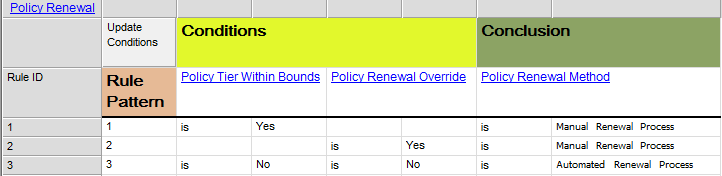
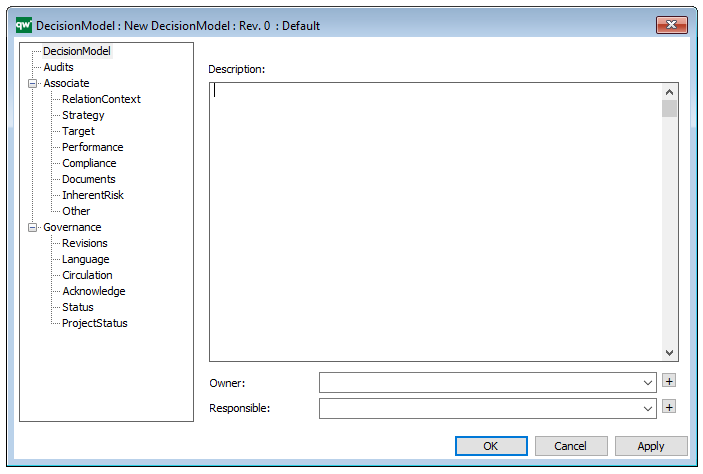
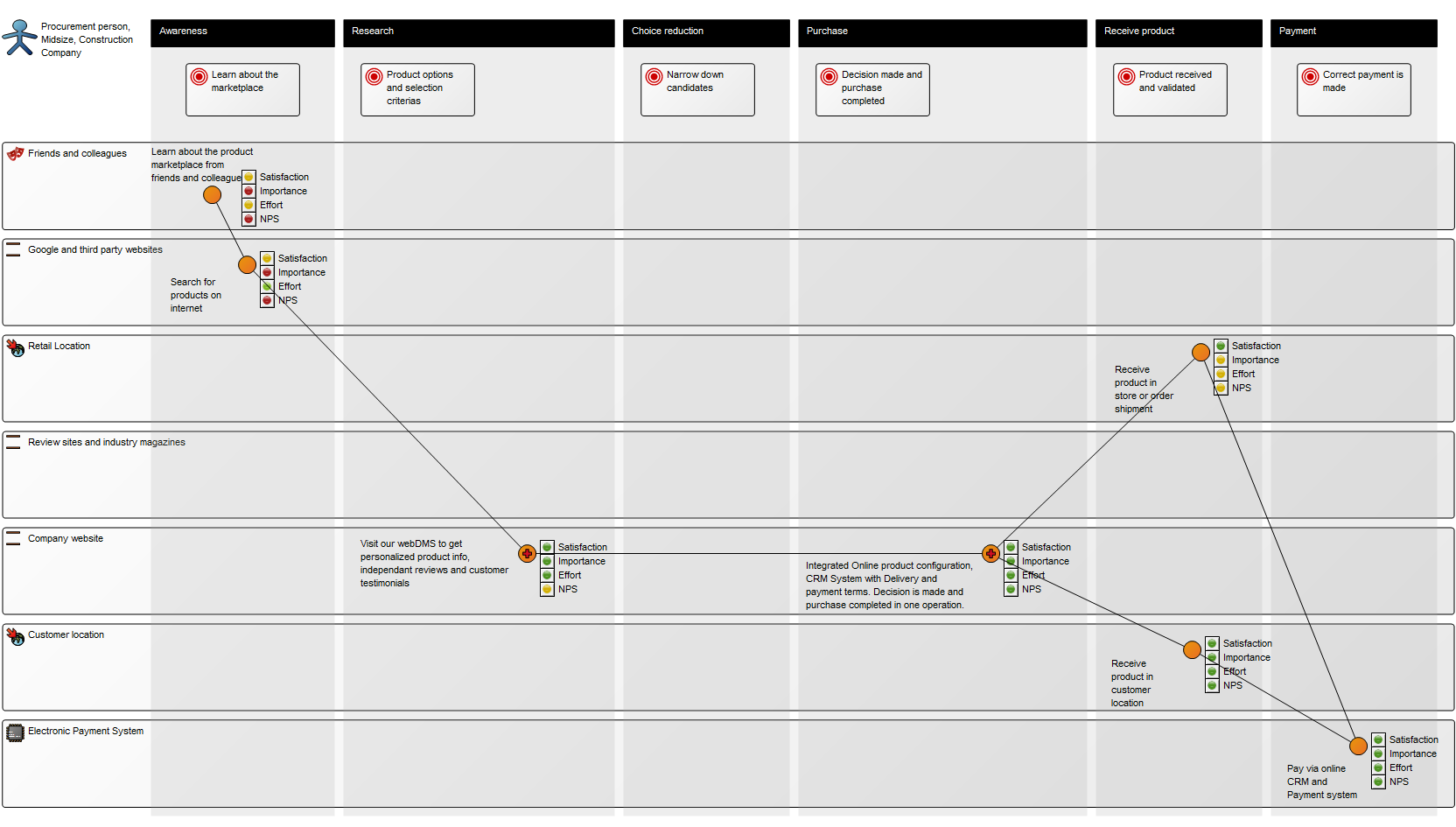
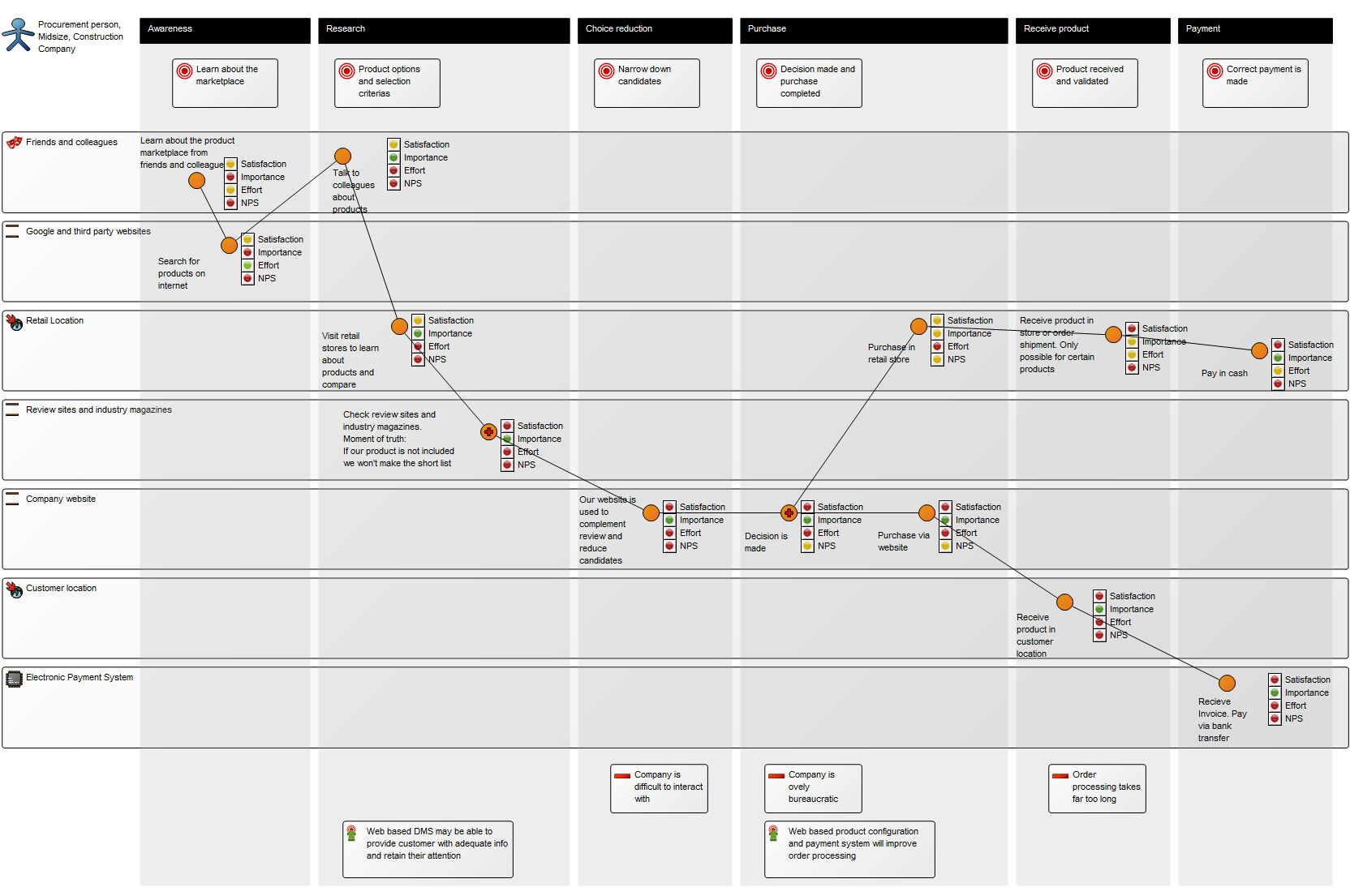
Purpose: The purpose of the Work Model template is to document development methods or project models.
Core concerns: The Work Model template enables you to model Project Activities, Milestones, Results, Quality Controls, Document Structures and Business Scopes. These objects are joined by Connections indicating a flow.
The Work Model template can, for example, be used by Enterprise Architects to document the Enterprise Architecture process from start to finish while covering all the project activities, milestones, and results. The Work Model helps ensure a standardized approach.
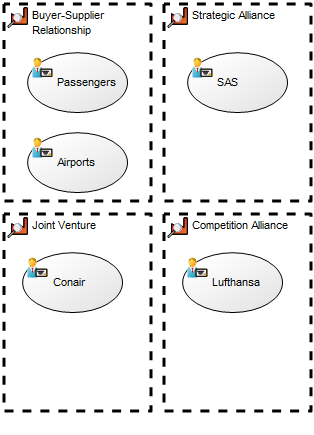
Below, you can see a few examples of Work Models utilizing a variety of the available objects:
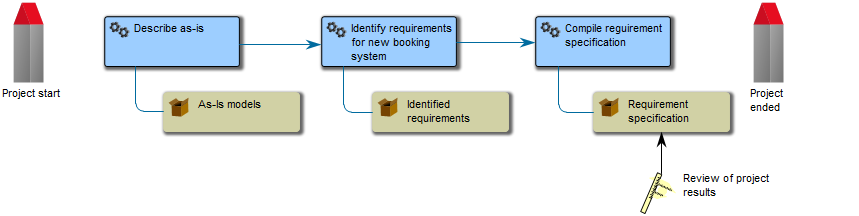
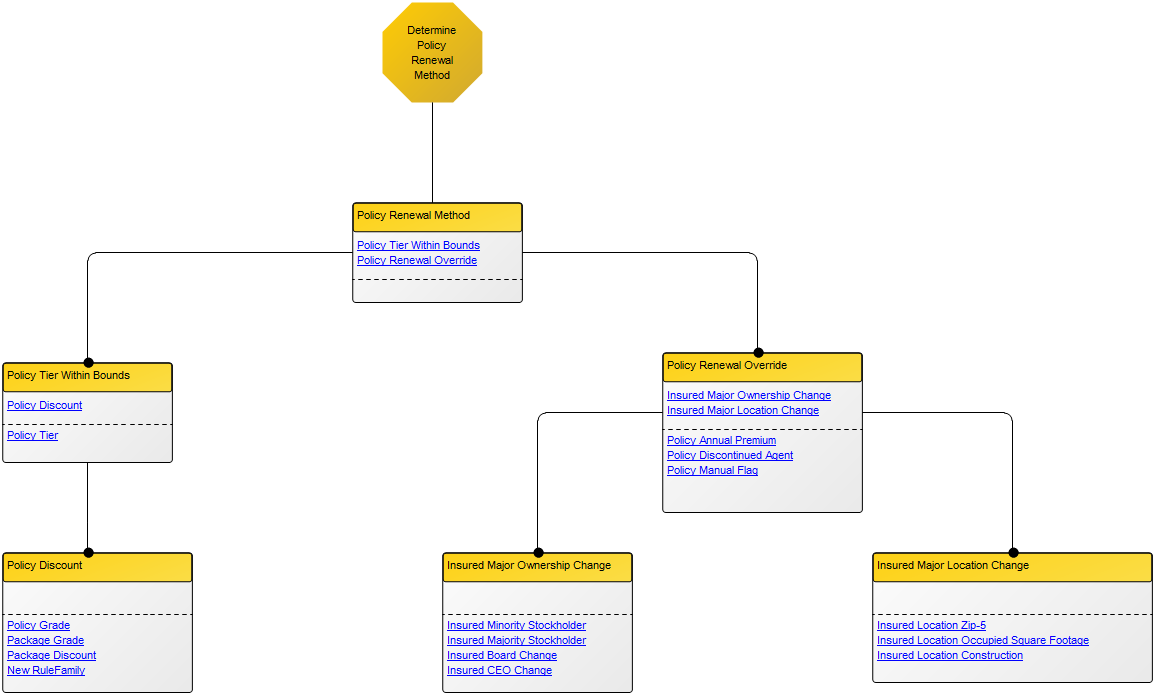
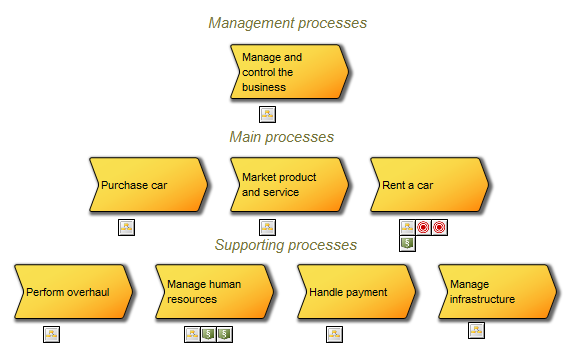
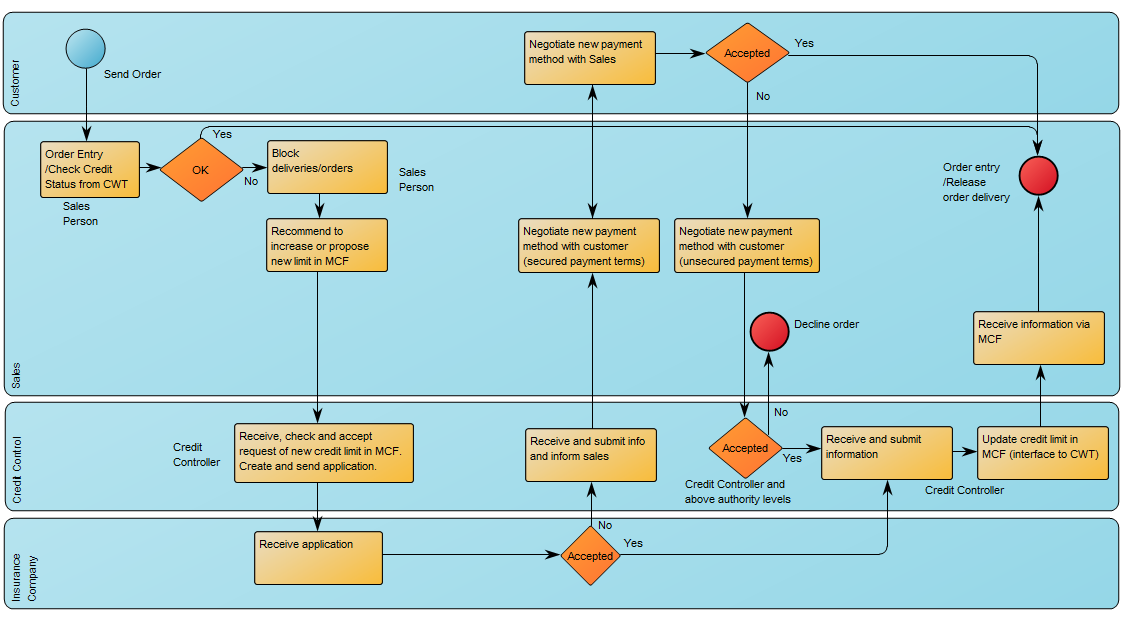
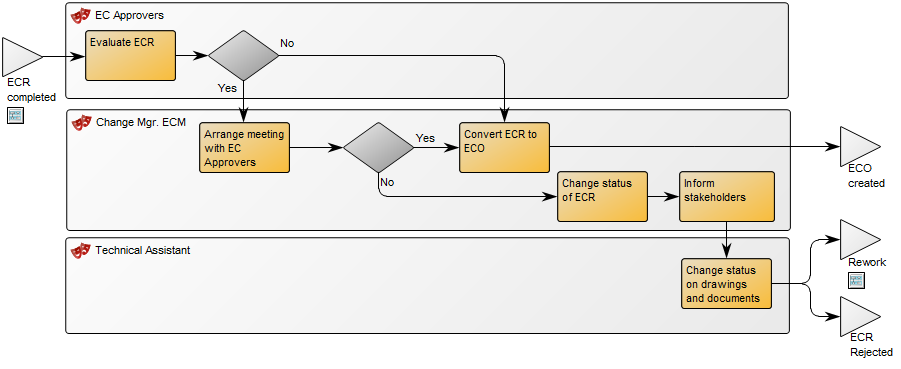
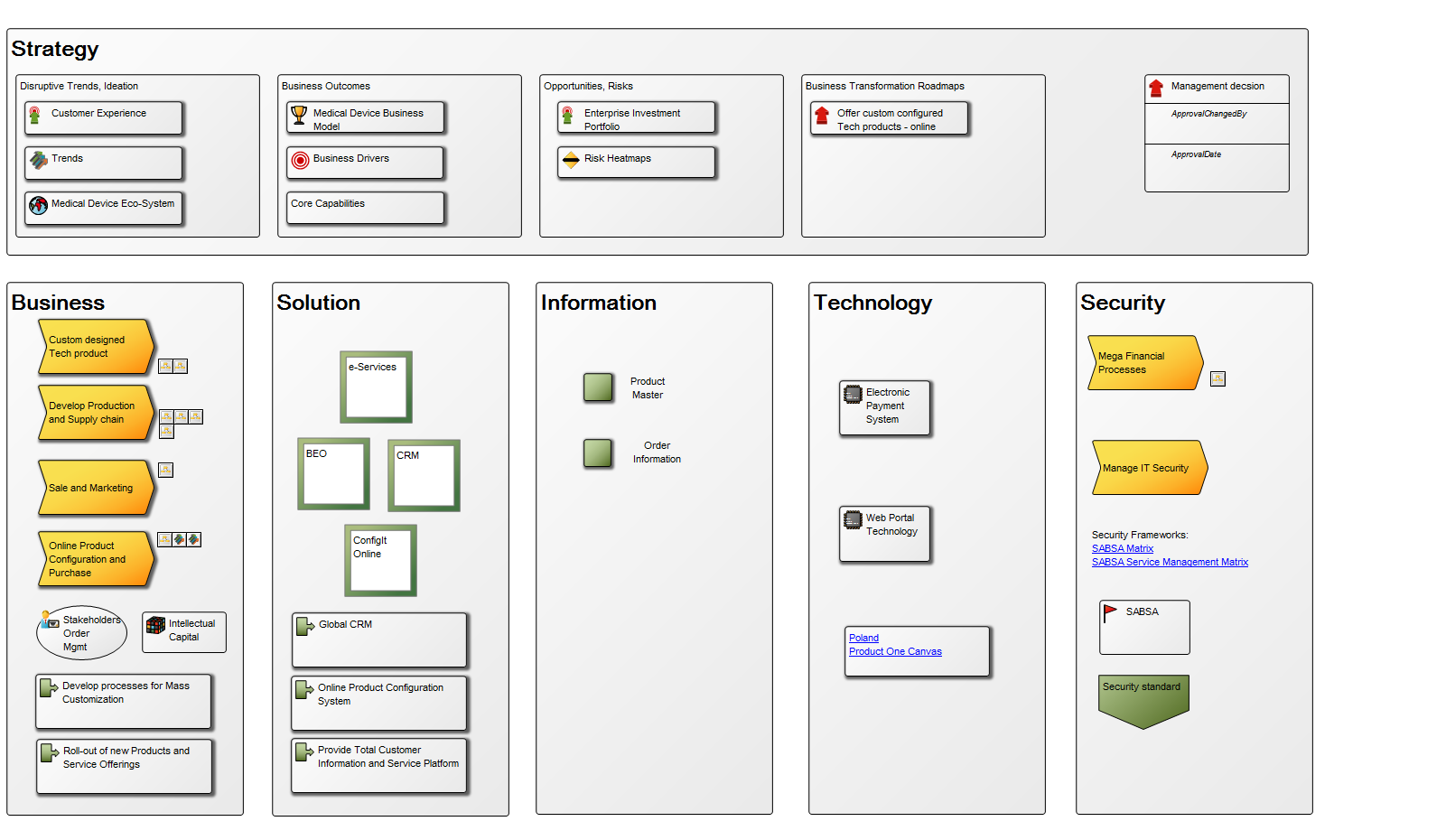
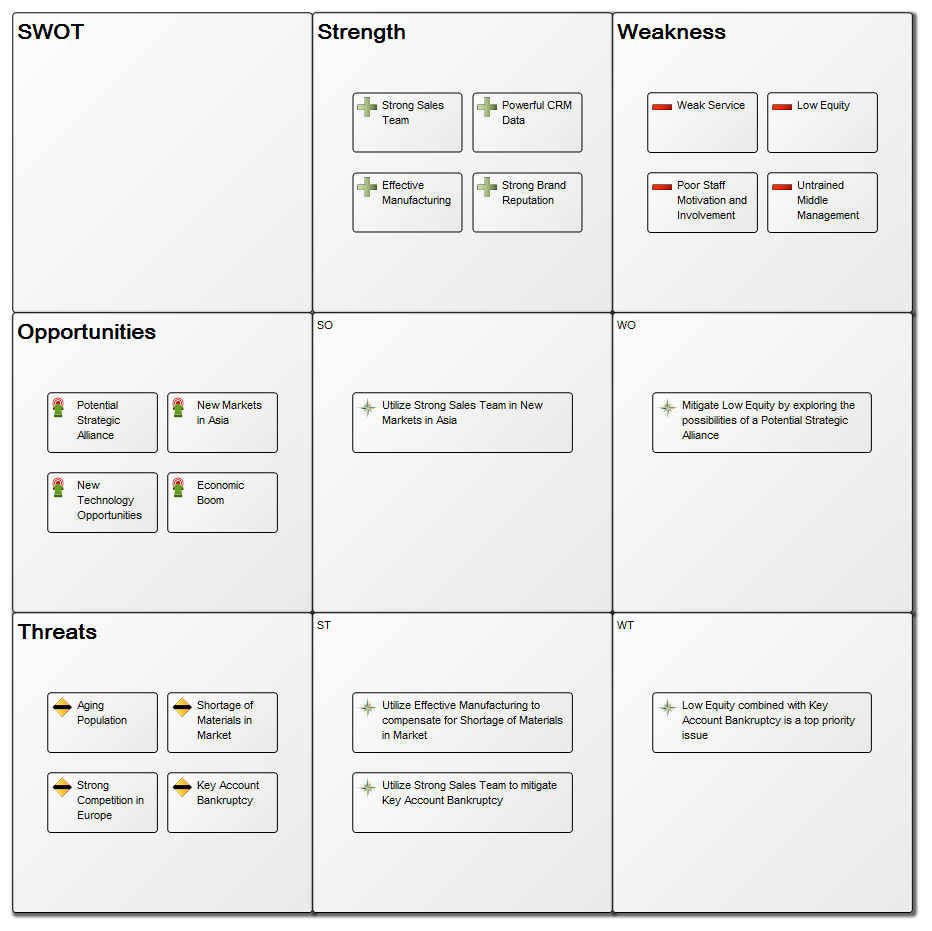
The above model shows a simple project flow enriched with mile stones, results and a quality control.
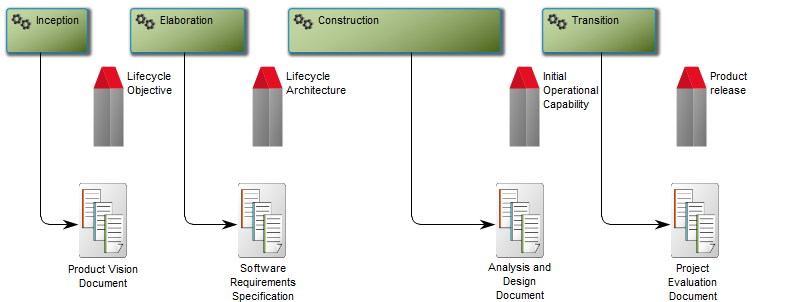
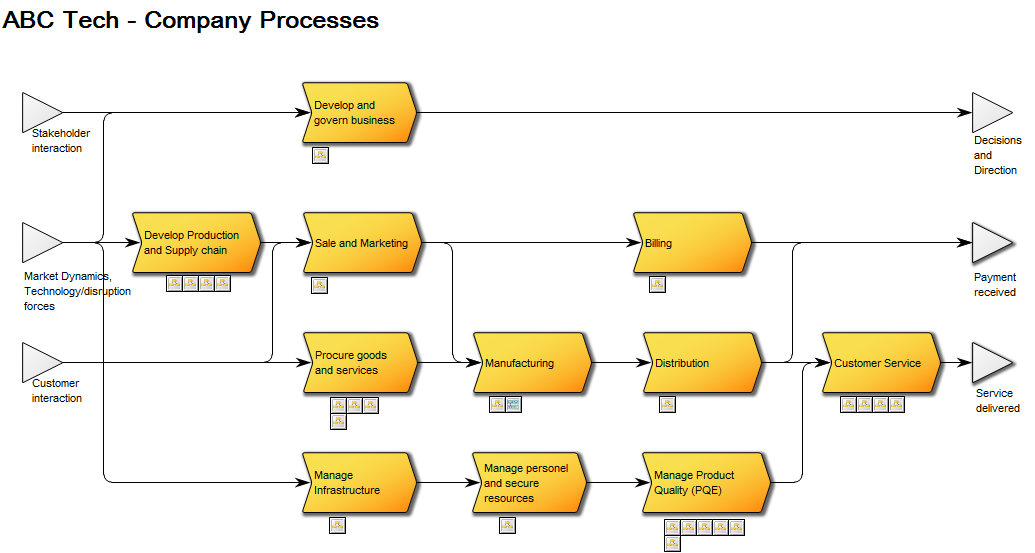
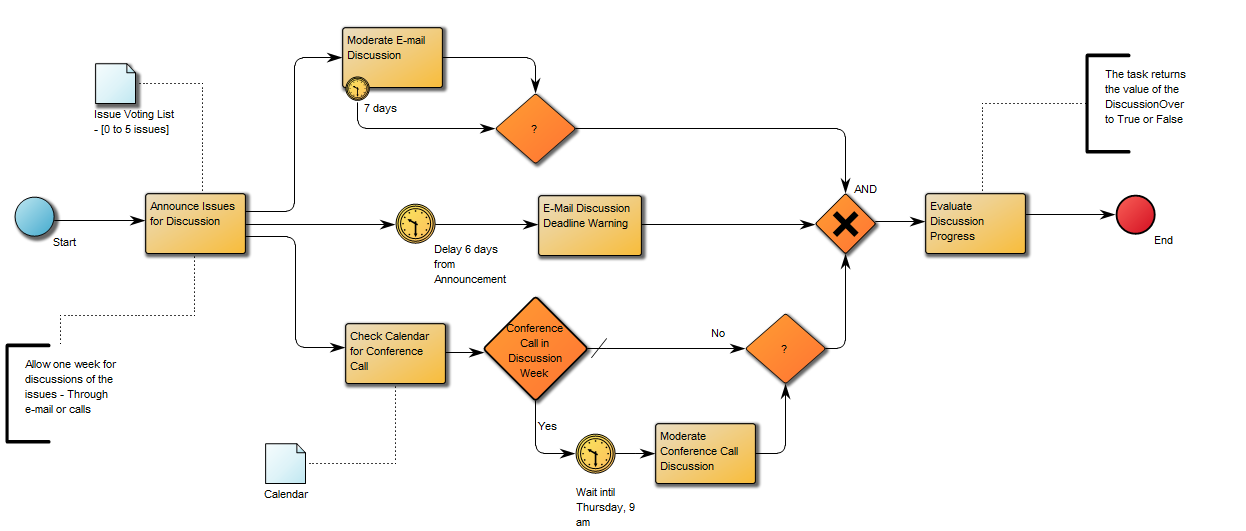
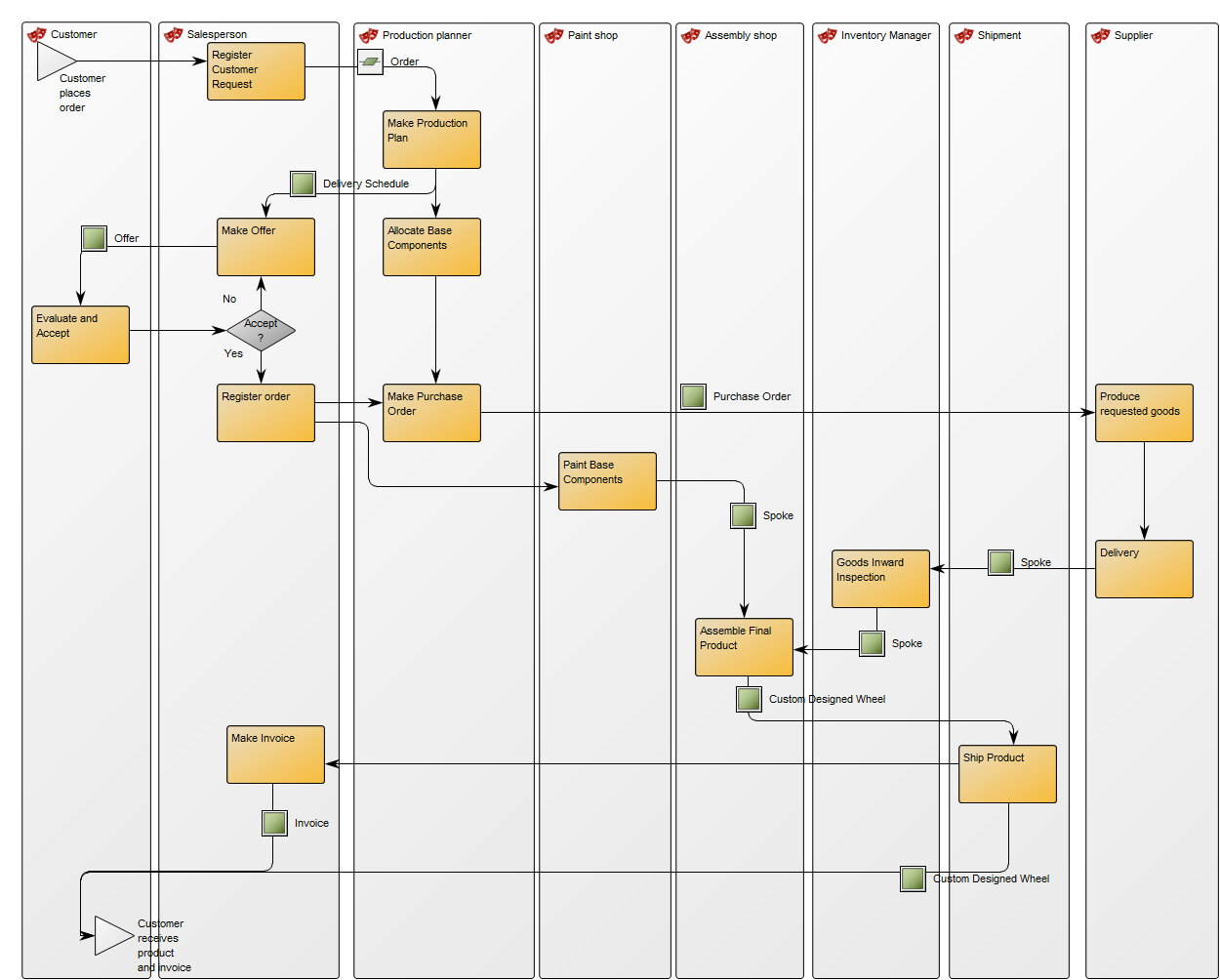
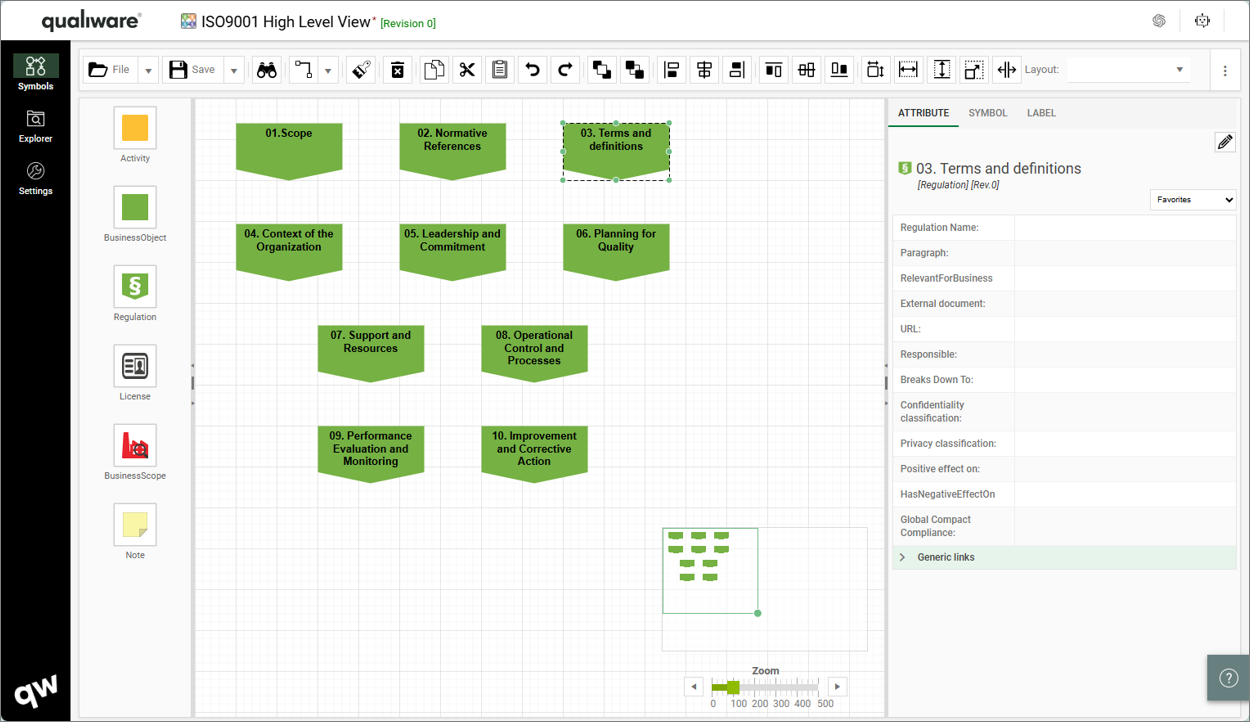
The above model illustrates another generic model for a software development project – this example has more milestones inserted as well as added document structures containing project deliverable templates.
Relation to other templates: The Work Model template should be used to document project activities – to document business processes and workflows should be documented in Business Process Networks, Workflow Diagrams or Business Process Diagrams.
For a more detailed view of the structure of a project’s results and resources, a Work Breakdown Structure template should be used.
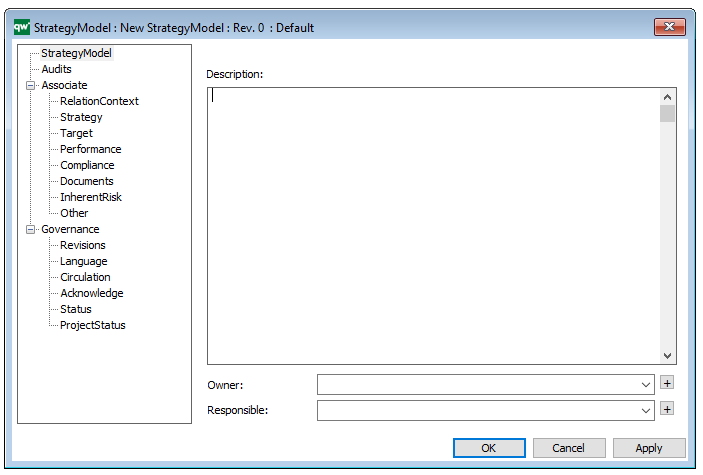
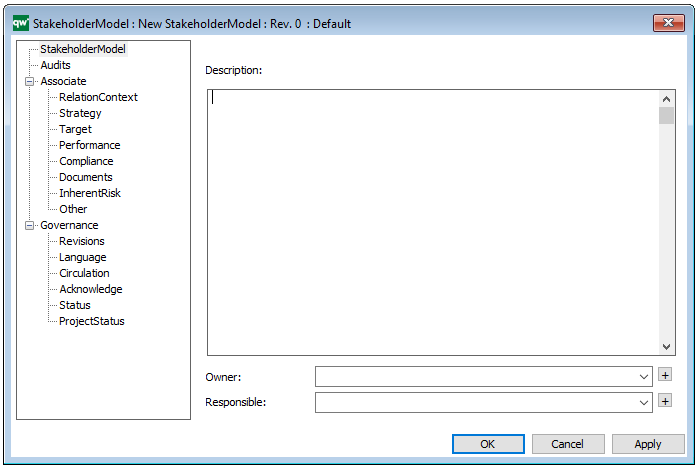
Properties and metadata: The Work Model can for example retain the following information:
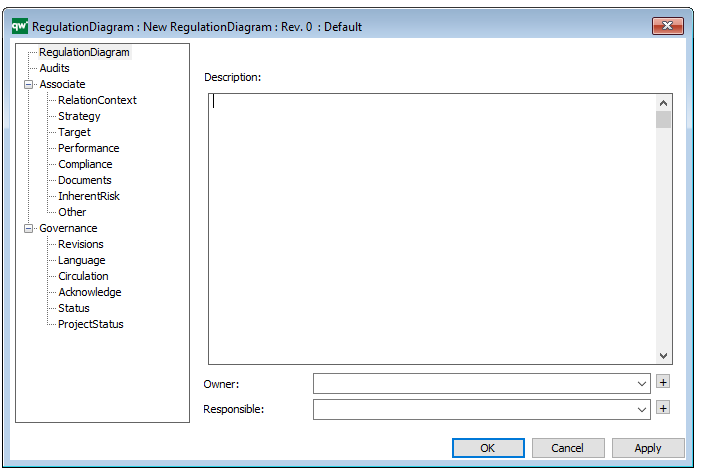
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the model
- Link to the one responsible for the model
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
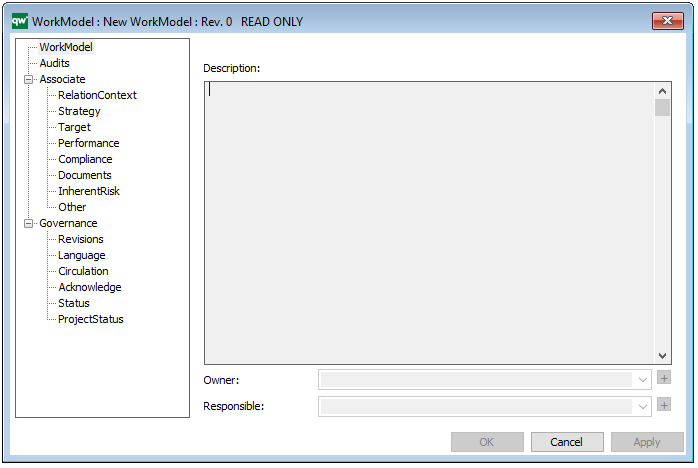
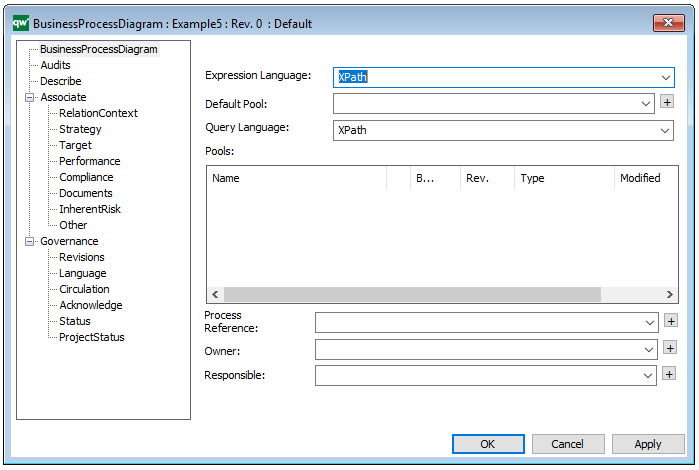
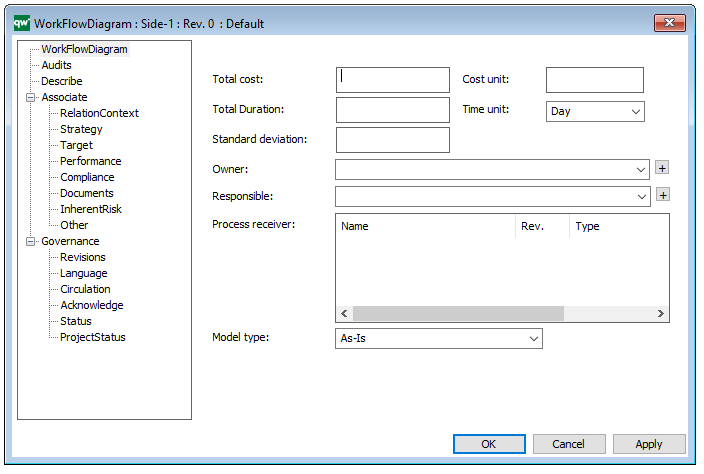
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Work Model, where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.
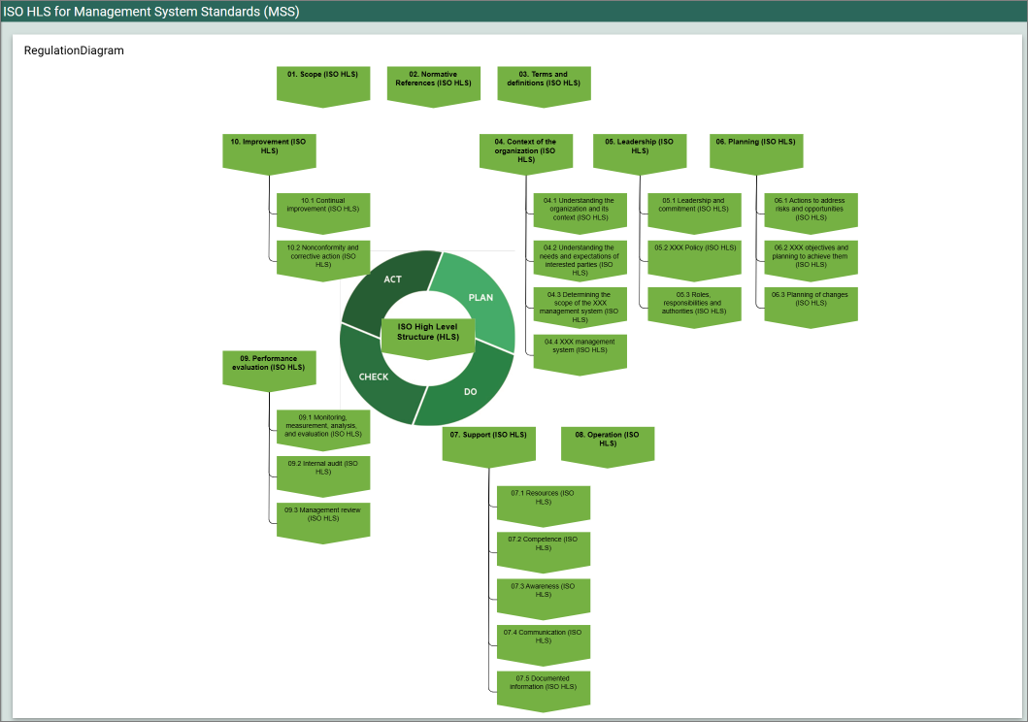
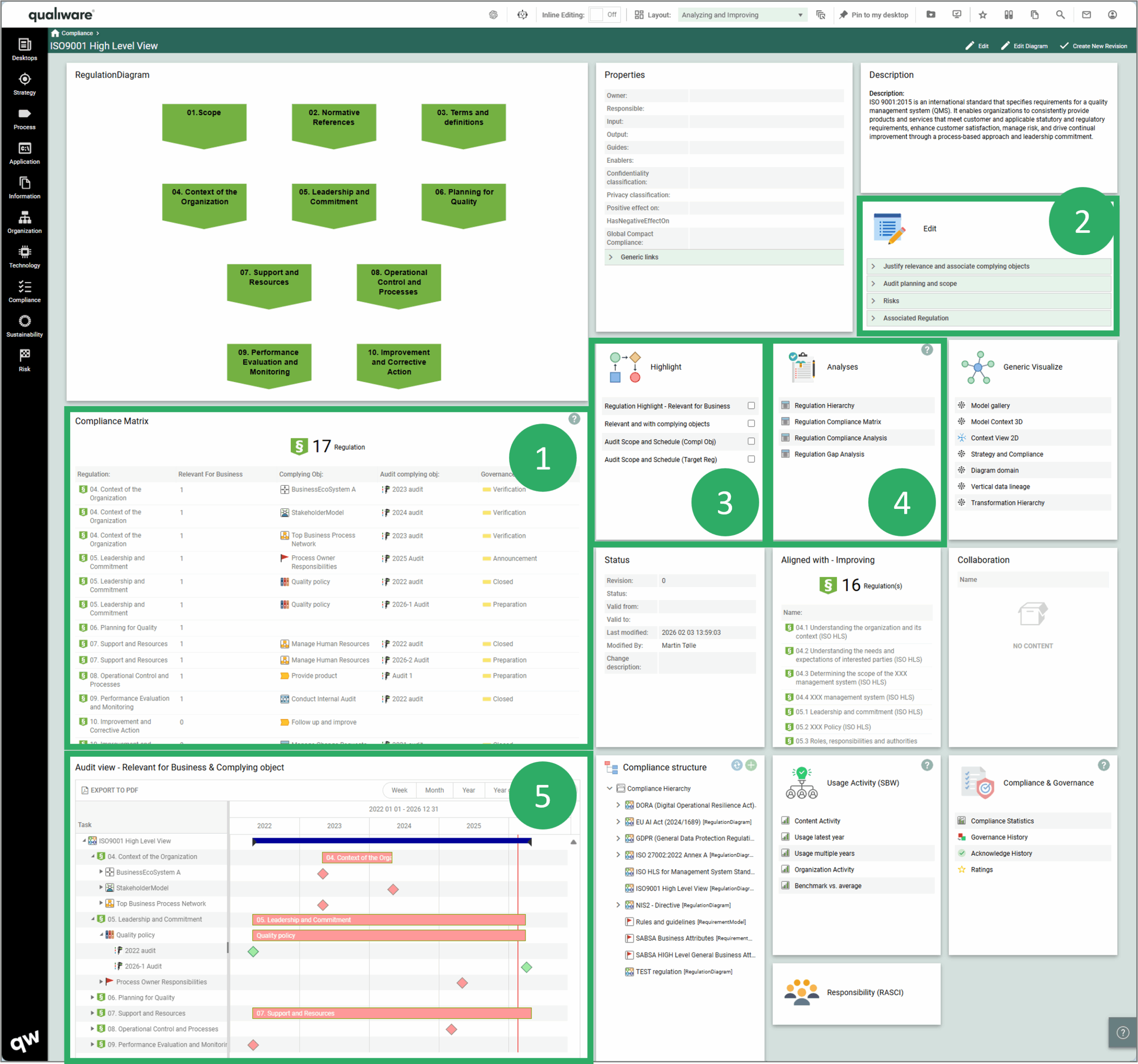 Relation to other templates: As mentioned, the regulations can be linked to the relevant Business Processes or Activities, that typically are detailed in a
Relation to other templates: As mentioned, the regulations can be linked to the relevant Business Processes or Activities, that typically are detailed in a