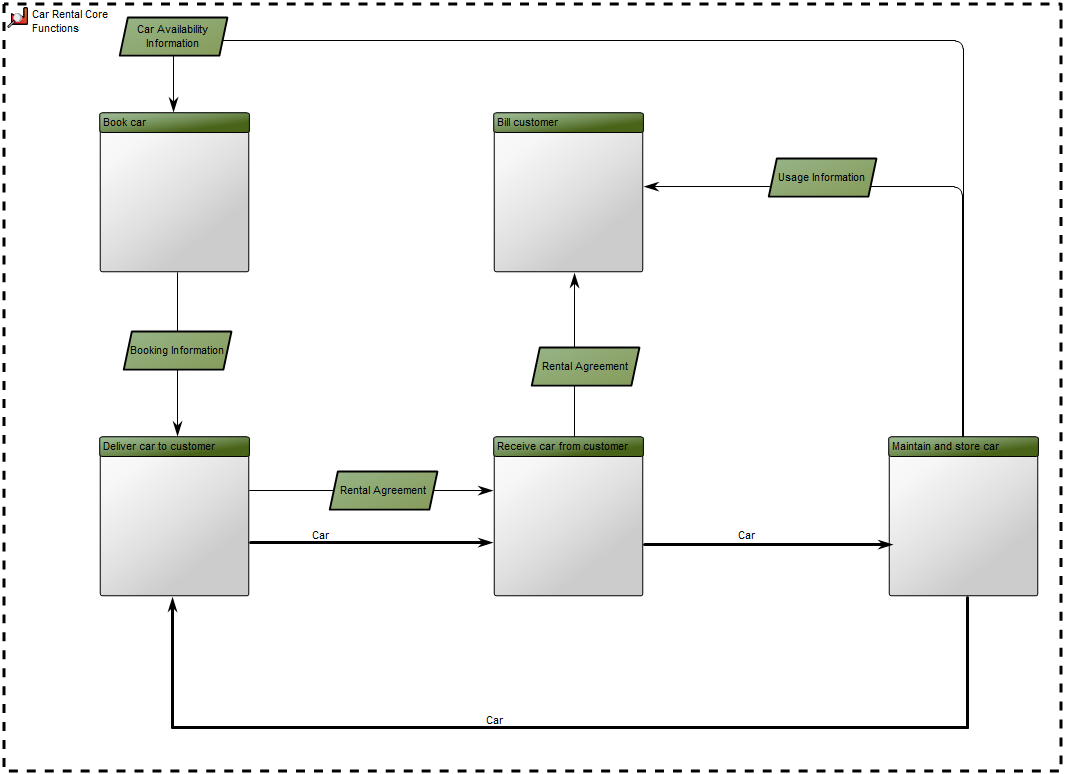
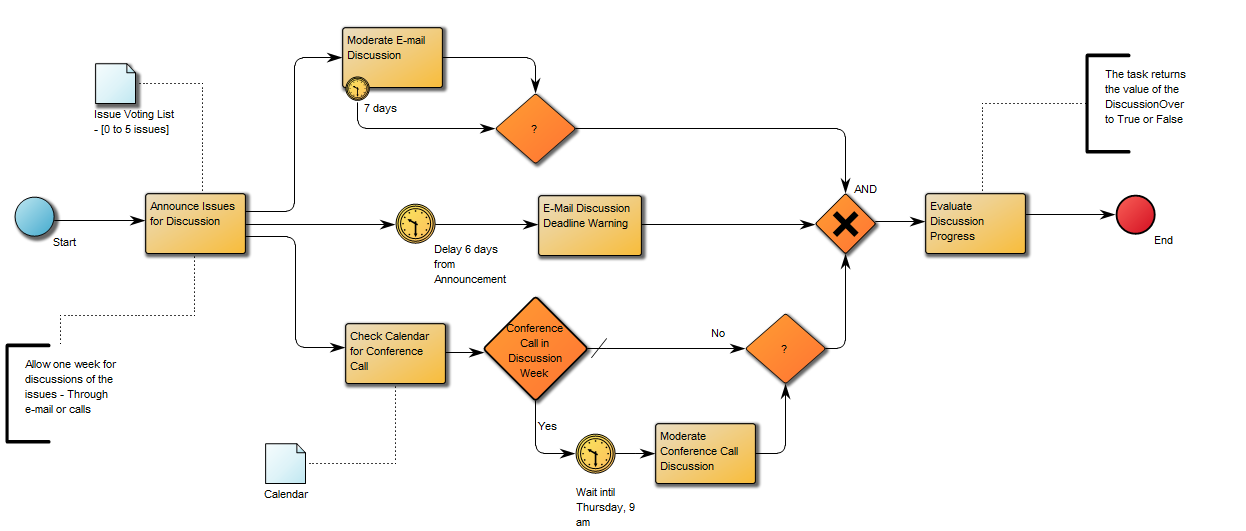
If you don’t wish to have a visible pool in your diagram, you can choose to have a ‘default pool’ that doesn’t have to be graphically represented. You can see an example of a diagram without pool and lanes below:
Relation to other templates: The Business Process Diagram template is exclusively aimed at modeling using the BPMN standard. If the BPMN is not chosen as a mandatory standard, the WorkFlow Diagram template, which has fewer syntax limitations, can be used instead.
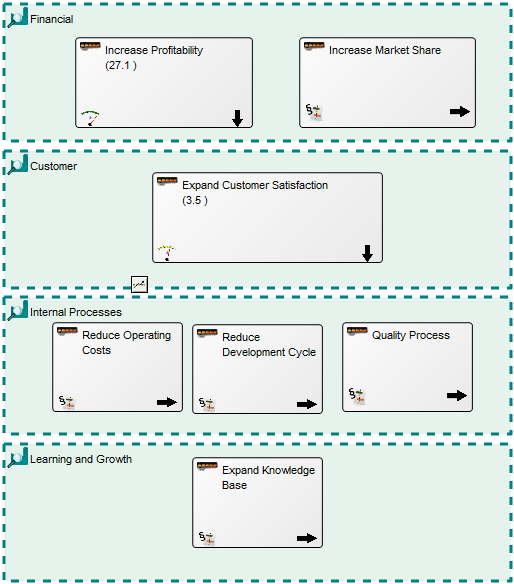
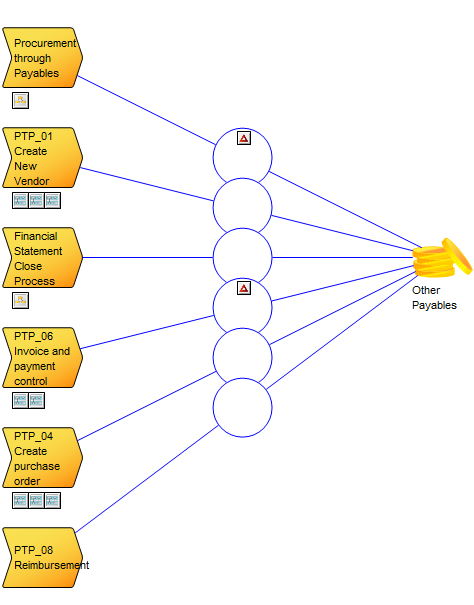
The Business Process Diagram is typically linked as a decomposition of a Business Process contained in a Business Process Network template.
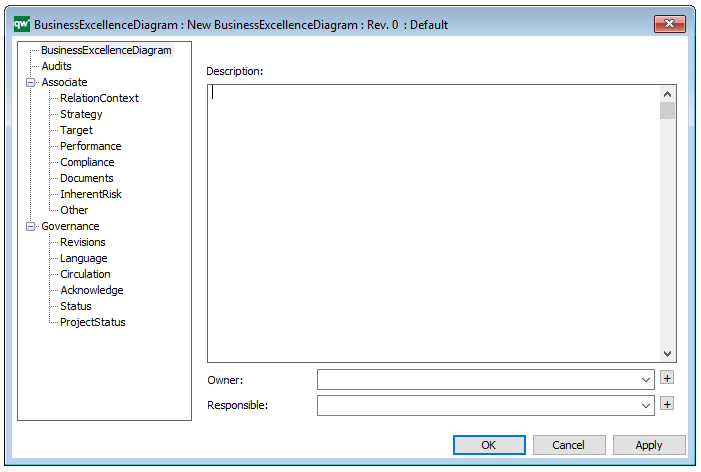
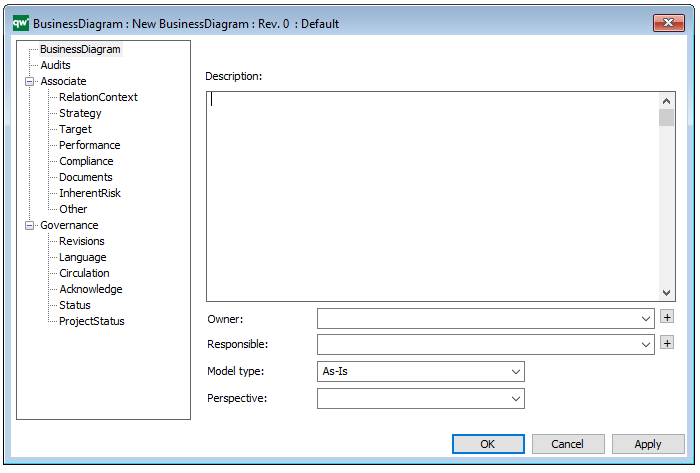
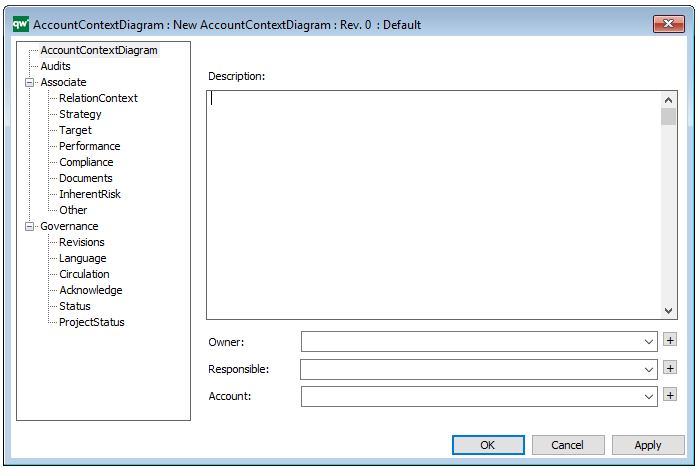
Properties and metadata: The Business Process Diagram can for example retain the following information:
- Description of the diagram
- Expression and query language
- Link to the owner of the process
- Link to the one responsible for executing the process
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
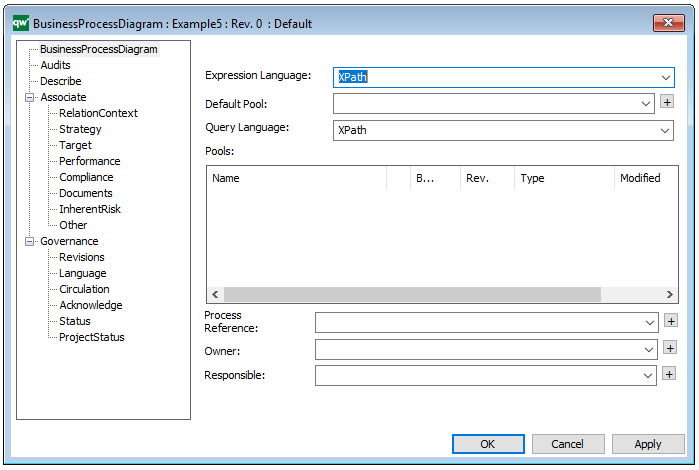
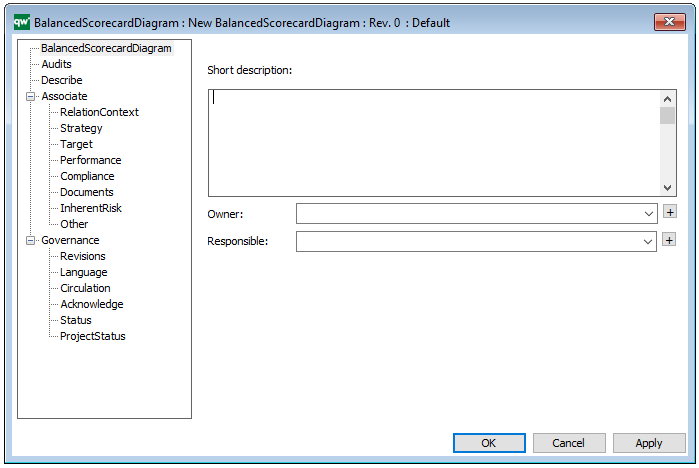
In the picture above you can see the Business Process Diagram’s properties dialogue window, where the diagram’s properties can be viewed and edited:
For more information: about the BPMN standard please visit OMG’s dedicated website.