![]() The Carnegie Mellon University Certified Enterprise Architect Program is one of QualiWare Academy‘s core certification offerings.
The Carnegie Mellon University Certified Enterprise Architect Program is one of QualiWare Academy‘s core certification offerings.
Currently offerings include:
Denmark
Norway
- EA Fundamentals, tba
- EA Applied, tba
- EA Advanced, tba
![]() The Carnegie Mellon University Certified Enterprise Architect Program is one of QualiWare Academy‘s core certification offerings.
The Carnegie Mellon University Certified Enterprise Architect Program is one of QualiWare Academy‘s core certification offerings.
Currently offerings include:
Denmark
Norway
There are many EA frameworks, and all EA practitioners should know at least a few different frameworks.
The EA framework identifies the scope of the architecture to be developed and establishes relationships between the architecture’s areas. The framework’s scope is reflected through its geometric design and the areas that are identified for documentation. The framework creates an abstracted set of “views” of an enterprise through the way that it collects and organizes architecture information.
Known as the EA³ Cube Framework™ the levels of this example framework are hierarchical so that the different sub-architectures (that describe distinct functional areas) can be logically related to each other. This is done by positioning high-level strategic goals/initiatives at the top, business products/services and data/information flows in the middle, and supporting systems/applications and technology/infrastructure at the bottom. In this way alignment can be also be shown between strategy, information, and technology, which aids planning and decision-making. Chapters 4 through 6 provide more details on EA frameworks, components, and methods.
To lower risk and promote efficient, phased implementation methods, the EA framework is divided into segments of distinct activity, referred to as Lines of Business (LOBs). For example, each LOB has a complete subarchitecture that includes all five hierarchical levels of the EA³ framework. The LOB therefore can in some ways stand alone architecturally within the enterprise except that duplication in data, application, and network functions would occur if each LOB were truly independent. An architecture encompassing all five framework levels that is focused on one or more LOBs can be referred to as a segment of the overall EA.
Key Term: Line of Business
A Line of Business (LOB) is a distinct area of activity within the enterprise. It may involve the manufacture of certain products, the provision of services, or internal administrative functions.
Key Term: Architecture Segment
A part of the overall EA that documents one or more lines of business at all levels and threads. A segment can exist as a stand-alone part of the EA.
The EA3 Approach suggests using the Living Enterprise EA repository design pattern with hierarchical rows and functional columns
The design of the Living Enterprise EA repository may look similar to Zachman’s classic framework, in that it uses hierarchical rows and functional columns. However, it is different in that:
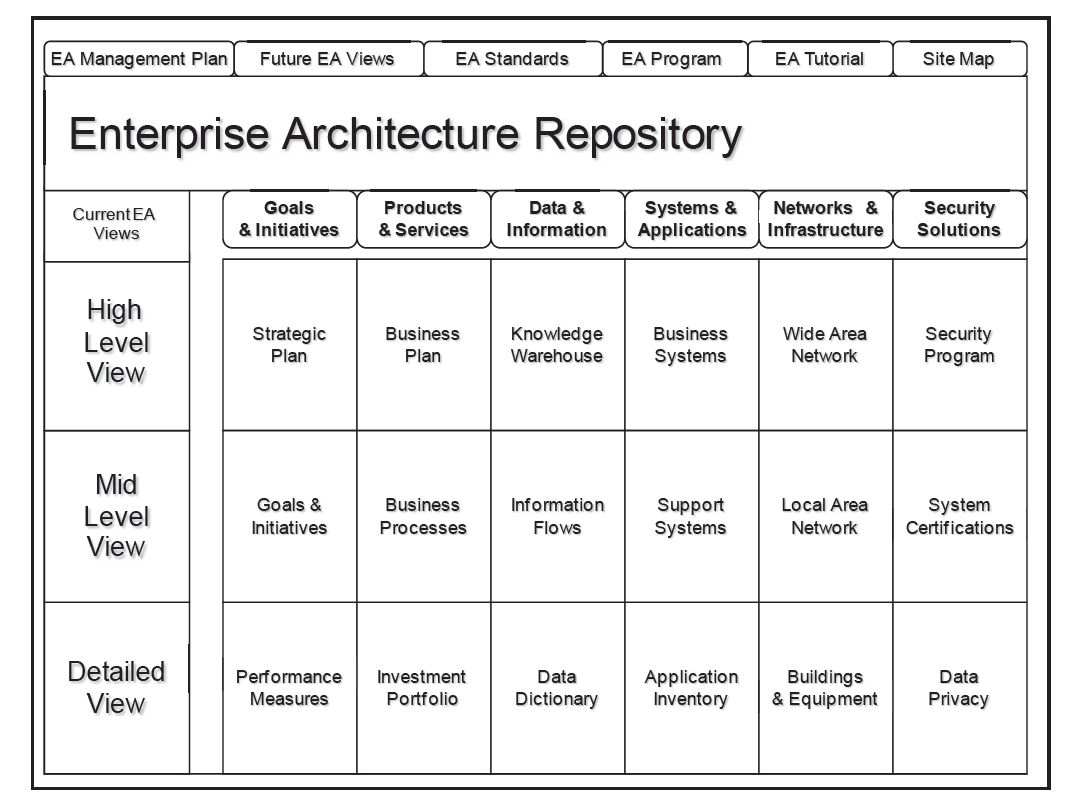
These six points are the basic Living Enterprise EA repository design rules, and can be seen as a way to measure conformance and compliancy of EA3 implementations.
QualiWare EA and EA3
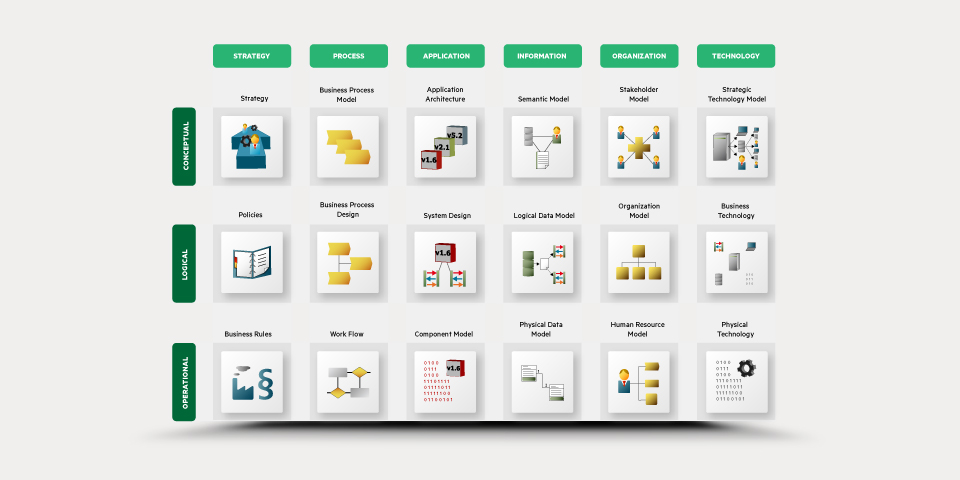 QualiWare’s EA ArchitectureFramework is fully compliant with the Living Enterprise requirements. It uses hierarchical rows and functional columns; it uses a meta-framework; its columns are architectural layers; it has changeable cells; it is supported by additional information and EA management functions; and the QualiWare EA toolset includes a very powerful web-platform with support for collaborative decision making, social collaboration, social analytics and governance workflow management such as delegation of responsibilities for information sharing and consultation.
QualiWare’s EA ArchitectureFramework is fully compliant with the Living Enterprise requirements. It uses hierarchical rows and functional columns; it uses a meta-framework; its columns are architectural layers; it has changeable cells; it is supported by additional information and EA management functions; and the QualiWare EA toolset includes a very powerful web-platform with support for collaborative decision making, social collaboration, social analytics and governance workflow management such as delegation of responsibilities for information sharing and consultation.
QualiWare’s framework orders the columns slightly different from the Living Architecture default, and has an Organization column instead of a Security column. A cell-by-cell comparison of the QualiWare framework and the default Living Enterprise is provided below. Implementers of an EA Framework and repository design are advised to review each cell (and column) in both these frameworks, and use whatever makes sense.
QualiWare |
EA3 Living Enterprise |
Strategy |
Strategic Goals and Initiatives Column |
| Strategy | Mission and Vision Cell: Here is where the enterprise’s mission and vision statements are located. These are the highest level policy statements that the enterprise has, reflecting why the enterprise exists and in general what it strives to be. |
| Policies | Goals and Initiatives Cell: Here is where a list of the enterprise’s strategic goals and initiatives is presented. For each strategic goal the desired outcome should be identified. For each strategic initiative, mapping to the goal(s) should be provided, as well as identification of the performance gaps that the initiative will correct. If there is an IT component in the initiative, that should be clearly identified. Each strategic initiative should then be hyperlinked to amplifying metrics information in the Performance Measures Cell, as well as related investments in the Business servIces column. |
| Business Rules | Performance Measures Cell: Here is where the IT performance gaps are again identified for each strategic initiative. Then the outcome and output measures are provided that will measure the success of each initiative. Tracking information on the measures should also be provided, beginning with the original levels of achievement in each measurement area (called the “baseline”), and subsequent levels of achievement, which will form a trend line that tracks toward a goal level of improved level of performance. |
Process |
Business Products and Services Column |
| Business Process Model | Lines of Business Cell: Here is where the basic areas of activity (lines of business) for the enterprise are identified. The lines of business should support the enterprise’s strategic goals and initiatives, or there is no reason to be doing those activities … they are not adding value. To better show this, the lines of business should be hyperlinked to the strategic goals and initiatives that they support in the Strategic Initiatives column. |
| Business Process Design | Investment Portfolio Cell: Here is where the enterprise’s investments in IT are shown. When aggregated, these investments form an “investment portfolio”. This portfolio should be documented along with categories for investments in IT (e.g., IT operations, office automation, IT research and development, IT infrastructure). Information on the business case for each particular investment should be shown, to include how the investment supports a particular strategic initiative and/or LOB. Investment performance information on the overall portfolio and individual investments should also be provided in this cell. |
| Work Flow | IT Projects Cell: Here is where information on all of the active IT projects throughout the enterprise are shown. Project Management Plans and other associated documentation are the types of EA artifacts that should be archived in this area. Summaries of Earned Value Management information regarding project status are also helpful (e.g., planned vs. actual cost, schedule, and performance graphs). |
Application |
Systems and Applications Column |
| Application Architecture | Support Services Cell: Here is where the overall view of business-related support services is presented in a format which promotes an understanding of how these resources are supporting the information sharing requirements of each LOB. There is a focus on supporting business operations in this cell. As was presented in Figure 7-7, an effective presentation format is a high level diagram that shows the applications being used within each LOB and across the enterprise, and shows this as distinct areas of support (e.g., databases, operating systems, websites, and middleware ). |
| System Design | Front Office Systems Cell: Here is where the overall suite of front office support systems and applications are presented in a format that promotes an understanding of how they support the enterprise’s information sharing requirements across all LOBs. This includes ERP solutions, supply chain management systems, customer relationship management systems, sales and marketing supports, manufacturing support, and on-line e-commerce transactions. |
| Component Model | Back Office Systems Cell: Here is where the overall suite of back office (administrative) systems and applications are presented in a format that promotes an understanding of how they support the enterprise’s administrative support requirements across all LOBs. This includes financial and accounting systems, human resource systems, a common email system, telephone, video-teleconferencing, fax, print, and copying systems. Also located here are the standard desktop, laptop, and personal digital assistant applications. Enterprises increasingly are distributed across multiple geographical locations, have individuals who are telecommuting, and have individuals in the field doing remote-site work and/or meeting with customers. This creates requirements for portable computing that should be documented in this cell, along with a clear picture of how information is being shared between these computing platforms to support LOB processes. |
Information |
Data and Information Column |
| Semantic Model | Knowledge Management Cell: Here is where the enterprise’s approach to Knowledge Management (KM) is provided. Items to be covered include the overall concept for sharing knowledge, information, and data, as well as whether there is an acknowledged commitment to being a learning enterprise. A learning enterprise is one which has a process for evaluating LOB processes and the management of programs and projects, and continually incorporating the lessons learned into the improvement of those processes, programs, and projects. In this way a culture of learning is created which can lead to increased levels of performance for the enterprise. Documentation of this can be effectively accomplished through a combination of diagrams and text descriptions of the EA Components that are active in aggregating data into information and then into knowledge, as well as how that knowledge is shared (e.g., knowledge warehouses, data marts, storage area networks, and databases). |
| Logical Data Model | Data Flows Cell: Here is where the sharing and transformation of information and data is documented for all processes in the enterprise’s LOBs. Documentation should also reveal how the information and data is used within each LOB, in the form of requirements. Documentation methods should provide the structure of basic data entities/objects, the rules for relationships between these data entities/objects, and the flow of the data entities/objects through the various EA Components at the Information Level of the EA3 Framework. This includes EntityRelationship Diagrams and Data Flow Diagrams that document relational databases and are used in procedural programming languages such as CaBaL, FORTRAN, and C. It also includes object-oriented documentation using the Unified Modeling Language, which documents object-based databases that are created using event-driven programming languages such as JAVA, SMALLTALK, and C++. |
| Physical Data Model | Data Dictionary Cell: Here is where standards and the format for the enterprise’s data entities/objects are documented, and where a link is provided to a library (database repository) of those entities and objects. The library promotes the reuse of data entities and objects throughout the EA components, which increases interoperability and lowers development costs. |
Organization |
Security Solution Column |
| Stakeholder Model | Policy and Procedures Cell: Here is where a high level view is presented of the enterprise’s policies regarding IT security. Key extracts form the enterprise’s IT Security Plan are appropriate that link to specific Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to handle various IT security activities and the response to security incidents (e.g., password policies, access procedures, user agreements, virus protection, inappropriate material, and incident handling). The full text of the IT Security Plan and the SOPs should be available in this cell, and links to additional educational information on IT security should be available in this cell and links to additional educational information on IT security should be provided. IT Security on particular vulnerabilities should not be part of the documentation available in this cell, as it should be protected from all but those with a need-to-know. This protected information includes EA component security plans, risk analysis reports, security test and evaluation results, disaster recovery procedures, and technical diagrams of security hardware and software. |
| Organization Model | Data Privacy Cell: Here is where the enterprise’s policy on information privacy is presented. How information and data are collected, archived, and disseminated should be covered for each EA component at the Business Process Level and the Information Flows Level of the EA3 framework, with comments on how privacy requirements are being met. For example, in on-line financial transactions credit card information must be protected. For general sales and marketing databases, customer contact information must be protected. |
| Human Resource Model | IT Inventory Cell: Here is where an inventory of all IT resources (hardware and software) in each EA component throughout the enterprise is maintained. This inventory not only promotes effective IT security, but also enables EA planners to obtain information on the “as-is” business and technology operating environment. For example, to support a decision on purchasing an upgrade to a COTS product, it is important to know how many licenses are currently owned, and when the expiration date is. In another example, knowing how many desktop PCs of a particular type exist can help procurement decisions that accompany “technology refreshments” throughout the enterprise that need to occur every two to three years. |
Technology |
Networks and Infrastructure Column |
| Strategic Technology Model | Common Operating Environment Cell: Here is where information about the enterprise’s Common Operating Environment (COE) is presented. The COE is the integrated business and technology operating environment, wherein a seamless voice, data, and video network infrastructure hosts front office and back office services and systems. |
| Business Technology | Wide Area Network Cell: Here is where information about the enterprise’s Wide Area Network (WAN) is presented. An effective way to present information about the WAN is a map with WAN symbols for hardware and communication links that are hyperlinks, that when clickedon lead to a new level of detail about that part of the WAN (e.g., dedicated voice and data lines, wireless links, interfaces with service providers). Also appropriate for documentation in this cell is the connectivity for Supply Chains and/or information transfer via Extranets that connect to specific external business partners and/or remote office locations. Standards for voice, data, and video WAN components should also be available in this cell. |
| Physical Technology | Local Area Network Cell: Here is where information about the enterprise’s Local Area Network(s) is provided. There may be several LANs (also called Intranets) in the enterprise … perhaps in particular LOBs or at headquarters and several remote offices. In this case, the relationship of these LANs and their external linkage via the WAN needs to be shown. An effective way to present information about the LAN is a map with LAN symbols for hardware and communication links that are hyperlinks, that when clicked-on lead to a new level of detail about that part of the LAN (e.g., location of segments, interface points, and hosted applications, databases, and websites). |
Cells in the repository check-list:
Corporate strategy plan
Corporate management team
Enterprise Architecture team
Strategic planning is a management process and the content of this cell
drives this process.
Board of directors
Chief executives of the organization
Enterprise Architecture team
Medium level “Strategic Initiatives” cell
High level “Business Process” cell
The content of this artifact must be simple, qualitative and visionary.
This content can be refreshed yearly.
John Gøtze, PhD
Enterprise Architecture is an emerging profession and management practice that is devoted to improving the performance of enterprises by enabling them to see themselves in terms of a holistic and integrated view of their strategic direction, business practices, information flows, and technology resources. By developing current and future versions of this integrated view, an enterprise can better manage the transition from current to future operating models and methods. This transition includes the identification of new goals, activities, and all types of capital and human resources (including information technology) that will improve bottom line financial and mission performance.
The strategic use of resources is increasingly important to the success of public and private sector enterprises, including extended enterprises involving multiple internal and external participants (e.g., supply chains). How to get the most from business, technology, and human resources requires an enterprise to think in terms of enterprise-wide solutions, rather than individual system development projects. Doing this requires a new approach to planning and systems development, an approach that has come to be known as Enterprise Architecture (EA). The word ‘enterprise’ implies a high-level, strategic view of the entire organization, while the word ‘architecture’ implies a structured framework for the analysis and design of all types of resources.
With regard to resources, one of the greatest challenges that many enterprises continue to face is how to identify the business and technology components of strategic initiatives. A big part of this challenge is that technology, information technology (IT) in particular, has historically not been viewed as a strategic asset in many enterprises. As such, traditional planning activities often focused on the development of individual technology solutions to meet particular organizational requirements. Today, a much more integrated and collaborative planning approach is called for. That is enterprise architecture in a nutshell.
The EA³ Cube approach

The EA³ Cube approach (“EA³″) was developed by Scott A Bernard and is today used in academic and professional EA training programs all over the world, including Carnegie Mellon University’s Certified Enterprise Architect program. The EA³ approach has also had a clear impact on many practitioners, who use it as a practice approach. EA³ has been the foundation for several government EA approaches, including the US Government’s Common Approach to Federal EA and the FEAF-II Framework. Today, EA³ is owned and maintained by the International EA Institute.
This paper provides an overview of the enterprise architecture approach known as EA³.
In EA³, the following equation is the ‘sound bite’ version of what enterprise architecture is all about, and is intended to help people remember the distinct difference between EA and the various types of IT planning: that EA is driven by strategic goals and business objectives:
EA = S+B+T
Enterprise Architecture = Strategy + Business + Technology
This “SBT” formulae is in EA3 more formally used when defining enterprise architecture:
Enterprise Architecture is the analysis and documentation of an enterprise in its current and future states from an integrated strategy, business, and technology perspective.
Enterprise Architecture is a strategy and business-driven activity that supports management planning and decision-making by providing coordinated views of an entire enterprise. These views encompass strategy, business, and technology, which is different from technology-driven, systems-level, or process-centric approaches.
Establishing an enterprise architecture practice typically involves implementing an enterprise architecture management program and adopting a framework-based design and analysis method for enterprise planning activities.
Enterprise Architecture is a management and technology practice that is devoted to improving the performance of enterprises by enabling them to see themselves in terms of a holistic and integrated view of their strategic direction, business practices, information flows, and technology resources.
By developing current and future versions of this integrated view, an enterprise can manage the transition from current to future operating states.
The strategic use of resources is increasingly important to the success of public, private, and non-profit sector enterprises, including extended enterprises involving multiple internal and external participants (i.e., supply chains). How to get the most from business, technology, and human resources requires an enterprise to think in terms of enterprise-wide solutions, rather than individual systems and programs (Figure 1-1). Doing this requires a new approach to planning and systems development, an approach that has come to be known as Enterprise Architecture. The word ‘enterprise’ implies a high-level, strategic view of the entire entity, while the word ‘architecture’ implies a structured framework for the analysis, planning, and development of all resources in that entity.
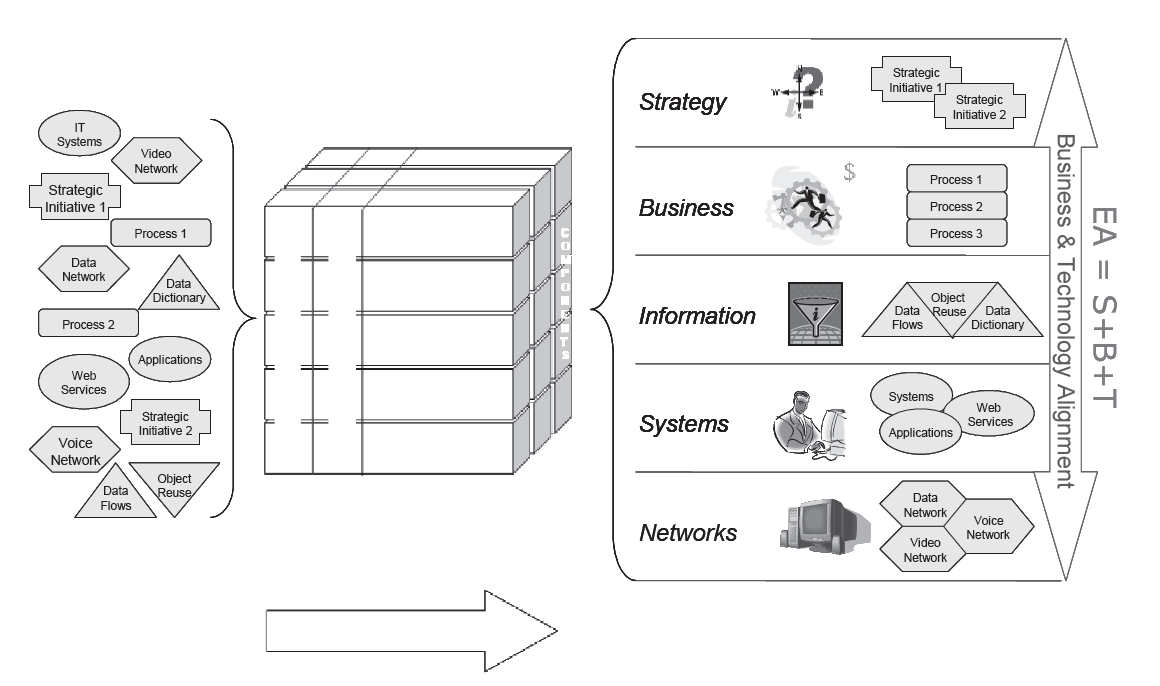
With regard to resources, one of the greatest challenges that many enterprises continue to face is how to identify the business and technology components of strategic initiatives. A big part of this challenge is that technology, information technology (IT) in particular, has historically not been viewed as a strategic asset. As such, planning activities often have focused on the development of individual technology solutions to meet particular organizational requirements.
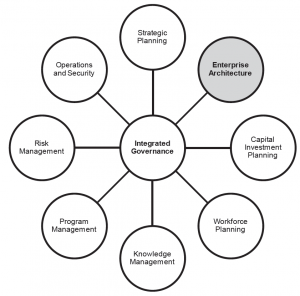
“Enterprise architecture” is both a noun and a verb. The architecture of an enterprise is a thing – captured as a collection of models and information. Creating an enterprise-wide architecture is accomplished through processes that are sustained through an ongoing management program. EA provides a strategy and businessdriven approach to policy, planning, decision-making, and resource development that is useful to executives, line managers, and support staff. To be effective, an EA program must be part of a group of management practices that form an integrated governance structure, as is shown in Figure 1-2.
An enterprise-wide architecture should serve as an authoritative reference, source of standards for processes / resources, and provider of designs for future operating states. An EA is therefore THE architecture of the enterprise and should cover all elements and aspects. Having a single source of reference is essential to avoiding waste and duplication in large, complex organizations. It also resolves the “battle of best practices” and competition between sub-architectural domains which can be problematic for organizations that are trying to become for efficient.
Developing an enterprise-wide architecture is a unique and valuable undertaking for organizations, in that the EA is holistic and serves as an umbrella or “metacontext” for all other management and technology best practices. The EA also creates abstract views, analyses, and models of a current or future enterprise that helps people make better plans and decisions. EA extends beyond technology planning, by adding strategic planning as the primary driver of the enterprise, and business planning as the source of most program and resource requirements. There is still a place for technology planning, which is to design systems, applications, networks, call centers, networks, and other capital resources (e.g. buildings, capital equipment) to meet the business requirements… which are the heart of the enterprises activities… creating and delivering those products and services that accomplish the strategic goals of the enterprise.
Regarding the “battle of the best practices”, organizations in the public and private sectors are often faced with decisions about which practices to adopt as they pursue quality, agility, efficiency; manage risk, and adopt new technologies. There are dozens of best practices out there, and most of them were created in isolation – relative to the other best practices. This is the “battle of the best practices” and it creates an expensive dilemma for organizations – what to adopt? Because the implementation and maintenance methods for many of the best practices are very resource intensive, and the scope is not all-inclusive, the organization is faced with the challenge of deciding which to adopt, how to do it, and what overlaps, contradictions, and gaps are produced from the resulting collection. When EA is THE architecture of an organization in all dimensions, it becomes the over-arching, highest level discipline and the authoritative reference for standards and practices. This is a tremendous and unique contribution, because when EA is used in this way, the dilemma disappears and organizations can use the EA framework to make rational decisions about which best practices need to be adopted, what they will cover, and how they can relate to each other. Figure 1-3 illustrates how EA serves as an organizing context for the adoption and use of best practices.
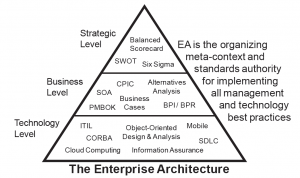
When identifying and selecting best practices enterprises should consider the following enterprise concerns:
For an EA approach to be considered to be complete, the six core elements shown in Figure 1-4 must be present and work synergistically together.
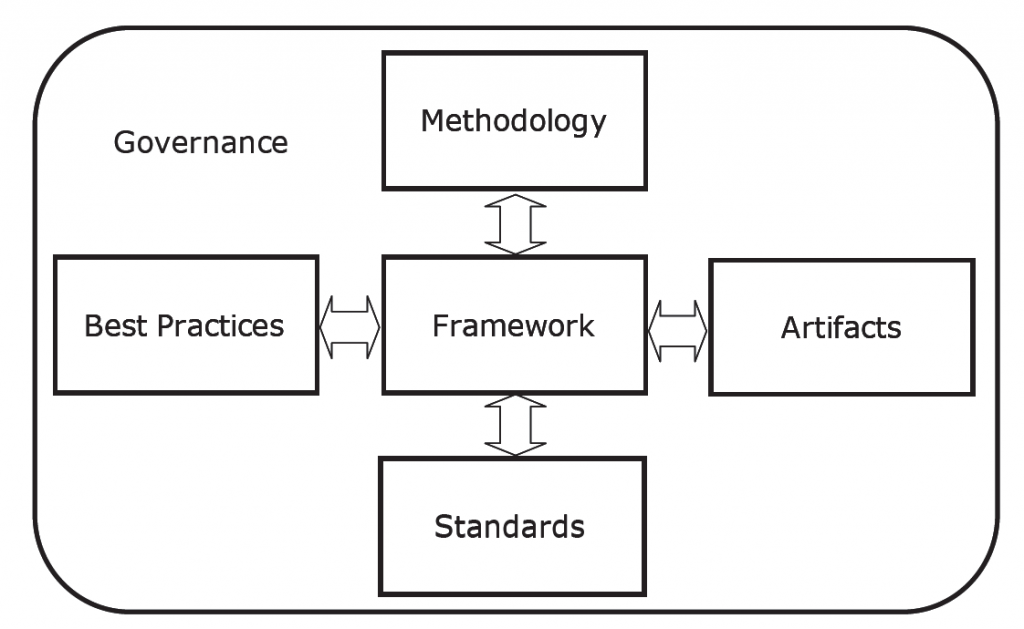
Governance
The first core element is “Governance” which identifies the planning, decision-making, and oversight processes and groups that will determine how the EA is developed and maintained, accomplished as part of an organization’s overall governance.
Methodology
The second core element is “Methodology” which are specific steps to establish and maintain an EA program, via the selected approach.
Framework
The third core element is “Framework” which identifies the scope of the overall architecture and the type and relationship of the various subarchitecture levels and threads. Not all frameworks allow for sub-domains or are able to integrate strategy, business, and technology planning.
The fourth core element is “Artifacts” which identifies the types and methods of documentation to be used in each sub-architecture area, including strategic analyses, business plans, internal controls, security controls, and models of workflow, databases, systems, and networks. This core element also includes the online repository where artifacts are stored.
Standards
The fifth core element is “Standards” which identify business and technology standards for the enterprise in each domain, segment, and component of the EA. This includes recognized international, national, local, and industry standards as well as enterprise-specific standards.
Best Practices
The sixth core element is “Associated Best Practices” which are proven ways to implement parts of the overall architecture or sub-architectures, in context of the over-arching EA.
Extended elements list: The Common Approach’s Basic Elements: Governance, Method, Standards, Principles, Tools, Use, Reporting, and Audit.
Enterprise architecture is accomplished through a management program and an analysis and design method that is applicable to various levels of scope. Together the EA program and method provide an ongoing capability and actionable, coordinated views of an enterprise’s strategic direction, business services, information flows, and resource utilization.
EA as a Management Program
The EA management program is ongoing and provides a strategic, integrated approach to capability and resource planning / decision-making. An EA program is part of an overall governance process that determines resource alignment, develops standardized policy, enhances decision support, and guides development activities. EA can help to identify gaps in the performance of line of business activities/programs and the capabilities of supporting IT services, systems, and networks. The following paragraphs will describe five different means that contribute to identifying and alleviating gaps.
Strategic Alignment
EA supports strategic planning and other operational resource planning processes by providing macro and micro views of how resources are to be leveraged in accomplishing the goals of the enterprise. This helps to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of these resources, which in turn will help to promote the enterprise’s competitive capabilities. Development projects within the enterprise should be reviewed to determine if they support (and conform to) one or more of the enterprise’s strategic goals. If a resource and/or project is not aligned, then its value to the enterprise will remain in question, as is shown in Figure 1-5.
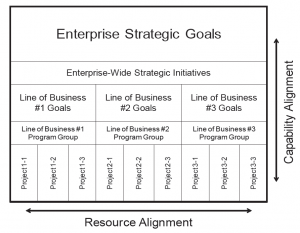
Standardized Policy
EA supports the implementation of standardized management policy pertinent to the development and utilization of IT and other resources. By providing a holistic, hierarchical view of current and future resources, EA supports the establishment of policy for: Identifying strategic and operational requirements Determining the strategic alignment of activities and resources Developing enterprise-wide business and technology resources Prioritizing the funding of programs and projects Overseeing the management of programs and projects Identifying performance metrics for programs and projects Identifying and enforcing standards and configuration management.
Policy documents include those which can be categorized as general guidance (e.g., high-level directives and memos); specific program guidance (e.g., plans, and manuals); and detailed process guidance (e.g., standard operating procedures). By using these hierarchical categories of documents, succinct and meaningful policy is established. It does so in a way that no single policy document is too long and therefore not too burdensome to read. It is also important to understand how the various areas of policy are inter-related so that program implementation across the enterprise is coordinated. EA policies must integrate with other policies in all governance areas, so as to create an effective overall resource management and oversight capability.
Decision Support
EA provides support for IT resource decision-making at the executive, management, and staff levels of the enterprise. At the executive level, EA provides visibility for large IT initiatives and supports the determination of strategic alignment. At the management level, EA supports design and configuration management decisions, as well as the alignment of IT initiatives with technical standards for voice, data, video, and security. At the staff level, EA supports decisions regarding operations, maintenance, and the development of IT resources and services.
Resource Oversight
EA supports standardized approaches for overseeing the development of capabilities and optimizing supporting resources. Depending on the scope of the resources involved and the available timeframe for development, various system development lifecycle methods can be used to reduce the risk that cost, schedule, or performance parameters may not be met. EA further supports standardized, proven approaches to project management that promote the comprehensive and effective oversight of ongoing programs and new development projects. Finally, EA supports the use of a standardized process for selecting and evaluating investment in IT resources from a business and financial perspective.
EA as an Analysis and Design Method
References to EA began to emerge in the late 1980’s in various management and academic literatures, with an early focus on technical or systems architectures and schemas for organizing information. The concept of ‘enterprise’ architecture analysis and design emerged in the early 1990’s and has evolved to include views of strategic goals, business services, information flows, systems and applications, networks, and the supporting infrastructure. Additionally, there are ‘threads’ that pervade every level of the architecture: standards, security, and skills.
EA analysis and design are accomplished through the following six basic elements: (1) an EA framework, and (2) a set of appropriate components that are described via (3) current and (4) future views of the architecture, as well as the development of (5) an EA Management Plan to manage the enterprise’s transition from current to future architectures. There are also several areas common to all levels of the framework that are referred to as (6) “threads” as shown in Figure 1-6.
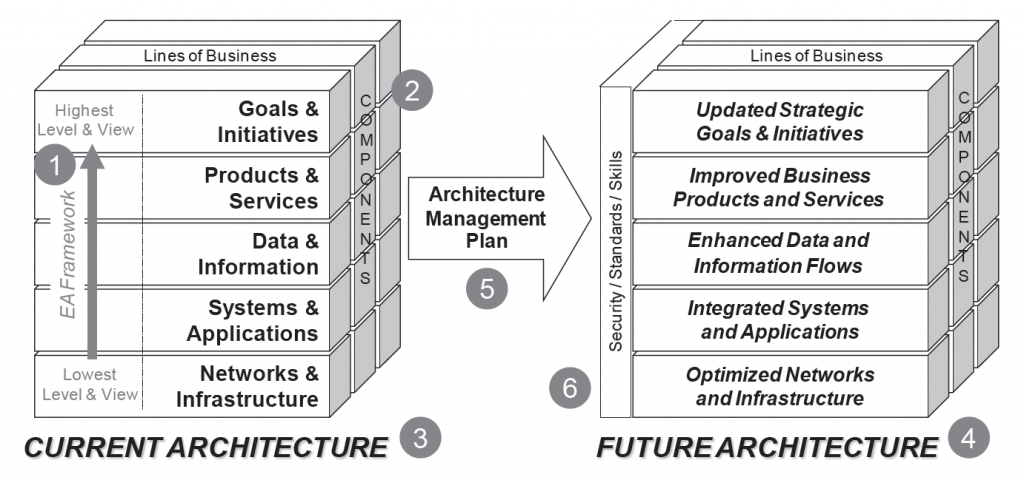
EA Analysis and Design Element #1: The Framework.
The EA framework identifies the scope of the architecture to be developed and establishes relationships between the architecture’s areas. The framework’s scope is reflected through its geometric design and the areas that are identified for documentation. The framework creates an abstracted set of “views” of an enterprise through the way that it collects and organizes architecture information.
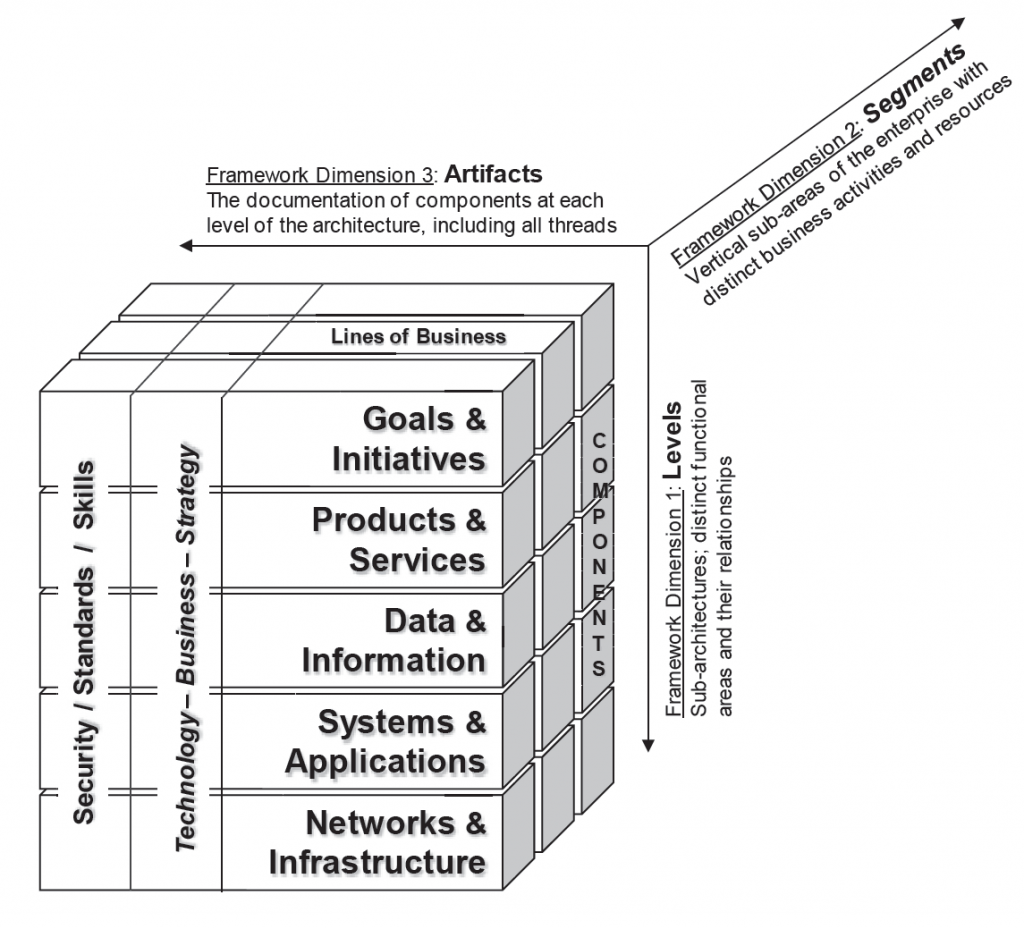
The EA³ Cube Framework has hierarchical levels – sub-architectures – so that the different distinct functional areas can be logically related to each other. This is done by positioning high-level strategic goals/initiatives at the top, business products/services and data/information flows in the middle, and supporting systems/applications and technology/infrastructure at the bottom. In this way alignment can also be shown between strategy, information, and technology, which aids planning and decision-making.
To lower risk and promote efficient, phased implementation methods, the EA framework is divided into segments of distinct activity, referred to as Lines of Business (LOBs). For example, each LOB has a complete subarchitecture that includes all five hierarchical levels of the EA³ framework. The LOB therefore can in some ways stand alone architecturally within the enterprise except that duplication in data, application, and network functions would occur if each LOB were truly independent. An architecture encompassing all five framework levels that is focused on one or more LOBs can be referred to as a segment of the overall EA.
Key Term: Line of Business
A Line of Business (LOB) is a distinct area of activity within the enterprise. It may involve the manufacture of certain products, the provision of services, or internal administrative functions.
Key Term: Architecture Segment
A part of the overall EA that documents one or more lines of business at all levels and threads. A segment can exist as a stand-alone part of the EA.
EA Analysis and Design Element #2: EA Components
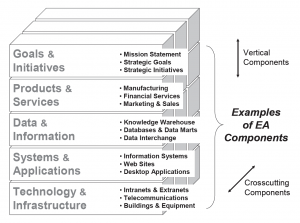
EA components are changeable goals, processes, standards, and resources that may extend enterprise-wide or be contained within a specific line of business or segment. Examples of components include strategic goals and initiatives; business products and services; information flows, knowledge warehouses, and data objects; information systems, software applications, enterprise resource programs, and web sites; voice, data, and video networks; and supporting infrastructure including buildings, server rooms, wiring runs/closets, and capital equipment. Figure 1-8 on the next page provides examples of vertical and crosscutting EA components at each level of the EA³ Cube framework.
EA Analysis and Design Element #3: Current Architecture
The current architecture contains those EA components that currently exist within the enterprise at each level of the framework. This is sometimes referred to as the “as-is” view. The current view of the EA serves to create a ‘baseline’ inventory of current resources and activities that is documented in a consistent way with the future view of the EA so that analysts can see gaps in performance between future plans and the current capabilities. Having an accurate and comprehensive current view of EA components is an important reference for project planning, asset management, and investment decision-making. The current view of the EA is composed of ‘artifacts’ (documents, diagrams, data, spreadsheets, charts, etc.) at each level of the framework, which are archived in an online EA repository to make them useable by various EA stakeholders.
EA Analysis and Design Element #4: Future Architecture
The future architecture documents those new or modified EA components that are needed by the enterprise to close an existing performance gap or support a new strategic initiative, operational requirement, or technology solution. As is shown in Figure 1-9, the future architecture is driven at both the strategic and tactical levels in three ways: new directions and goals; changing business priorities; and emerging technologies. The EA cannot reflect these changes in the future architecture unless the enterprise’s leadership team provides the changes in strategic direction and goals; unless the line of business managers and program managers provide the changes in business processes and priorities that are needed to accomplish the new goals; and unless the support/delivery staff identifies viable technology and staffing solutions to meet the new business requirements.
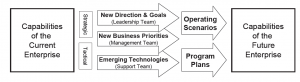
The future architecture should cover planned changes to EA components in the near term (tactical changes in the next 1-2 years), as well as changes to EA components that are a result of the implementation of long-term operating scenarios that look 3-10 years into the future. These scenarios incorporate different internal and external drivers and can help to identify needed changes in processes, resources, or technology that translate to future planning assumptions, which in turn drive the planning for new EA components.
– a methodology that enables enterprise planners – enterprise architects, organization and program managers, strategic planners, capital planners, and other planners – to work with sponsors and stakeholders to design an enterprise roadmap that defines needs of the enterprise, what can and will be done to address those needs, and what and when benefits will be achieved, and how those benefits will be measured.
EA Analysis and Design Element #5: EA Management Plan
The EA Management Plan articulates the EA program and documentation approach. The EA Management Plan also provides descriptions of current and future views of the architecture, and a sequencing plan for managing the transition to the future business/technology operating environment. The EA Management Plan is a living document that is essential to realizing the benefits of the EA as a management program. How the enterprise is going to continually move from the current architecture to the future architecture is a significant planning and management challenge, especially if IT resources supporting key business functions are being replaced or upgraded.
EA Analysis and Design Element #6: Threads
In the FEAF-II Framework, security is treated as a sixth sub-architecture domain that pervades all of the other five areas of the EA framework because security and privacy controls, to be most effective, need to be “built into” service workflows, data flows, systems, applications, and host networks. FEAF-II uses Governance instead of “Threads” to label the crosscuts, which include:
EA documentation includes ‘threads’ of common activity that are present in all levels of the framework. These threads include IT-related security, standards, and skill considerations.
Reference Architecture and Segment Architecture
A reference architecture is the part of an EA that provides standards and documentation for a particular type of capability throughout the enterprise – such as mobile services or cloud computing. A segment architecture is somewhat similar, but usually focuses one or more particular business units or functions – such as the finance and accounting group, or how an ERP system and all of its modules are going to be implemented (general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, benefits, etc.).
While the basic elements of EA analysis and design provide holistic and detailed descriptions of the current and future architecture in all areas of the underlying framework, it is important to also be able to articulate these relationships in discussions and presentations with executives, managers, support staff, and other EA stakeholders. Being able to understand and relate how the architecture fits together is essential to being able to use the EA in planning and decision-making throughout the enterprise. This communication is supported through two EA program resources: the EA Management Plan and the EA Repository. As was mentioned in the previous section, the EA Management Plan is a living document that is periodically updated so that it remains relevant as the ongoing primary reference for describing where the current and future architectures are at. The EA Repository is the on-line archive for EA information and the documentation artifacts that are described in the EA Management Plan.
The following is an example of how to communicate about EA with stakeholders. In this example, some questions are presented about how to apply an EA framework to an enterprise. These are the types of questions that should be answered in the first few sessions of EA program meetings in order to promote an understanding of how the EA framework and documentation can reflect the enterprise. In the following example (see as check-list) of how to talk about EA, the five levels and three vertical threads of the EA3 Cube framework are used for illustration. Notice how the questions build in a way that reflects the hierarchical relationships between the levels of the EA Framework.
Each area of the EA Framework represents a functional area of the enterprise. The EA3 Framework can be used in a top-down, bottom-up, or single-component manner. To begin to use the framework in a top down-manner, a series of questions at each level should be asked in order to determine how information about the enterprise will fit within that level of the framework.
The first questions to ask relate to the strategic ’Goals and Initiatives’ level of the framework. The questions are: (1) for what purpose does the enterprise generally exist (usually expressed in the mission statement) and (2) what kind of organization does the enterprise generally intend to be (often given in the vision statement)? What are the primary goals (strategic goals) of the enterprise? What then are the strategic initiatives (ongoing programs or new projects) that will enable the enterprise to achieve those goals? Finally, for this level, when will the enterprise know that it has successfully reached these strategic goals or is making progress toward these goals (outcome measures)?
Second is the business ‘Products and Services’ level of the framework, and it is important to first ask what are the ongoing activity areas (lines of business) that the enterprise must engage in to support and enable the accomplishment of both strategic initiatives and normal ‘maintenance/housekeeping’ functions? What then are the specific activities in each line of business (business services)? What are the products that are delivered in each line of business? How do we measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the line of business processes (input/output measures) as well as their contribution to strategic goals (outcome measures)? Do any of these business services or manufacturing processes need to be reengineered/improved before they are made to be part of the future architecture? What are the workforce, standards, and security issues at this framework level?
Third is the ‘Data and Information’ level of the framework. When the lines of business and specific business service/products have been identified, it is important to ask what are the flows of information that will be required within and between activity areas in order to make them successful? How can these flows of information be harmonized, standardized, and protected to promote sharing that is efficient, accurate, and secure? How will the data underlying the information flows be formatted, generated, shared, and stored? How will the data become useable information and knowledge?
Fourth is the ‘Systems and Applications’ level of the framework and it is important to ask which IT and other business systems and applications will be needed to generate, share, and store the data, information, and knowledge that the business services need? How can multiple types of IT systems, services, applications, databases, and web sites be made to work together where needed? How can configuration management help to create a cost-effective and operationally efficient ‘Common Operating Environment’ for systems and applications? What are the workforce, standards, and security issues at this level?
Fifth is the ‘Network and Infrastructure’ level of the framework and it is important to ask what types of voice, data, and video networks or computing clouds will be required to host the IT systems/applications and to transport associated data, images, and conversations, as well as what type of infrastructure is needed to support the networks (e.g. buildings, server rooms, other equipment). How can these networks be integrated to create a cost-effective and operationally efficient hosting and transport environment? Will these networks and clouds extend beyond the enterprise? What are the workforce, standards, and security issues at this level? What are the physical space and utility support requirements for these infrastructure resources?
Providing easy access to EA documentation is essential for use in planning and decision-making. This can be accomplished through the establishment of an EA repository to archive the documentation of EA components in the various areas of the EA framework. The EA repository is essentially a complex database that stores enterprise information, and exposes it via a website or other relevant channels such as tablets.
Using a holistic approach to Enterprise Architecture as a strategic initiative has become increasingly more popular among QualiWare users. The QualiWare toolset is being used for building and maintaining the Enterprise Architecture repository including all aspects of the enterprise such as strategy models, process architecture, application architecture, information architecture, organization architecture and infrastructure architecture. In security architecture and risk management the tool and repository covers features such as Risk Heatmaps to show the risk profile for a business area, and Control Coverage Maps to show the combination of the residual risk with the level of investment required to achieve that risk level. Due to the strategic nature of the EA work the results are often materialized in new initiatives and business transformation projects.
A typical scenario for mid-size to large size enterprise using QualiWare for EA or business transformation projects starts with a decision on the modeling standard (metamodel) to be used. Then the project model is decided and the tool is automatically configured to support this setup. When the analysts and designers have started building and approving models these models are published to the web by the QualiWare publishing server and the relevant employees or projects stakeholders are able to browse the published models, and also provide feedback or updates to content and relationships from their web browser.
A program or systems-level perspective is not sufficient for the management and planning of technology and other resources across enterprises with significant size and complexity. EA is the one discipline that looks at systems holistically as well as provides a strategy and business context. EA was described as being as both a management process and an analysis and design method that helps enterprises with business and technology planning, resource management, and decisionmaking. The purposes of an EA management program were described: strategic alignment, standardized policy, decision support, and resource development. The six basic elements of an EA analysis and design method were presented: the EA documentation framework, EA components, current EA views, future EA views, an EA Management Plan and multilevel threads that include security, standards, and workforce planning. An example of how to communicate the various areas of an EA framework was also provided.
EA3 version 2.0 is fully compliant with the Common Approach to Federal Enterprise Architecture and the FEAF-II artifacts.
| EA3 2.0 | Common Approach | |
| S-1 | Concept Overview | Concept Overview |
| S-2 | Strategic Plan | Strategic Plan |
| S-3 | Concept of Operations Scenarios | Concept of Operations Scenarios |
| S-4 | SWOT Analysis | SWOT Analysis |
| S-5 | Performance Measures Scorecard | Performance Measures Scorecard |
| B-1 | Business Process Diagram (core) | Business Process Diagram (core) |
| B-1.1 | Business Process/Product Matrix | |
| B-2 | Business Operating Plan | Business Operating Plan |
| B-2.1 | Node Connectivity Diagram | |
| B-3 | Business Service Catalog | Business Service Catalog |
| B-4 | Organization Chart | Organization Chart |
| B-5 | Use Case Narrative and Diagram | Use Case Narrative and Diagram |
| B-6 | Business Case / Alternatives Analysis | Business Case / Alternatives Analysis |
| D-1 | Logical Data Model (core) | Logical Data Model (core) |
| D-2 | Knowledge Management Plan* | Knowledge Management Plan* |
| D-3 | Data Quality Plan | Data Quality Plan |
| D-1.1 | Information Exchange Matrix | |
| D-4 | Data Flow Diagram | Data Flow Diagram |
| D-5 | Physical Data Model | Physical Data Model |
| D-6 | CRUD Matrix | CRUD Matrix |
| D-7 | State-Transition Diagram | State-Transition Diagram |
| D-8 | Event Sequence Diagram | Event Sequence Diagram |
| D-9 | Data Dictionary | Data Dictionary |
| D-10 | Object Library | Object Library |
| A-1 | Application Interface Diagram (core) | Application Interface Diagram (core) |
| A-2 | Application Communication Diagram | Application Communication Diagram |
| A-2.1 | System Data Flow Diagram | |
| A-2.2 | System/Operations Matrix | |
| A-3 | Application Interface Matrix | Application Interface Matrix |
| A-4 | Application Data Exchange Matrix | Application Data Exchange Matrix |
| A-5 | Application Service Matrix | Application Service Matrix |
| A-6 | Application Performance Matrix | Application Performance Matrix |
| A-7 | System/Application Evolution Diagram | System/Application Evolution Diagram |
| A-8 | Enterprise Service Bus Diagram | Enterprise Service Bus Diagram |
| A-9 | Application Maintenance Procedure | Application Maintenance Procedure |
| A-10 | Application Inventory | Application Inventory |
| A-11 | Software License Inventory | Software License Inventory |
| I-1 | Network Diagram (core) | Network Diagram (core) |
| I-2 | Hosting Concept of Operations | Hosting Concept of Operations |
| I-3 | Technical Standards Profile | Technical Standards Profile |
| I-4 | Technology Forecast | Technology Forecast |
| I-5 | Cable Plant Diagram | Cable Plant Diagram |
| I-6 | Wireless Connectivity Diagram | Wireless Connectivity Diagram |
| I-7 | Rack Elevation Diagrams (front and back) | Rack Elevation Diagrams (front and back) |
| I-8 | Data Center/Server Room Diagram | Data Center/Server Room Diagram |
| I-9 | Wiring Closet Diagram | Wiring Closet Diagram |
| I-10 | Point of Presence Diagram | Point of Presence Diagram |
| I-11 | Asset Inventory | Asset Inventory |
| I-12 | Facility Blueprints | Facility Blueprints |
| SP-1 | Security Controls Catalog (core) | Security Controls Catalog (core) |
| SP-2 | Security and Privacy Plan | Security and Privacy Plan |
| SP-3 | Certification & Accreditation Documentation | Certification & Accreditation Documentation |
| SP-4 | Continuous Monitoring Procedures | Continuous Monitoring Procedures |
| SP-5 | Disaster Recovery Plan | Disaster Recovery Plan |
| SP-6 | Continuity of Operations Plan | Continuity of Operations Plan |
 EA3 artifact SP-6: Continuity of Operations Plan
EA3 artifact SP-6: Continuity of Operations Plan
The Continuity of Operations Plan (COOP) uses a standard format for describing where all or part of the enterprise will relocate to if the normal operating location cannot be occupied for an extended period (more than a few days) due to a natural or man-made event.
The activation of the COOP relocation site may have to be accomplished in the midst of a local or national disaster that makes clarity, brevity, completeness, and flexibility (backups) key to success. The following are some of the recommended elements in a COOP document:
1. COOP Activation. Conditions for Activating the COOP.
2. COOP Roles and Responsibilities. A matrix of the roles and responsibilities (by position) of all personnel throughout the enterprise who are involved in activating the COOP. Alternates are provided for each position.
3. COOP Checklist. A step-by-step checklist of actions for each person participating in the COOP.
4. COOP Relocation Site Map and Directions. How to get to the COOP site from various probable routes.
5. COOP Relocation Site Activation. The process for activating the COOP site, establishing internal/external communications, and reconstituting key enterprise functions at the COOP site.
6. COOP Relocation Site Inventory. An inventory of systems, equipment, and supplies at the COOP relocation site, along with the person(s) responsible for ensuring that the systems are operational and the equipment is present when needed.
7. COOP Relocation Site De-Activation. Procedures for de-activating the COOP site and restoring it to a ‘ready status’ after a real relocation event or training exercise.
Enterprise Functions Have to Relocate
 EA3 artifact SP-5: Disaster Recovery Plan
EA3 artifact SP-5: Disaster Recovery Plan
The Disaster Recovery Plan is an assessment matrix and set of procedures to handle outages in various business and/or technology capabilities that do not require the enterprise to relocate its operations. Outages can be caused by natural or man-made events (e.g. fire, flood, power outage).
The activation of the Disaster Recovery Plan may have to be accomplished in the midst of a natural or man-made disaster that makes clarity, brevity, completeness, and flexibility (backups) key to success. The following are some of the recommended elements in a Disaster Recovery Plan:
1. Disaster Recovery Activation. Conditions for Activating the COOP.
2. Recovery Roles and Responsibilities. A matrix of the roles and responsibilities (by position) of all personnel throughout the enterprise who are involved in activating the COOP. Alternates are provided for each position.
3. Disaster Impact and Recovery Assessment. A standard matrix for assessing the type and duration of the outage, as well as the systems and functions throughout the enterprise that are affected. Depending on the type of outage and the projected period of outage (minutes, hours, days), the recovery procedure may differ.
4. Recovery Procedures. The procedures that are used to restore the business and/or system functions that have been disrupted. Examples include:
Enterprise Functions Do Not Relocate
 EA3 artifact SP-4: Continuous Monitoring Procedures
EA3 artifact SP-4: Continuous Monitoring Procedures
Continuous monitoring is the process and technology used to detect compliance and risk issues associated with an organization’s financial and operational environment.
Three operational disciplines:

 EA3 artifact SP-3: Certification & Accreditation Documentation
EA3 artifact SP-3: Certification & Accreditation Documentation
The System Accreditation Document uses a standard format for evaluating the security status of information systems throughout the enterprise. There are a number of parts to a system security accreditation as are illustrated in the example.