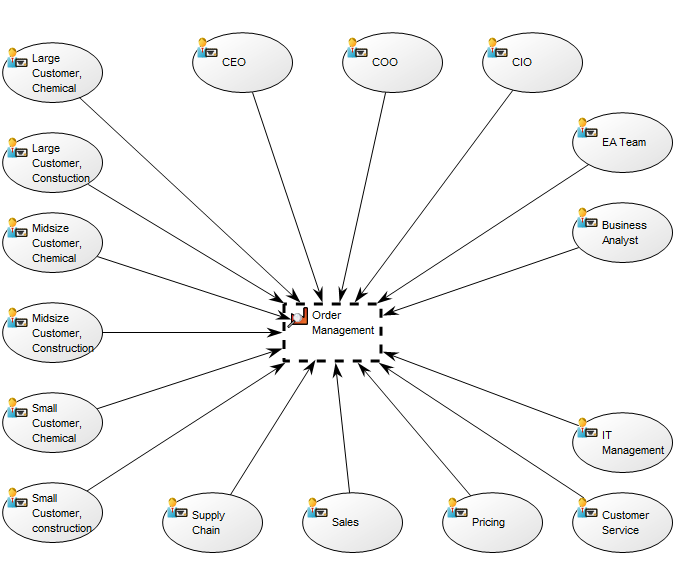
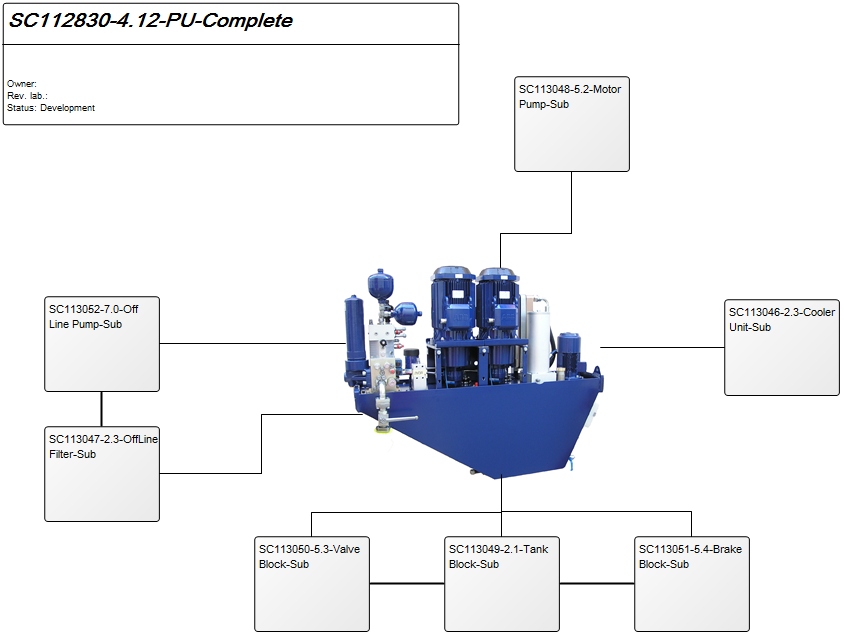
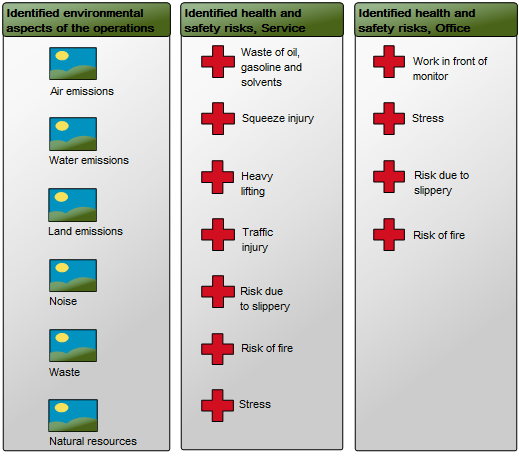
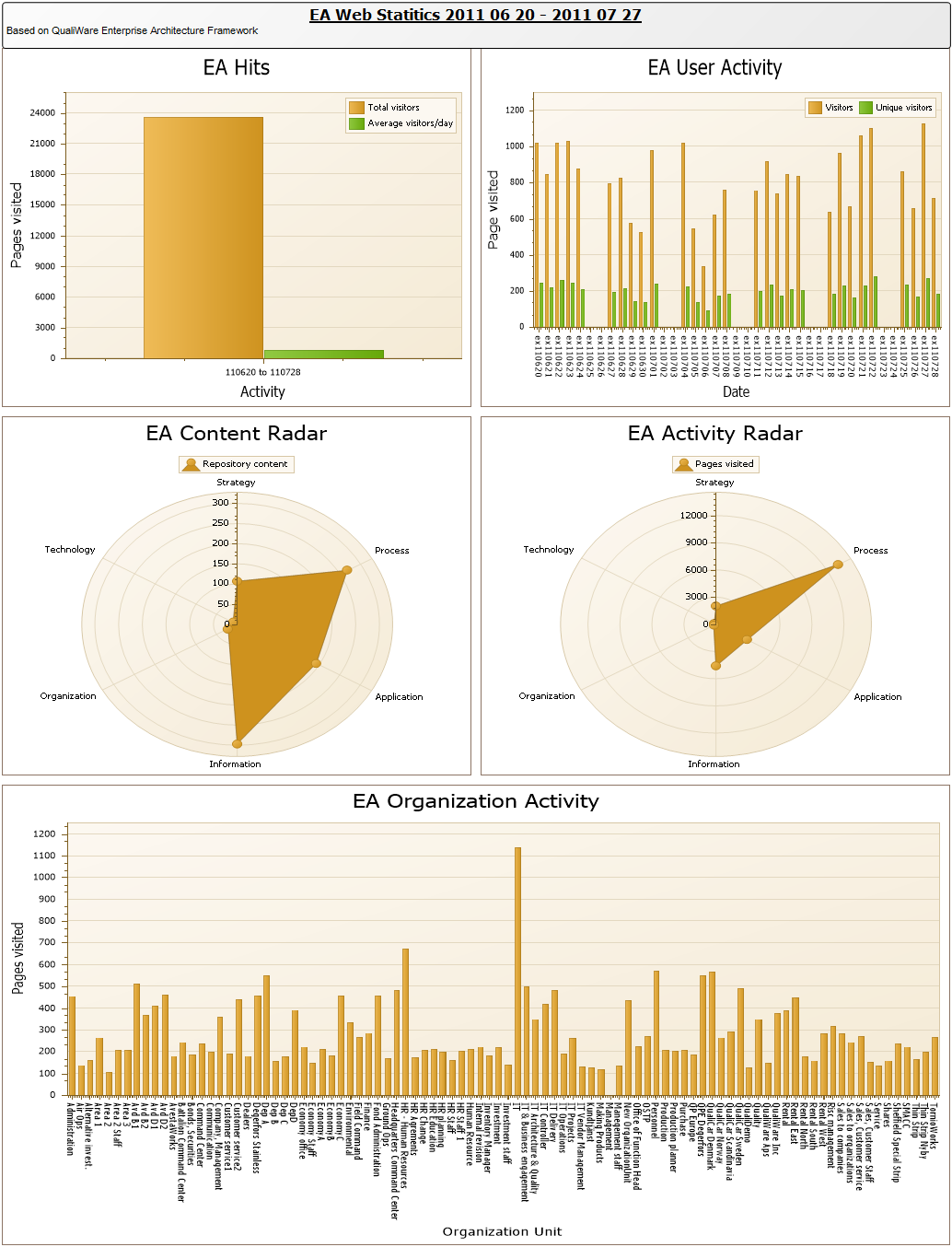
Purpose: The purpose of the Workflow Diagram template is to document the Business Processes of an enterprise at the activity level.
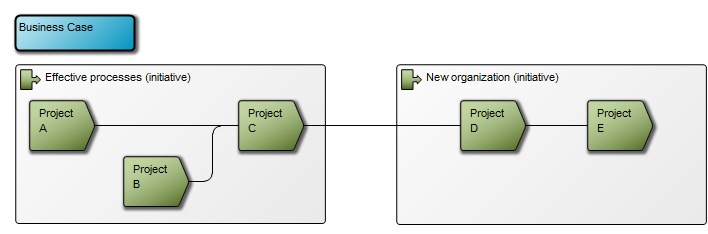
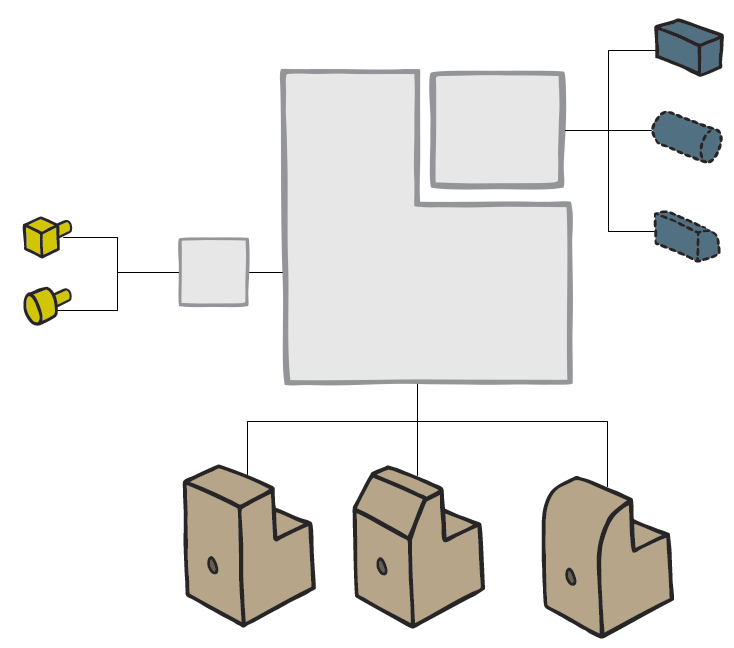
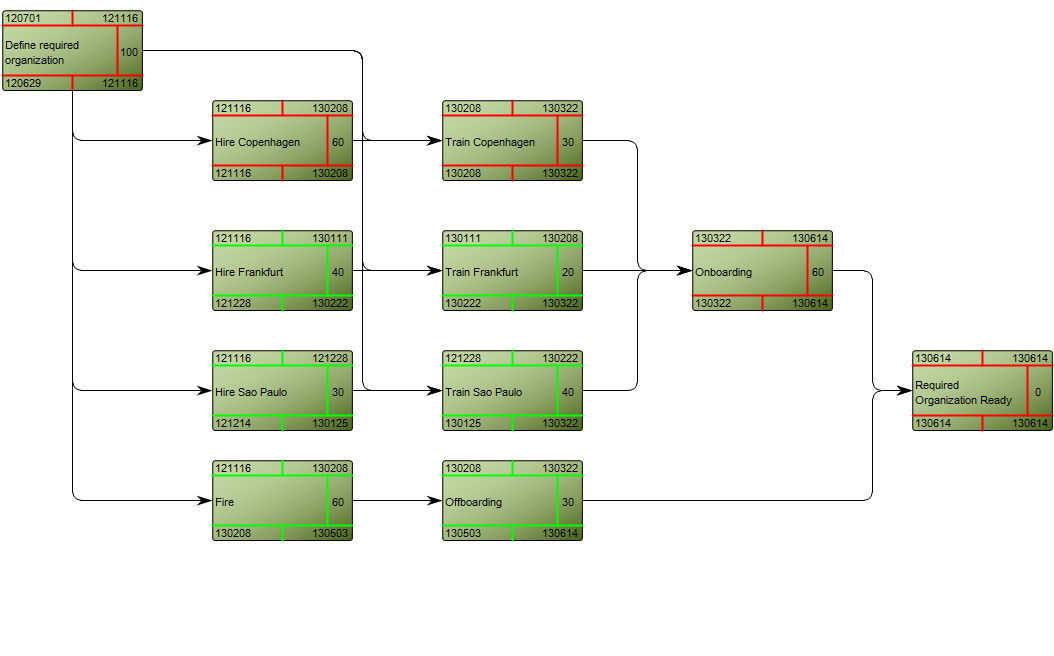
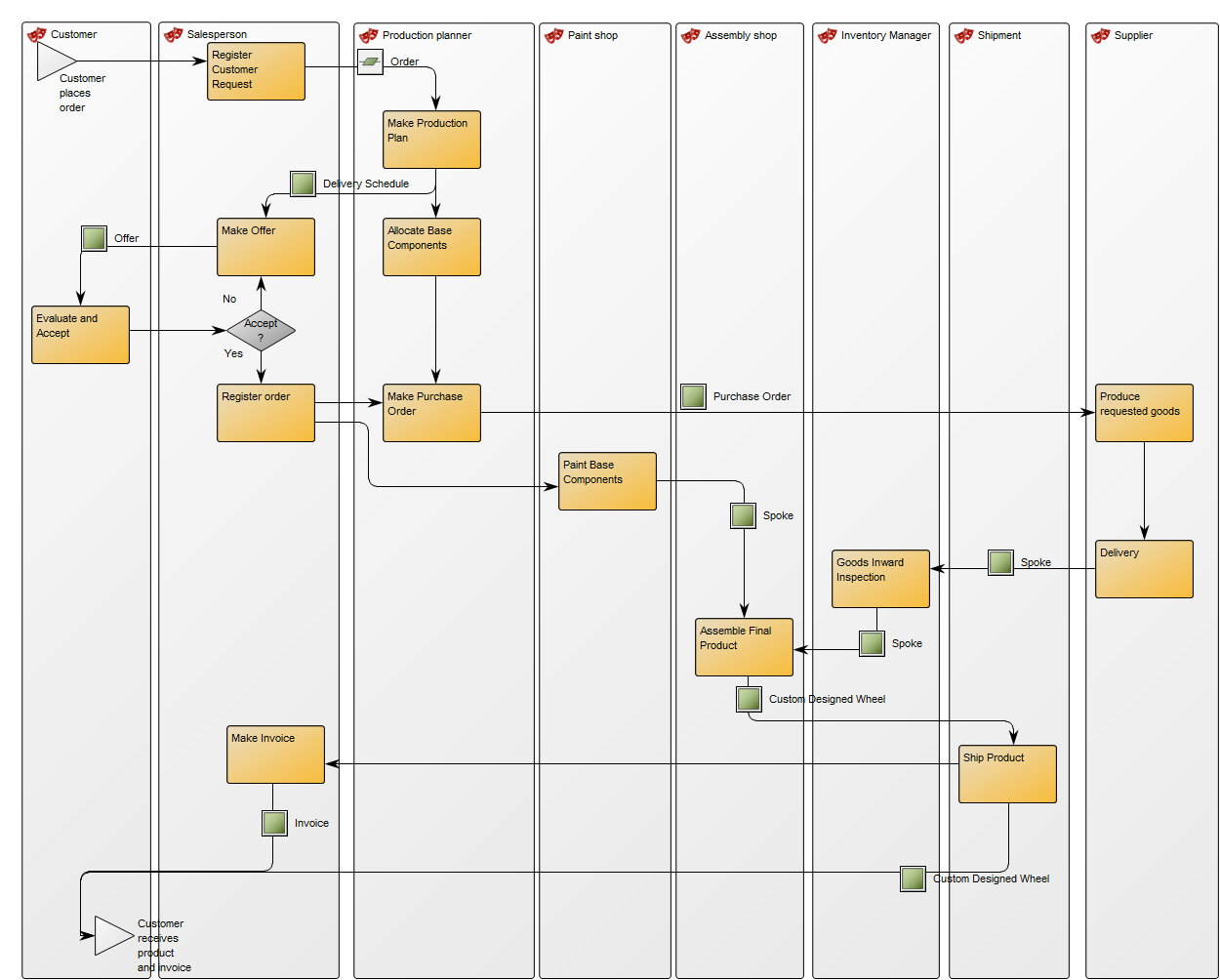
Concerns: The Workflow Diagram template should be used to document the Activities, Roles, Business Events, Activity Paths and Workflow Conditions of a Business Process. Available in the default modeling syntax are also Business Objects, External Objects, Information Systems, Database, Inventory, Information Flow and Logistical Flow. The syntax can be easily extended to include more objects such as Requirements, Business Rules and Goals. Below you can see an example of a Workflow Diagram with multiple Roles that are modelled vertically:
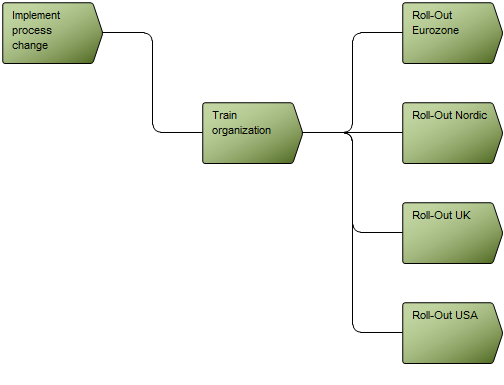
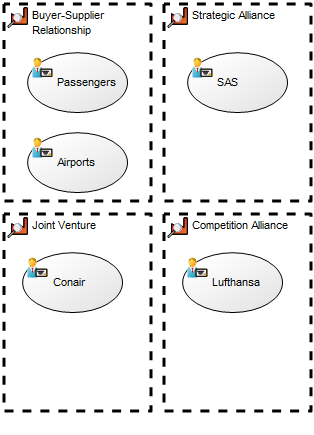
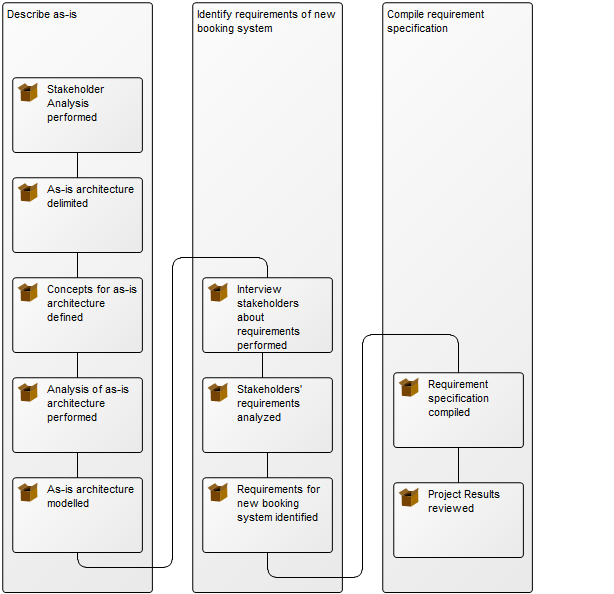
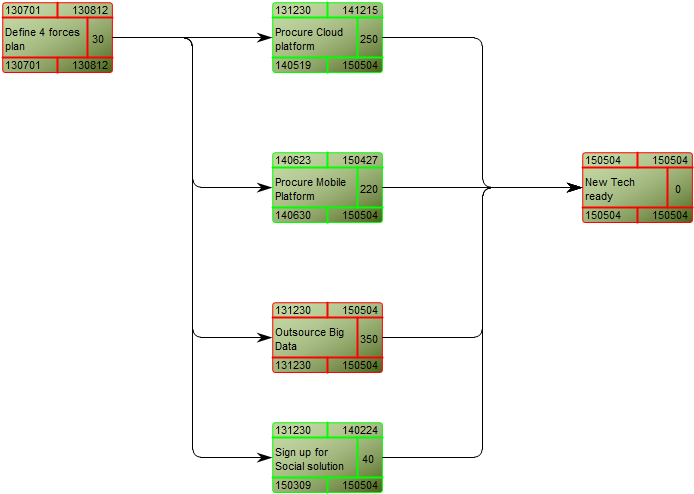
Relation to other templates: The Workflow Diagram does not support BPMN, if using that notation, you should model in the Business Process Diagram template. The Workflow Diagram can link to other Workflow Diagrams and are typically linked to by Business Process Networks. In the picture below, you can see another example of a Workflow Diagram. Here the Roles are modelled horizontally and you can see the links to and from other diagrams at two Business Events (‘ECR completed’ and ‘Rework’):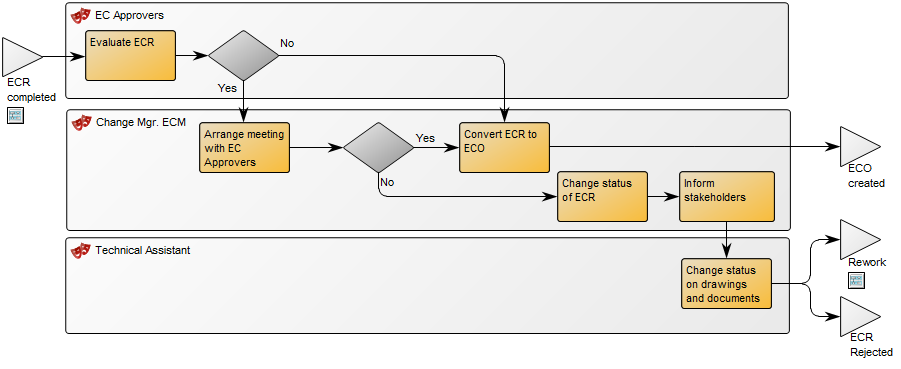
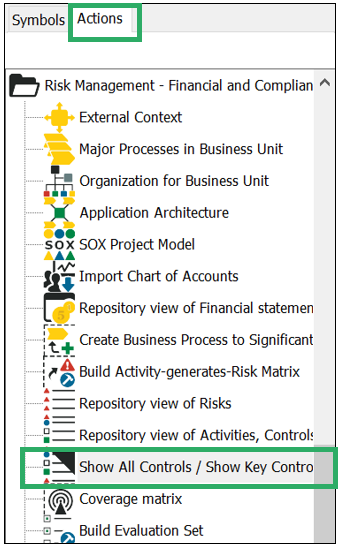
Other functionalities: In QLM, you can control which buttons related to risk management are shown below activities. You can choose to hide or show Risks, Controls and Key Controls. Both Controls and Key Controls are a type of Activity. From the Risk related toolbars (available via the “Actions” tab on the right-hand side of the Canvas in QLM) choose the following button to control what button panels appear on the Activity objects:
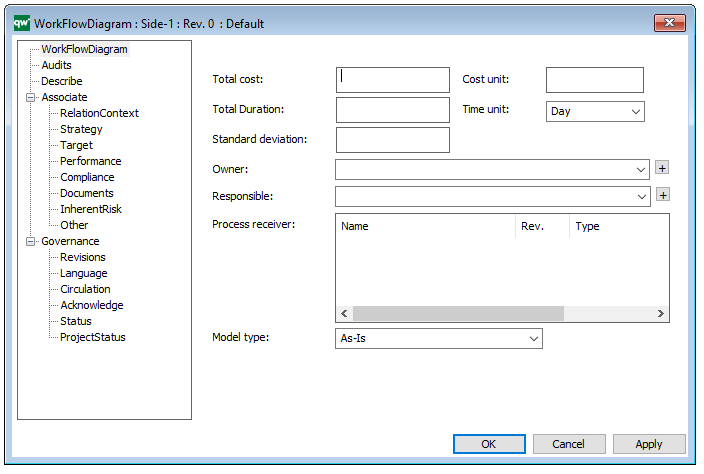
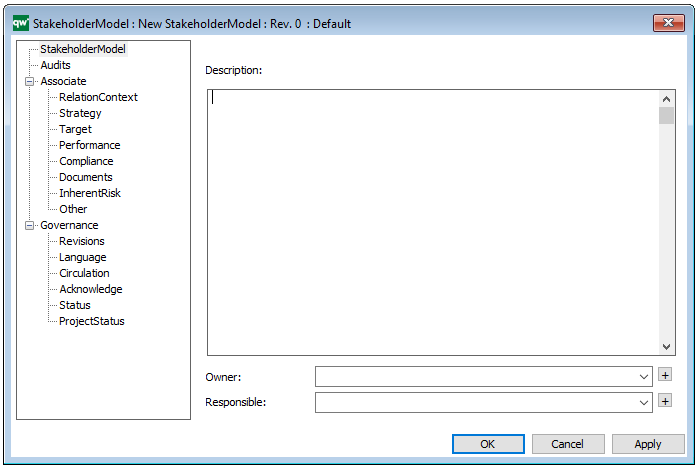
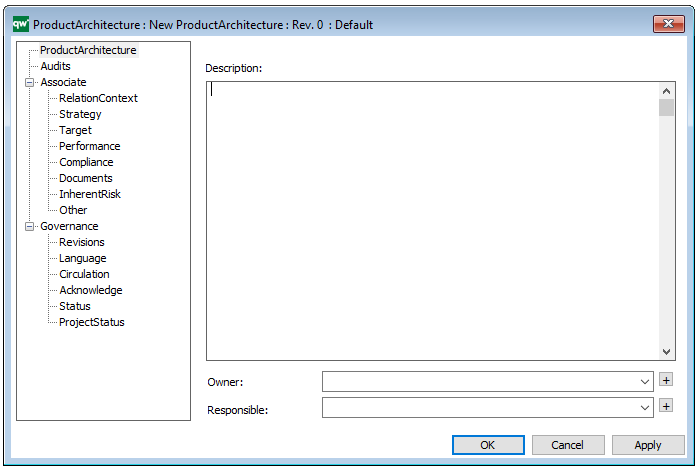
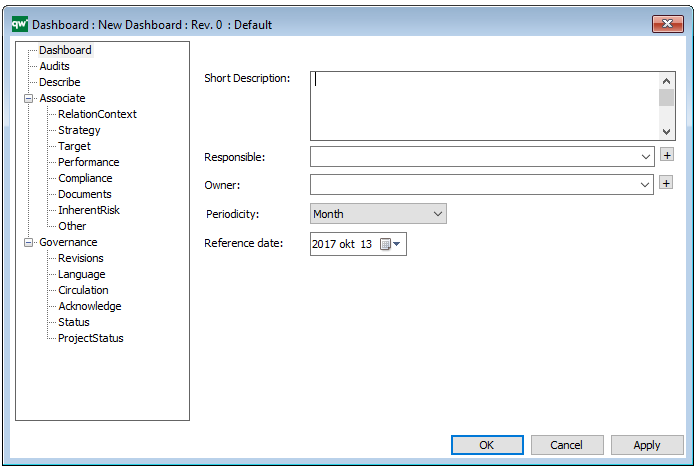
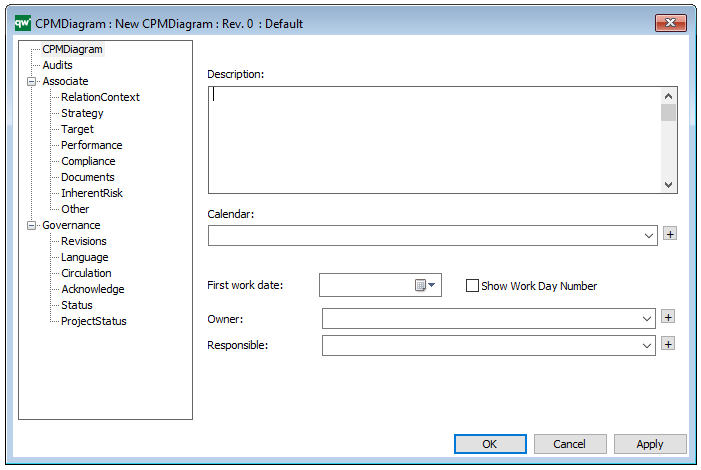
Properties and metadata: The Workflow Diagram can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Information on cost and duration of the process
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the accuracy of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
- Project status: information about budgeted and actual man-hours spent, percentage completed and the latest milestone, result and quality control of a change process.
In the picture below you can see the Workflow Diagram’s properties dialogue window, where the diagram’s properties can be viewed and edited: