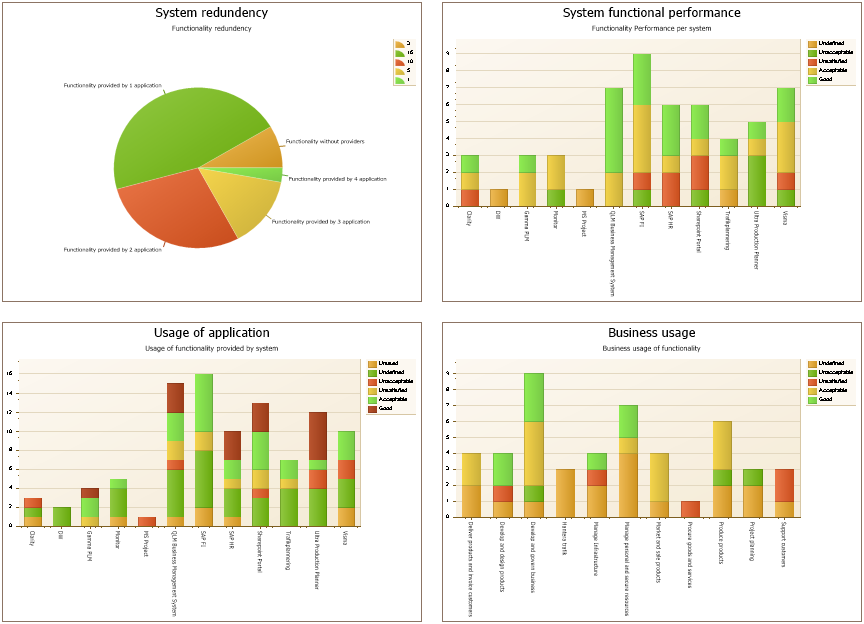
Purpose: The purpose of the Life Cycle Assessment Diagram template is to document the relations for an activity or product in a lifecycle context.
Core concerns: The Lifecycle Assessment Diagram concerns itself with modelling elements in a company that interact with the environment. The template enables you to model Environmental Aspects and Objectives for Activities in your organization. This template allows you to model Business Objects, Activities, Performance Indicators, Business Connection, Goals, Policies, Critical Success Factors, Change Requests and Problems. These elements can be grouped into Categories and connected by Impact Quantity, Recycling, Logistical Flows, Information Flows, and Activity Paths.
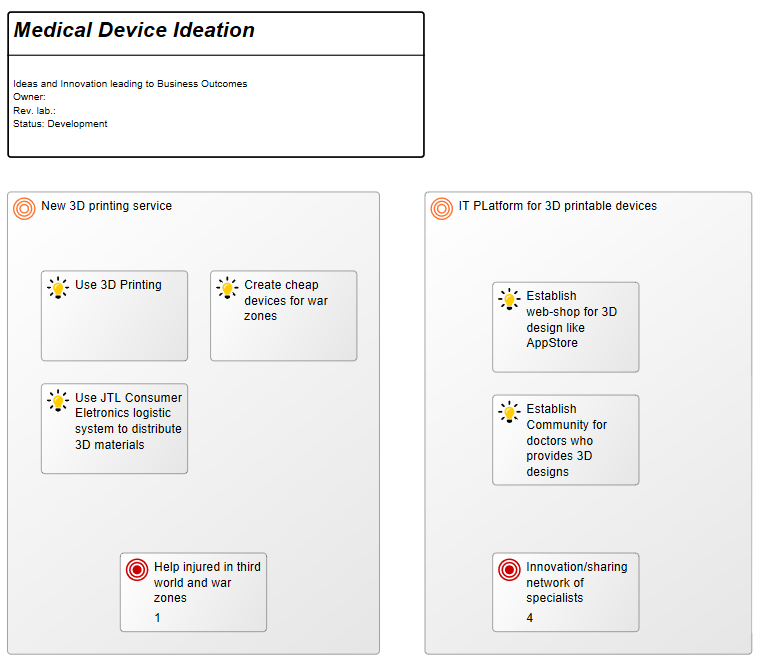
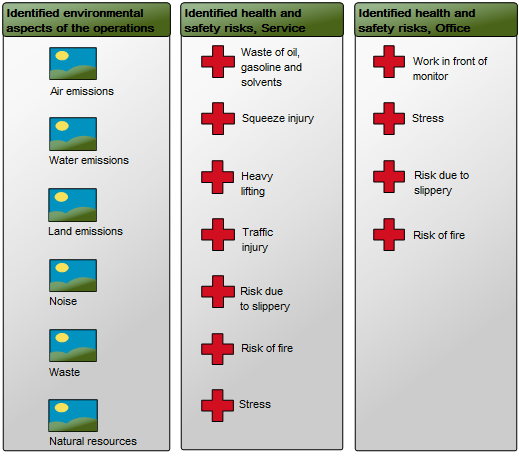
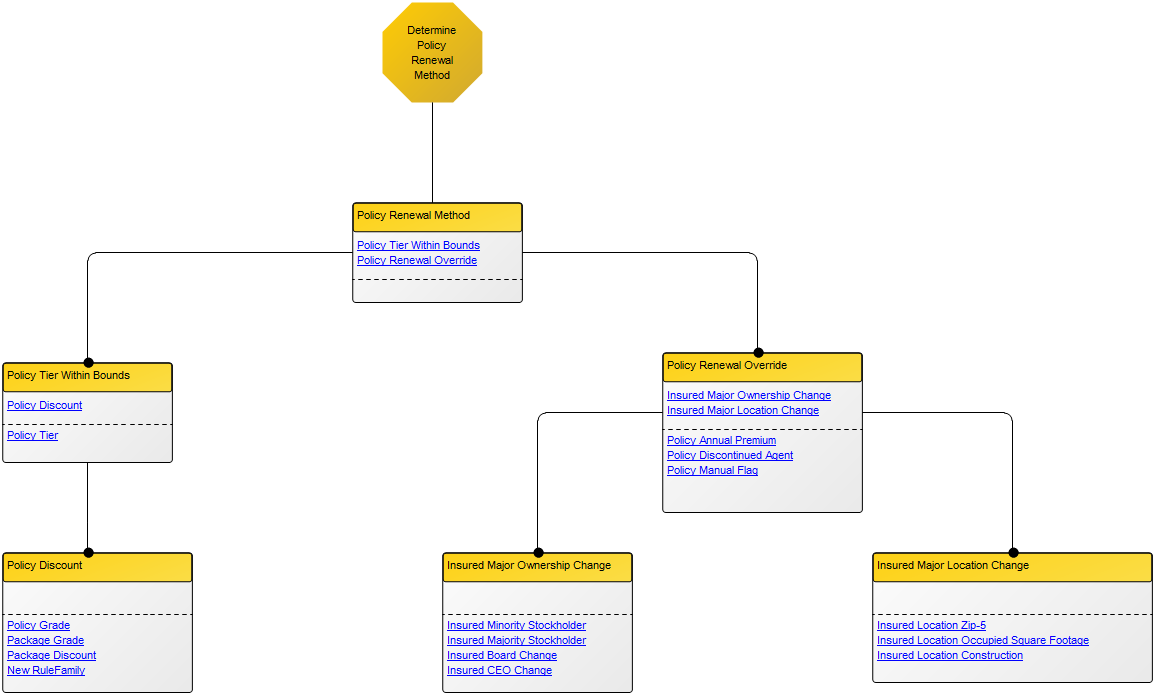
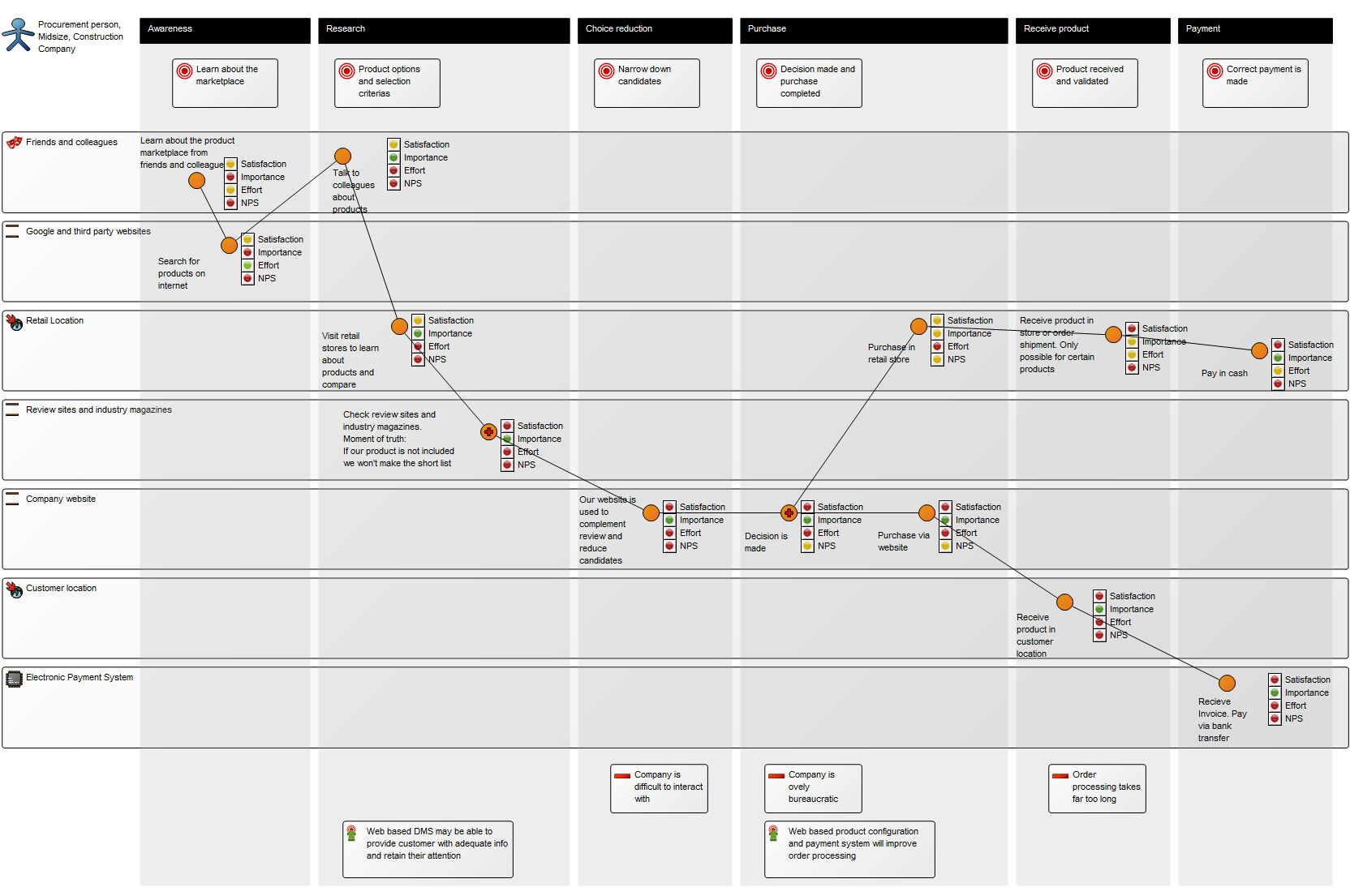
Below, you can see an example of a Lifecycle Assessment Diagram for a Product, from production to packaging, focusing on reducing unbiodegradable waste:
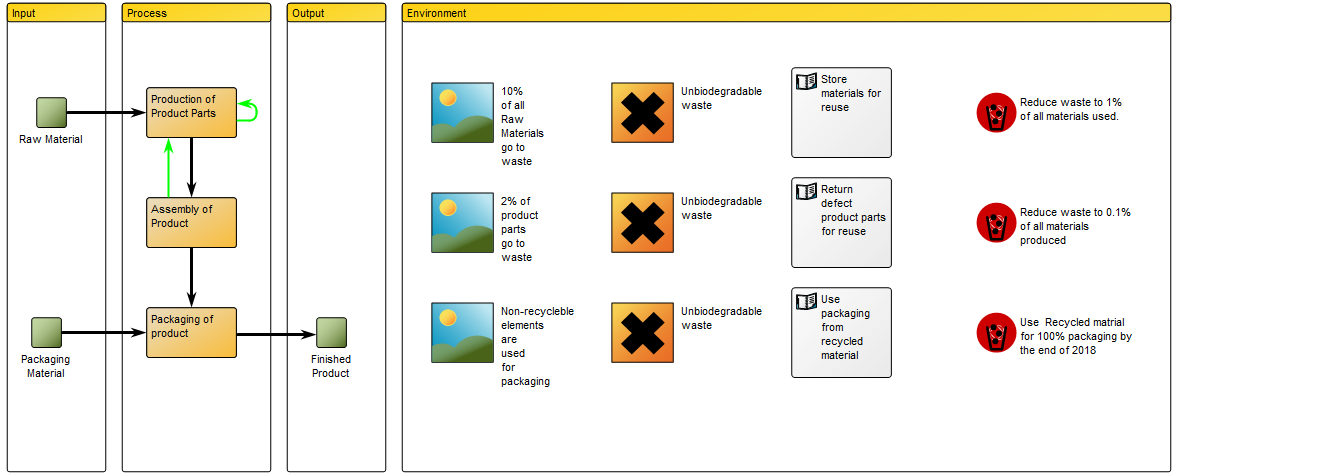
The elements used in this example are Business Objects as input and output, Activities showing Logistical Flows and Recycle under Process. Under the Environment Category, Environmental Aspects, Impact and Objectives are identified and Policies for reaching the Objectives are also included. The diagram focus on a single Environmental impact: Waste. You can also choose to map out several Environmental impacts that are relevant to a specific activity or product.
Relation to other templates: The Environmental Aspects and Impacts from the Lifecycle Assessment Diagram can be further explored in the Environmental Impact Diagram. The Lifecycle Assessment Diagram is also related to the Business Process Diagram and Workflow Diagram, in the sense that they all are related to detailing aspects of processes. The Lifecycle Assessment Diagram can also be decomposed from the Inventory object shown in, for example, the Production Site template.
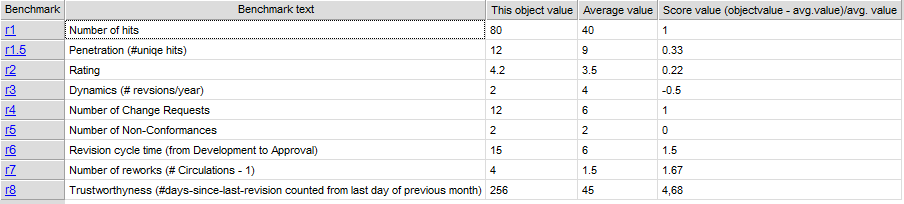
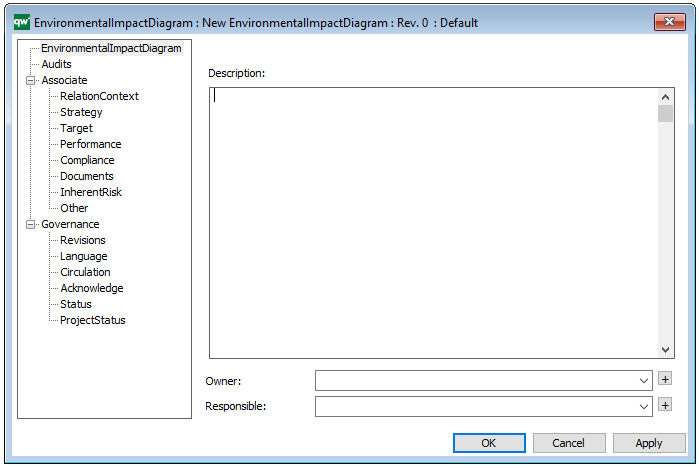
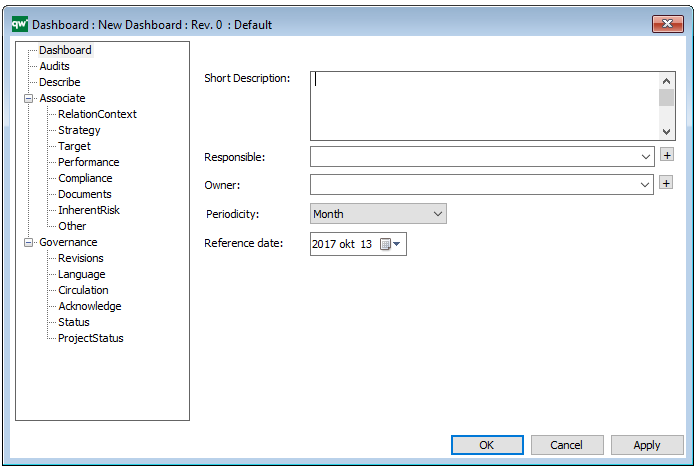
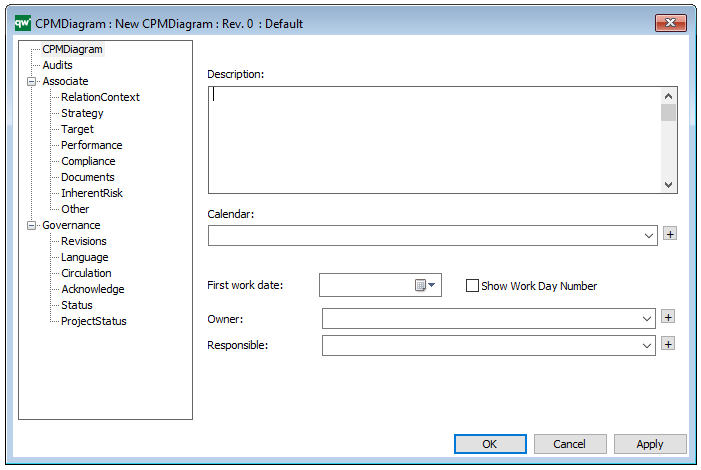
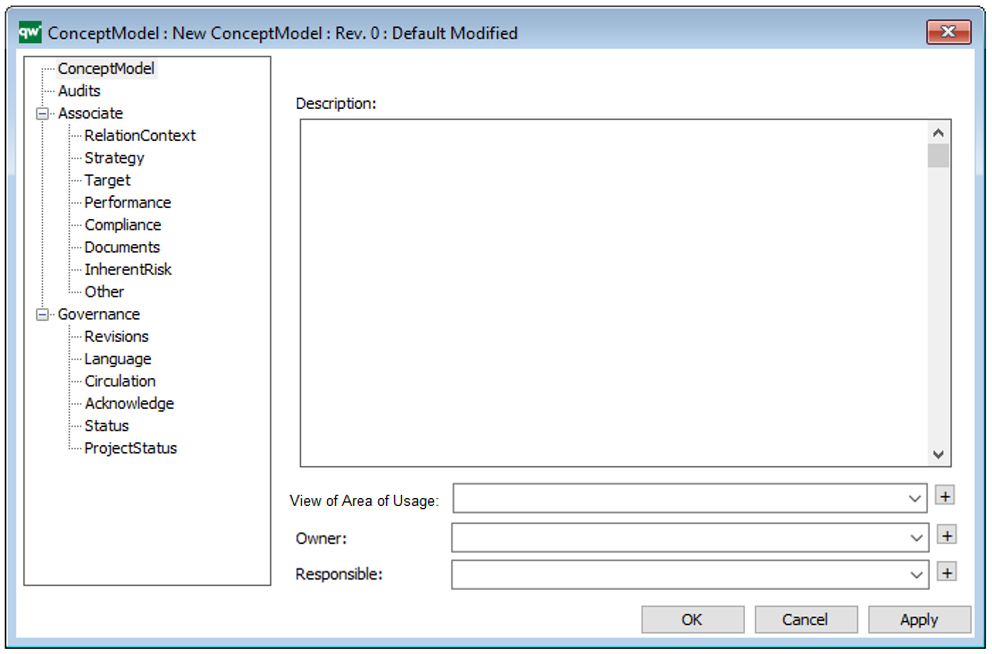
Properties and metadata: The Lifecycle Assessment Diagram template can for example retain the following information:
- A description of the diagram
- Link to the owner of the diagram
- Link to the one responsible for the diagram
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Associated documents, diagrams and other objects
- Inherent Risk detailing risk considerations
- Governance information detailing information about the published diagram and who has been involved in the approval of the diagram
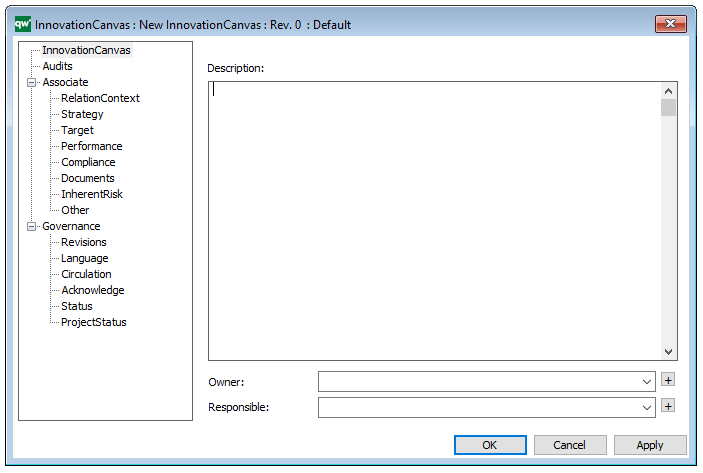
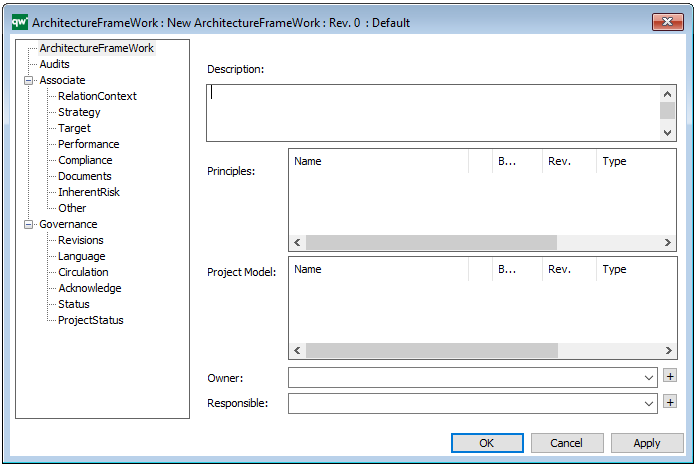
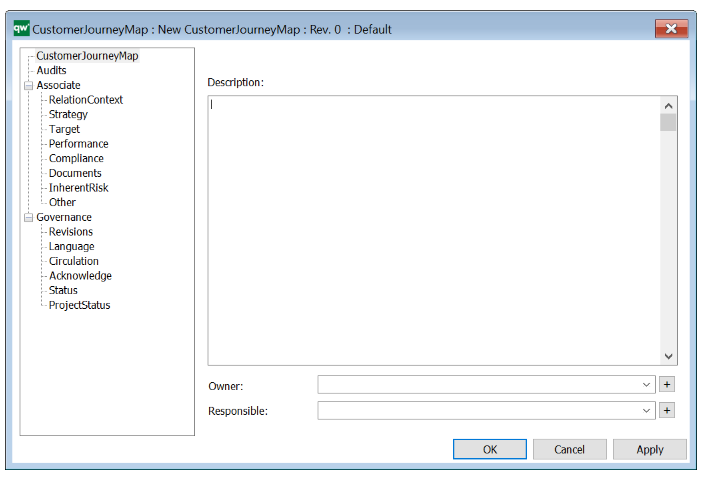
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Lifecycle Assessment Diagram template, where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.
For more information: You can learn more about Lifecycle Assessment on the US Sustainable Facilities Tool website or turn to ISO standard 14040.