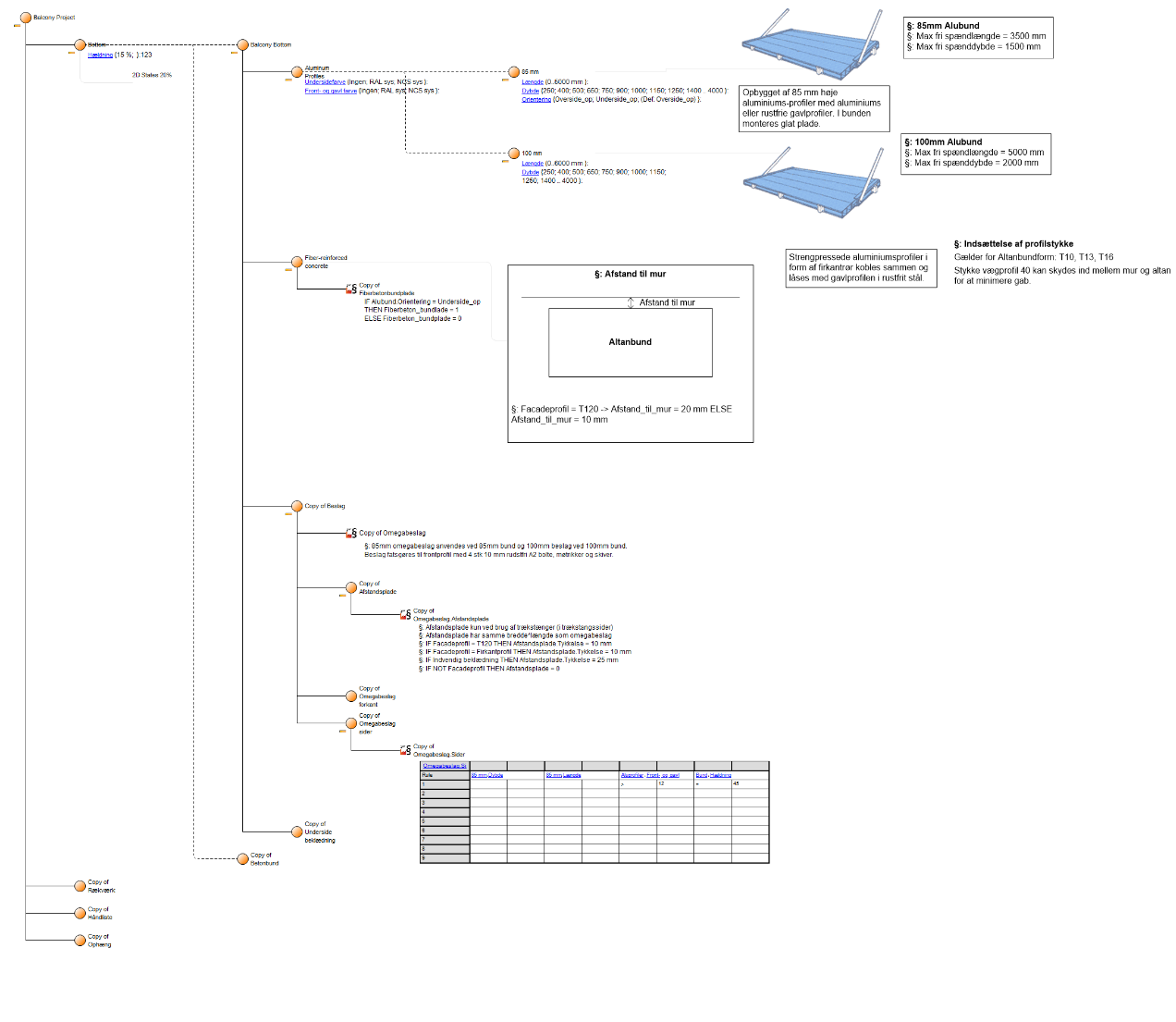
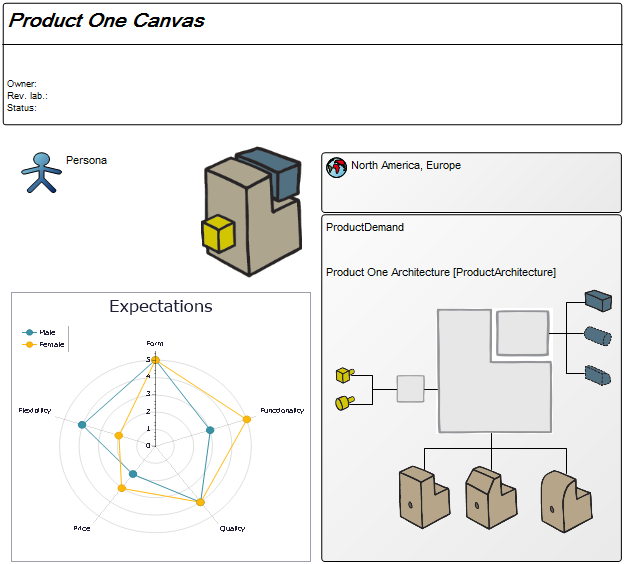
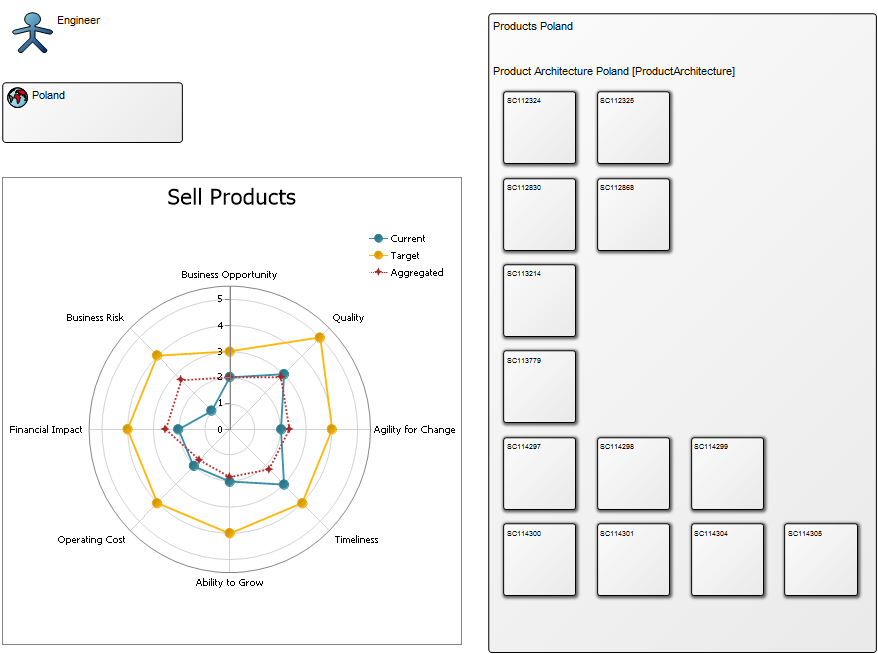
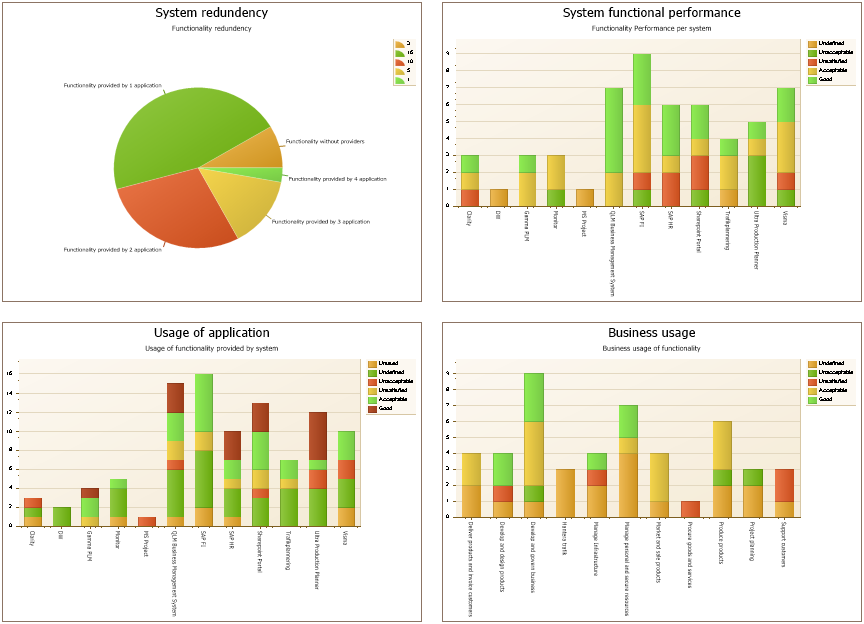
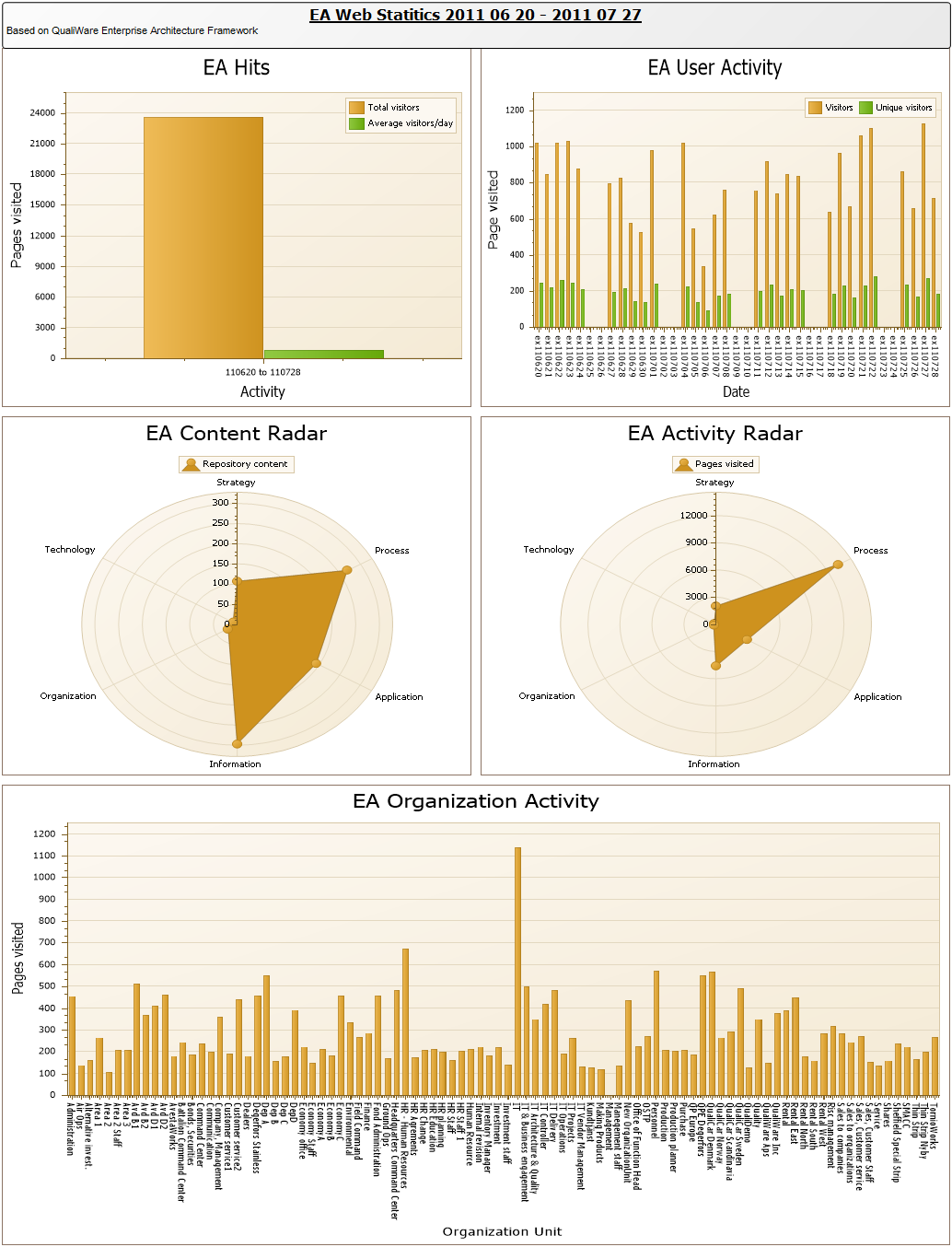
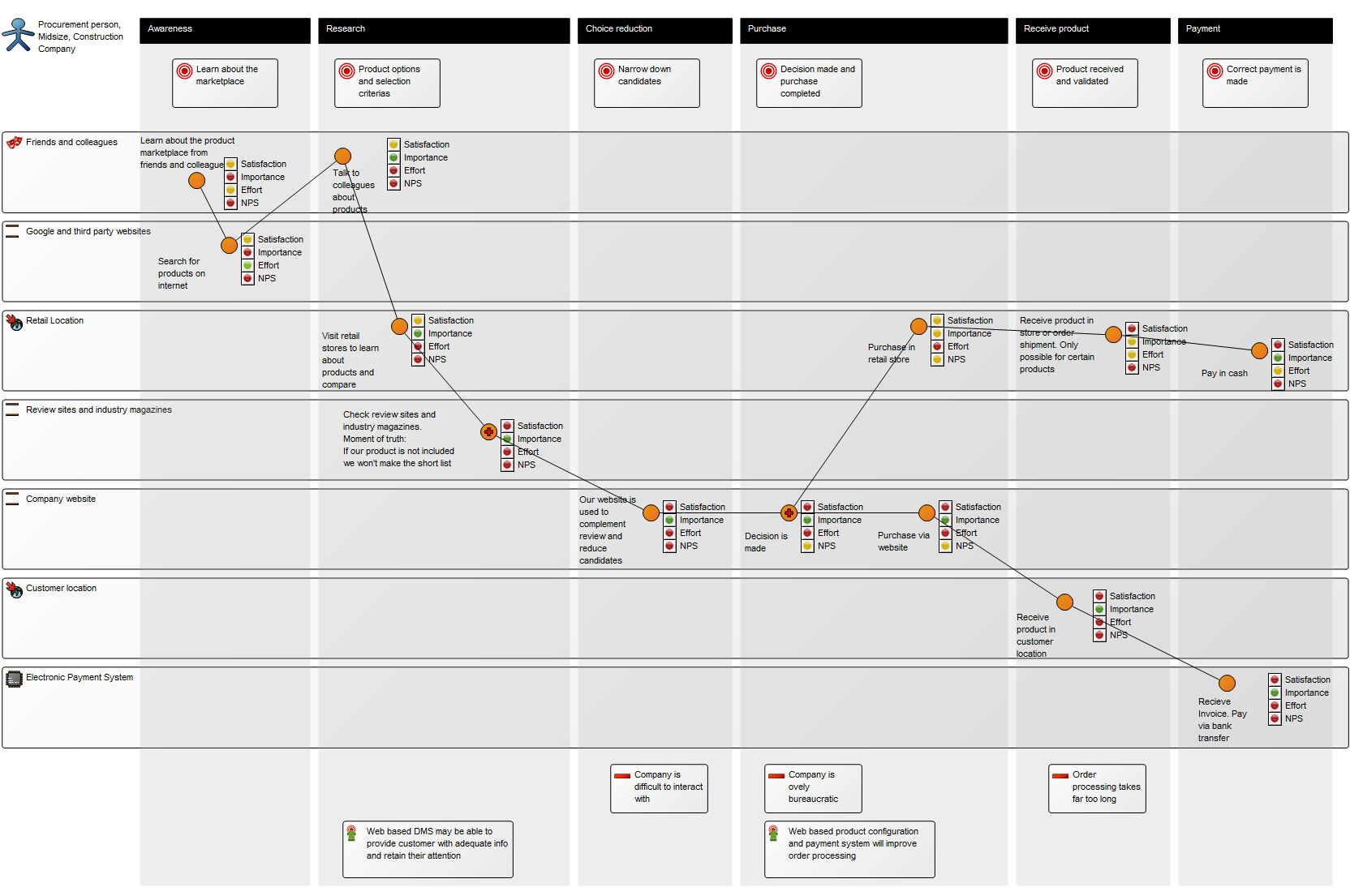
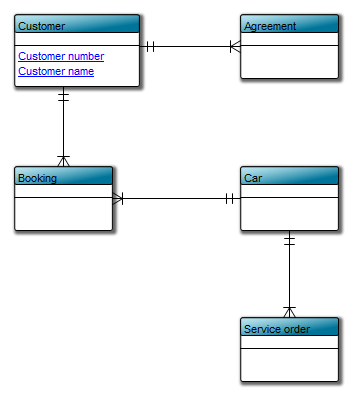
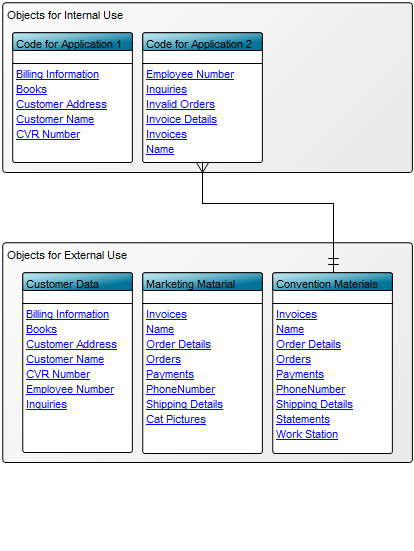
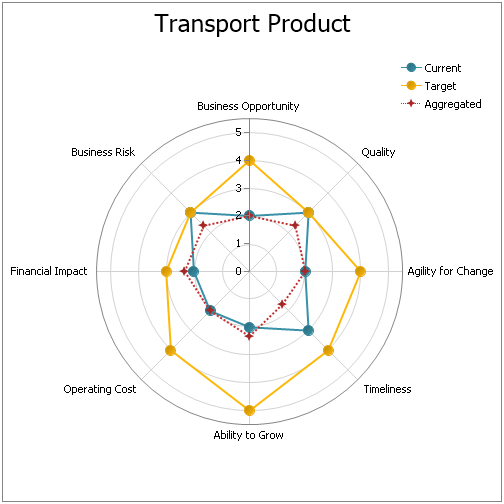
Purpose: The purpose of the Product Variant Master template is to provide an overall view of a product’s variants and can be modelled from the viewpoints of the Customer, Engineer, Part, or Production.
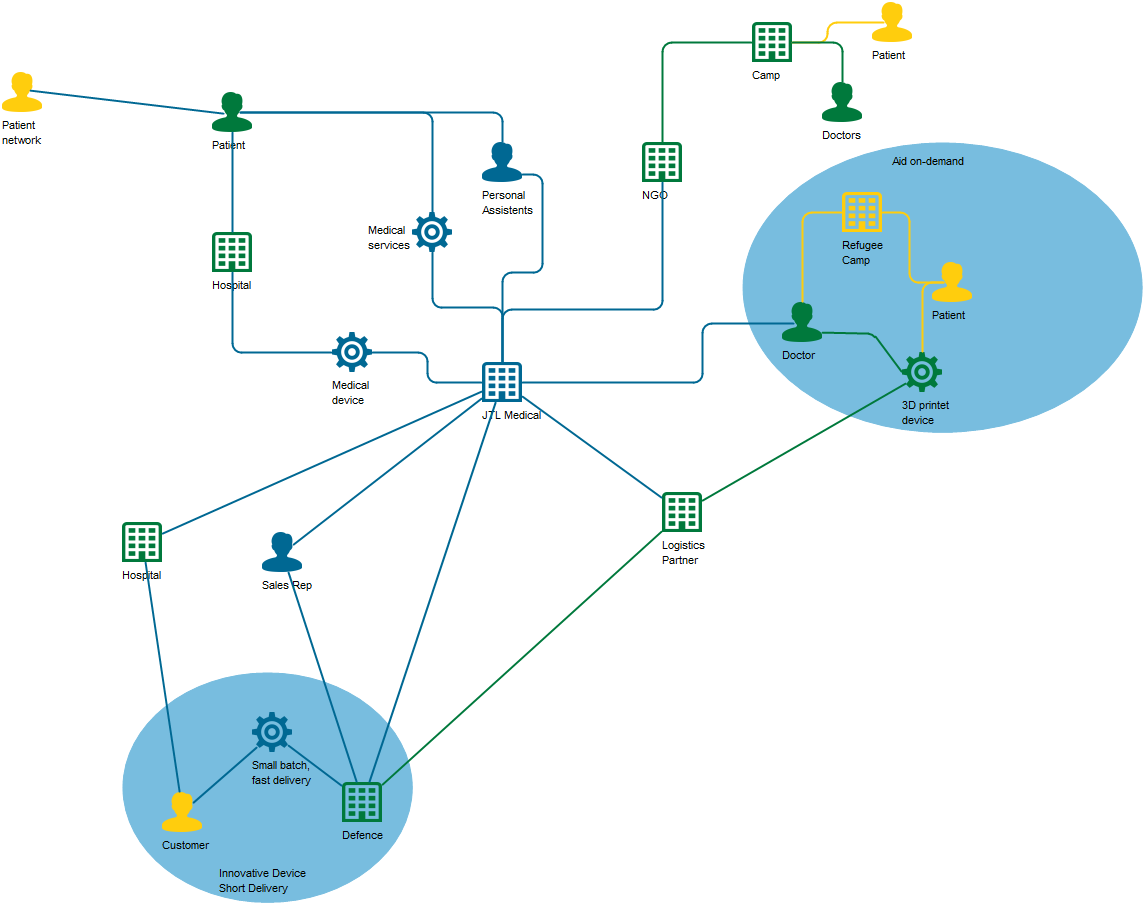
Core concerns: The Product Variant Master template enables you to model product variants by mapping their parts and part variants. The template includes the following objects: Product, Product Rule, Product Attribute, External Document and General Concept. These objects can then be connected as being Part of Product, Kind of Product, or by a “View Connection”.
The abstraction level that defines whether the model is from the viewpoint of the Customer, Engineer, Part or Production is chosen in the model’s property window.
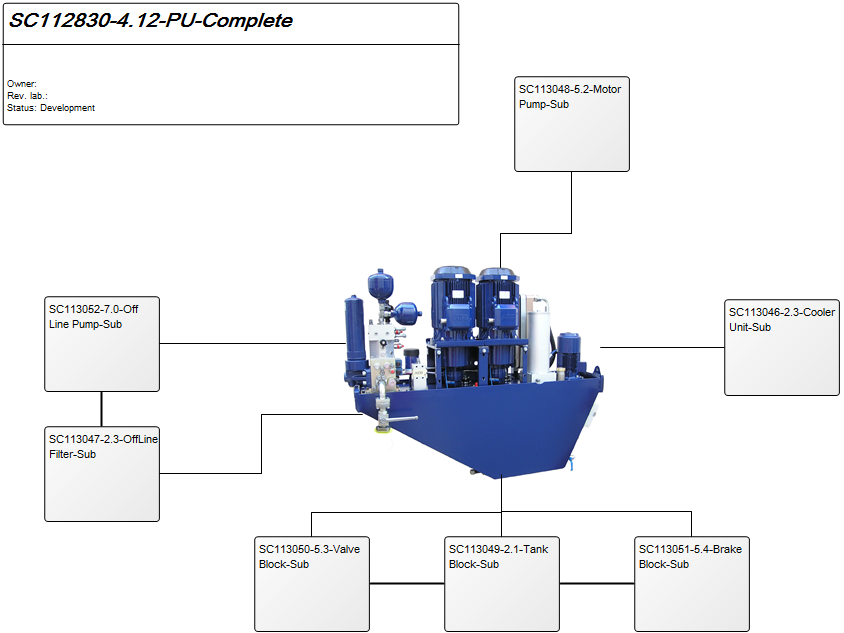
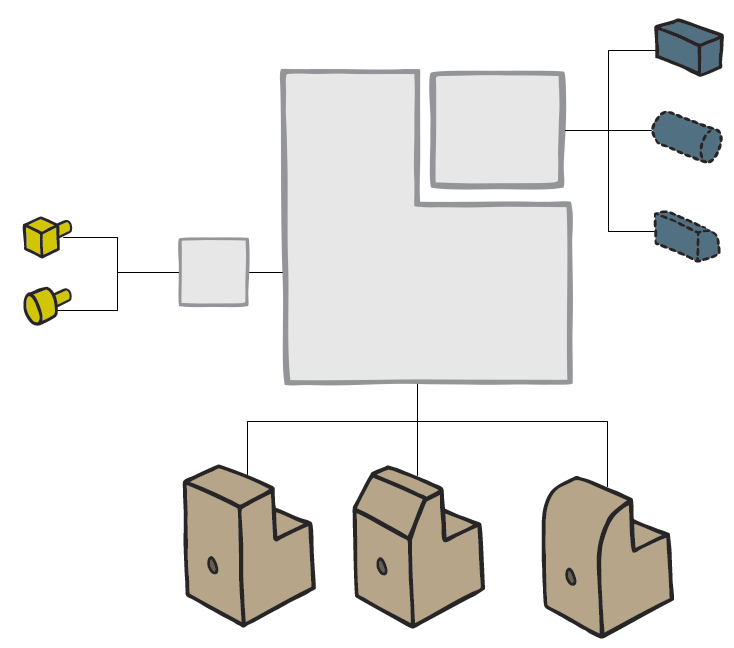
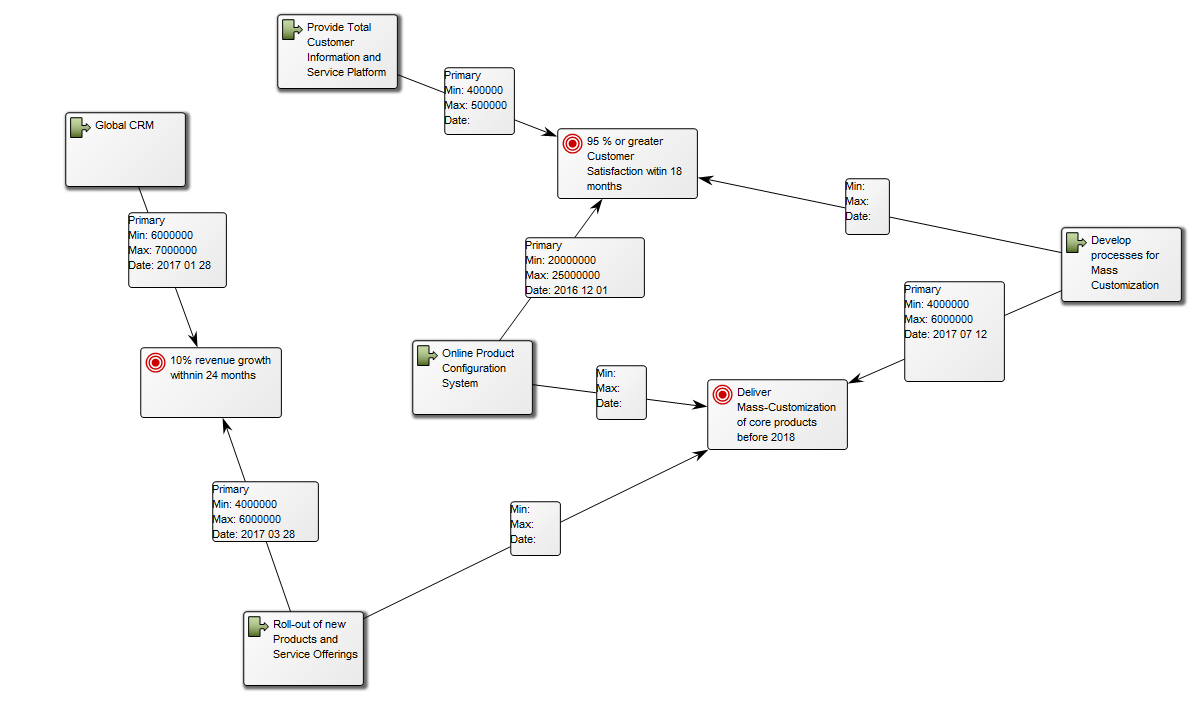
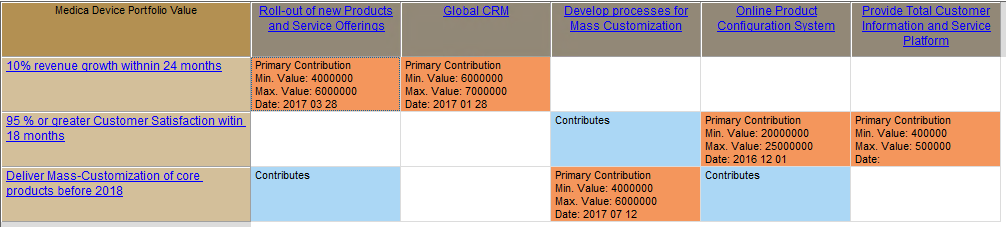
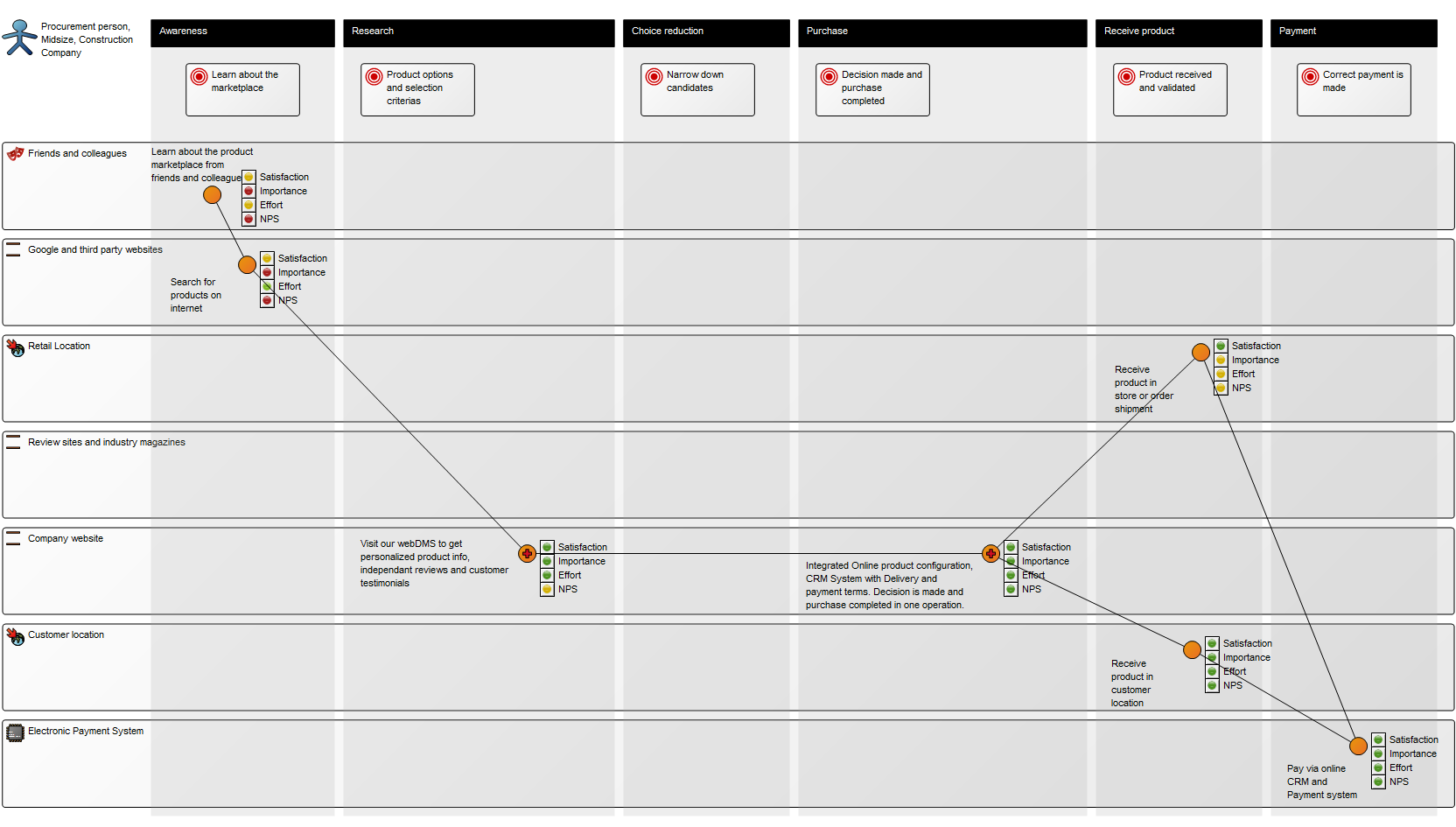
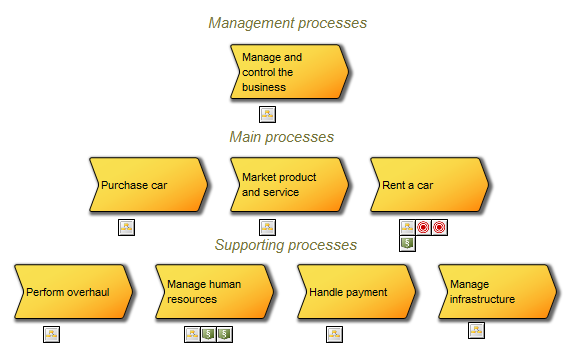
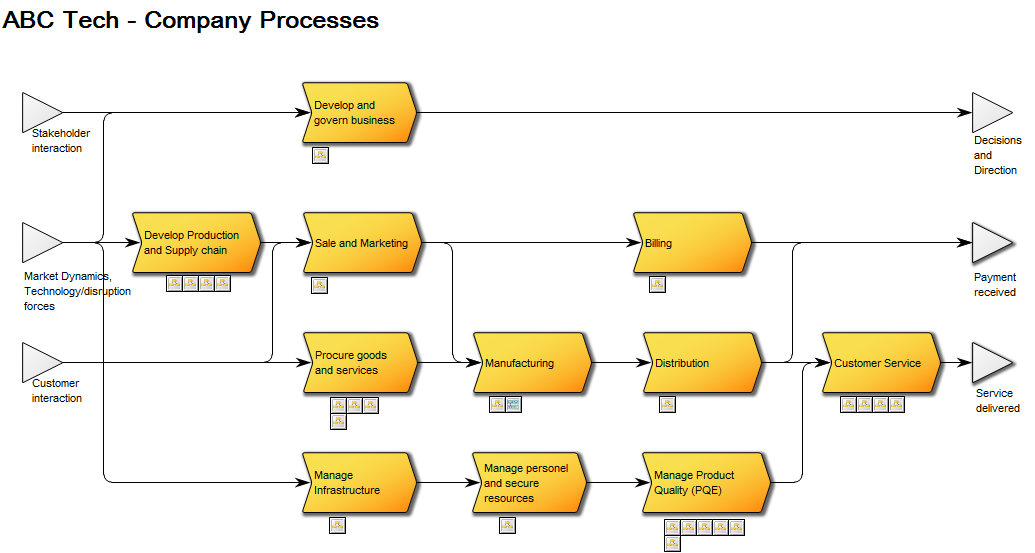
The model below is a Product Variant Master of a balcony:
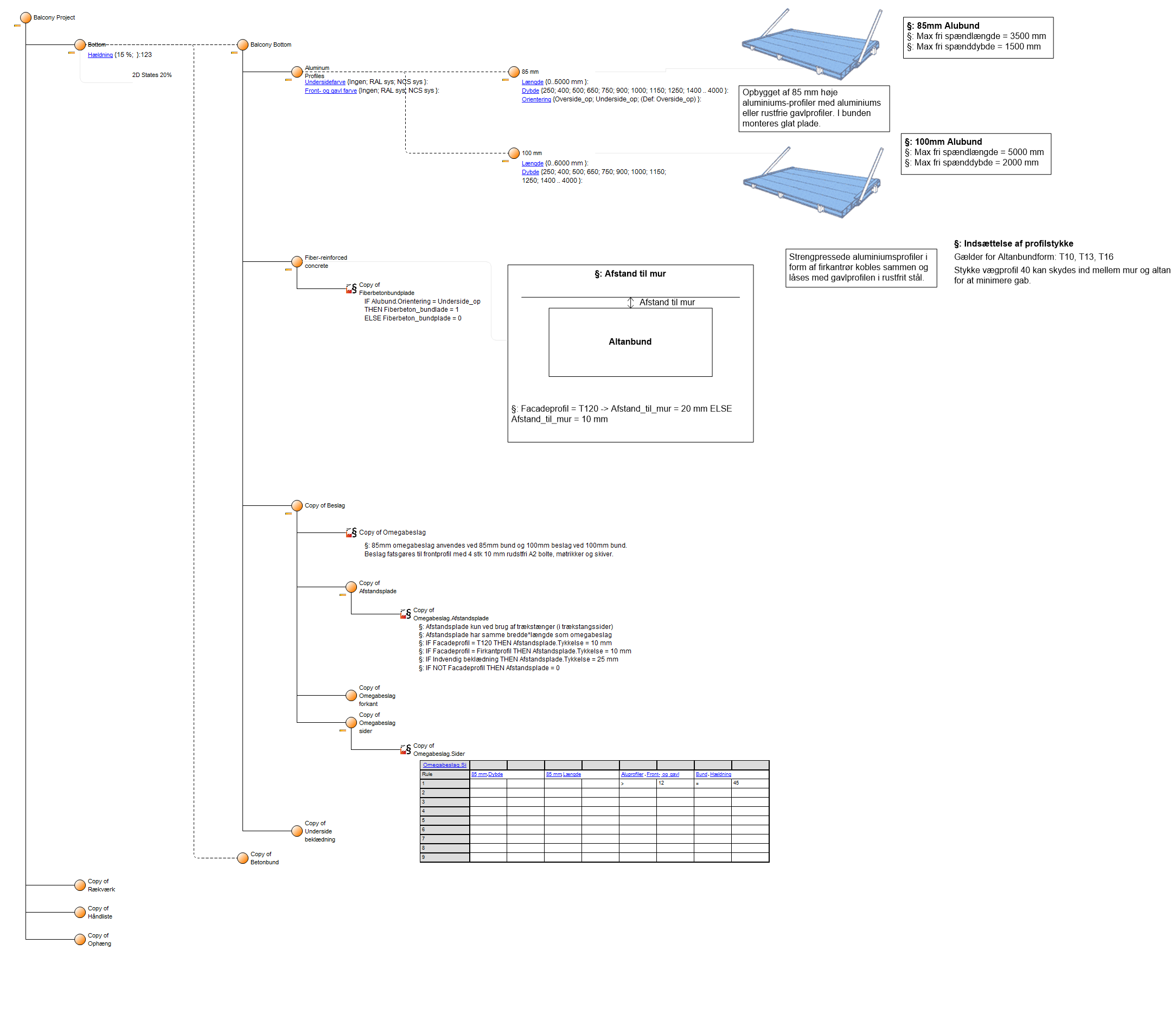
Relation to other templates: The Product Variant Master is a decomposition of a Product. As such it is related to the Product Canvas and Product Architecture. It can contain a Product Rule Table and could also be linked to from a Product Roadmap.
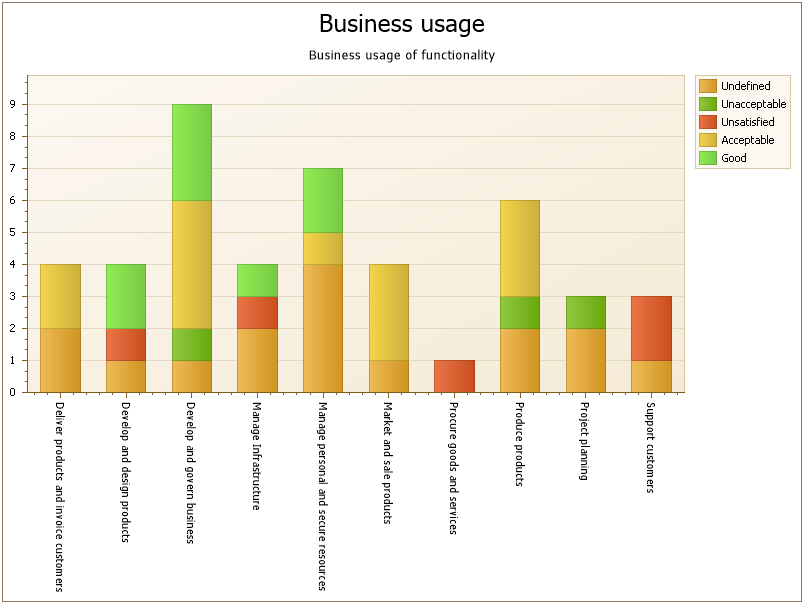
Properties and metadata: The Product Variant Master can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the model
- Choice of the Kind of Notations Graphics
- Choice of Abstraction Level
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
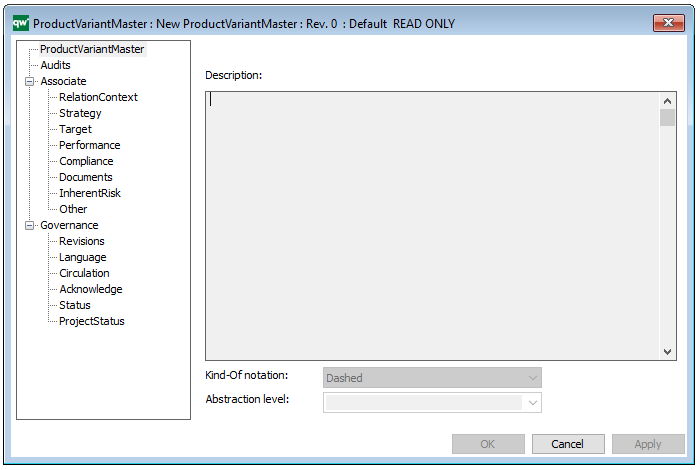
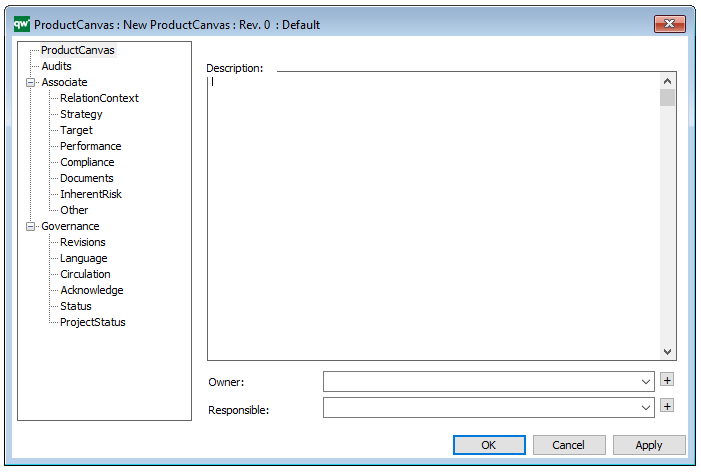
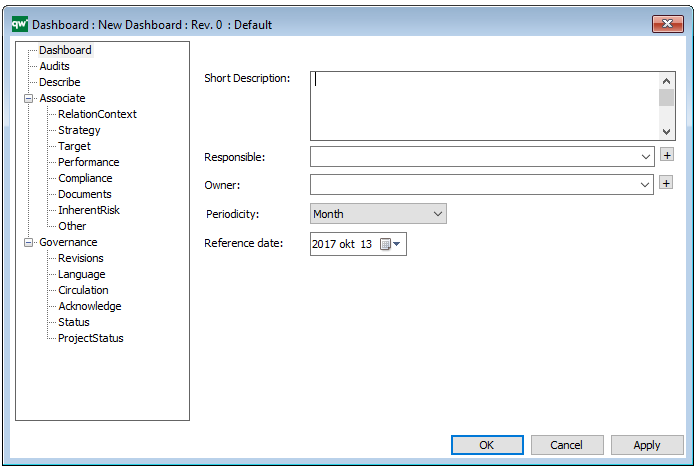
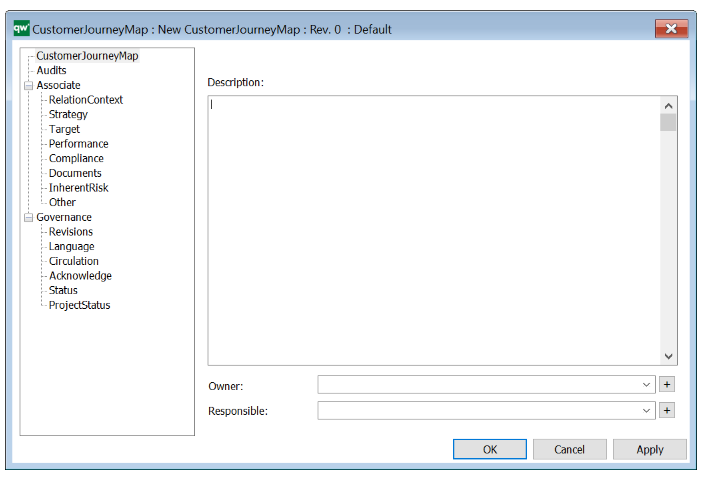
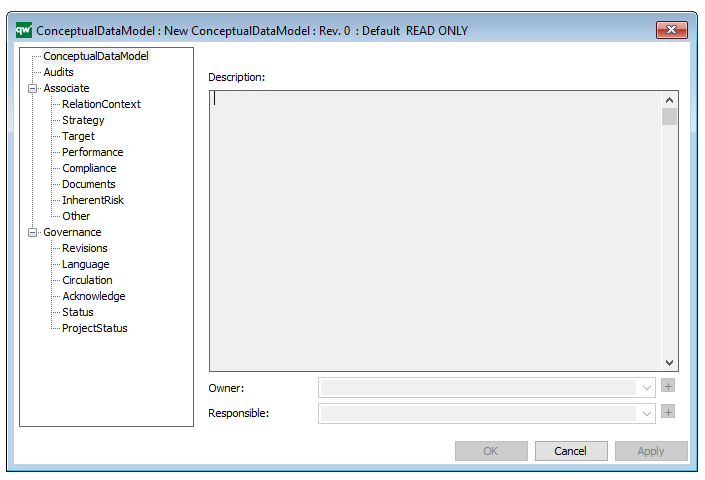
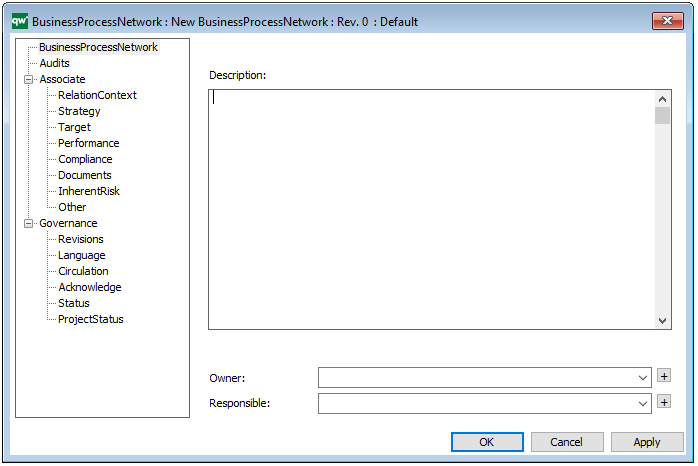
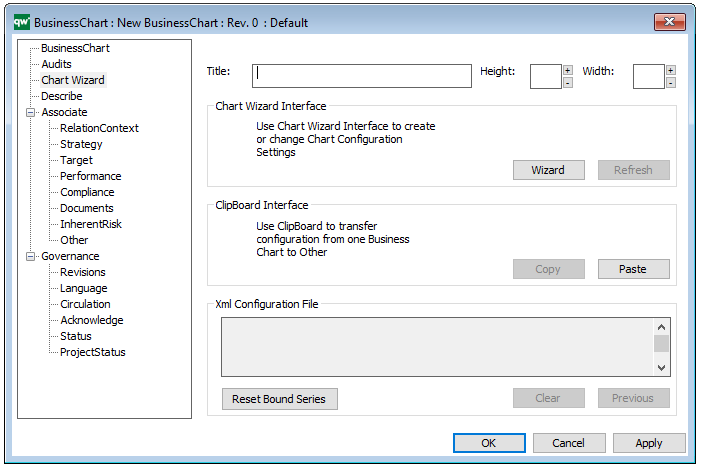
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Product Variant Master where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.
For more information: You can learn more about the Product Variant Master model by reading the following article (page 1-7):