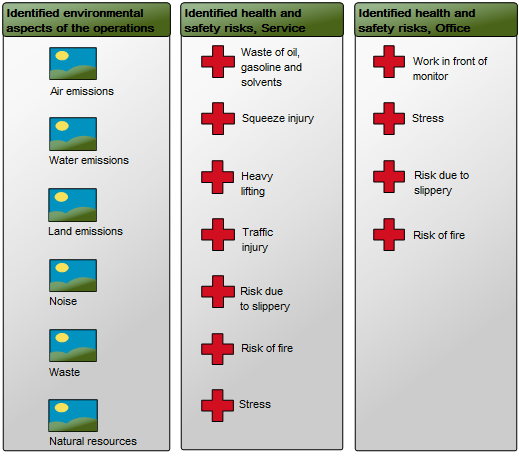
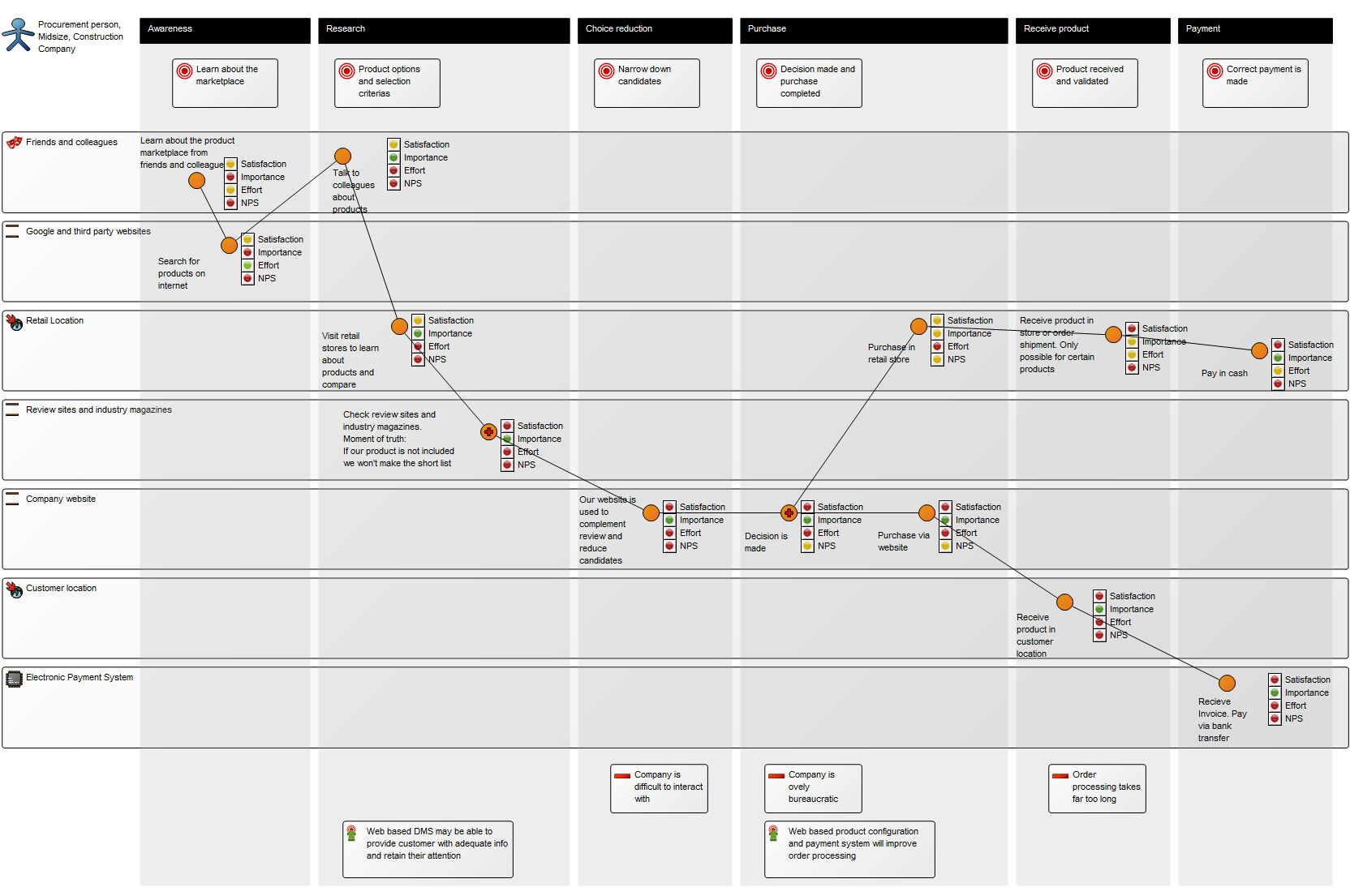
Purpose: The purpose of the Integration View template is to document the routing of integrations between systems.
Core concerns: The Integration View template enables you to model Information Systems, System Components and External Entities (a source to or a receiver of information from a system), and connect them using Integration Flows.
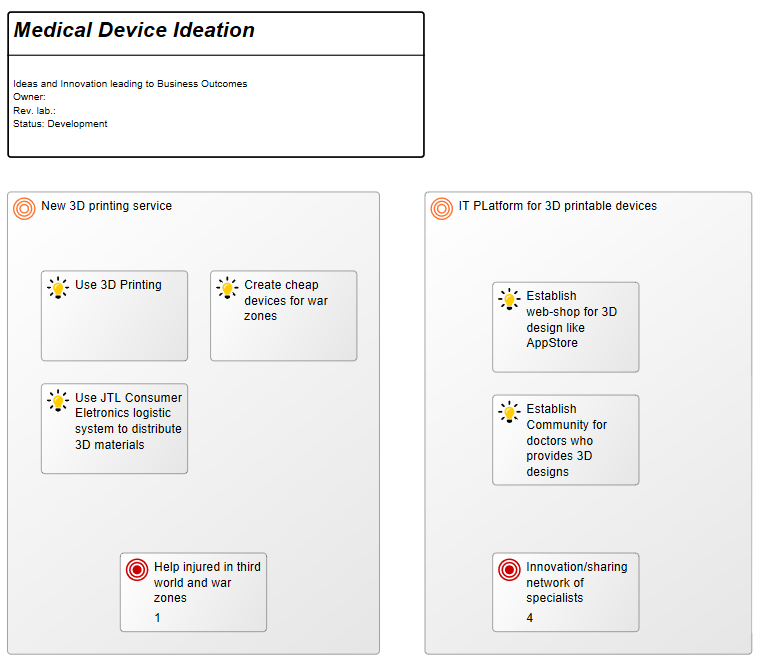
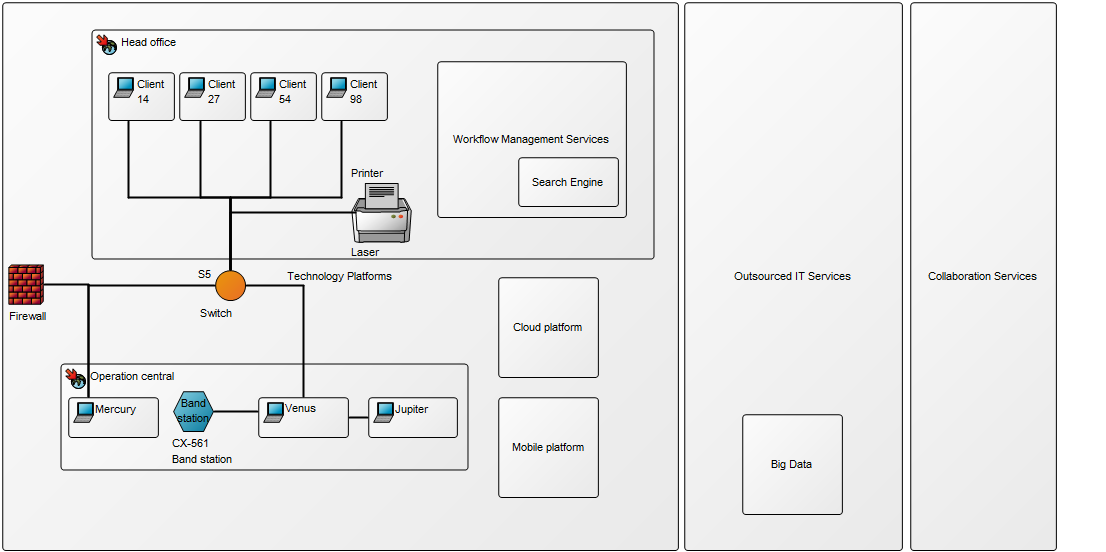
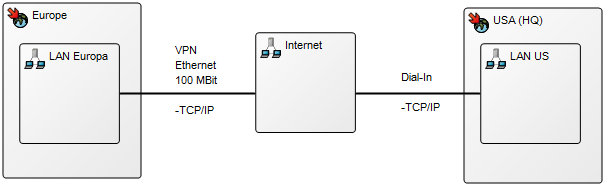
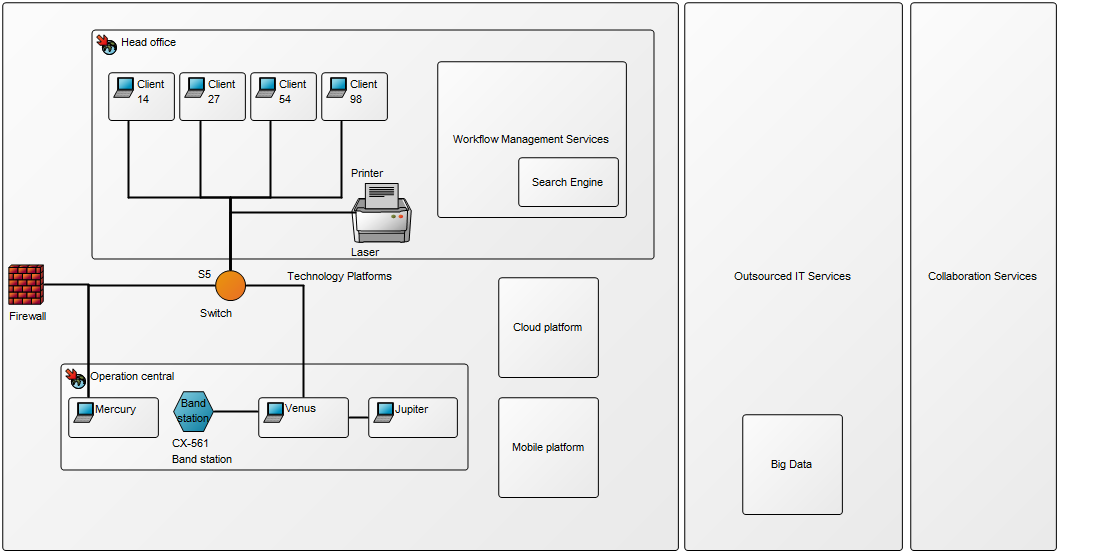
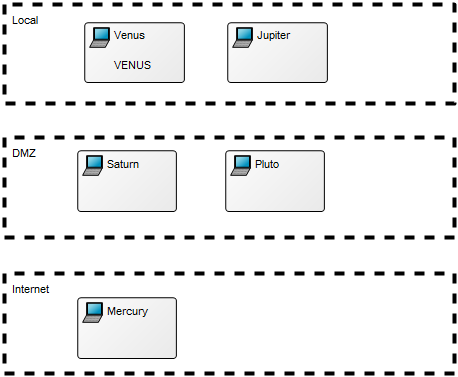
Below is an example of an Integration View concerning the flow of test data:
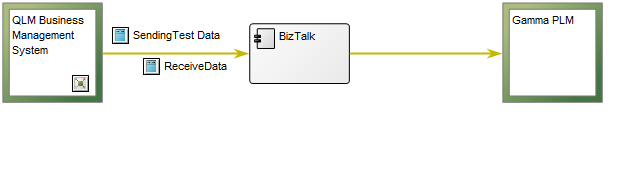
Relation to other templates: The Integration View belongs to the Application layer of the architecture and is as such related to the Application Architecture Diagram, the Data Flow Diagram and the Component Diagram.
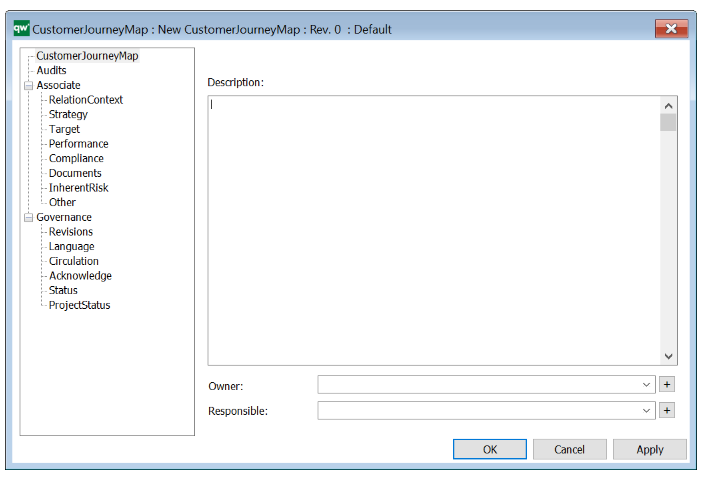
Properties and metadata: The Integration View template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the model
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
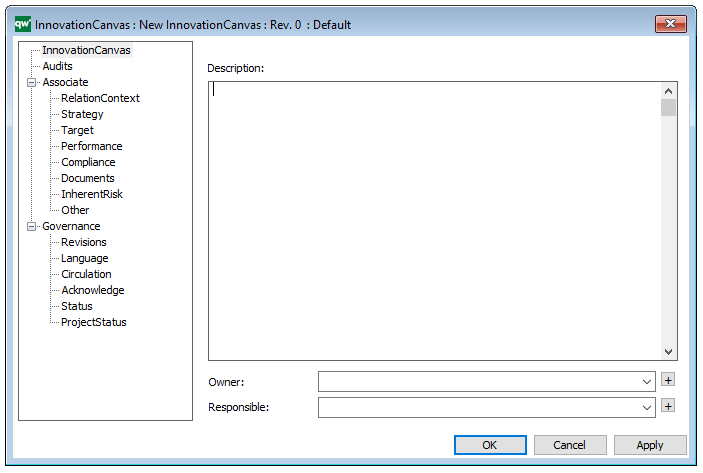
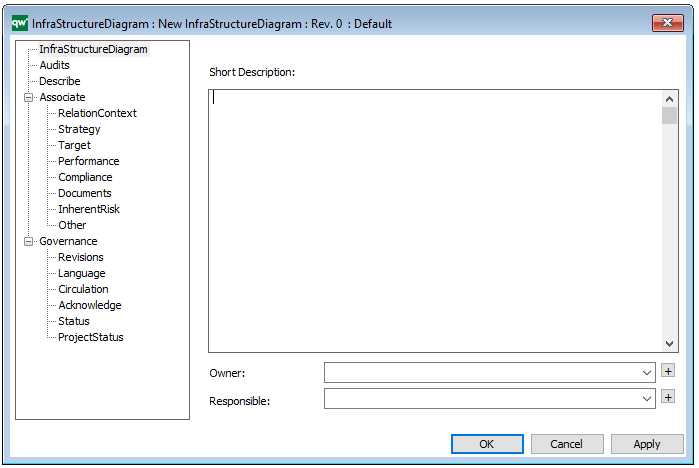
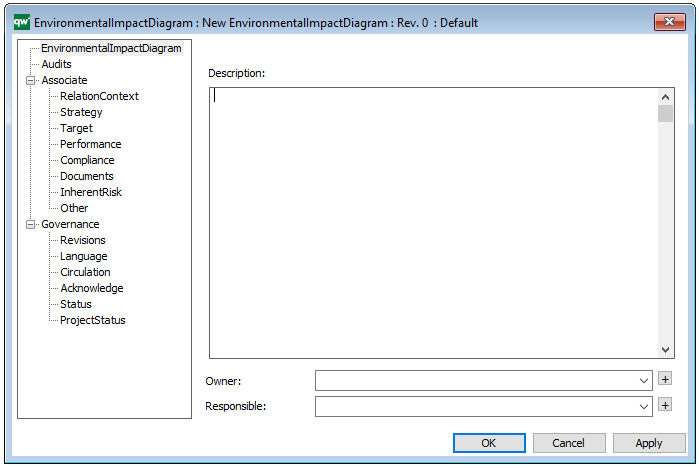
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Integration View template where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.