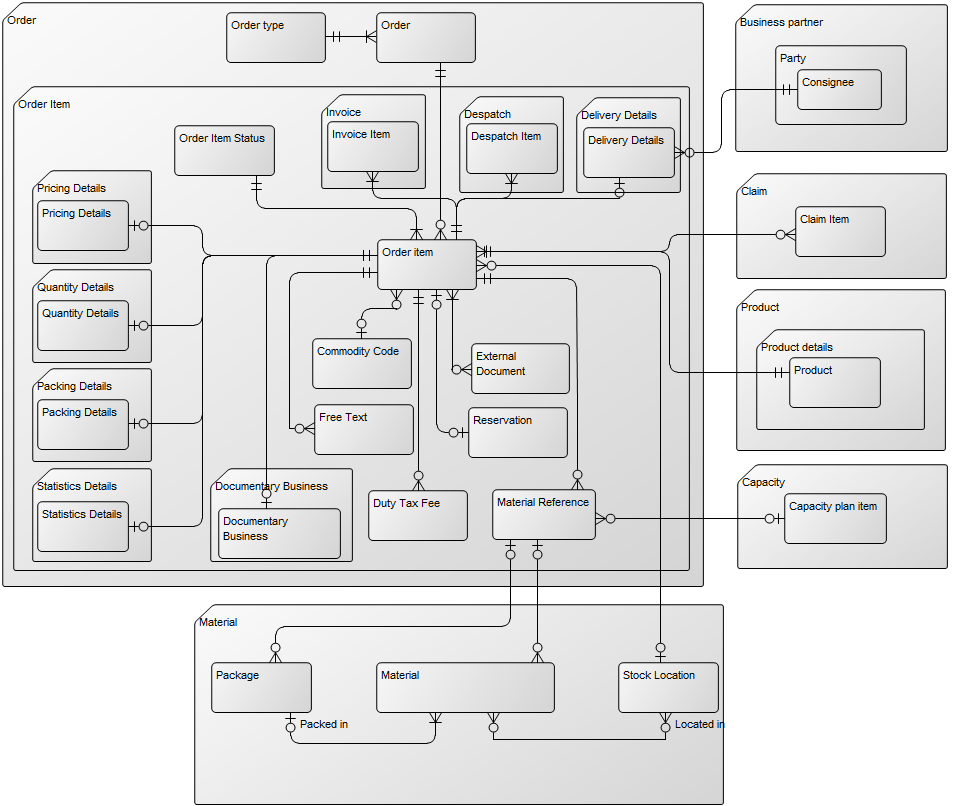
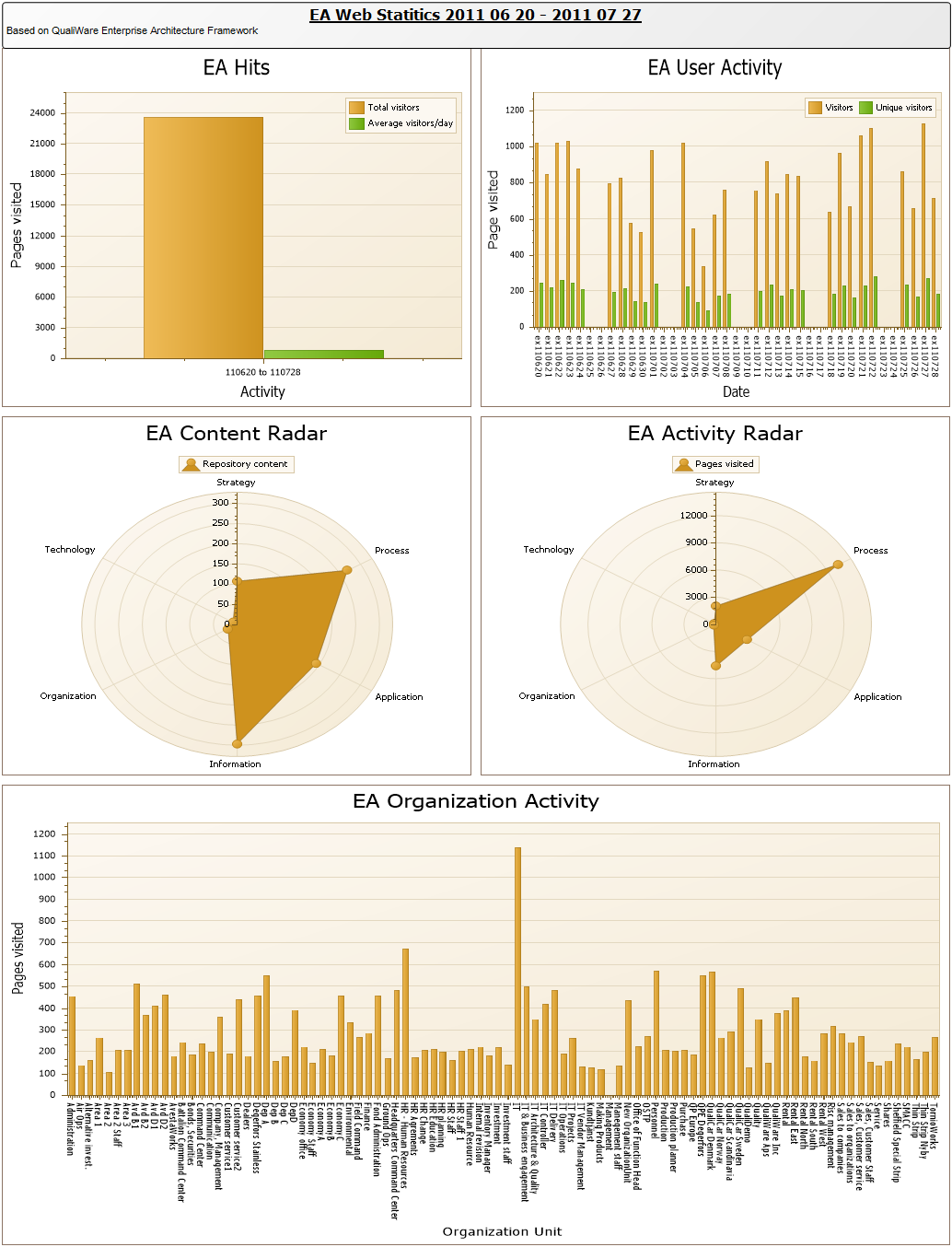
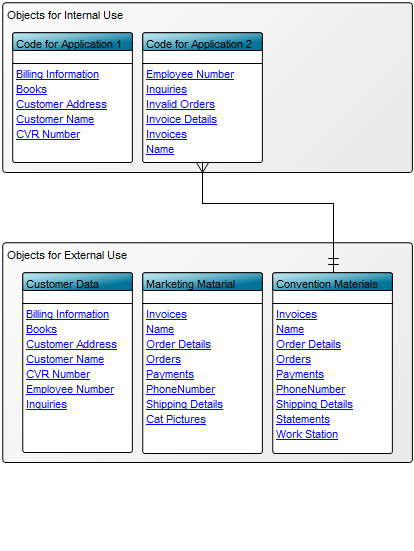
Purpose: The purpose of the Data Replication Diagram template is to map a high-level view of the movement and replication of information between data sources.
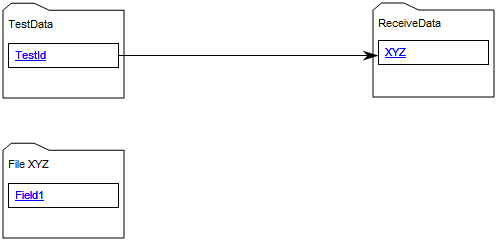
Core concerns: The Data Replication Diagram template enables you to map Data Sources, Data Files, Data Transformations and Data Warehouses. These elements can then be connected by either a Data Extract or a Data Apply.
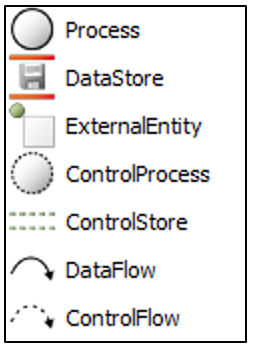
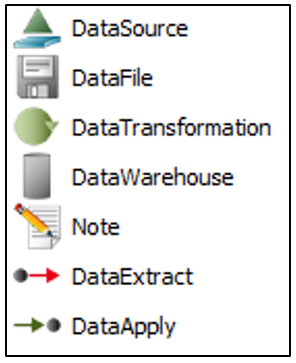
Graphical representation of the elements:
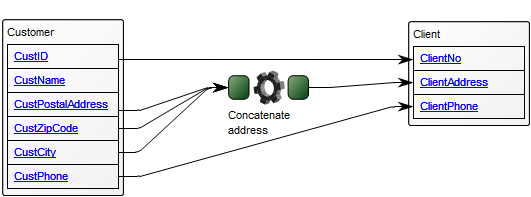
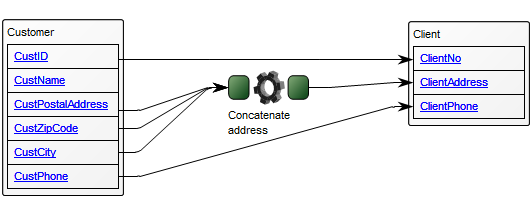
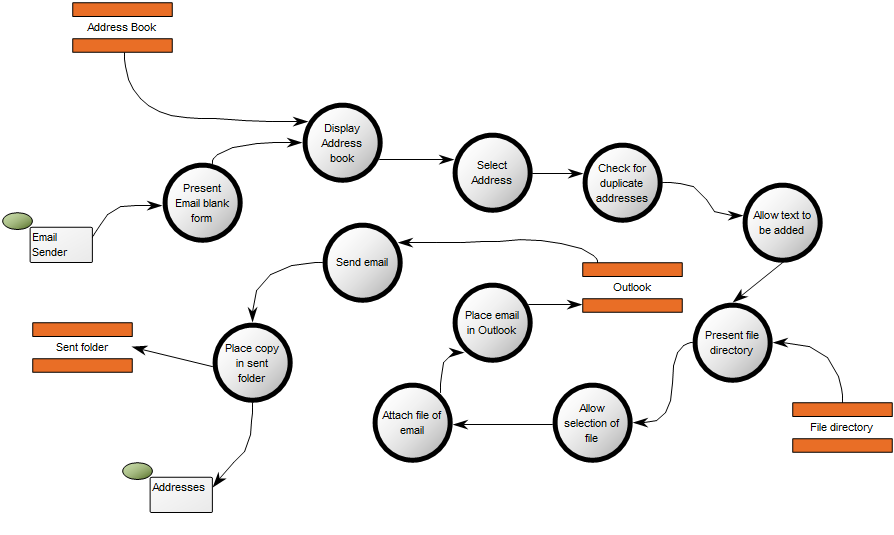
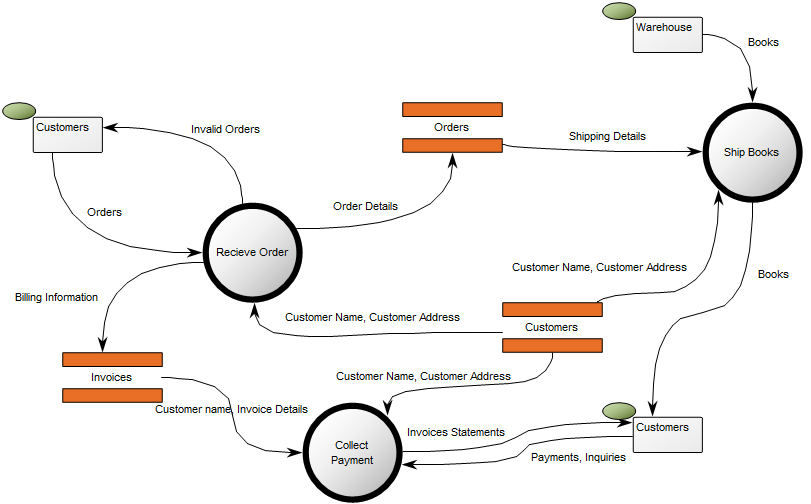
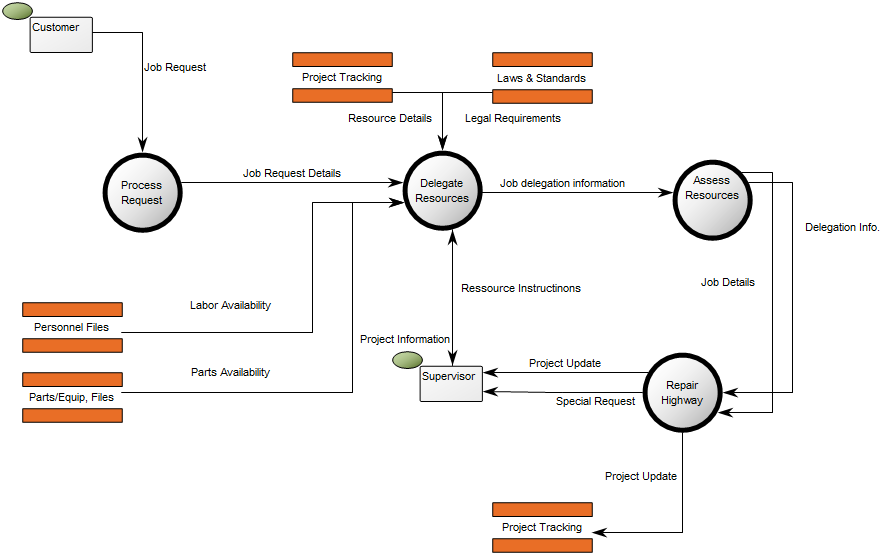
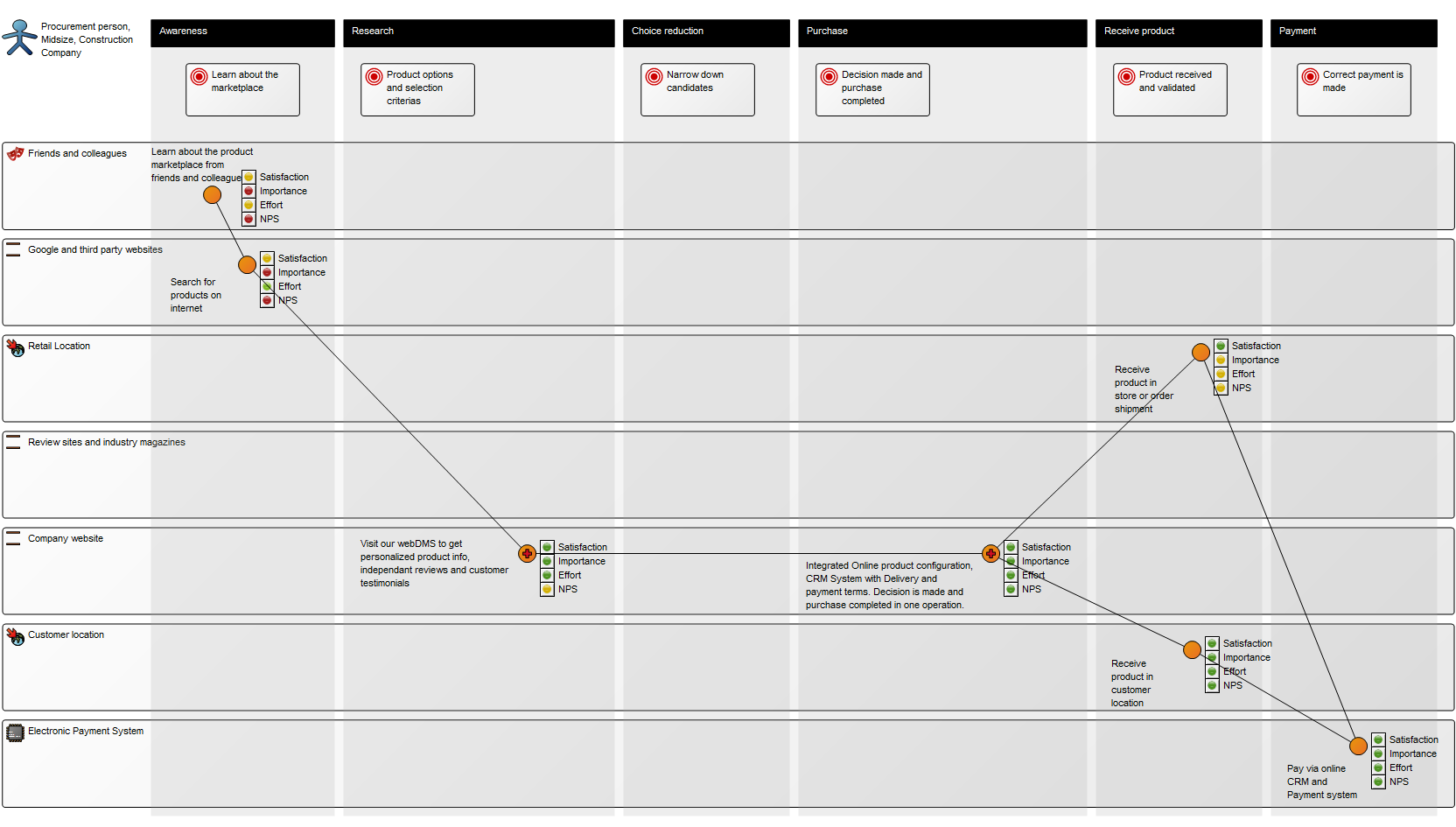
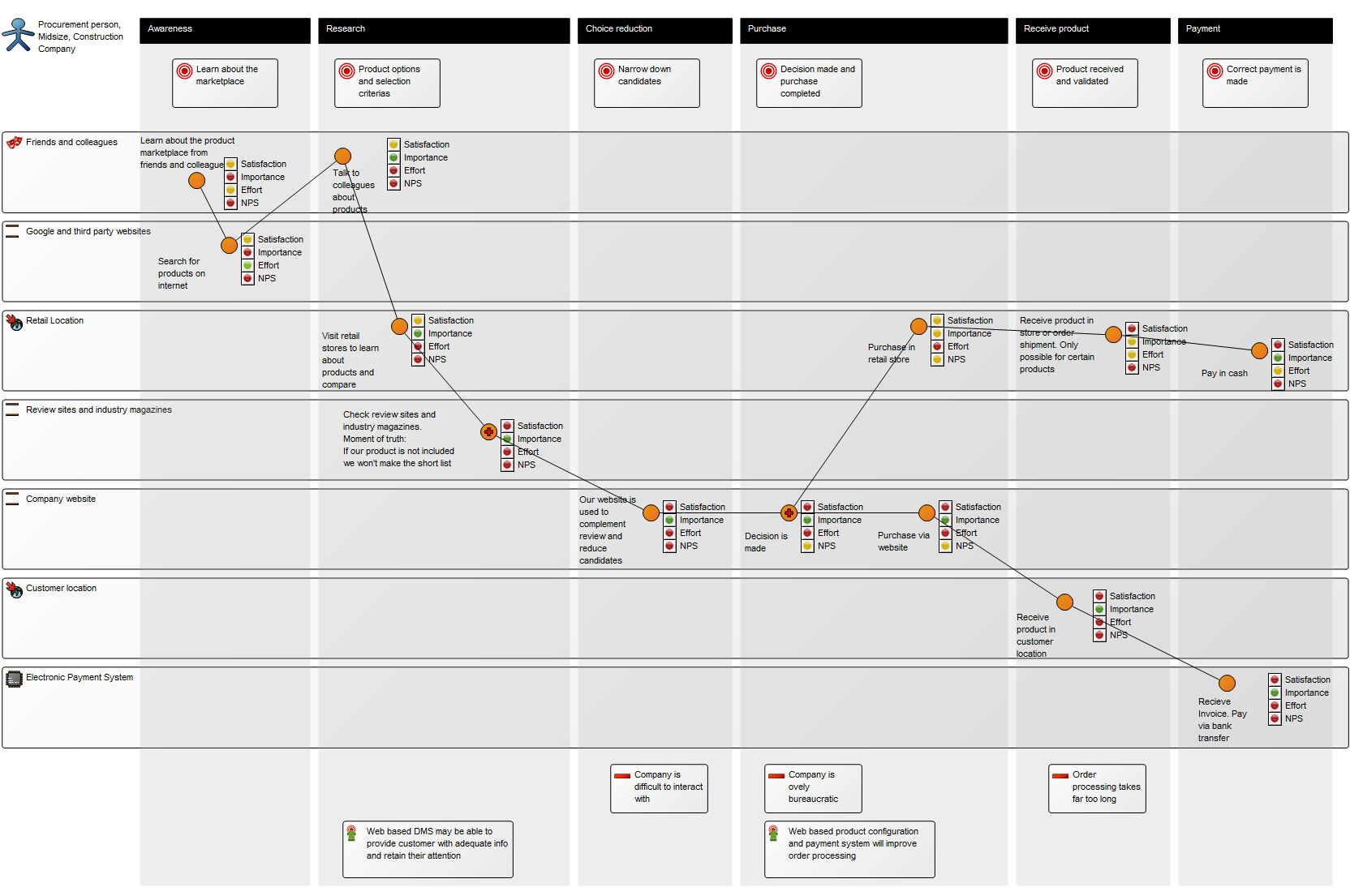
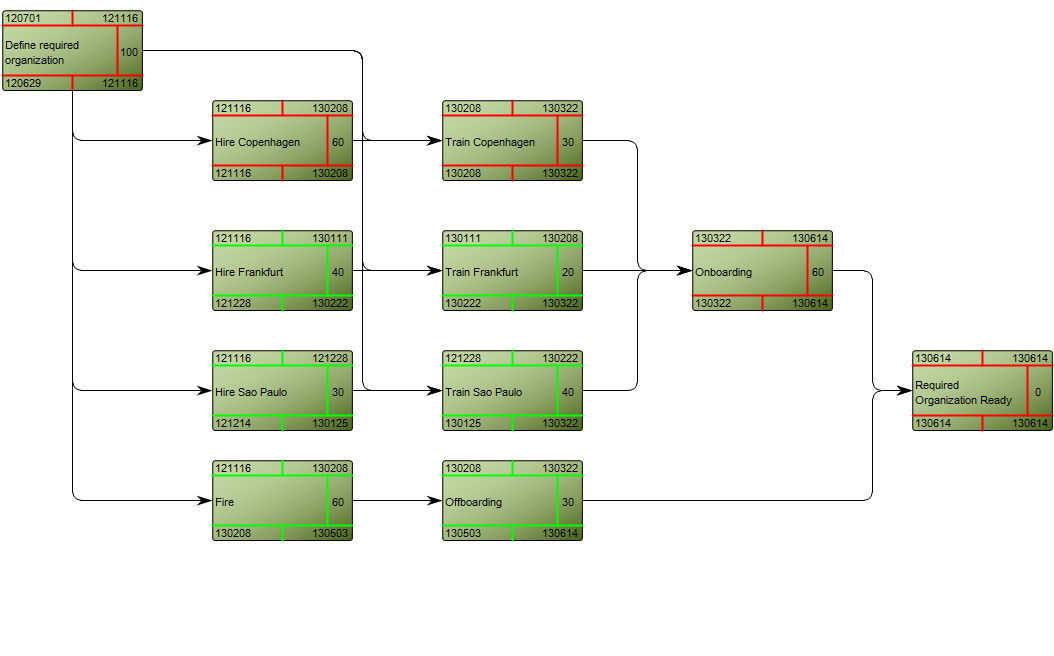
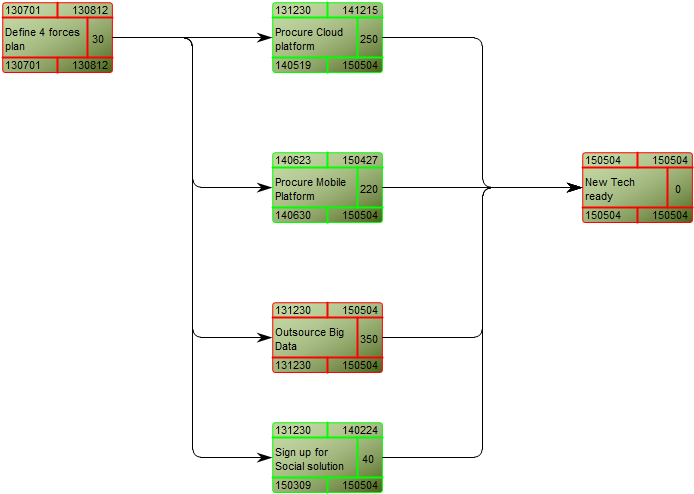
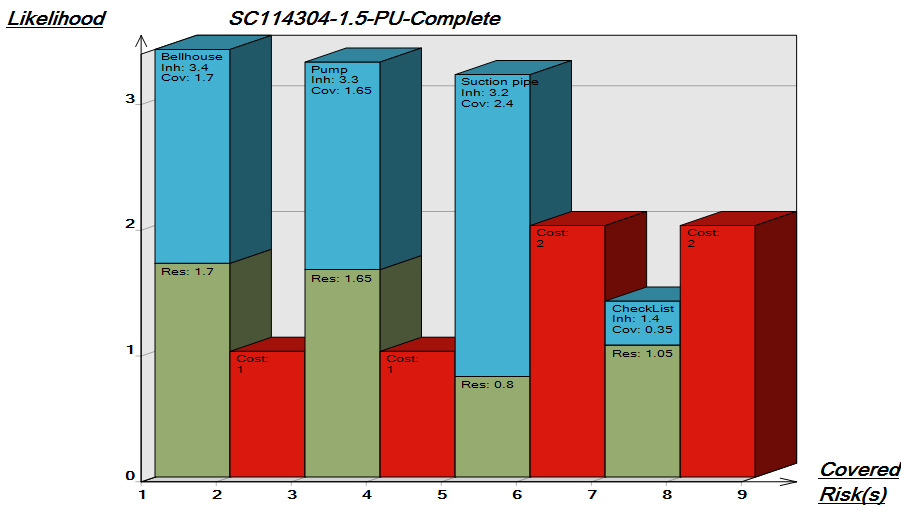
Below, is an example of a Data Replication Diagram for a commercial Data Warehouse:
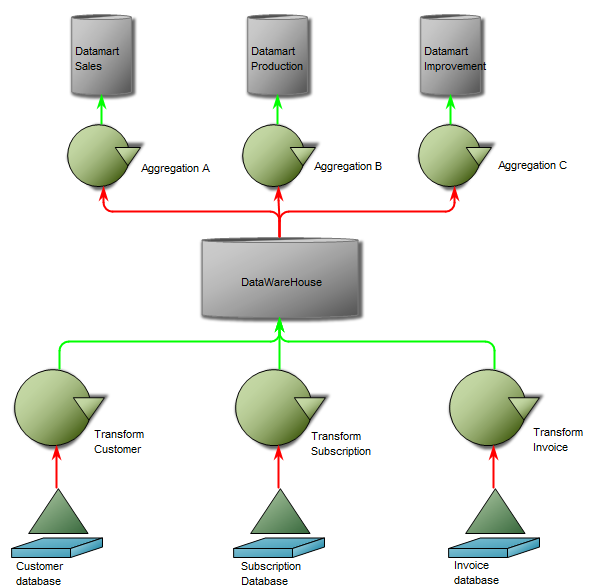
The model shows that the data is extracted from different data sources, transformed and applied to the Data Warehouse from which it is extracted, aggregated and either applied to sales, production or improvement.
Relation to other templates: The Data Replication Diagram offers a high-level data mapping. The Data Transformations contained in the Data Replication Diagram can be further decomposed into more detailed Data Mapping Diagrams.
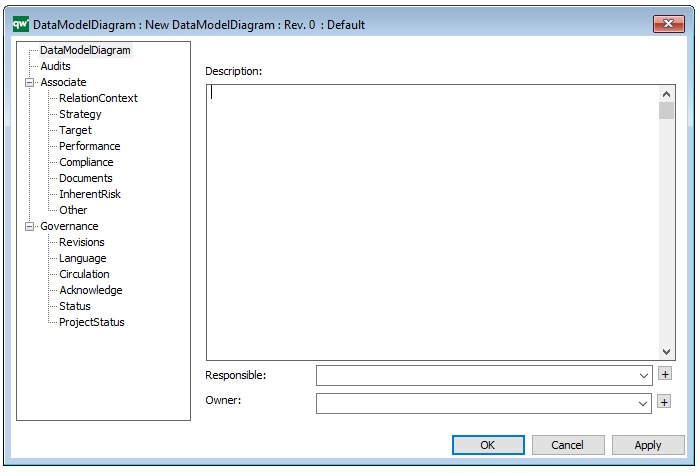
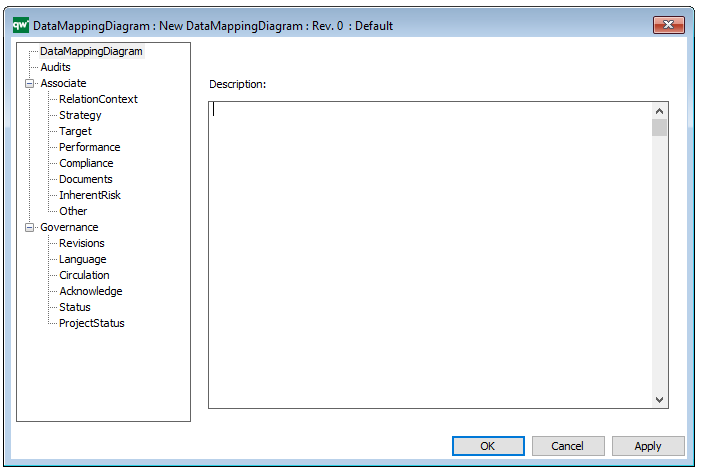
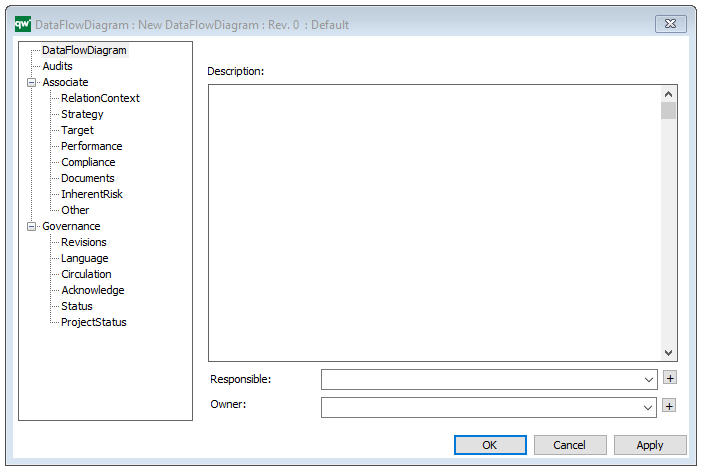
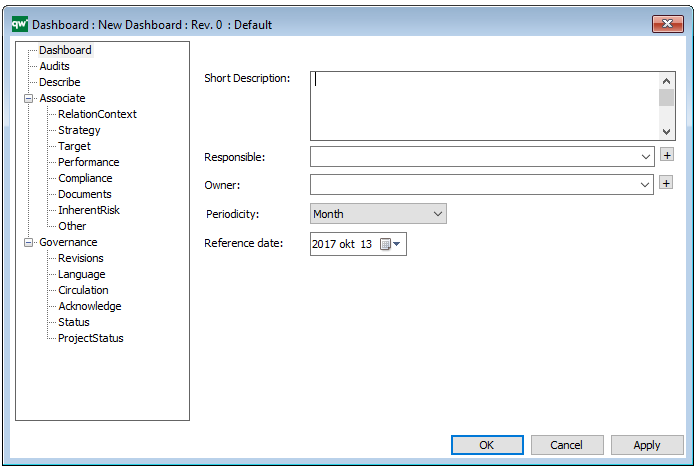
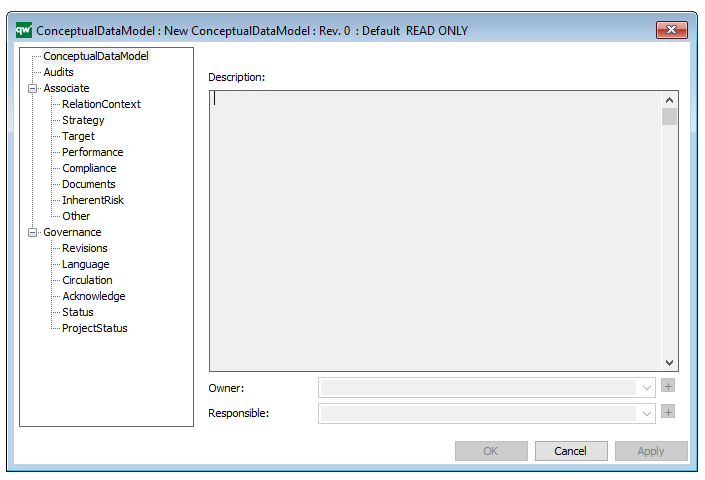
Properties and metadata: The Data Replication Diagram template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval it
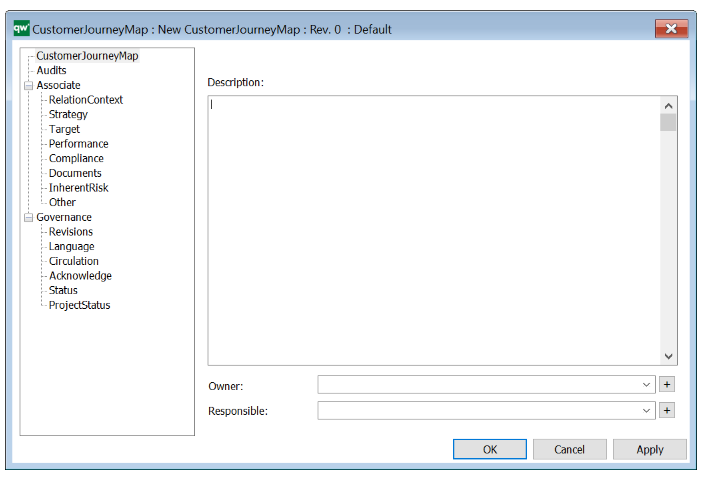
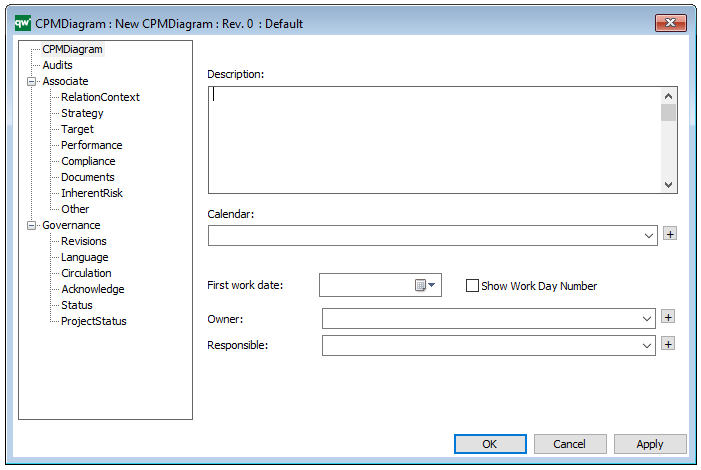
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Data Replication Diagram, where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.