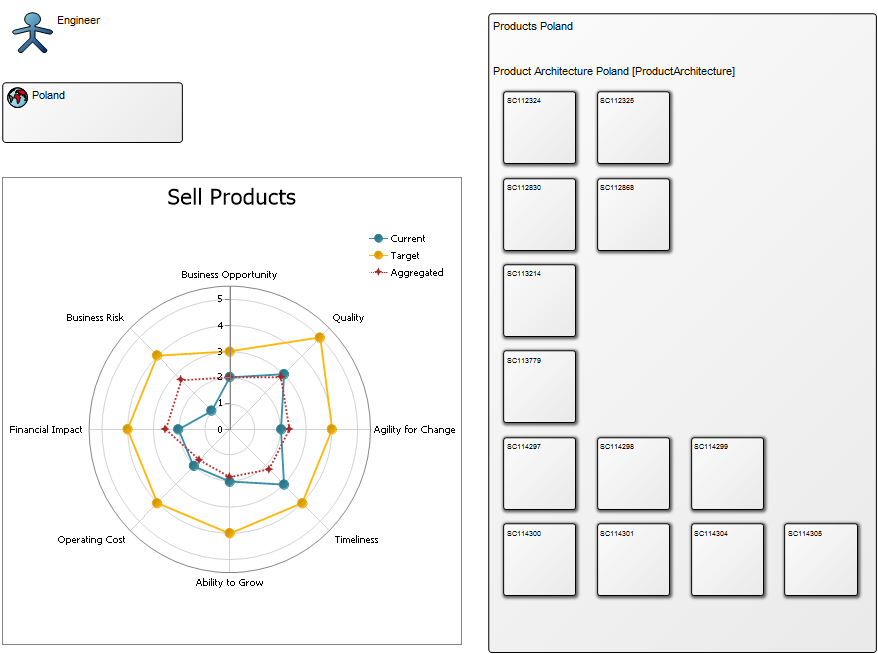
Purpose: The purpose of the Business Operating Model is to visualize how an organization functions and delivers value to its customers. The model presents a ‘one-page-overview’ of the organization and offers a quick way to communicate an organization’s value structure to different types of stakeholders.
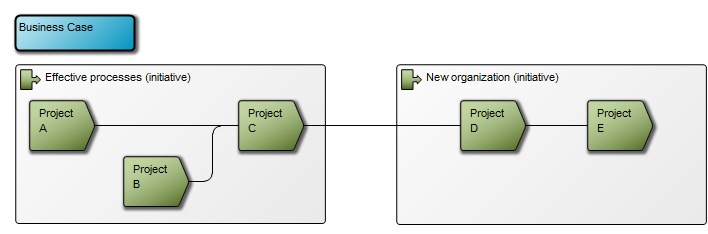
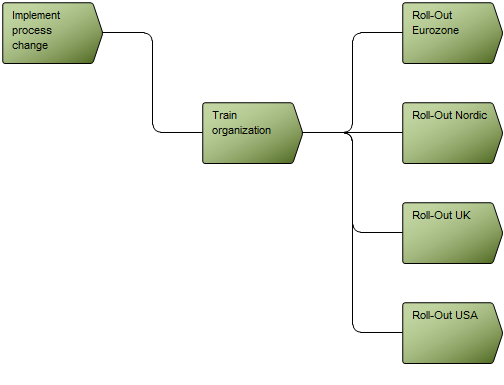
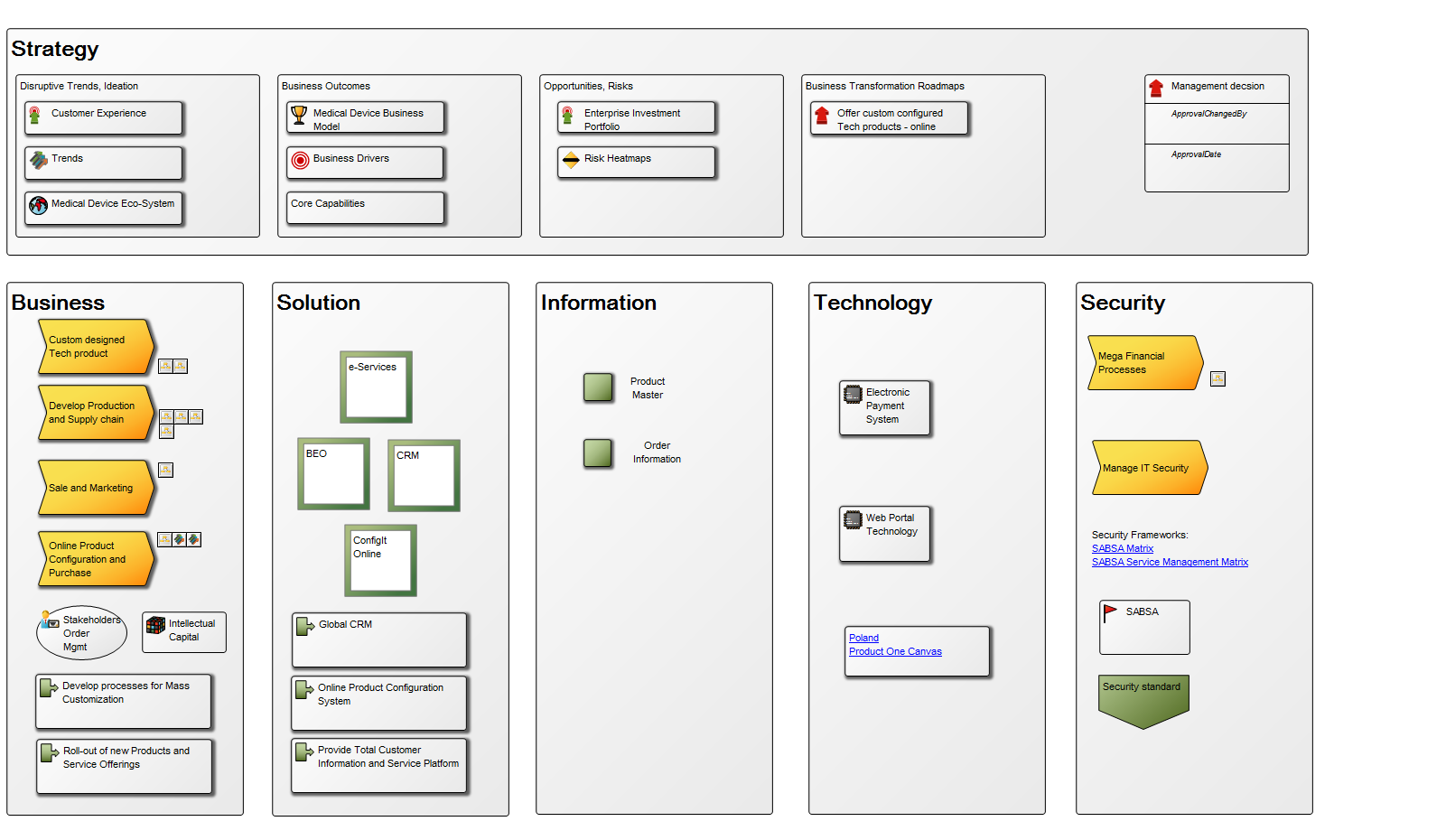
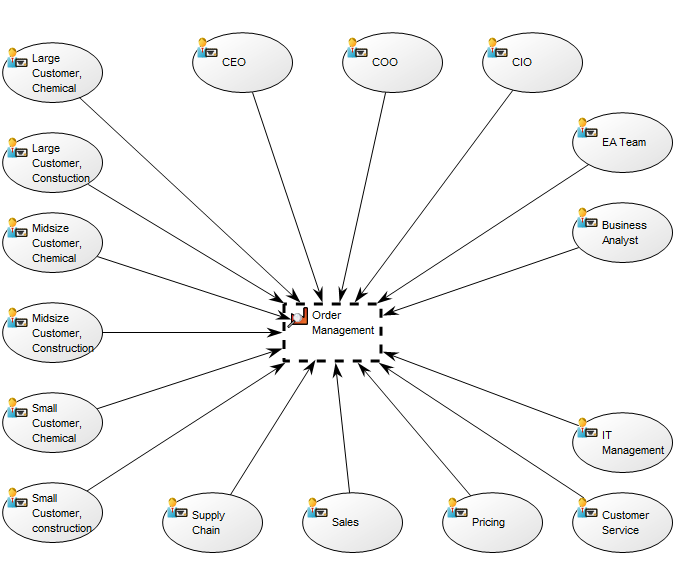
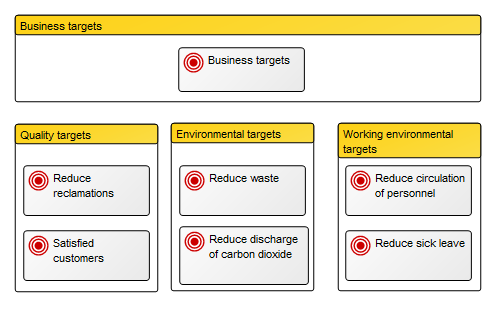
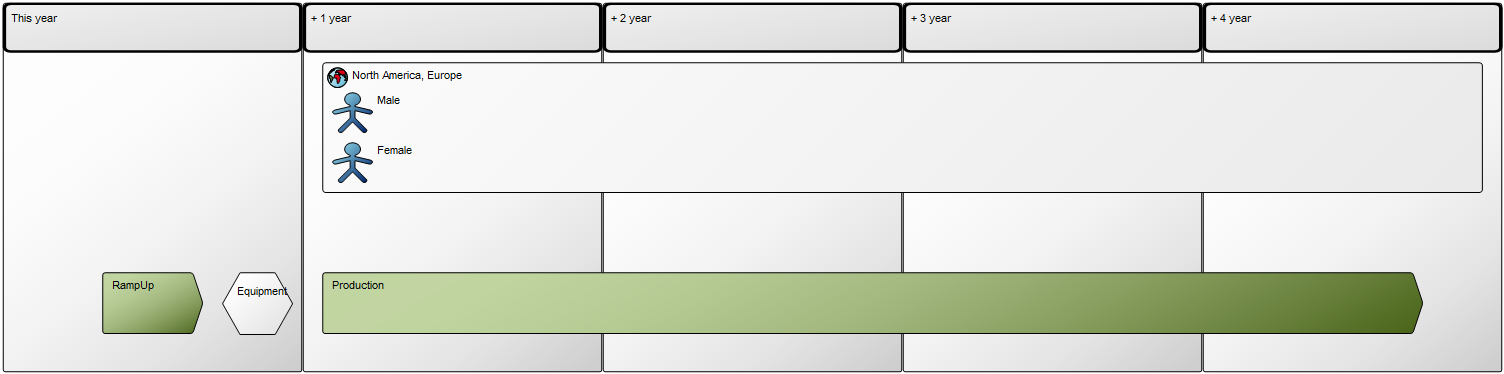
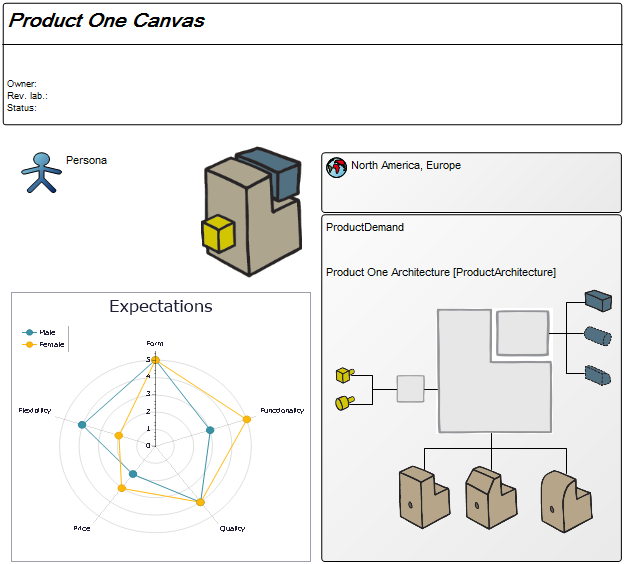
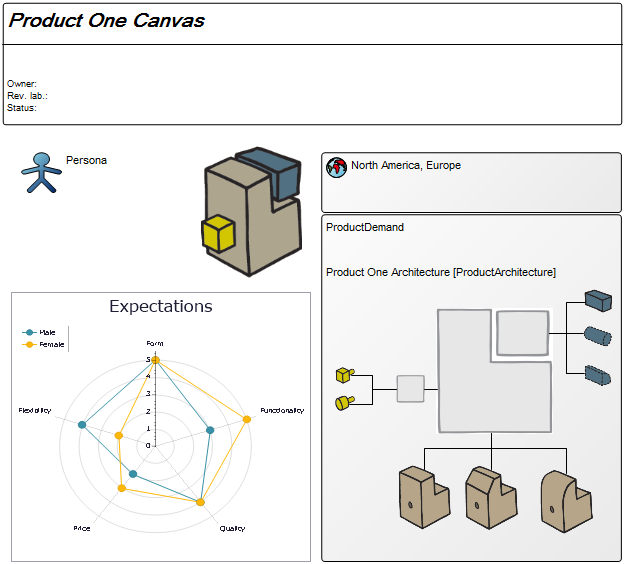
Core concerns: The Business Operating Model can be put together in numerous ways including information on Stakeholders, Business Processes, Products, Projects, Channels, Key Performance Indicators and more. This enables you to create a Business Operating Model that reflects your organization’s specific value chain in detail. Below is an example of a Business Operating Model that shows a business’s suppliers, high-level processes, products & services, channels and customer segments:
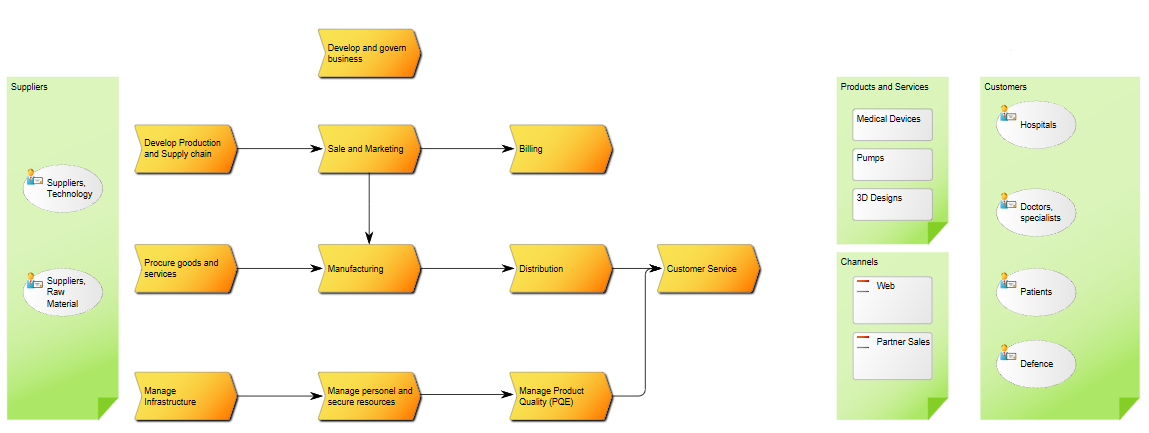
Relation to other templates: The Business Operating Model is a strategic model that can be supplied with more detailed models such as a Business Capability Model, Requirement Models, Stakeholder Models and the Business Ecosystem Model.
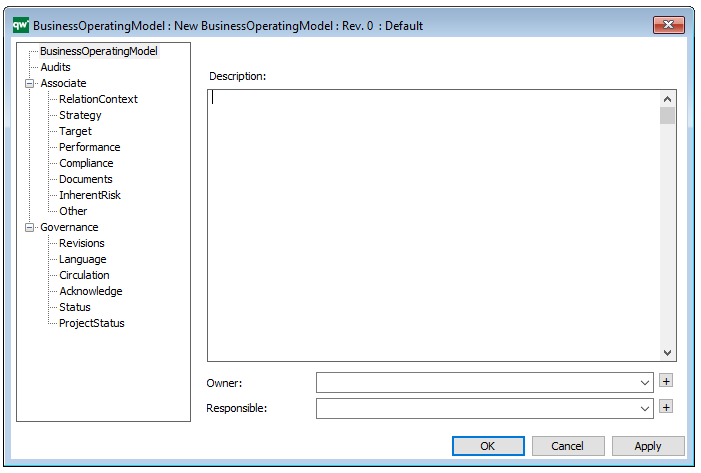
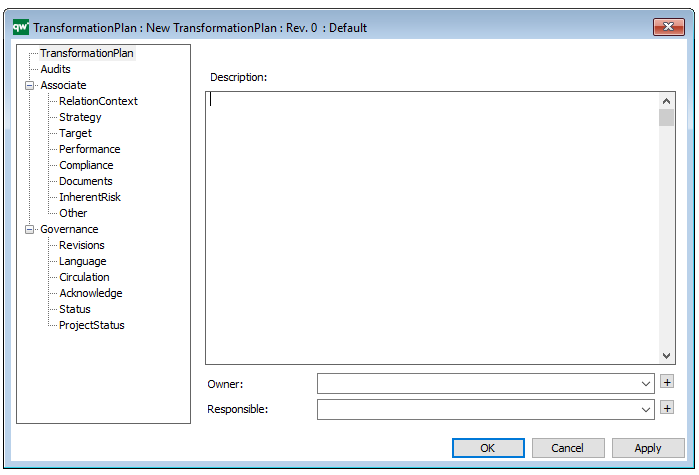
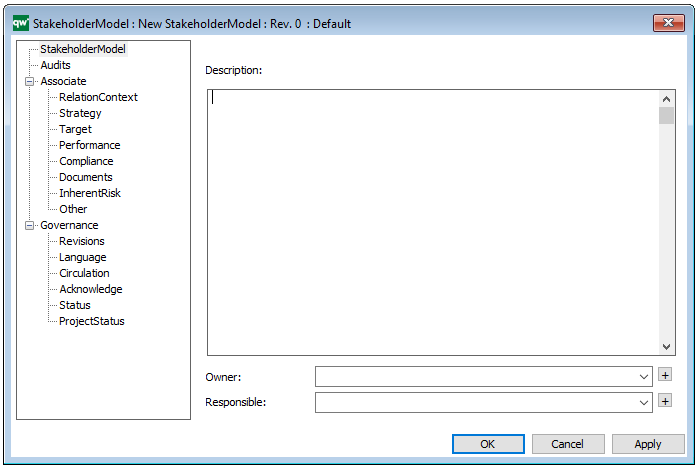
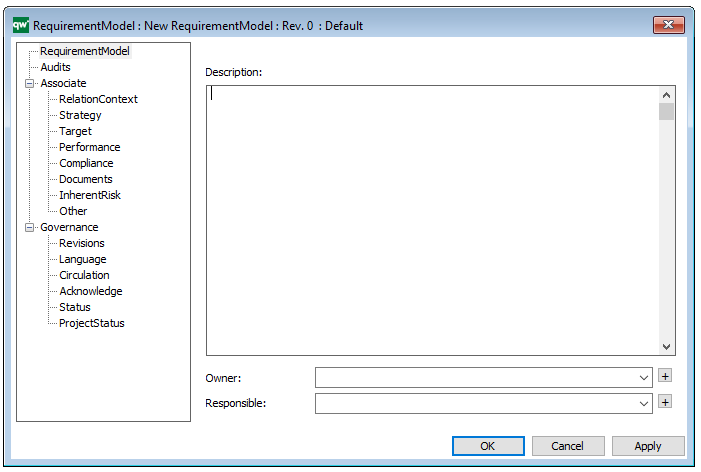
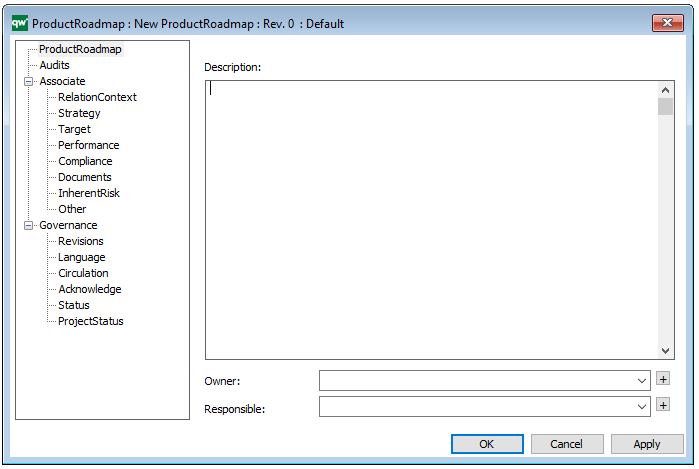
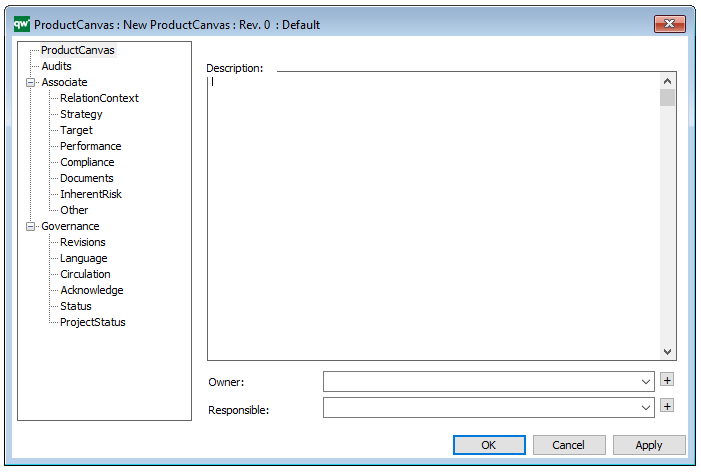
Properties and metadata: The Business Operating Model can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the accuracy of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
- Project status: information about budgeted and actual man-hours spent, percentage completed and the latest milestone, result and quality control of a change process.
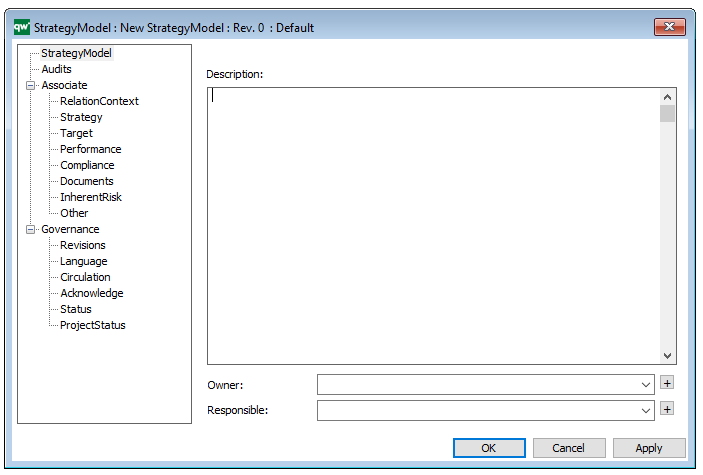
In the picture below you can see the Business Operating Model’s properties dialogue window, where the information can be viewed and edited: