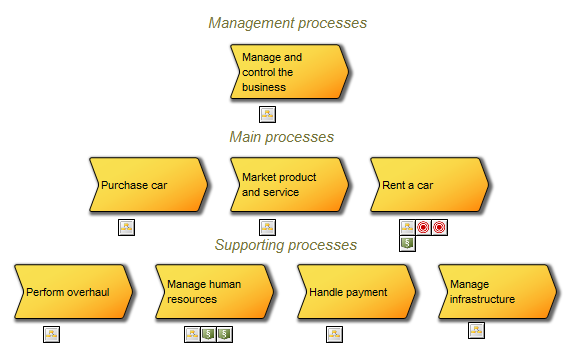
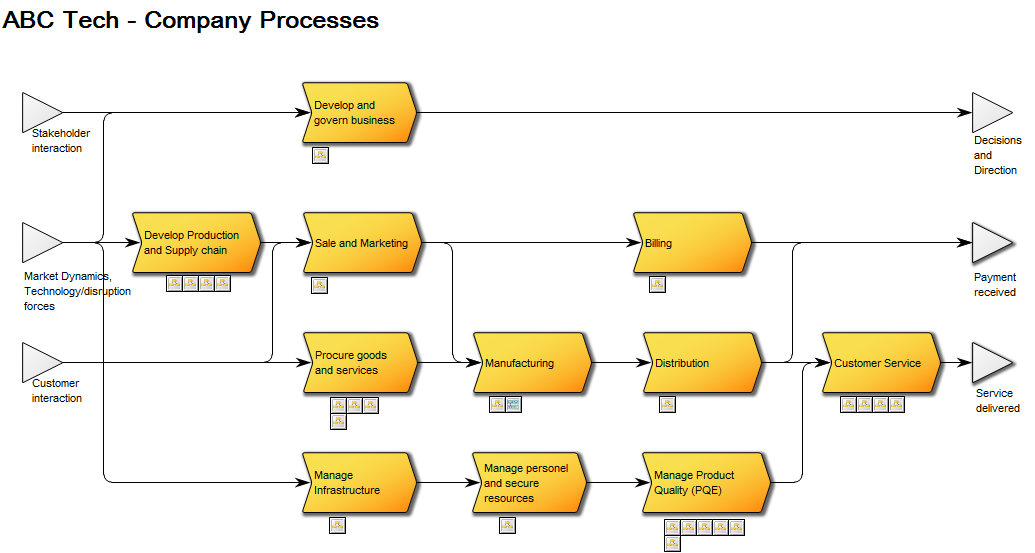
Purpose: The Purpose of the Generic Query template is to provide datasets for QualiWare System templates.
Core concerns: The Generic Query template is an auxiliary template. The Generic Query can be created using a Query Design template which enables you to easily structure the query for creating reports. When creating a Report for a diagram, the Generic Query created using the Query Design should be used as a Data Set in the Report Definition.
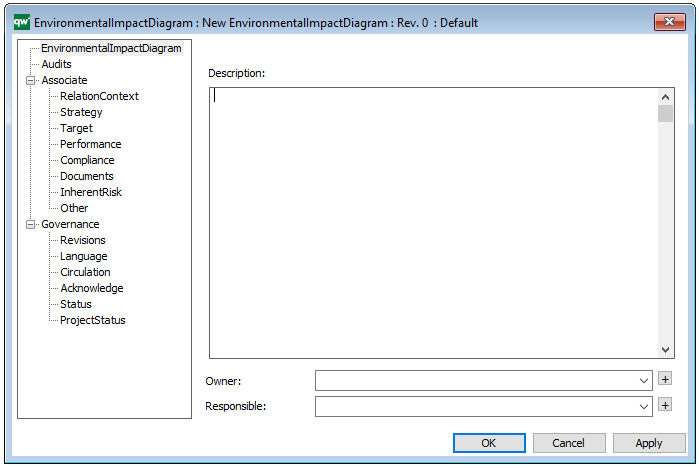
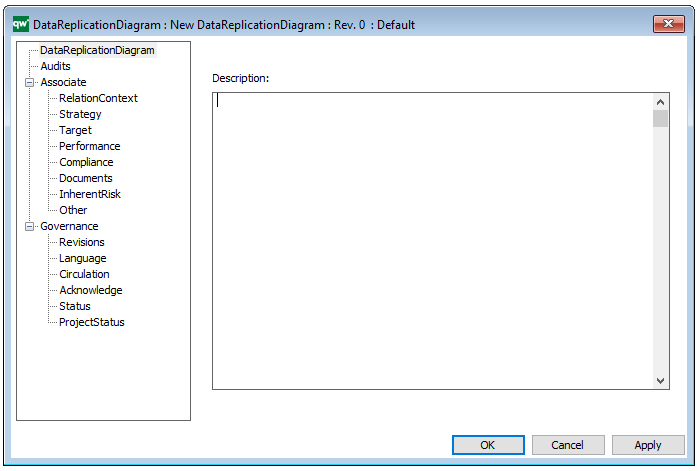
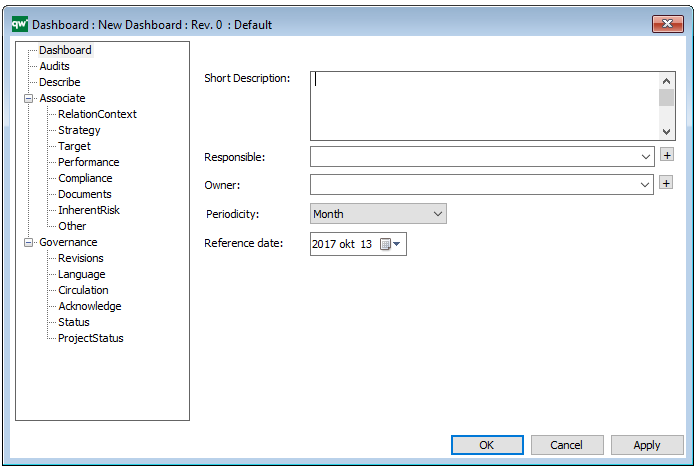
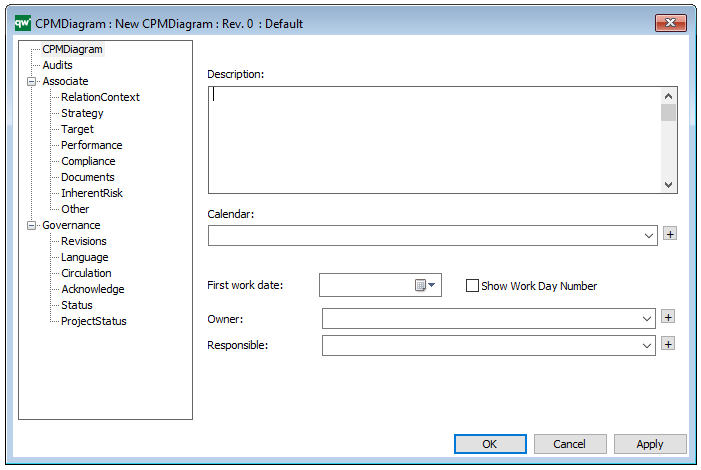
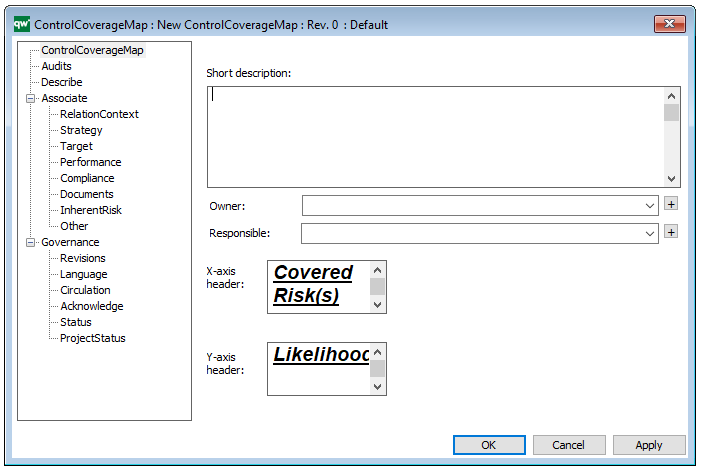
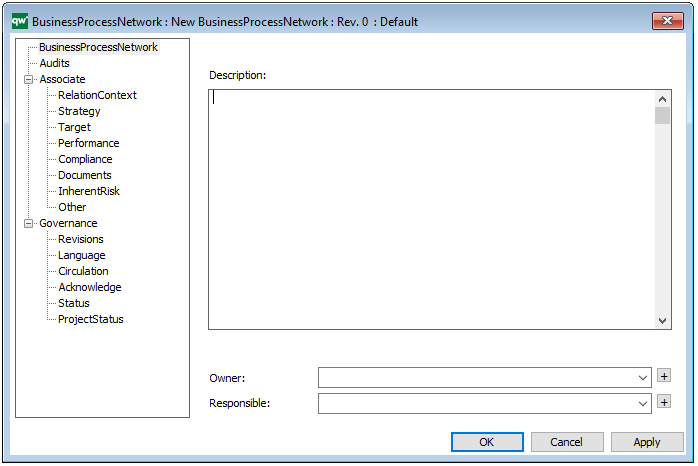
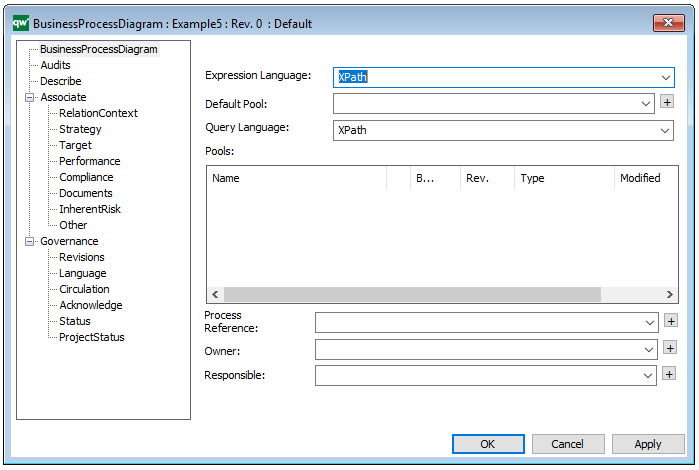
A Generic Query can also be generated using its Property Dialog, where you can link to Data Source and filter the data selection using a wizard – see example of the property dialog below:
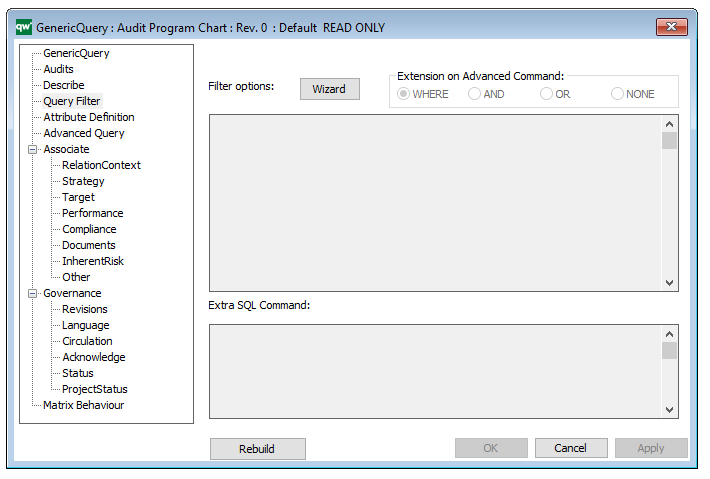
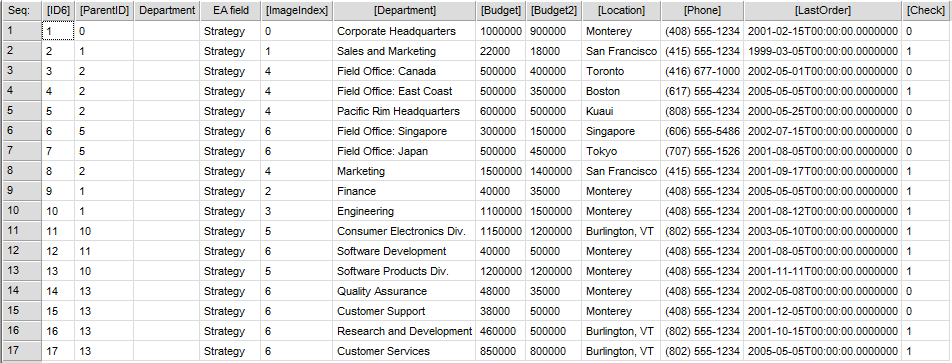
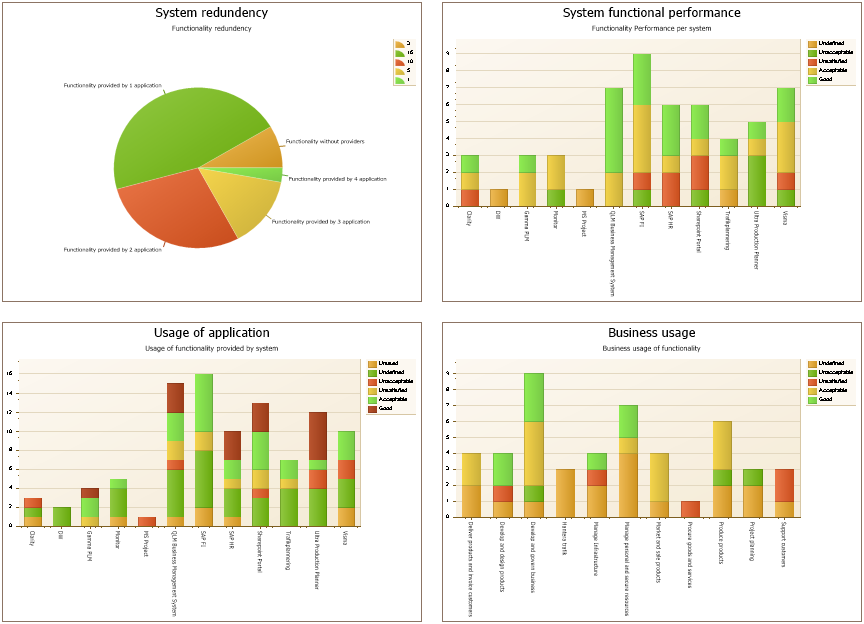
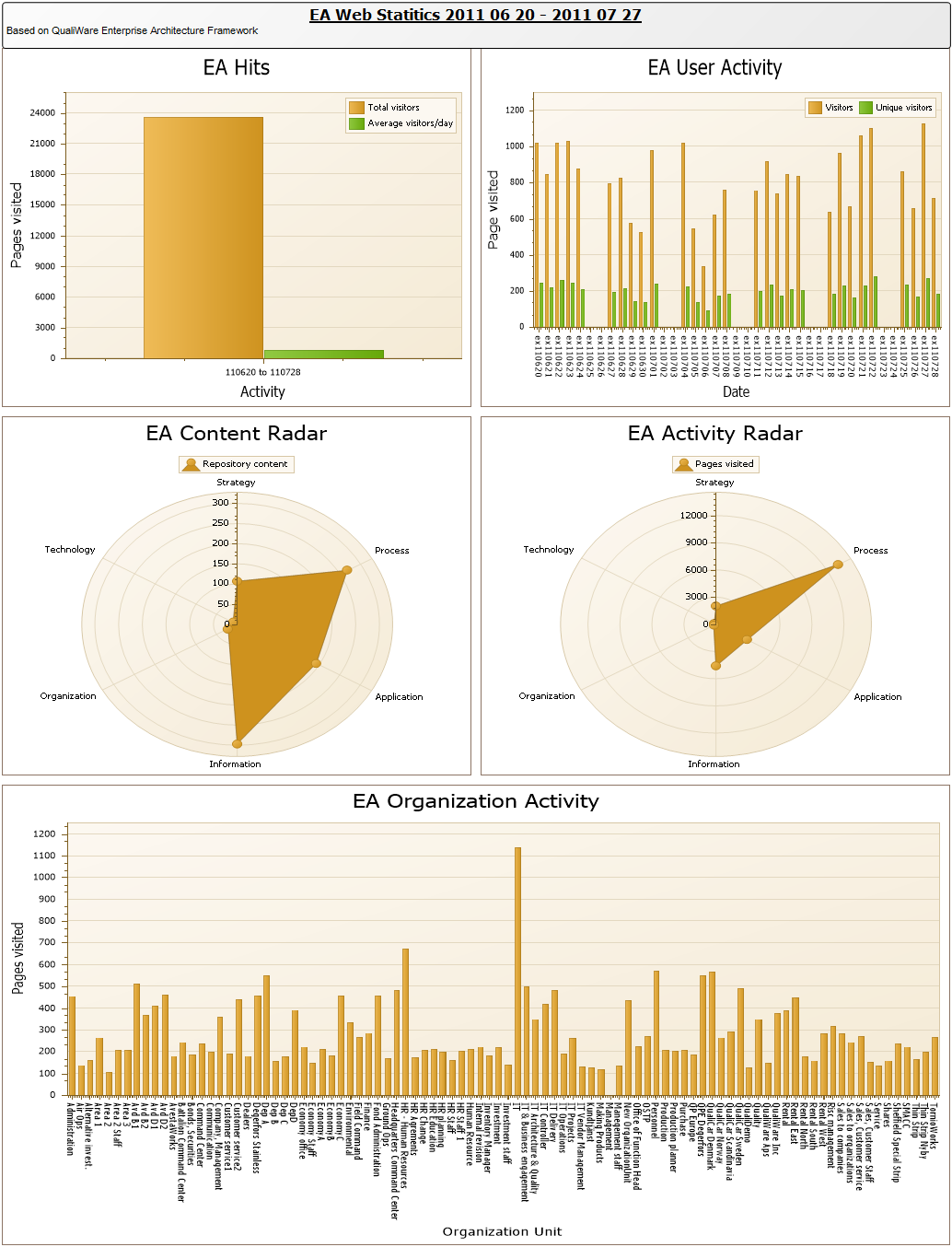
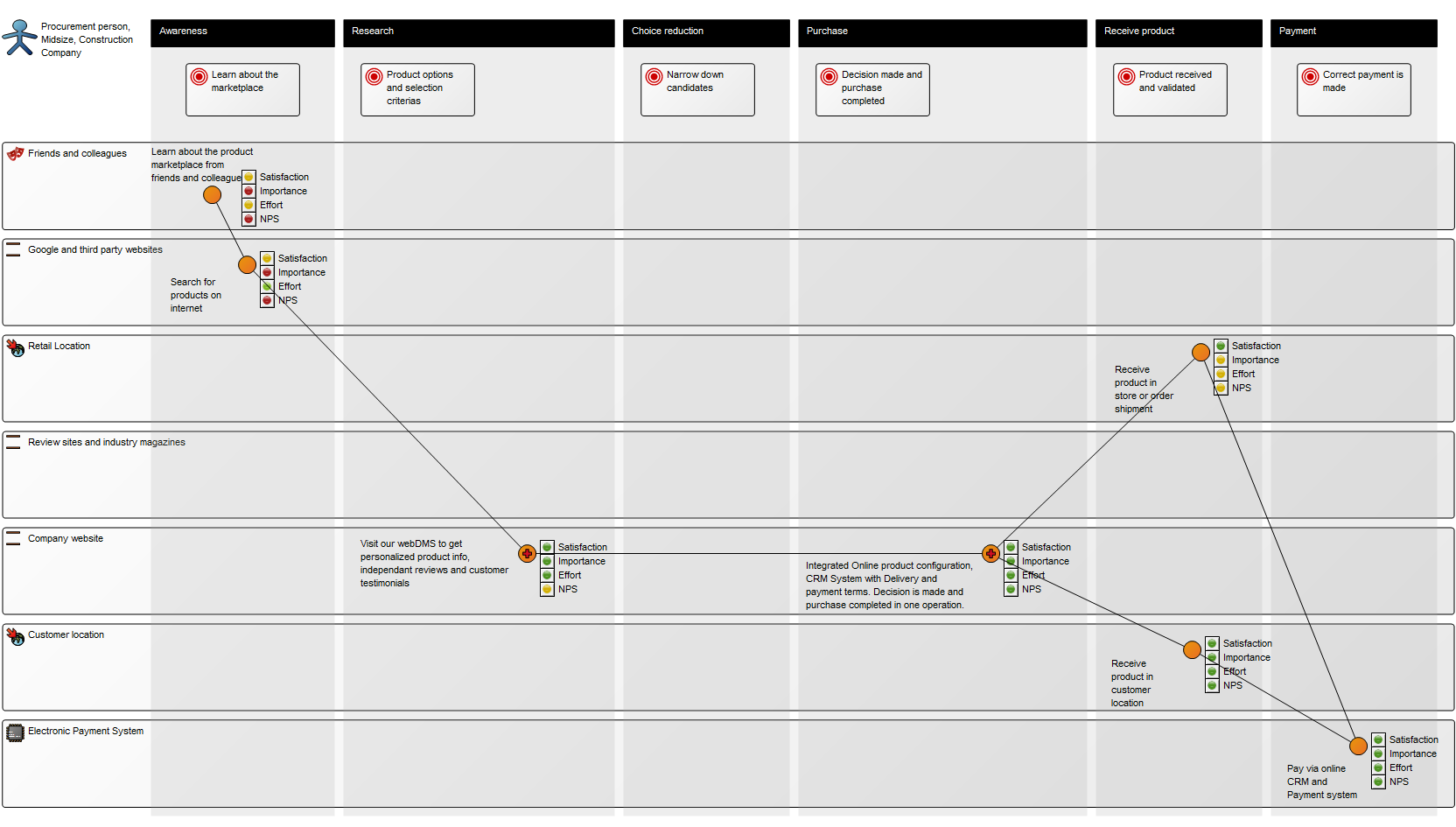
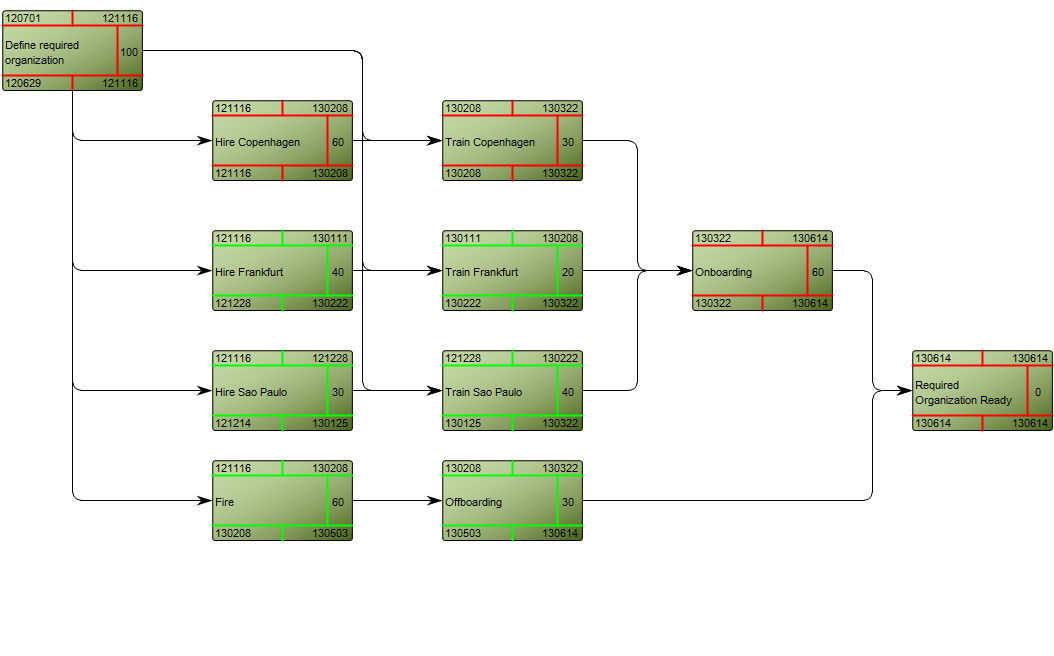
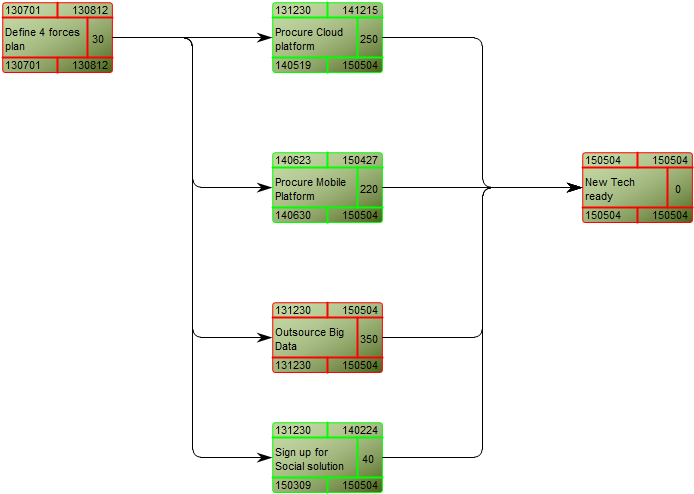
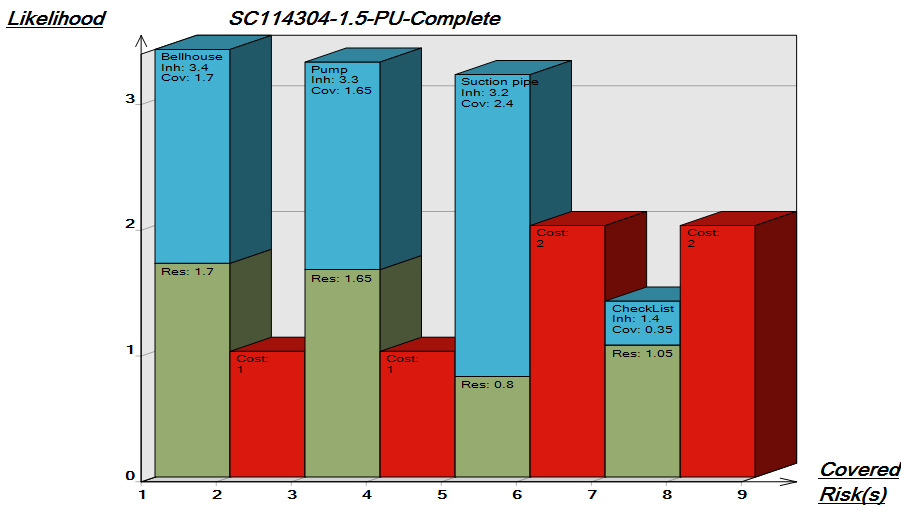
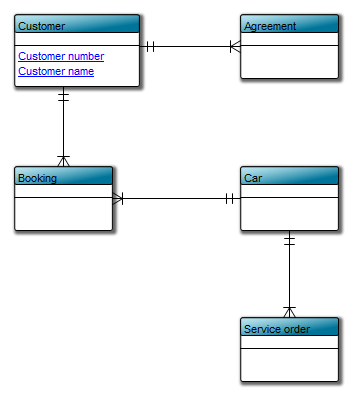
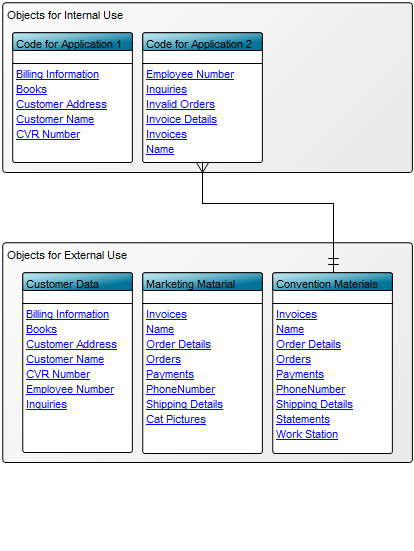
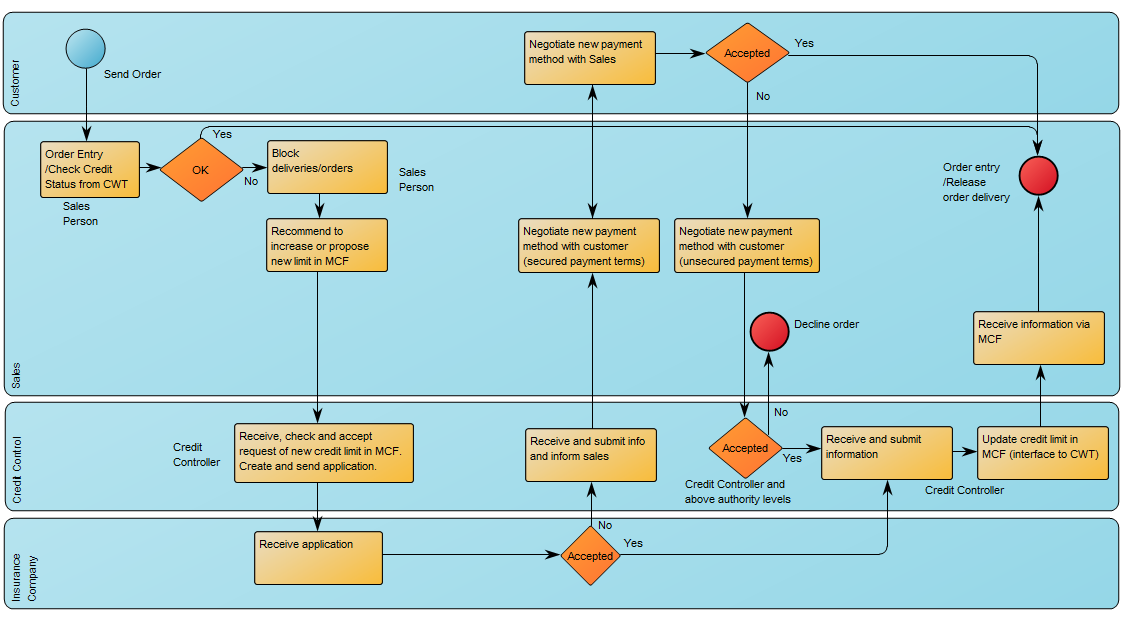
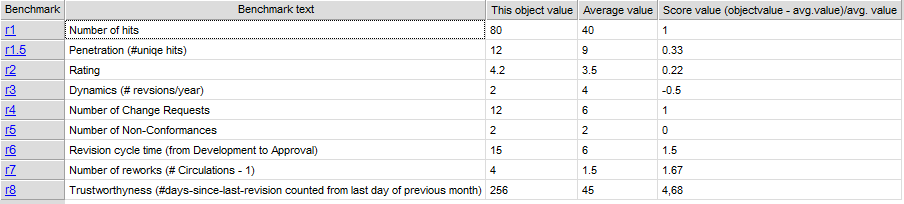
The Generic Query can, for example, take the form of data sheets:
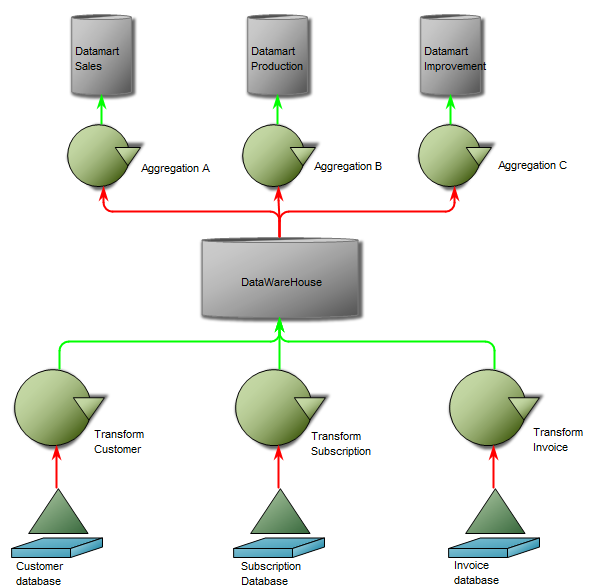
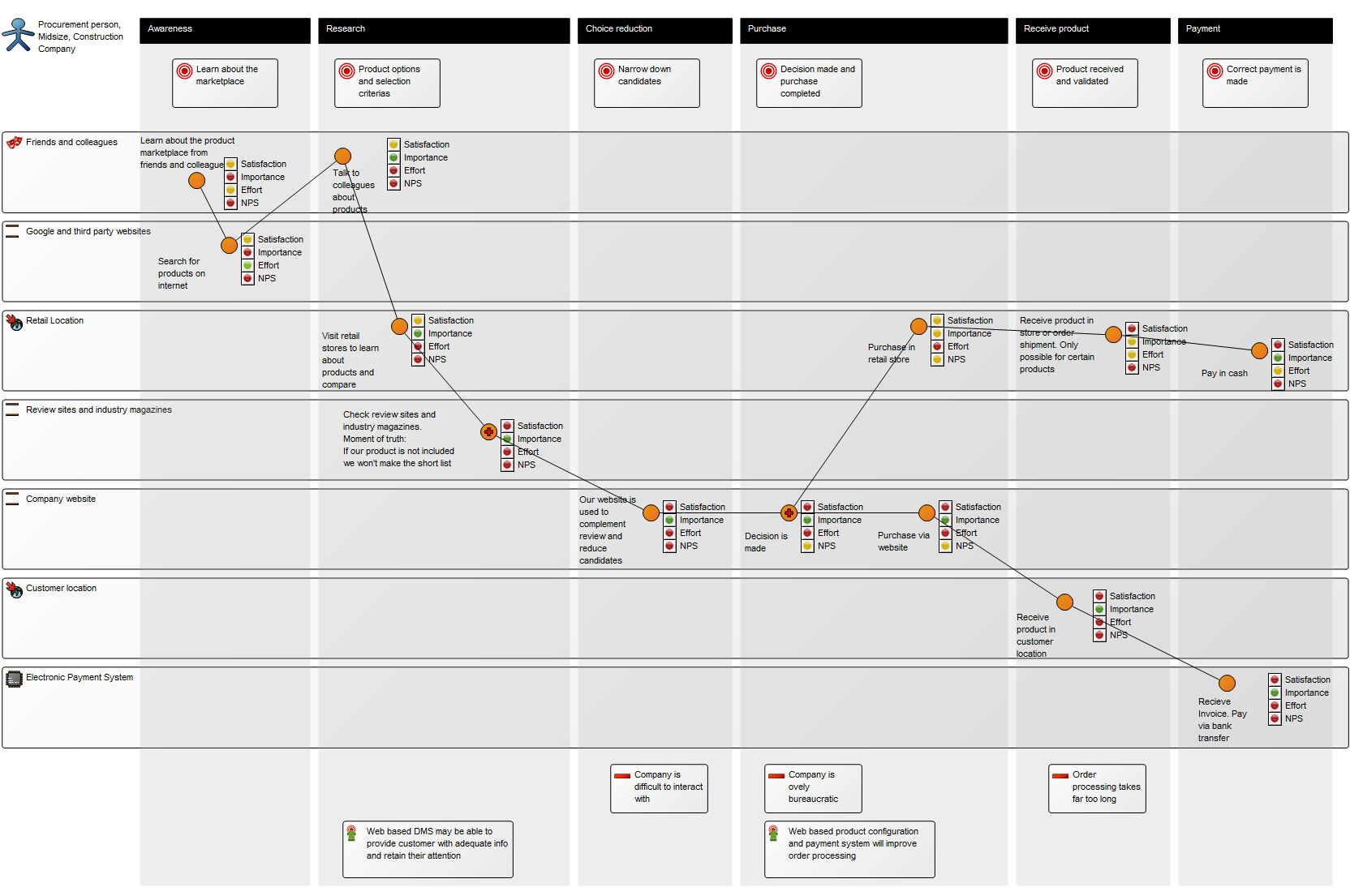
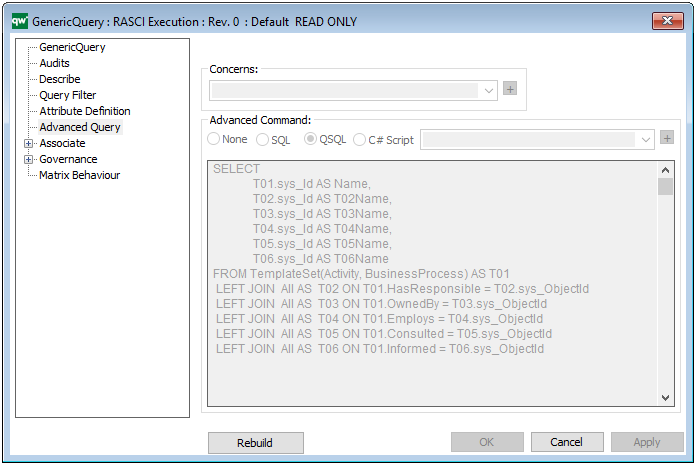
The Generic Query template can also execute a command using the Advanced Query tab:
Relation to other templates: Generic Queries are automatically created when creating a Query Design. Generic Queries are used in the following templates: HTML Template Definitions, HTML Embedded content, HTML Publisher and HTML Content tab.
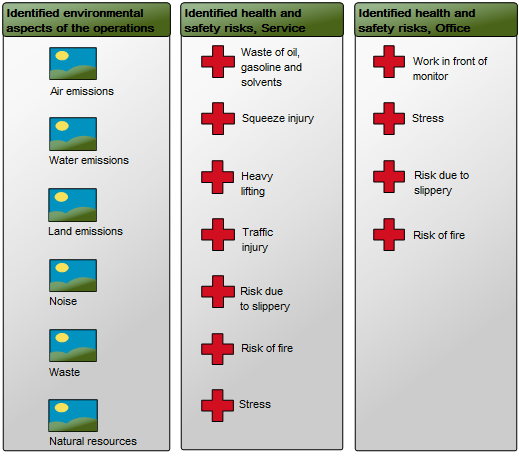
Properties and Metadata: The Generic Query can for example rentain the following information:
- A description
- Audits (auto generated information regarding its current state and access rights)
- Query Filter, including a wizard for filter options
- Attribute Definition
- Advanced Query
- Matrix Behavior
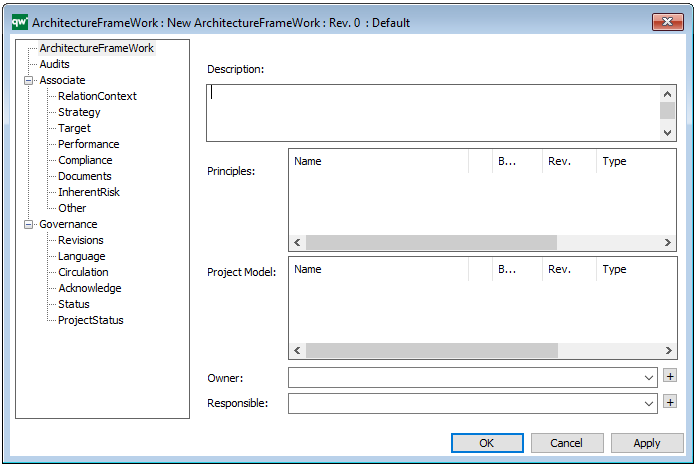
The above picture shows the properties dialogue window for the Generic Query where you can view and edit the diagram’s properties in QualiWare Lifecycle Manager.
Read more about Query Design and GenericQuery here.