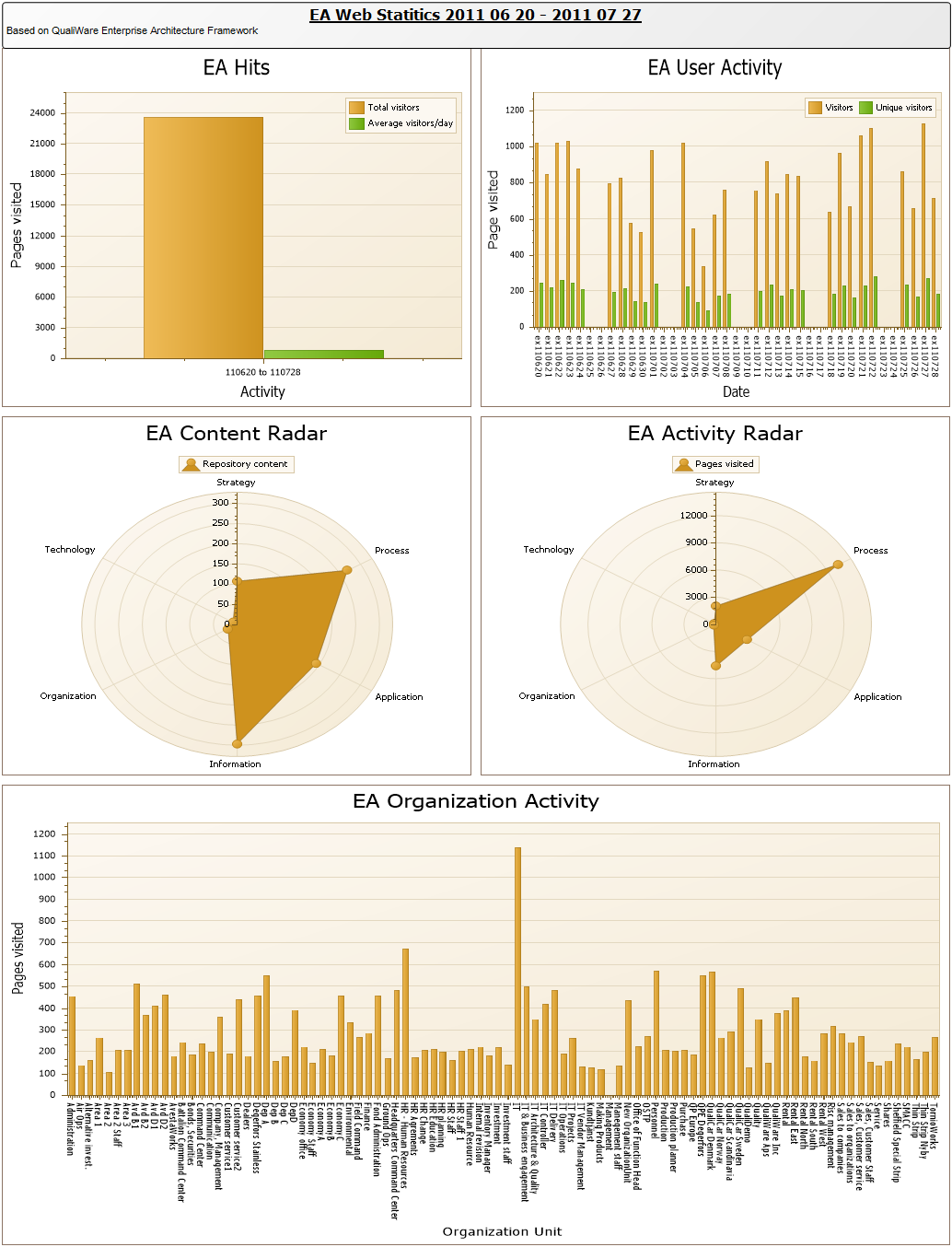
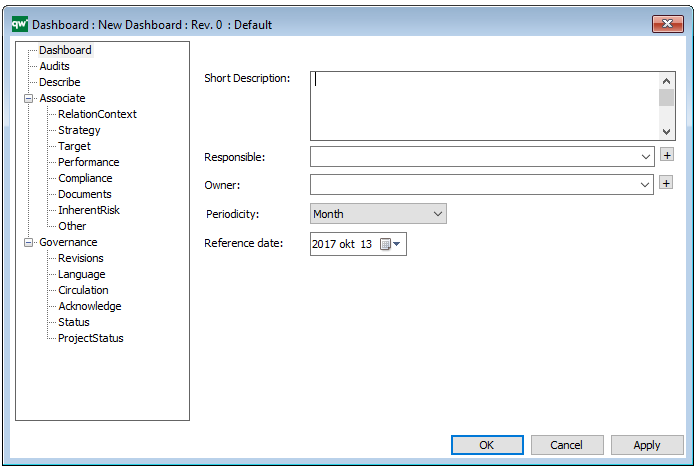
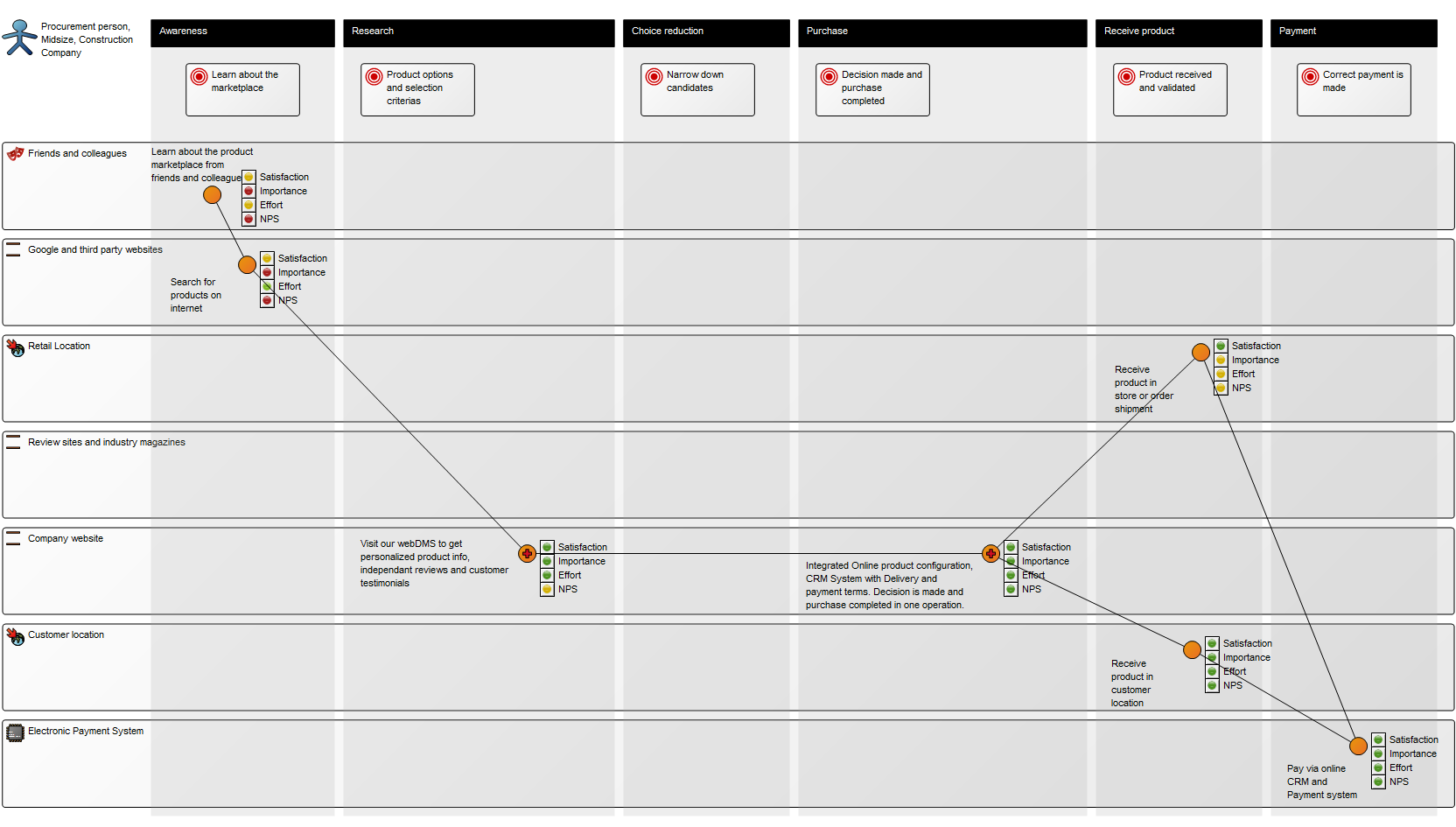
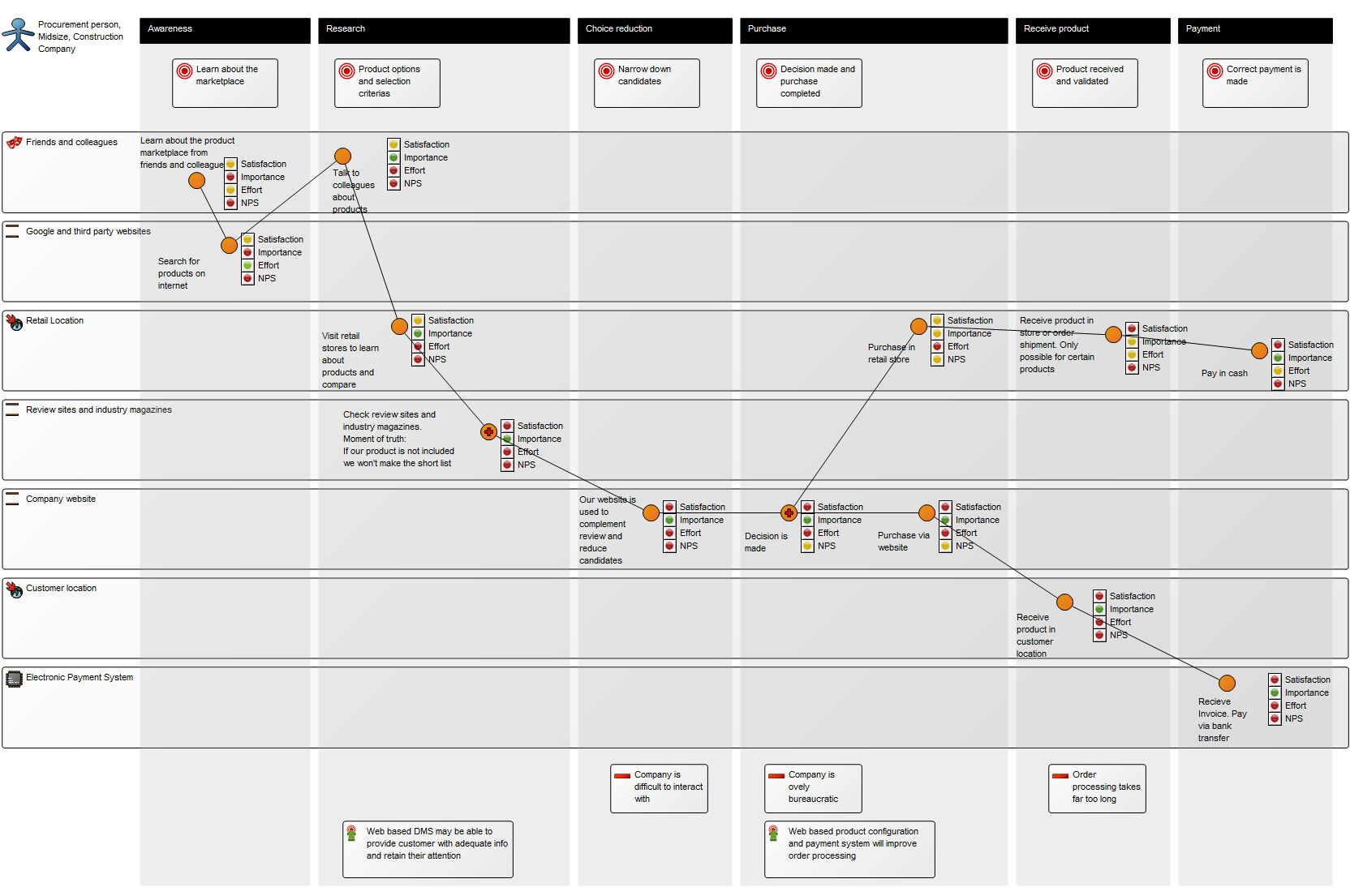
Purpose: The purpose of the Product Canvas template is to present the relevant information related to a specific product.
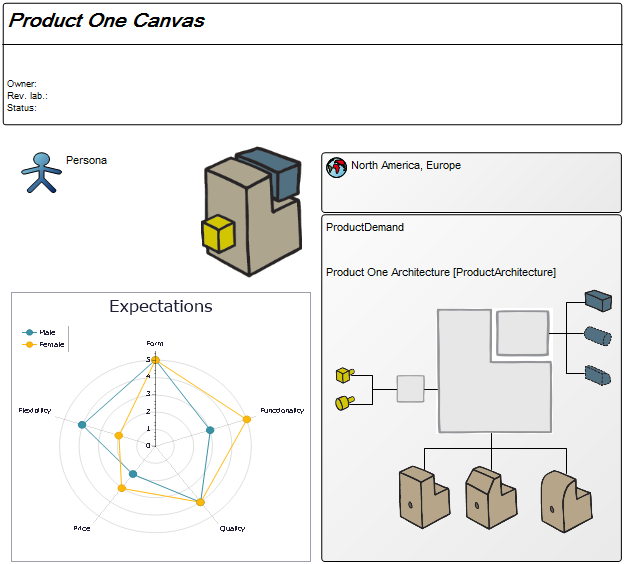
Core concerns: The Product Canvas template enables you to gather relevant Business Charts and model Personae, Product Demands, Markets, Locations and Products. Additionally, you can model a SWOT analysis that details the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats the product is affected by.
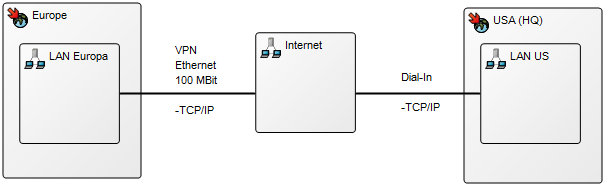
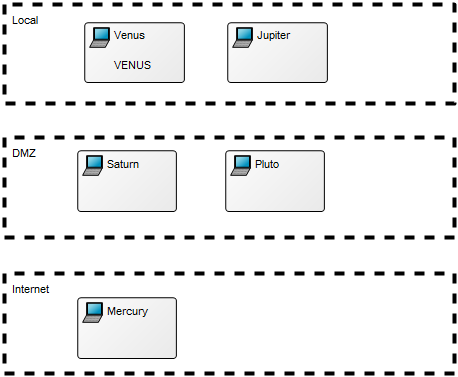
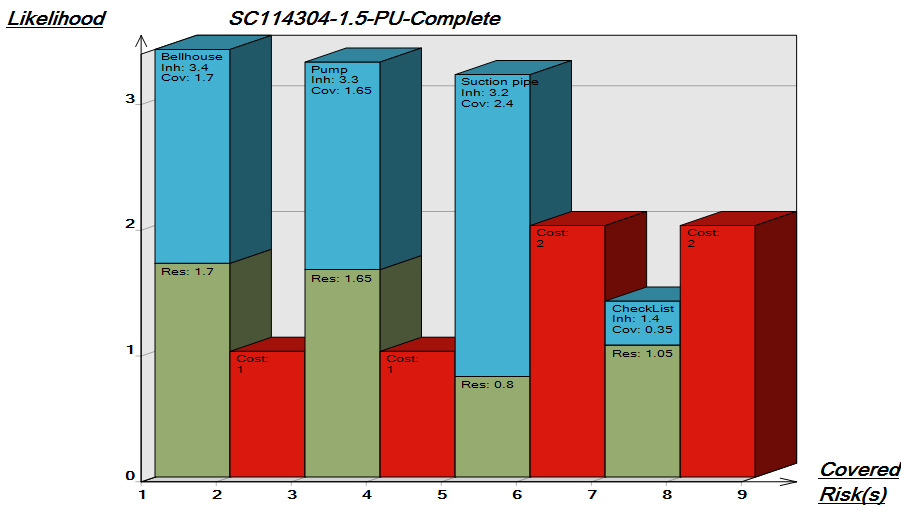
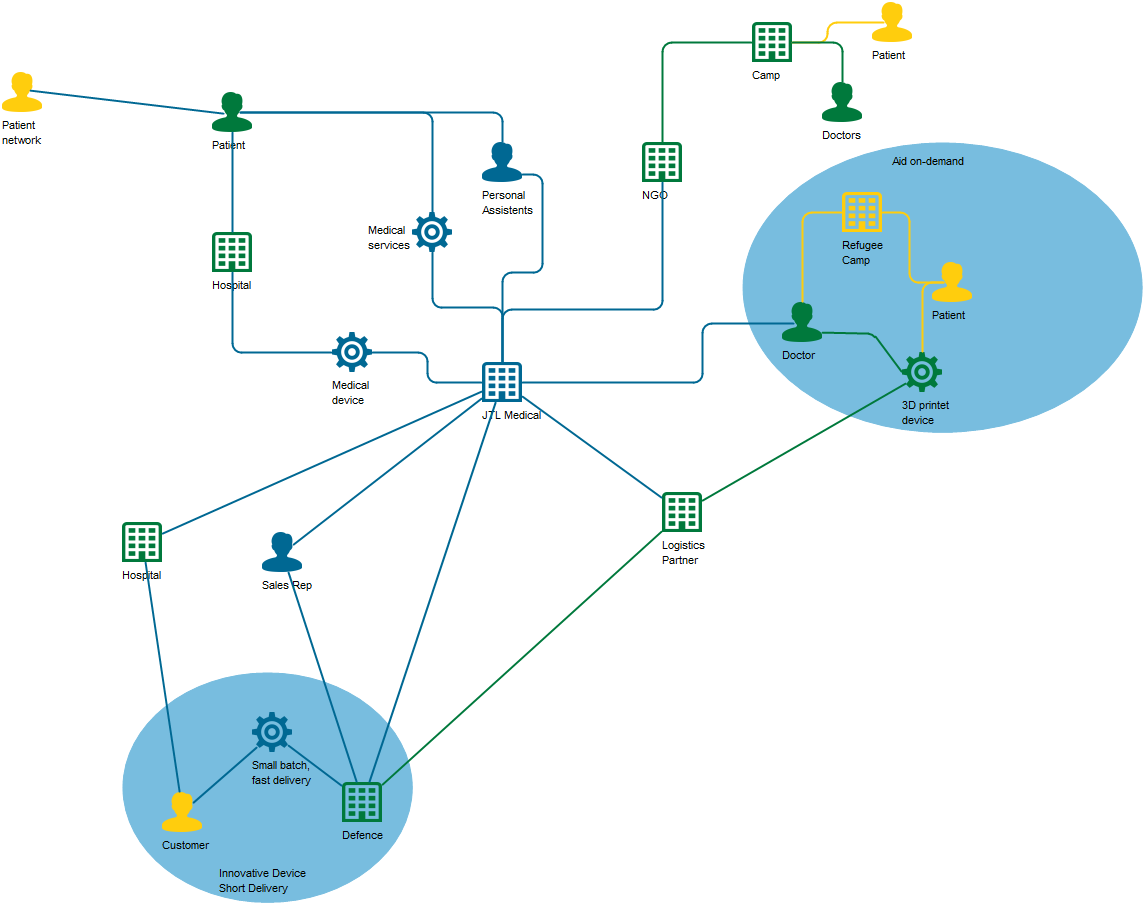
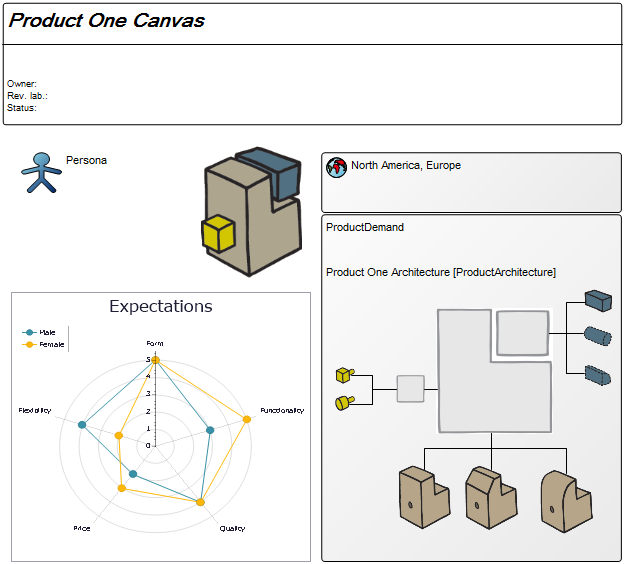
Below, you can see two Product Canvases. The first has its focus on a product within two markets, showing the expectations two different customer segments have to the product.
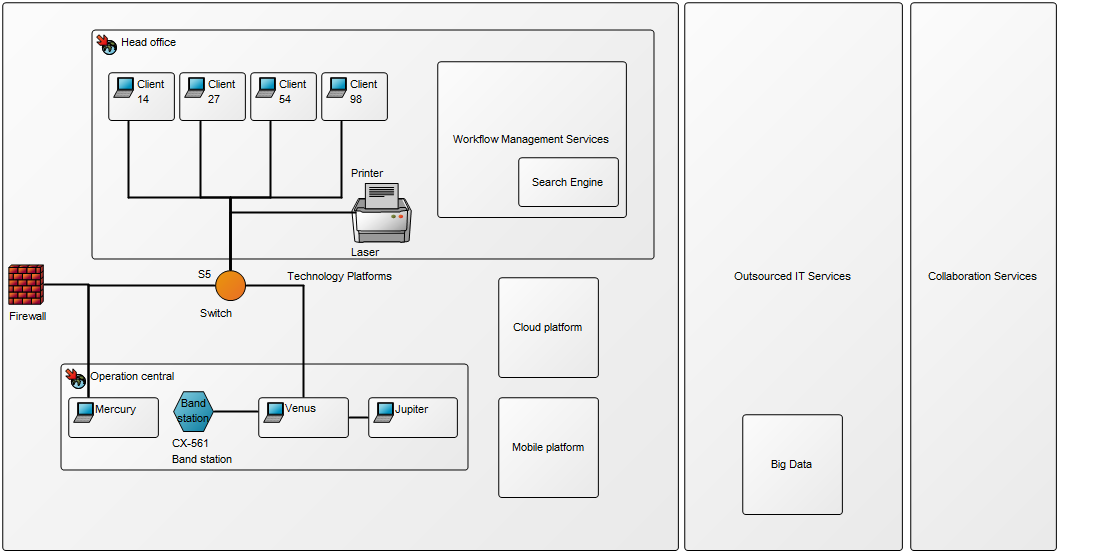
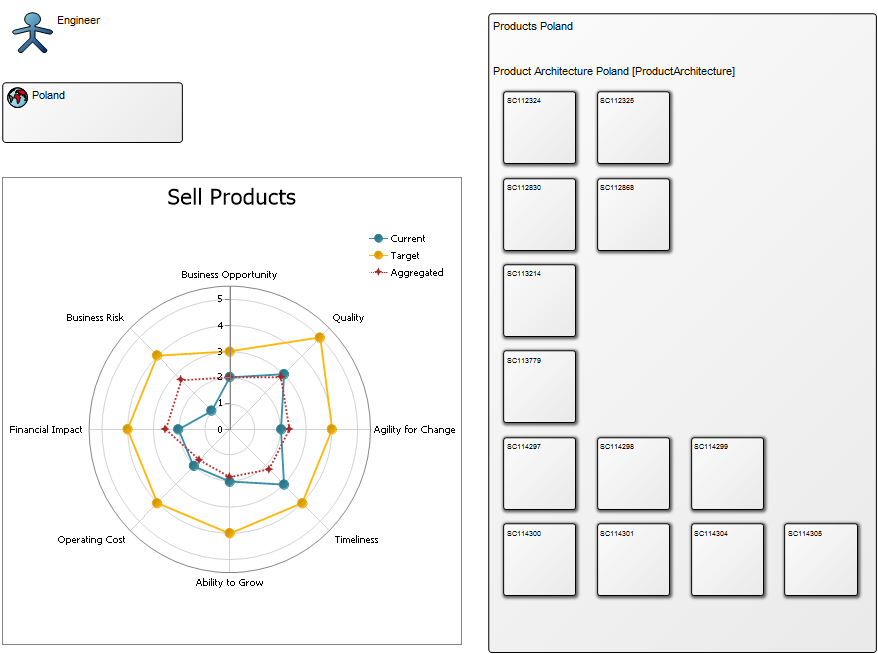
The second example shows information related to a specific market, Poland, including product architecture and business assessment:
Relation to other templates:
The Product Canvas Template is inherently related to the Product Architecture, Product Roadmap and Product Variant Master, in the sense that all these models focus on different aspects of the lifecycle of a product. Furthermore, you can create additional Business Charts for the Product Canvas by using the dedicated template. Another view on projects and initiatives are provided from the Enterprise Investment Portfolio. There, the reasoning behind the investment in the project is visualized by connecting the initiative (in this case a new product) to the specific goals of the enterprise that it contributes to. Another view on how the product meets customer needs can be documented in the Value Proposition Canvas.
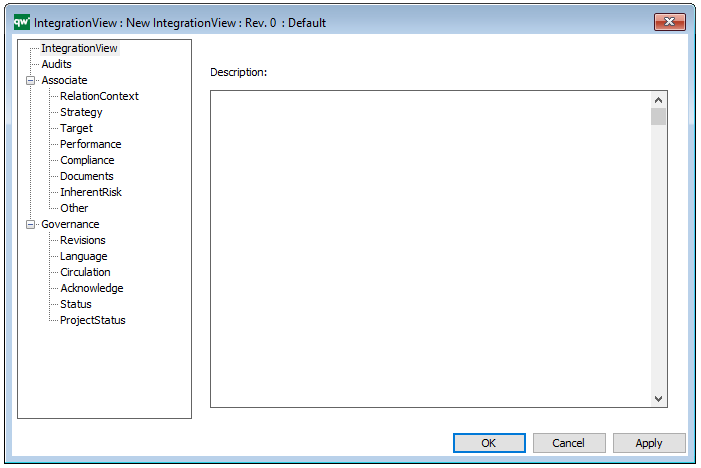
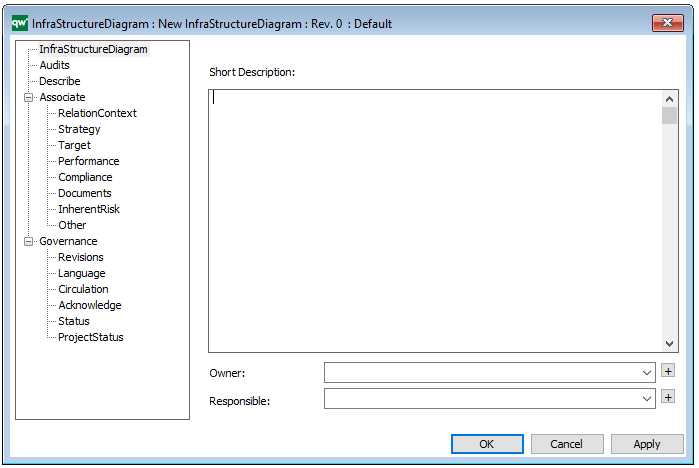
Properties and metadata: The Product Canvas can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the canvas
- Link to the one responsible for the canvas
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
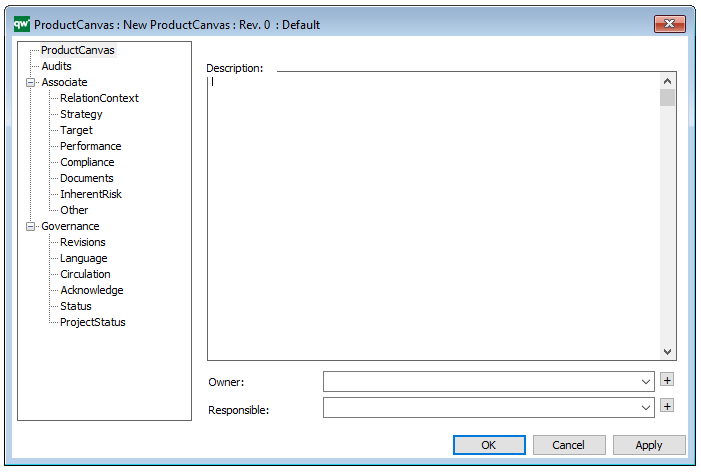
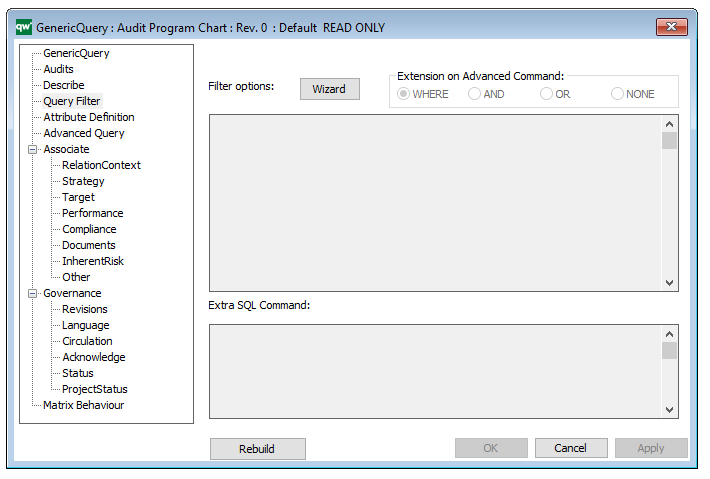
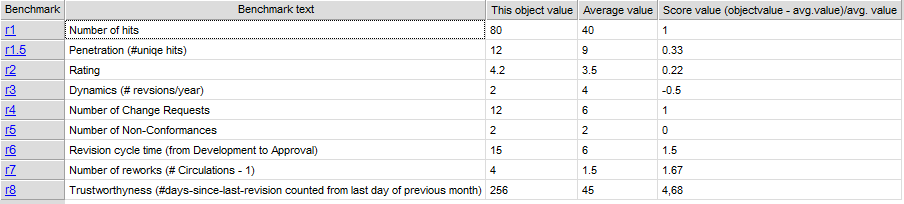
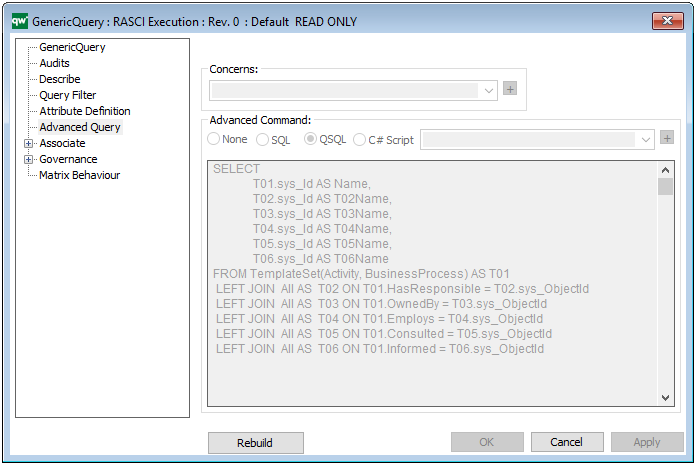
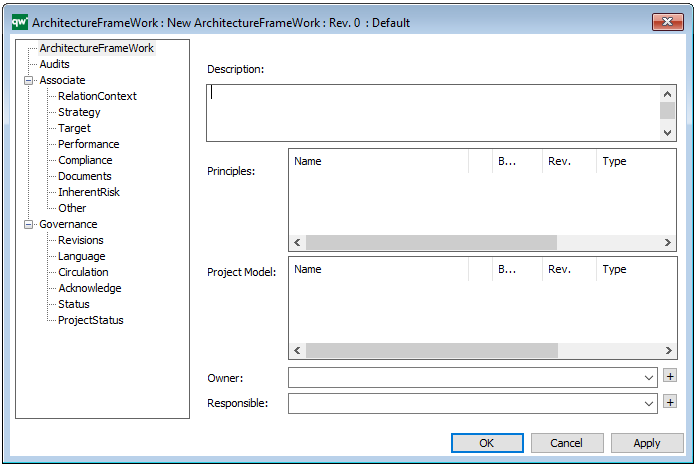
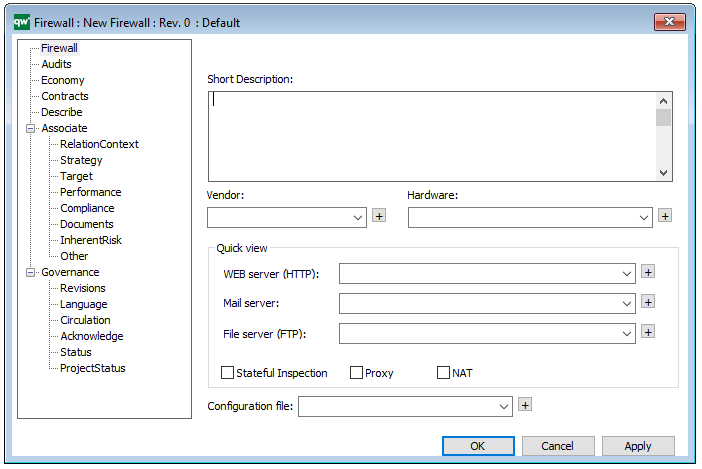
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Product Canvas where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.