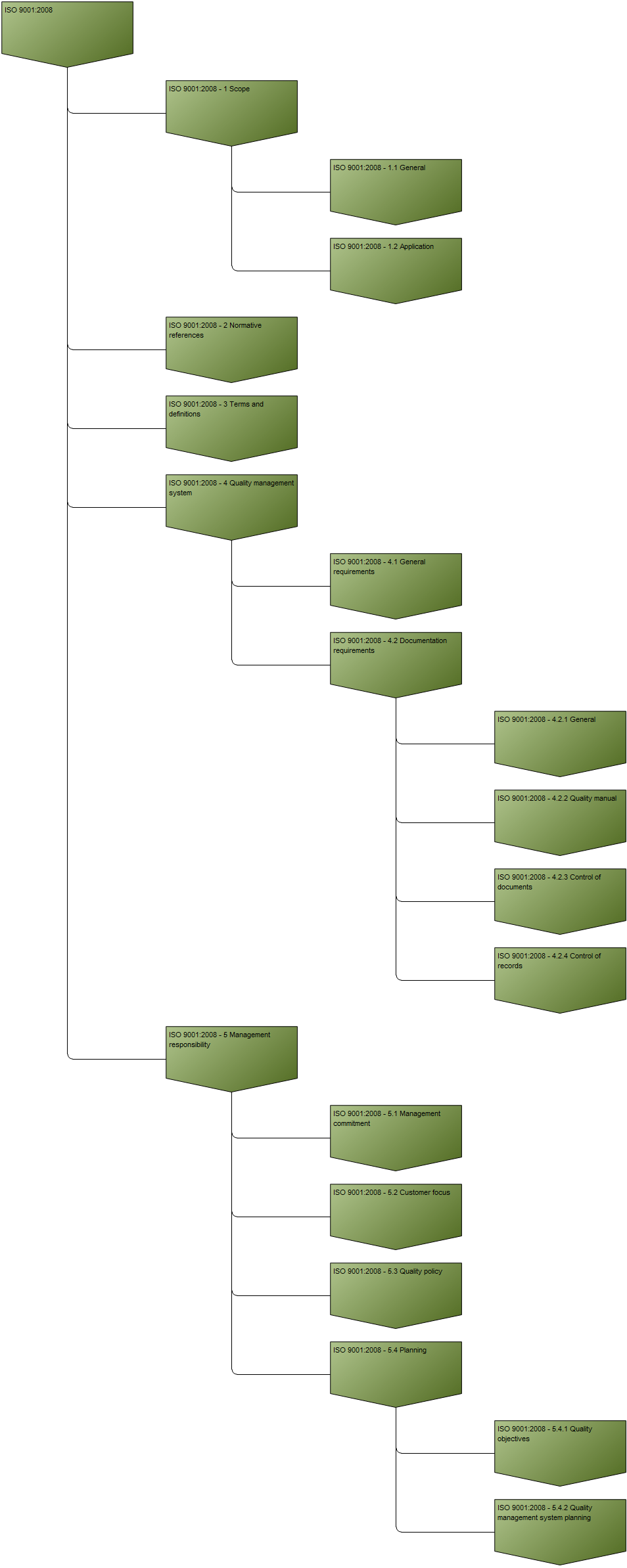
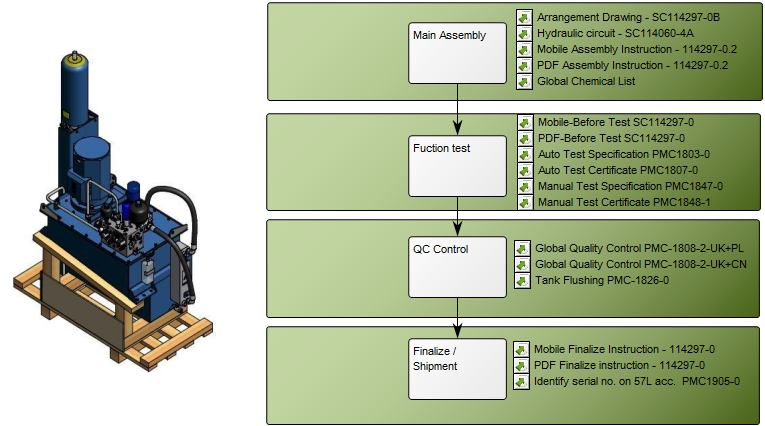
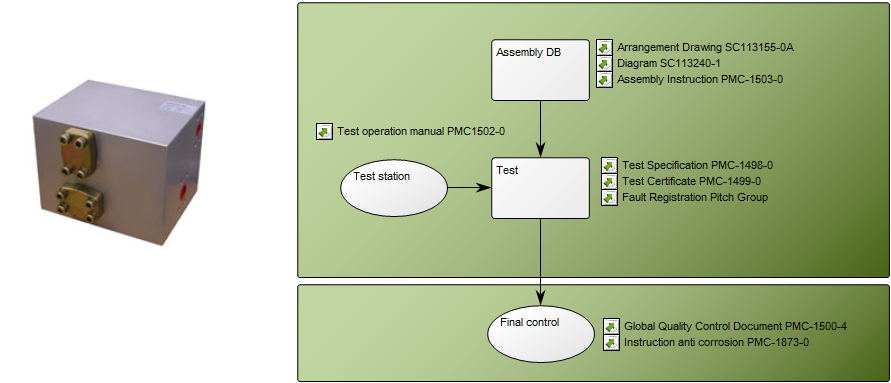
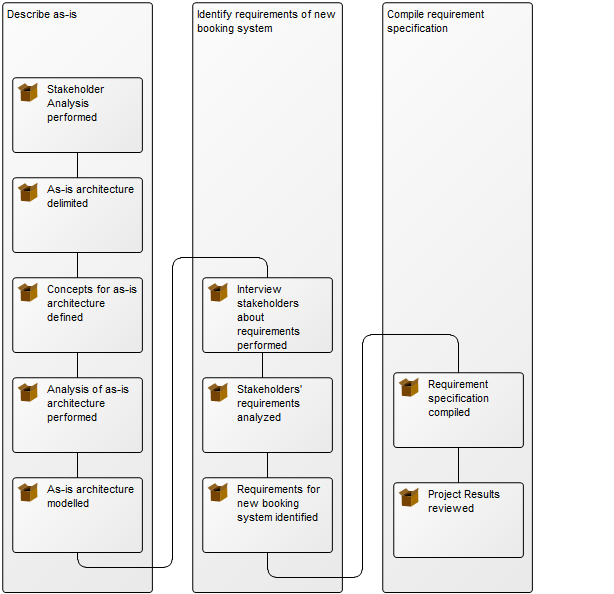
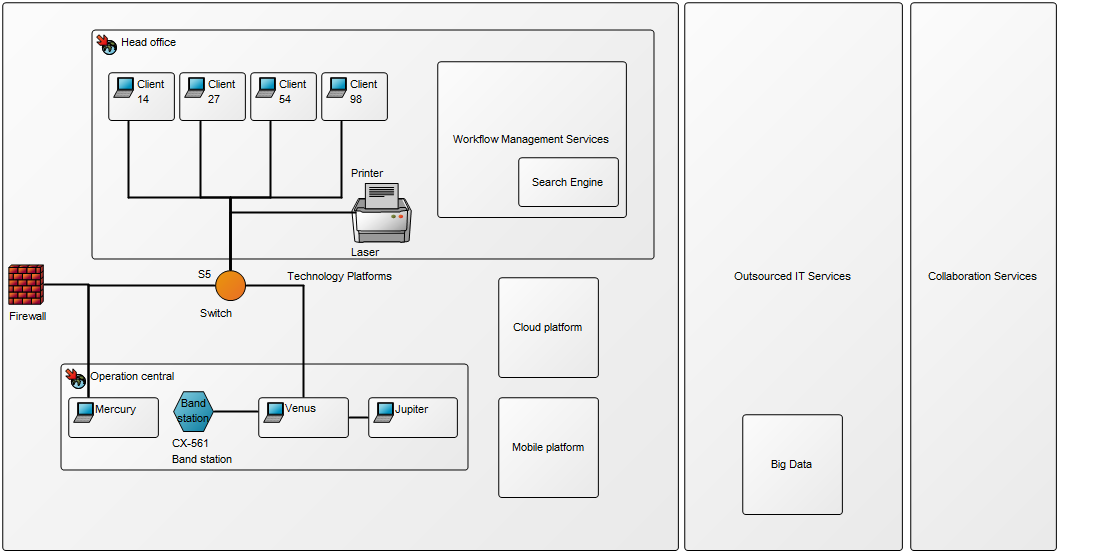
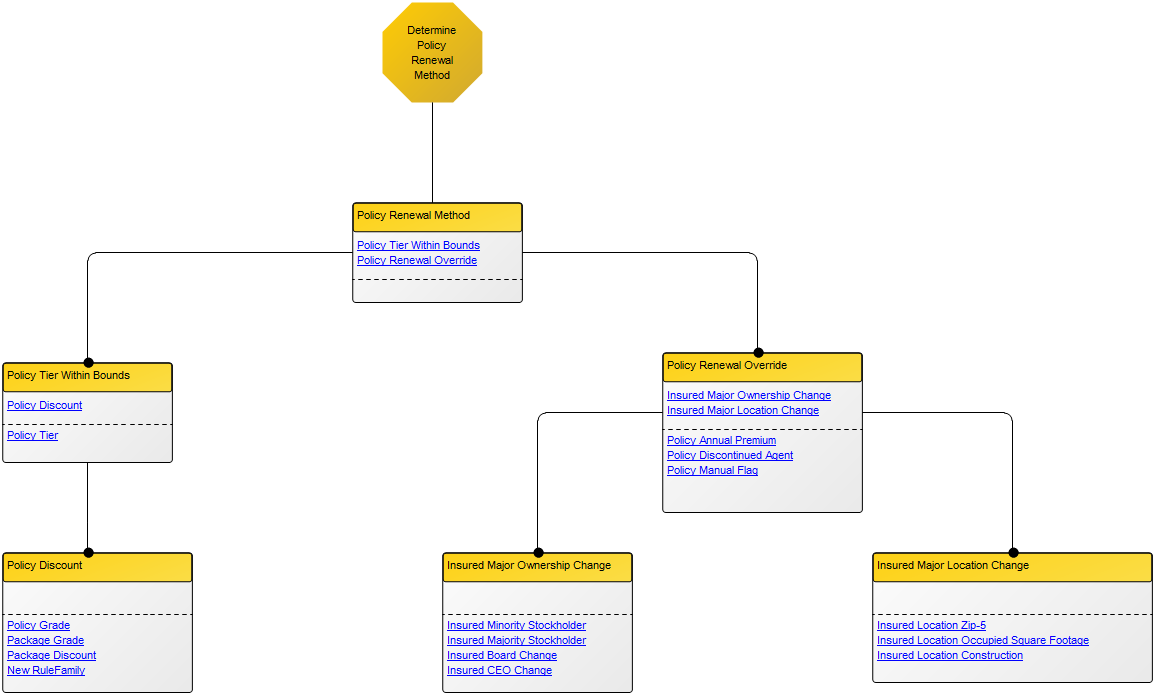
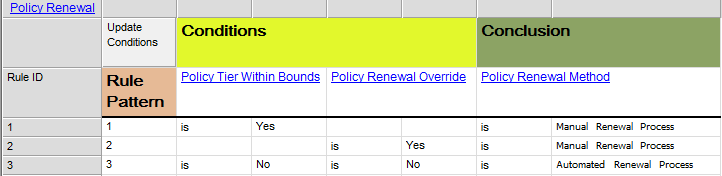
Purpose: The purpose of the Requirement Model template is to document goals, objectives and other requirements for the enterprise or a specific project. Below, you can see an example of a Requirement Model showing the Policies and Business Rules of an organization:

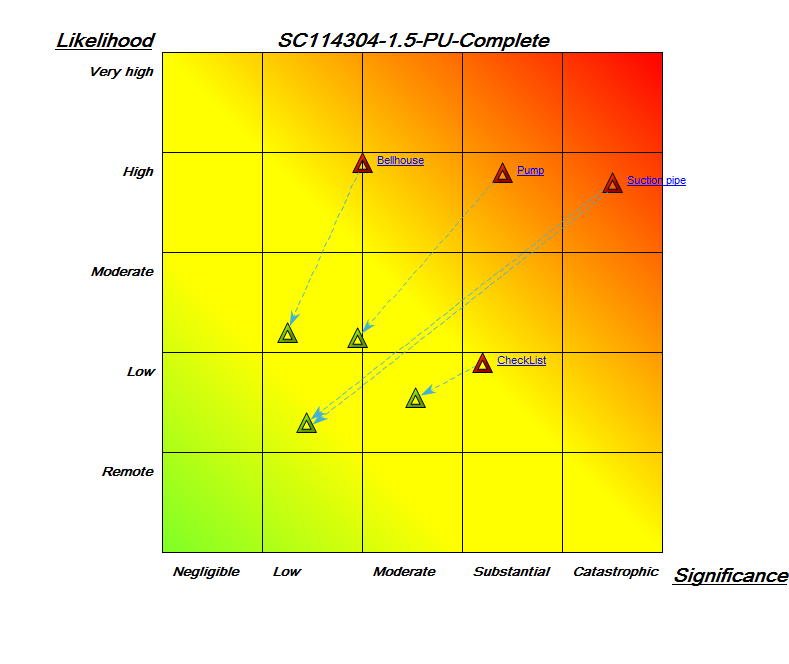
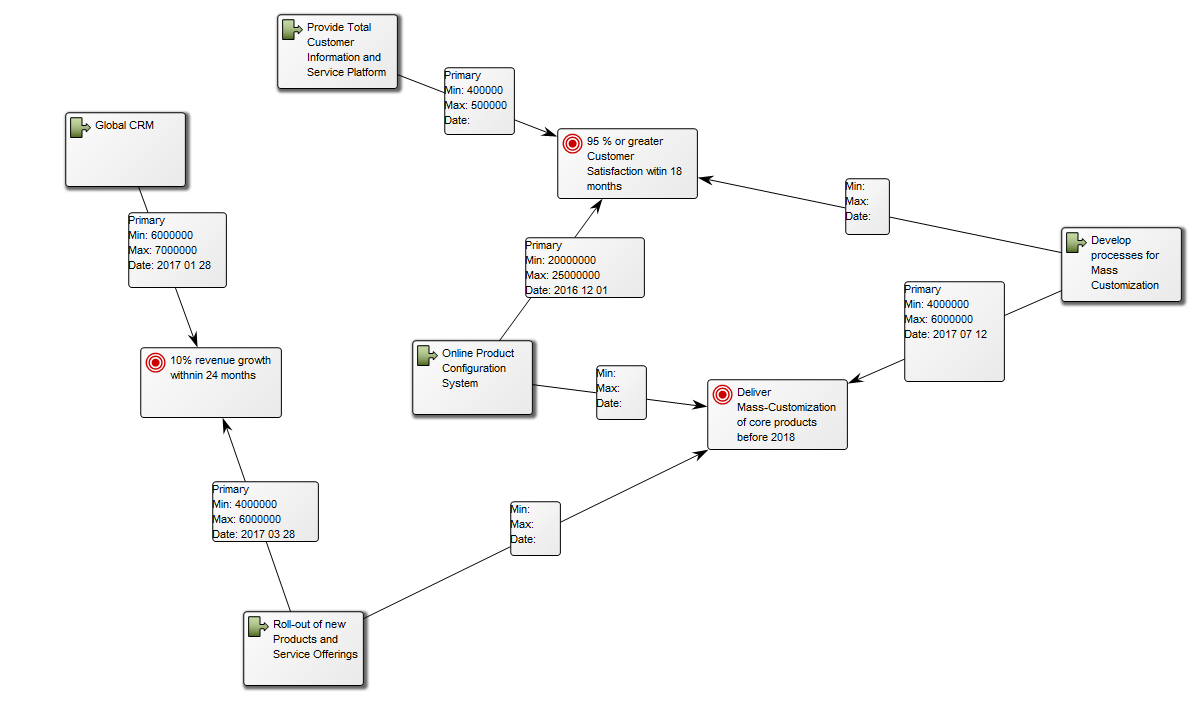
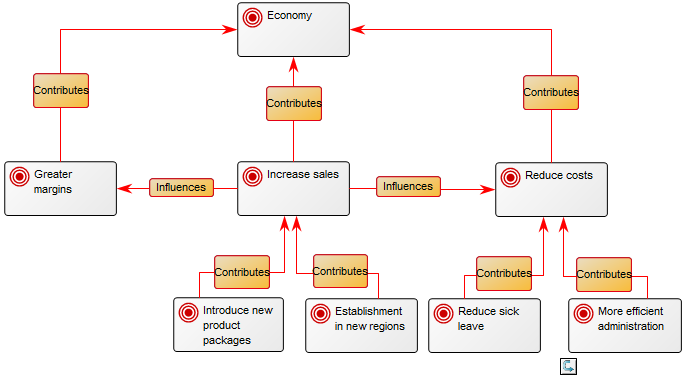
Core concerns: With the Requirement Model template, you can for example model Requirements, Goals, Change Requests, Policies, Business Rules, Critical Success Factors and Problems. This enables you to illustrate the interrelationships of requirements, for example showing which goals influence or contribute to each other, as the example below shows:
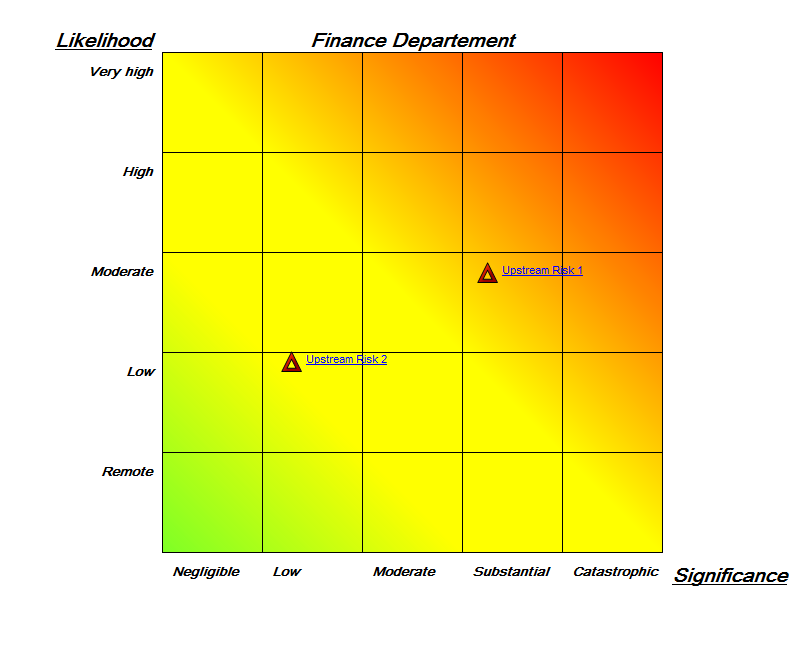
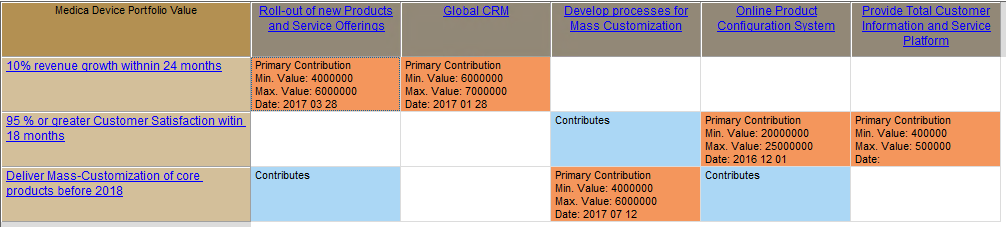
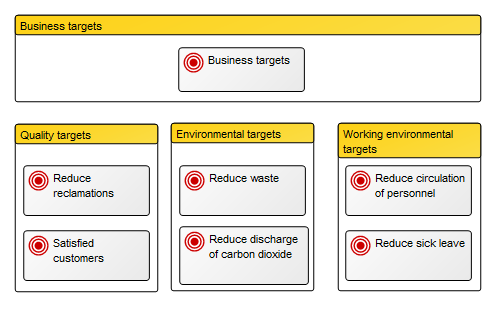
You can also divide goals up in different areas that may for example be subject to different regulations as below:
Relation to other templates: The Requirement Model offers a more detailed view on Requirements and Goals filtering out elements such as vision and mission compared to the Strategy Model. It can be used to detail how your organization live up to requirements specified in a Regulation Diagram or Requirements indicated in a Stakeholder Model.
Properties and metadata: The Requirement Model can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the accuracy of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
- Project status: information about budgeted and actual man-hours spent, percentage completed and the latest milestone, result and quality control of a change process.
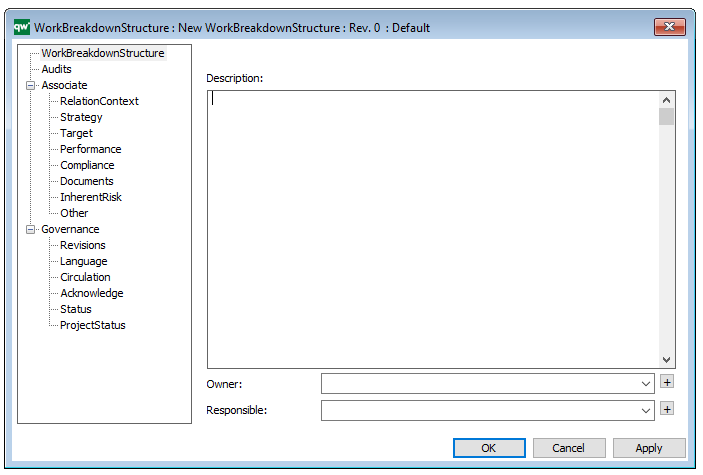
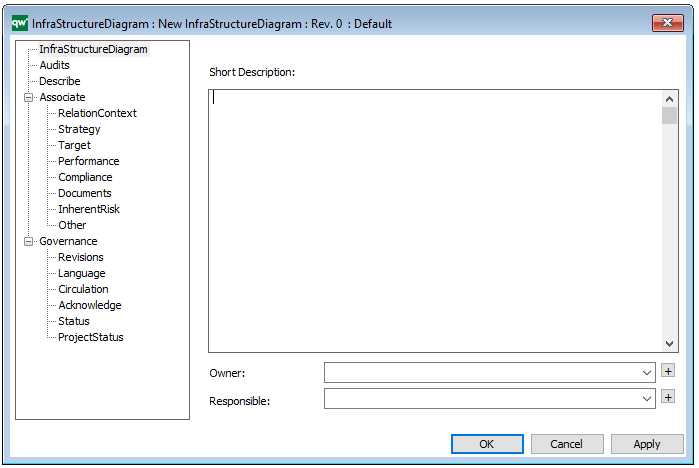
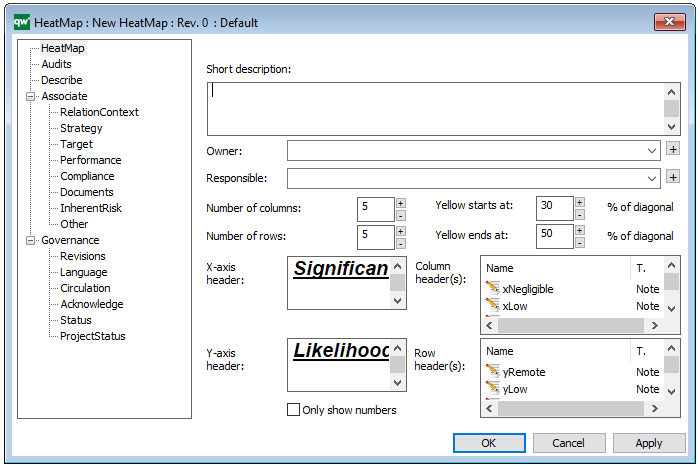
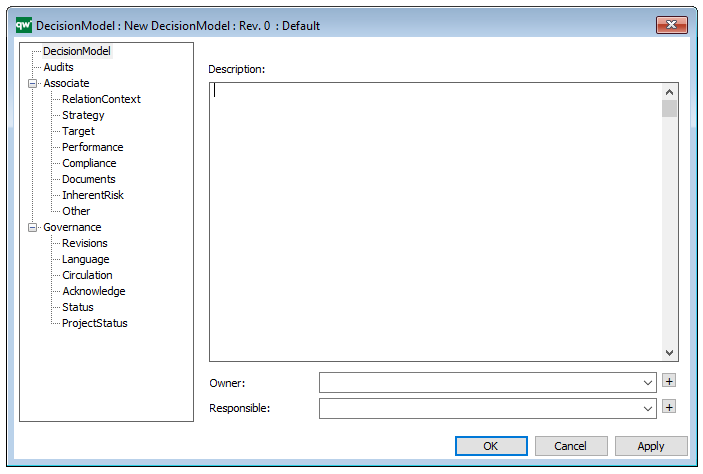
In the picture below you can see the Requirement Model’s properties dialogue window, where the properties can be viewed and edited: