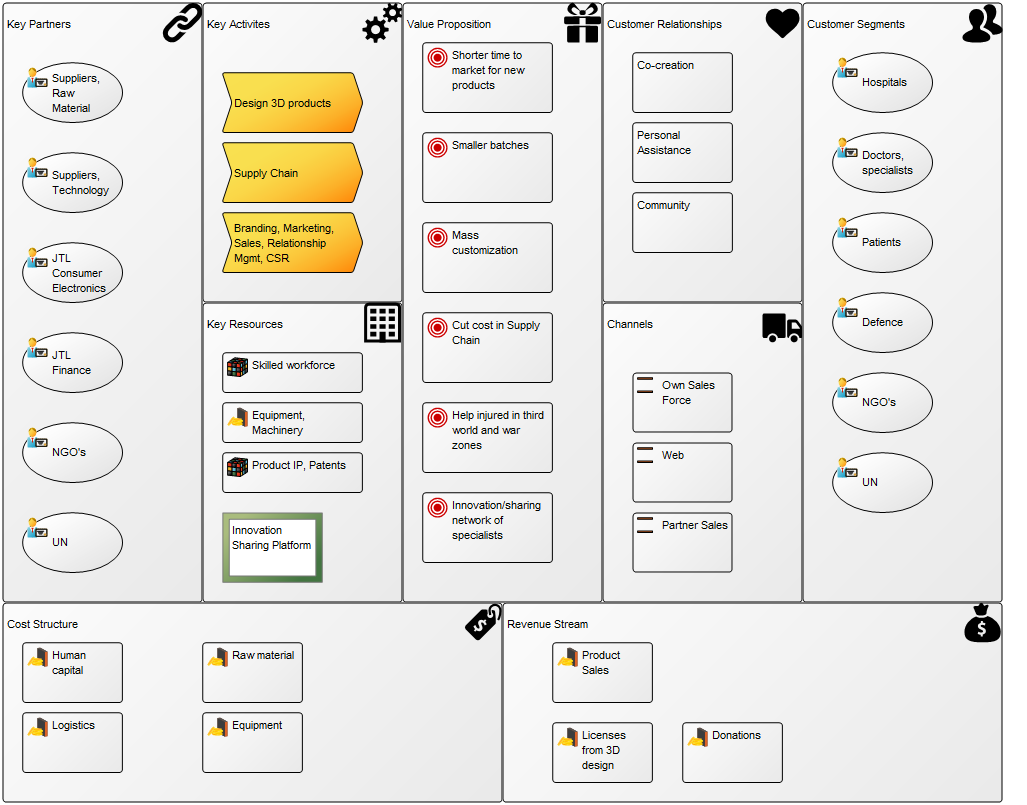
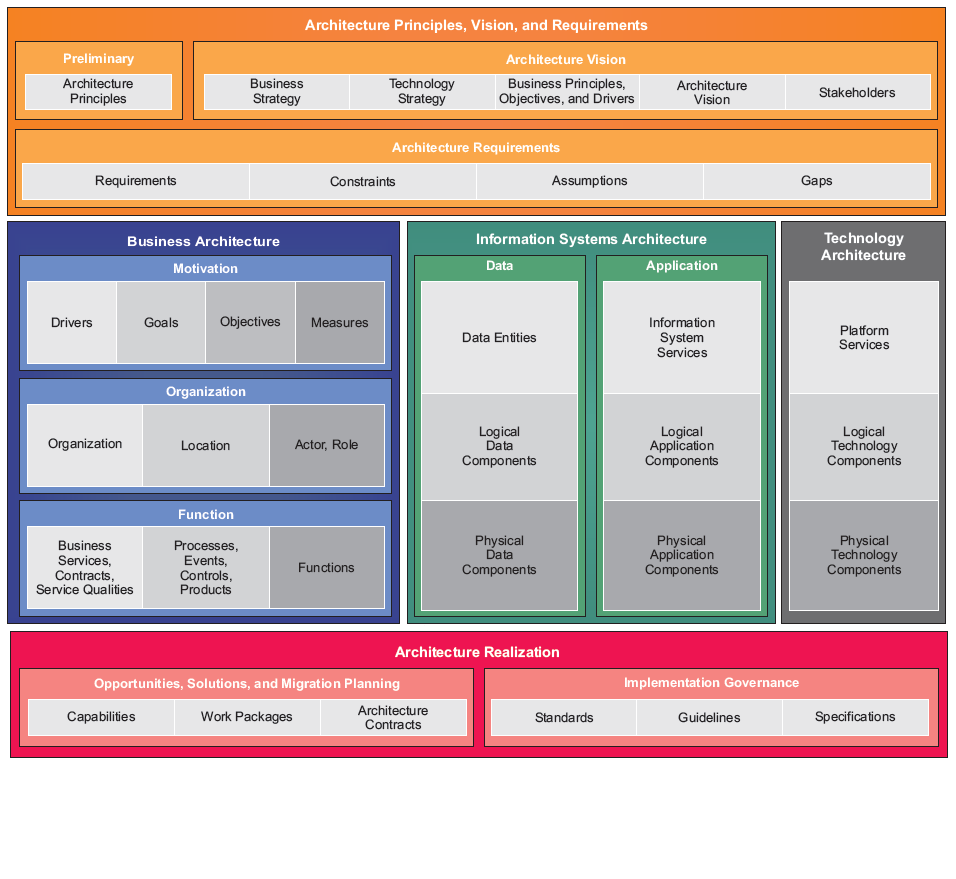
Purpose: The purpose of the Business Capability Model template is to provide an overview of the of the state and health of an enterprise in the form of its Capabilities.
Core concerns: The Business Capability Model is a simple template that by default only allows for the modelling of Capabilities with the possibility to add notes if needed. The metadata of the Capabilities – such as status and importance can then be graphically displayed in the business capabilities to create a useful overview.
The stripe on the left side to represent Business Importance and two dots representing Business Maturity and Target Maturity. The new design scales better and provides management with a single view of important strategic capabilities with a plan for improvements. Also it allows the business architect to highlight a set of capabilities by coloring the symbol’s background – a widely used technique.

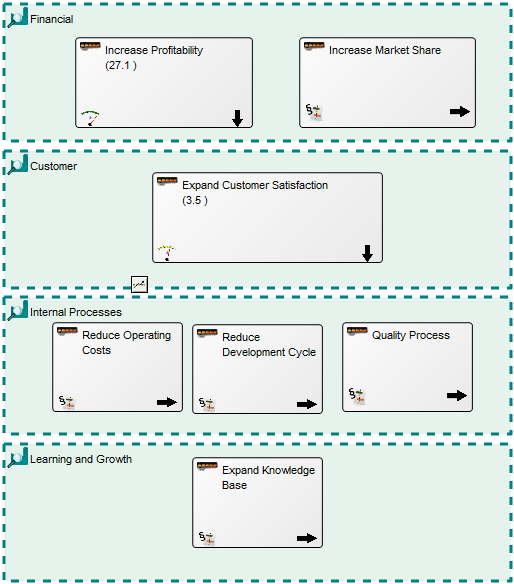
In the picture above you can see an example of a Business Capability Model. Here the Business Capabilities are grouped in different areas and the status and importance of them are shown by their green, yellow or red colorings.
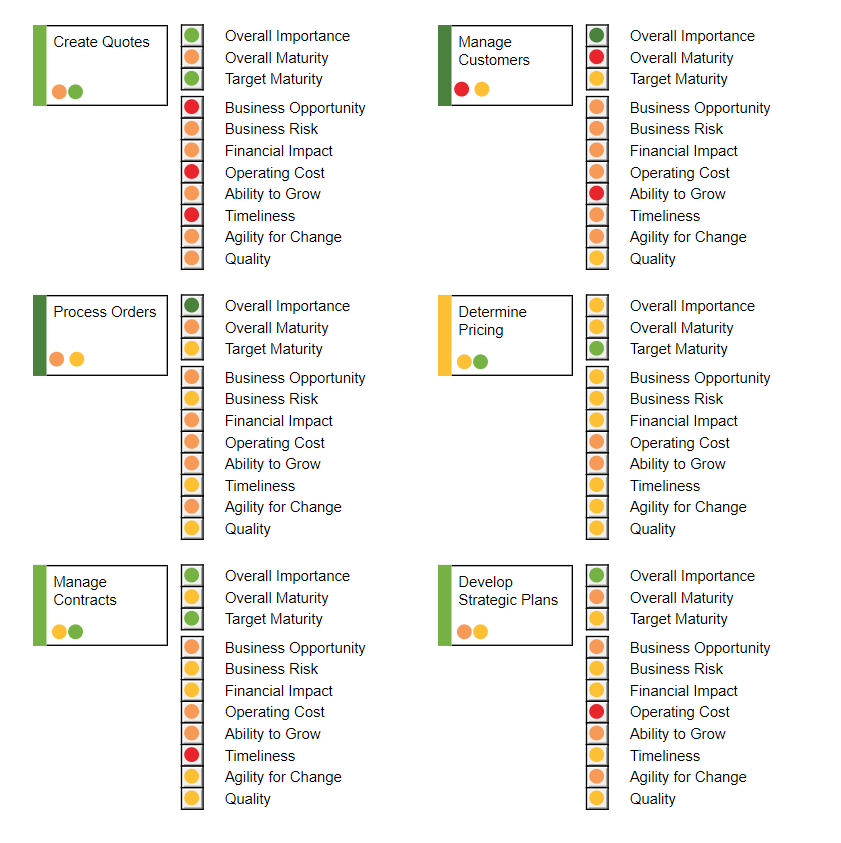
In this Business Capability Model (shown above), more attributes are shown at the right-hand side of the Capability. This way you can get a more detailed view of the state of your enterprises Capabilities.
Other functionalities: Using the Analysis tool, the information from the Business Capability Model template can generate maturity- and score heat maps, hierarchies, score views, capability contexts, gap analyses, dashboards, and what-if-, impact- and investment analyses.
Relation to other templates: The Business Capability Model is a strategic template and is as such complimentary to for example the Strategy Model and Work Model. It can be used to illustrate a change process going from one set of capabilities to another. A Capability can link to the Business Processes that uses it as well as the resources it employs. This way it can also be analyzed which Business Processes would be affected by the improvement or worsen of a given Capability.
It is easy to update and analyse the capability models via the standard views on the web:
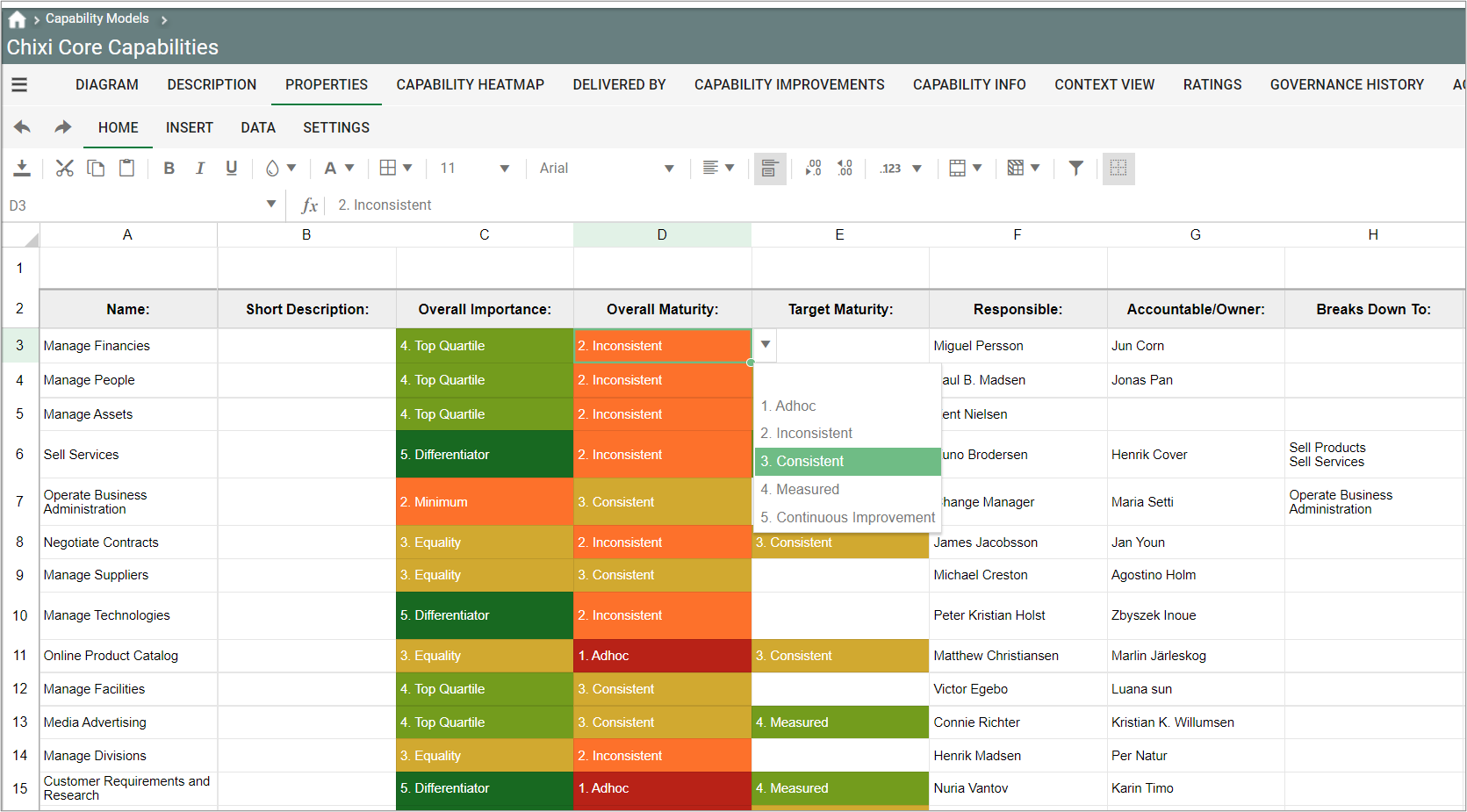
- The capabilities in a Business Capability Model can easily be scored and presented in filterable and editable lists via the spreadsheet functionality in e.g. the Properties view
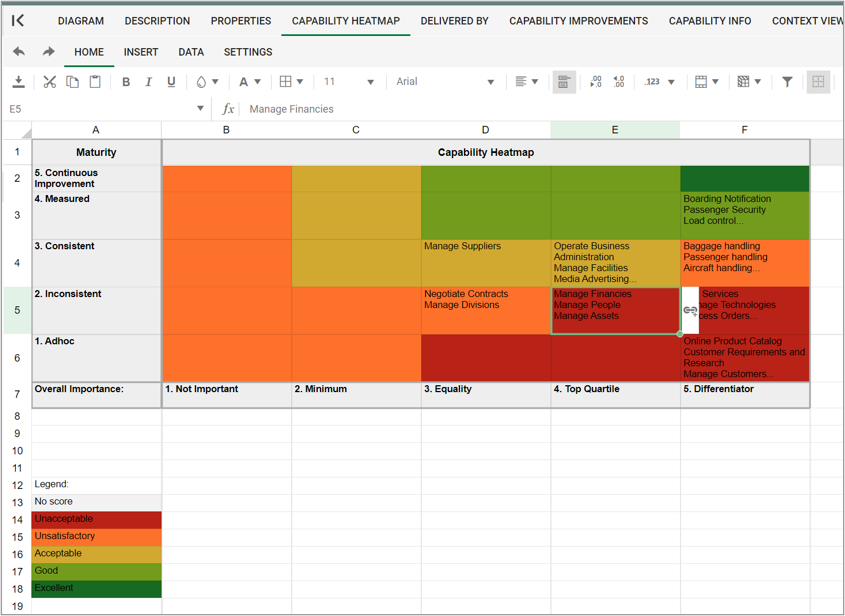
- The capabilities can be presented in a Capability heatmap
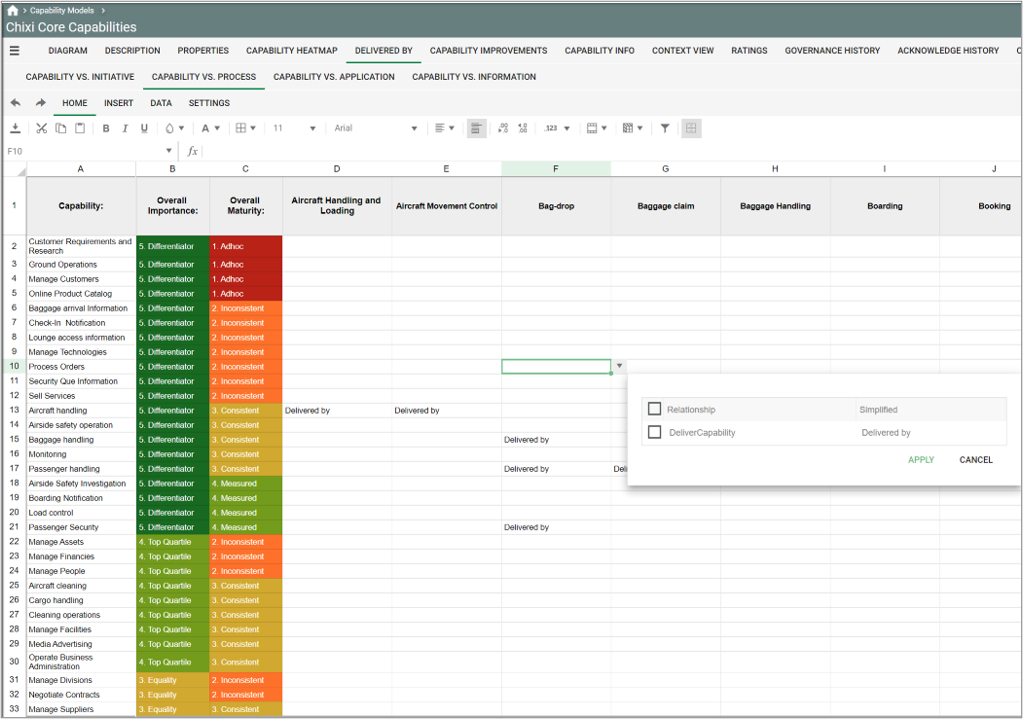
- From the Delivered by view you can analyze and update relations between capabilities and initiatives, processes, applications and information-objects.
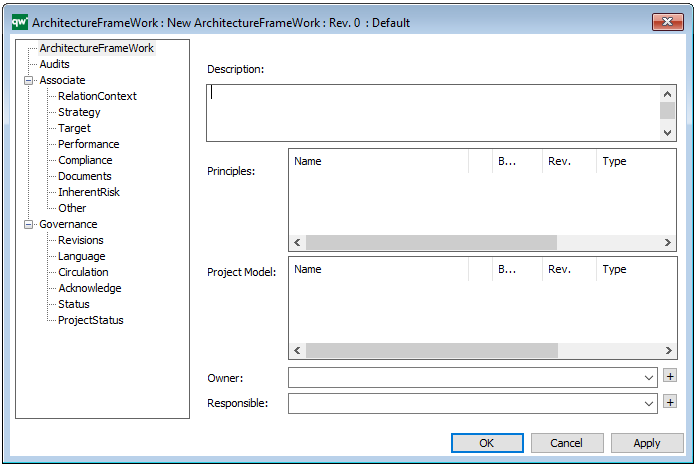
Properties and metadata: The Business Capability Model can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the accuracy of the diagram
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
- Project status: information about budgeted and actual man-hours spent, percentage completed and the latest milestone, result and quality control of a change process.
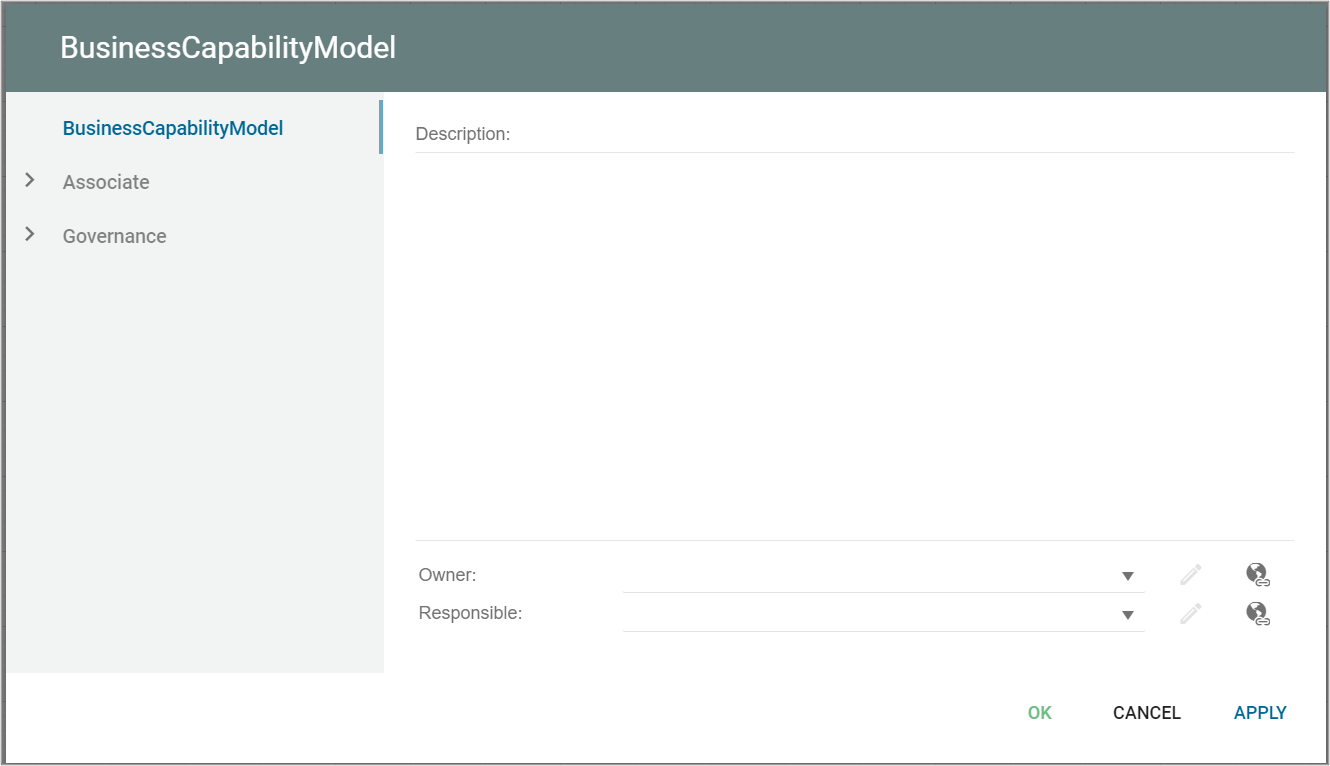
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Business Capability Model where you can edit the diagram’s properties.
Note that the Capabilities’ metadata that are exhibited in the Business Capability Model is not further described here as they belong to the Capability object and not the Business Capability Model template.