To help facilitate a consistent and an aligned level of process documentation, a set of completeness score are available in the tool.

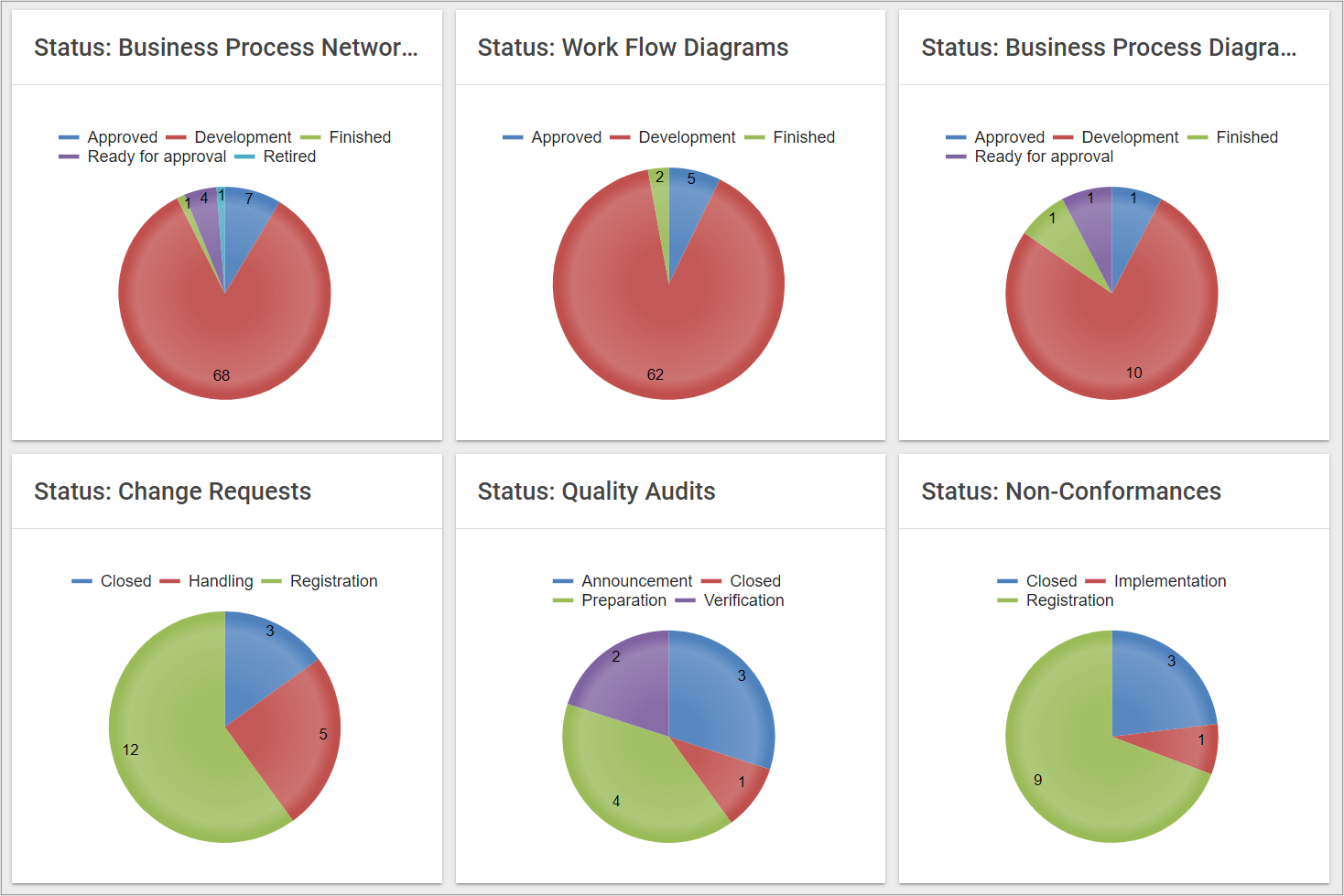
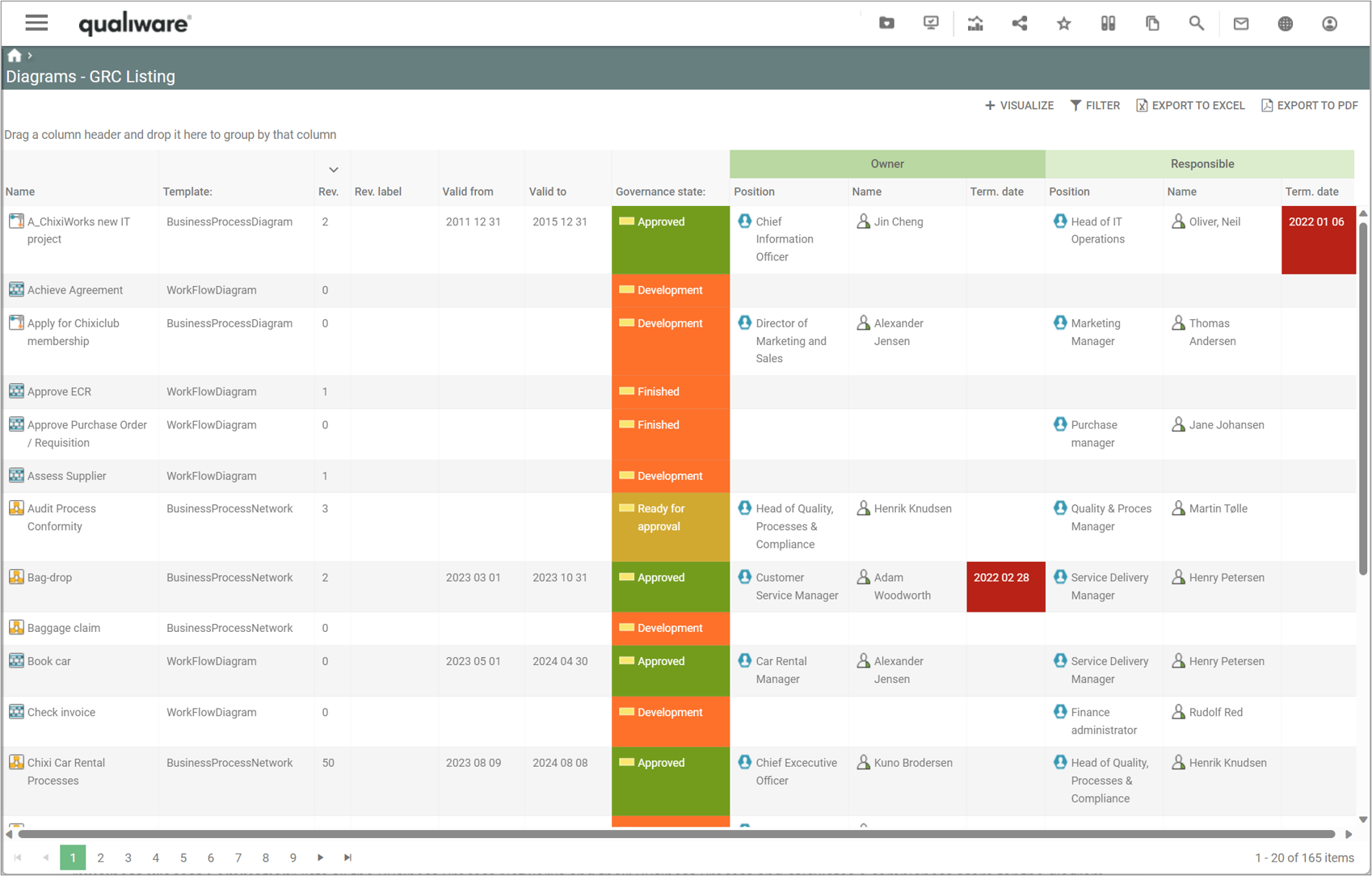
Two process completion lists are available from the standard Process menu. The lists are structured in a similar way, but differ in the scope. The first list contains all the business process networks in the repository, the 2nd list includes all workflow diagrams and Business Process Diagrams.
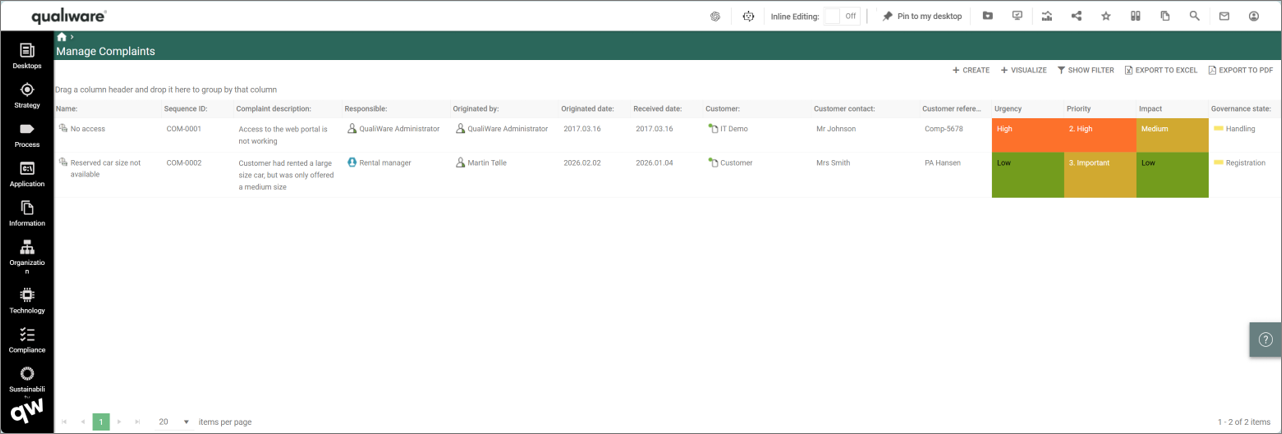
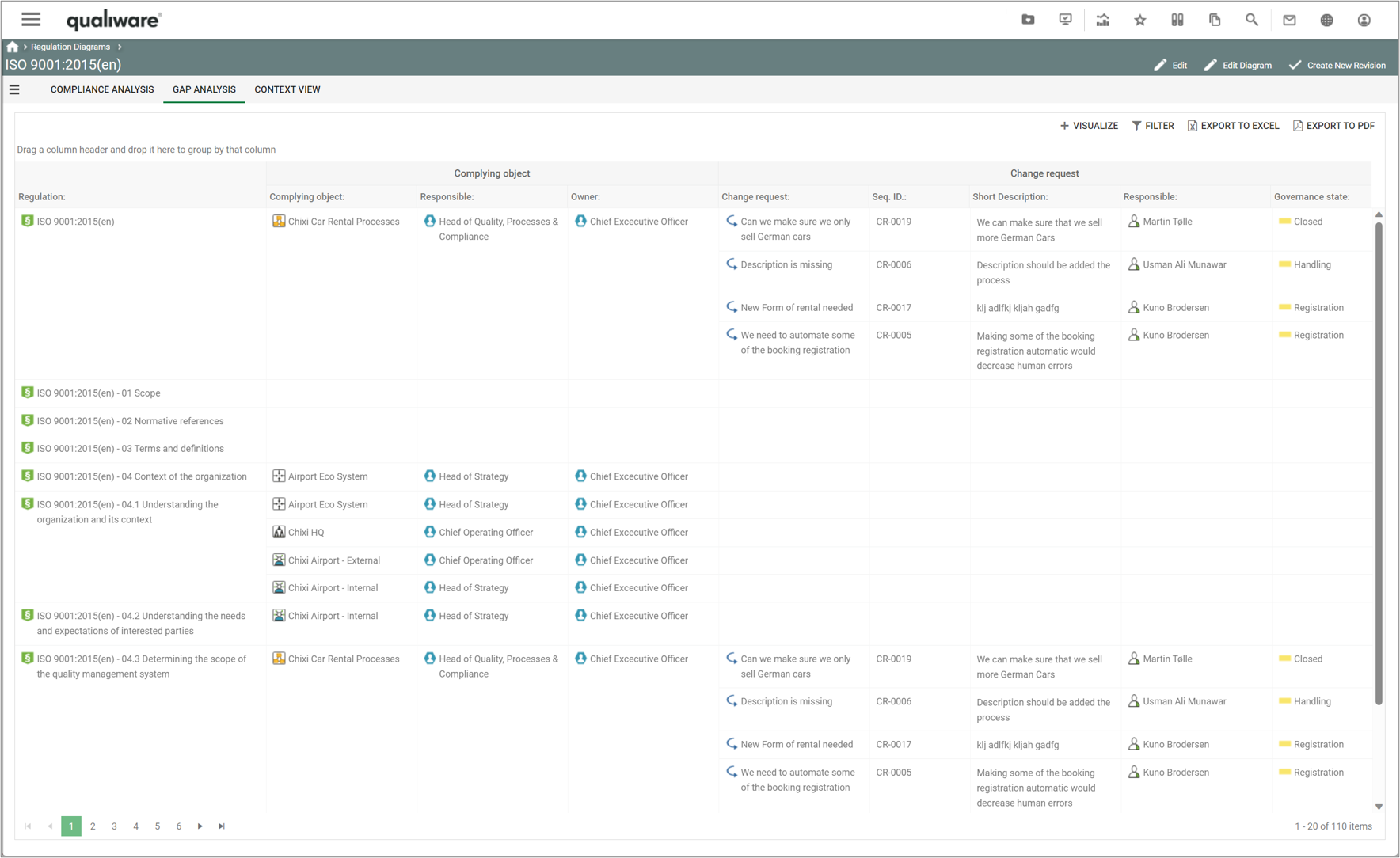
“Business Process Completion” lists all the Business Process Networks and their Business Processes and calculates a completeness score for the diagram as well as each business process.
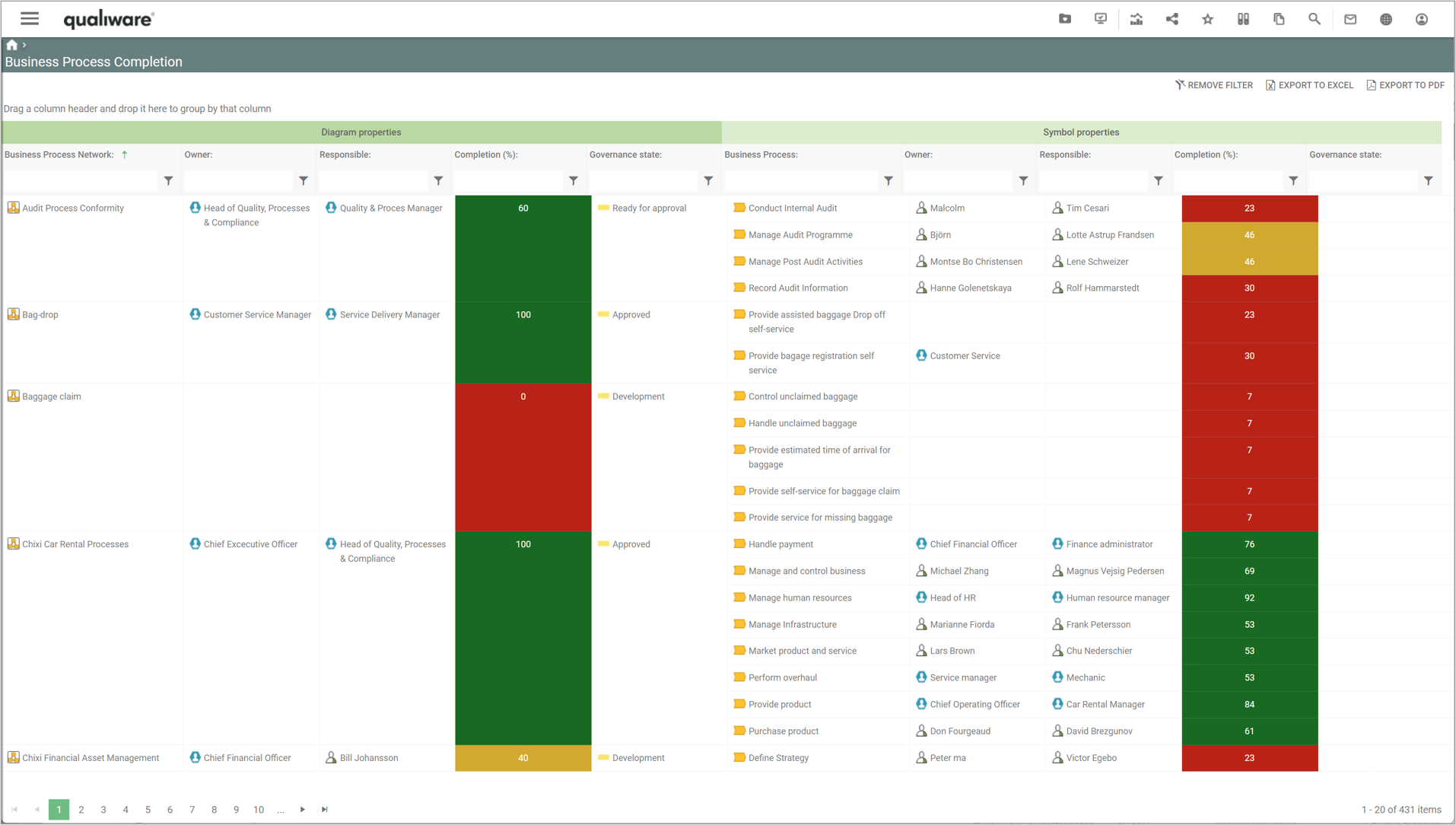
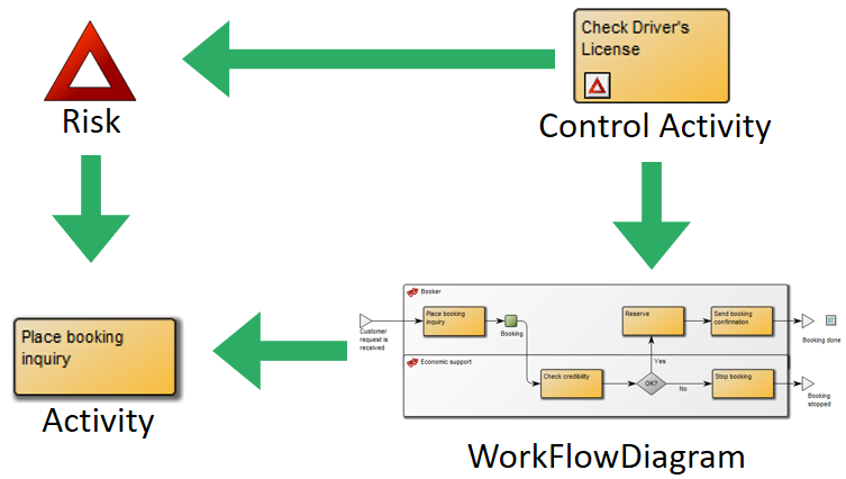
The completeness score of the diagram is a calculated based upon how many of the following fields have been filled out:
- Owner (OwnedBy),
- Responsible (HasResponsible),
- Description (Description),
- Valid from (RevisionValidFrom),
- Valid to (RevisionValidTo)
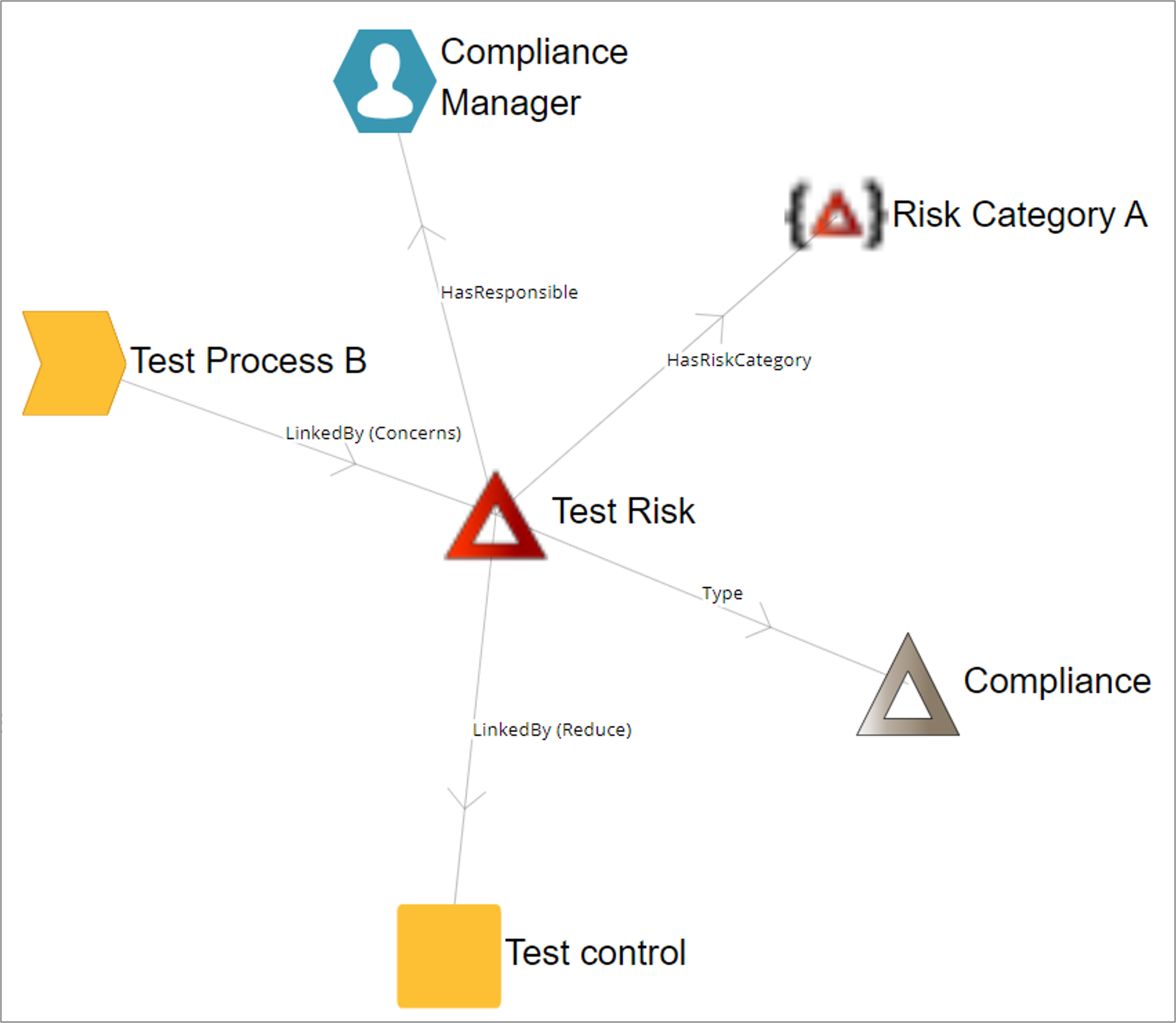
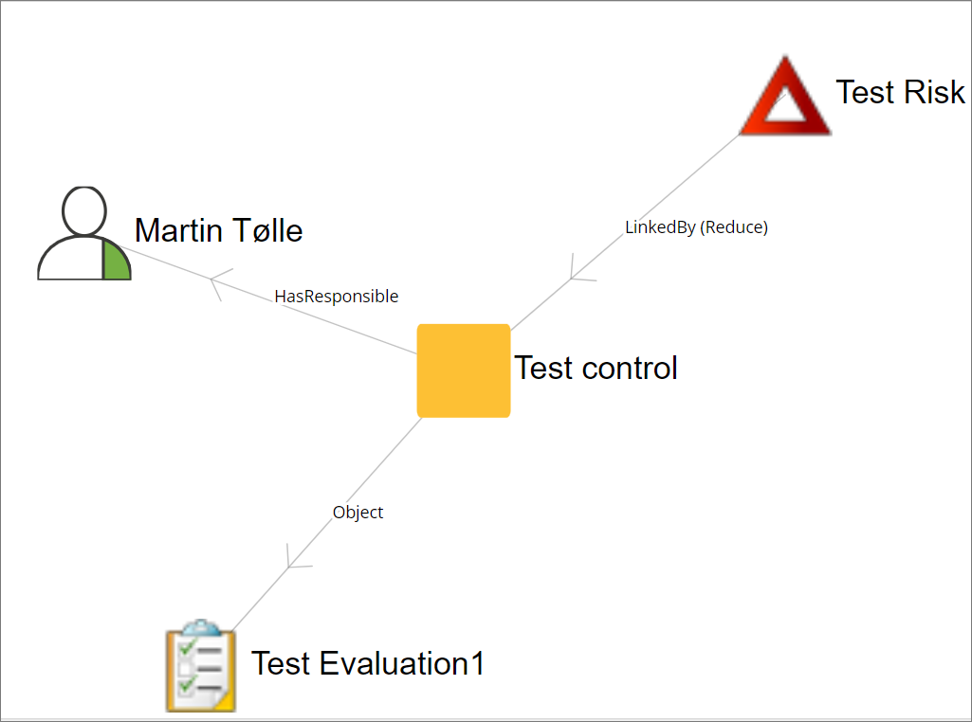
The completeness score of the business process is a calculated based upon how many of the following fields have been filled out:
- Owner (OwnedBy),
- Responsible (HasResponsible),
- ShortDescription (ShortDescription),
- Description (Description),
- Purpose (Purpose),
- Resources (Employs),
- UsesInformation (UsesInformation),
- IT Support (HasITSupport),
- Deliver Capability (DeliverCapability),
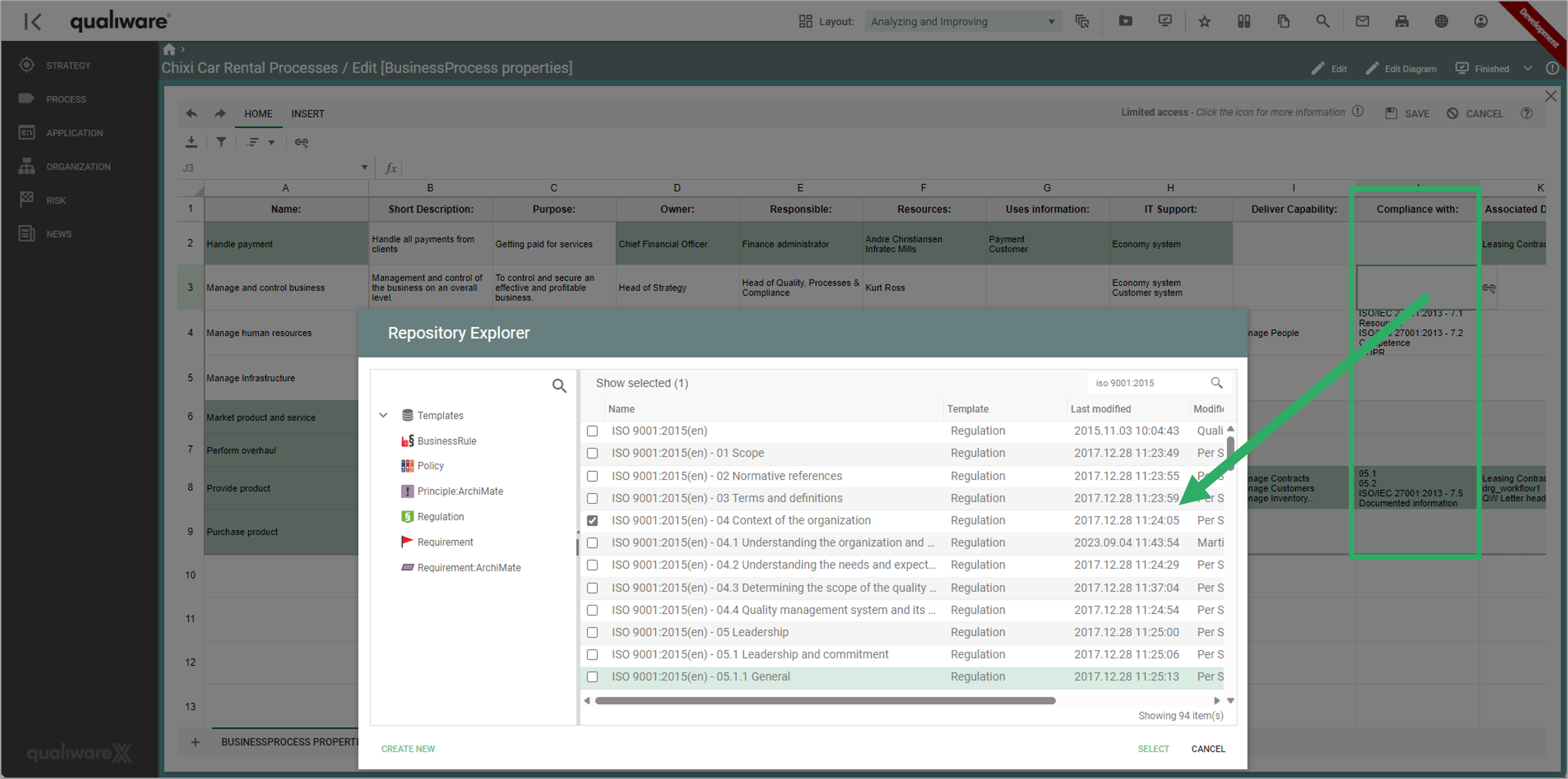
- Compliance With (ComplianceWith),
- Associated Document (AssociatedDocument),
- Valid from (RevisionValidFrom),
- Valid to (RevisionValidTo)
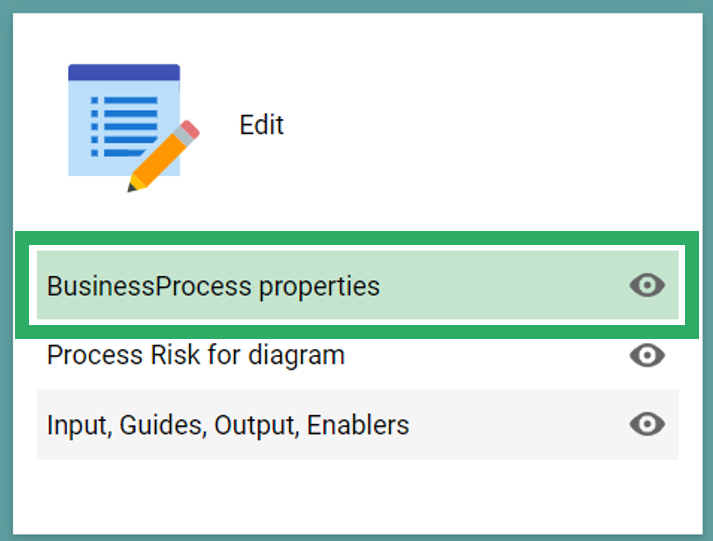
The fields in the calculation corresponds to the fields in the standard “Business Properties” spreadsheet available in the diagram view on the dashboard layout or on the tab in the classic view. In addition to the 11 fields in the spreadsheet, the completeness score includes the two validation dates (Valid from and Valid to).
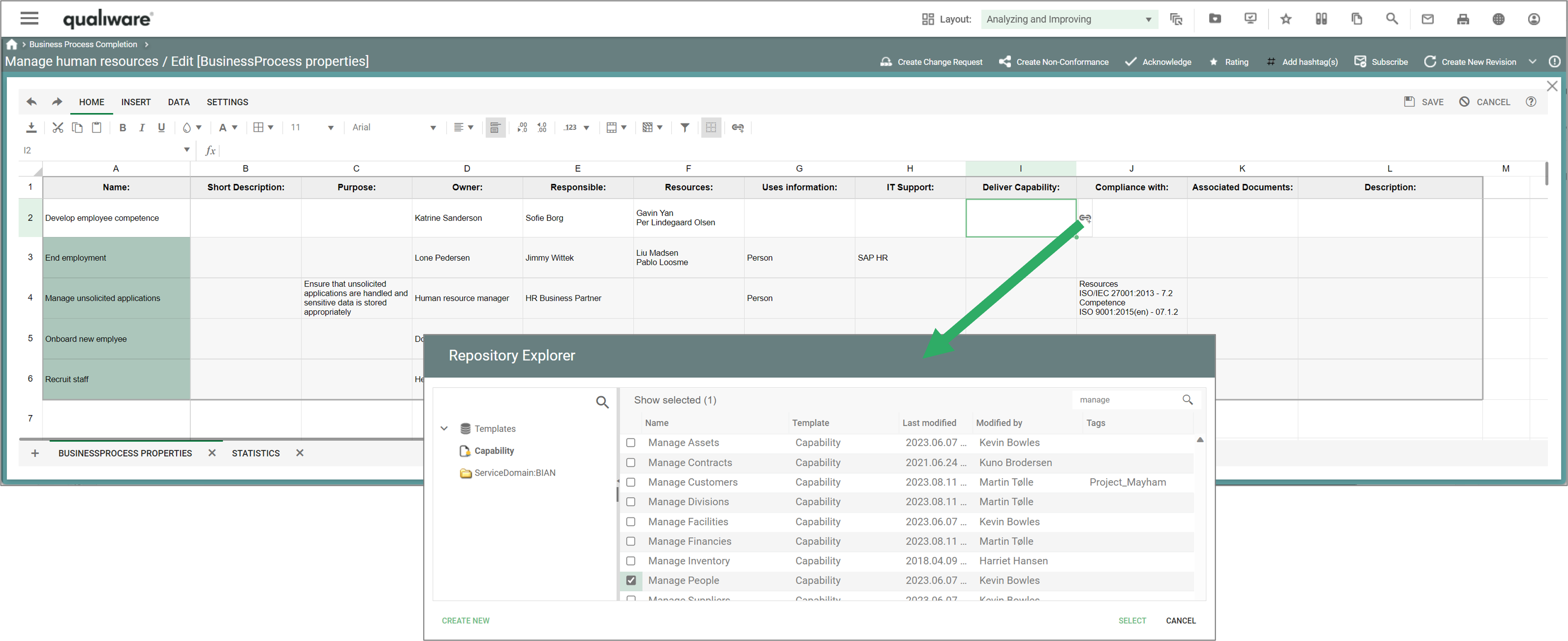
It is possible to configure the scope of the completeness score, selecting the appropriate fields in the underlying query.
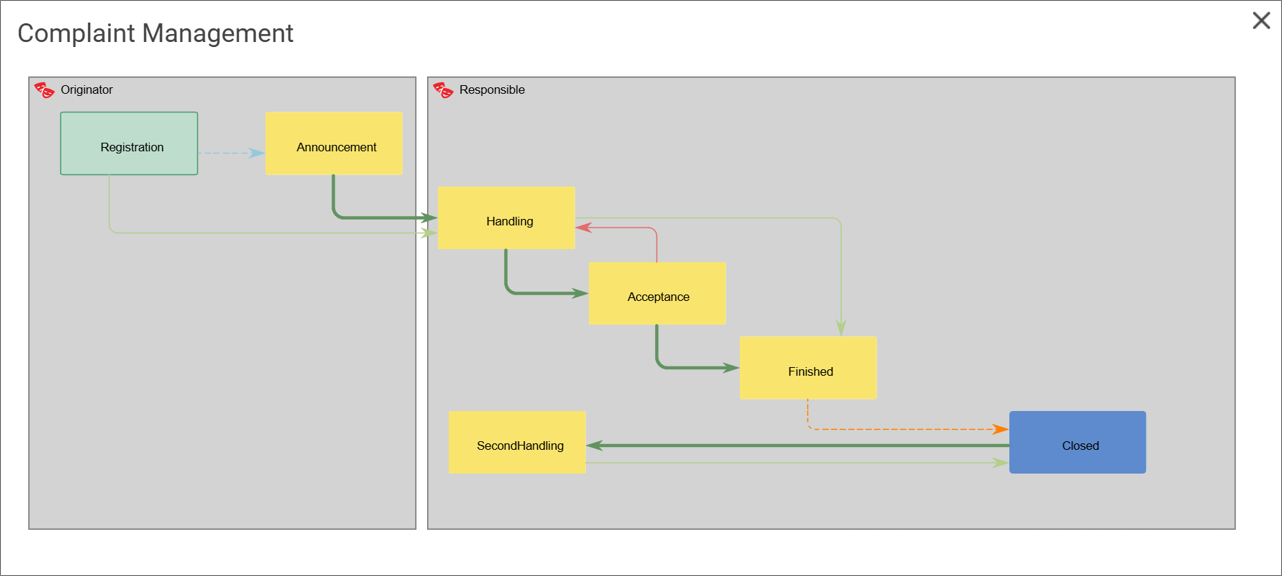
“Work Process Completion” lists all WorkFlowDiagrams and BusinessProcessDiagrams and their Activities, and calculates their completeness score for the diagram and each of the activities.
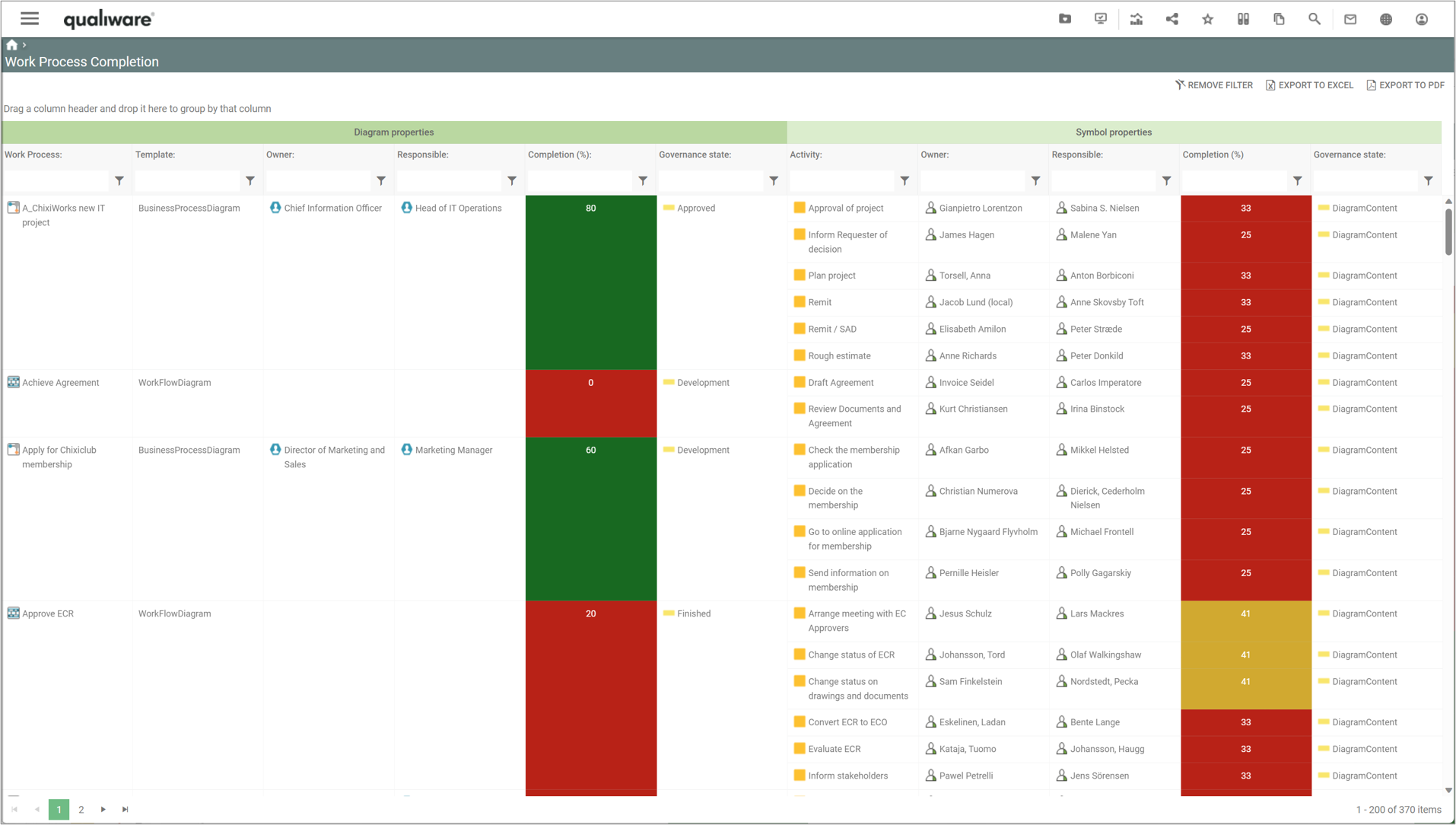
The calculation is similar to the one above for the Business Process Network. The only exception is that the activity completion is calculated based upon 12 fields, since “Purpose” is not part of an activity-object.
Diagram level completion
The two lists in the left menu, shows the completion level for all process-diagrams in the repository.
The completion level for a specific diagram is also available from the diagram-dashboards, under the “Analyses” tiles.
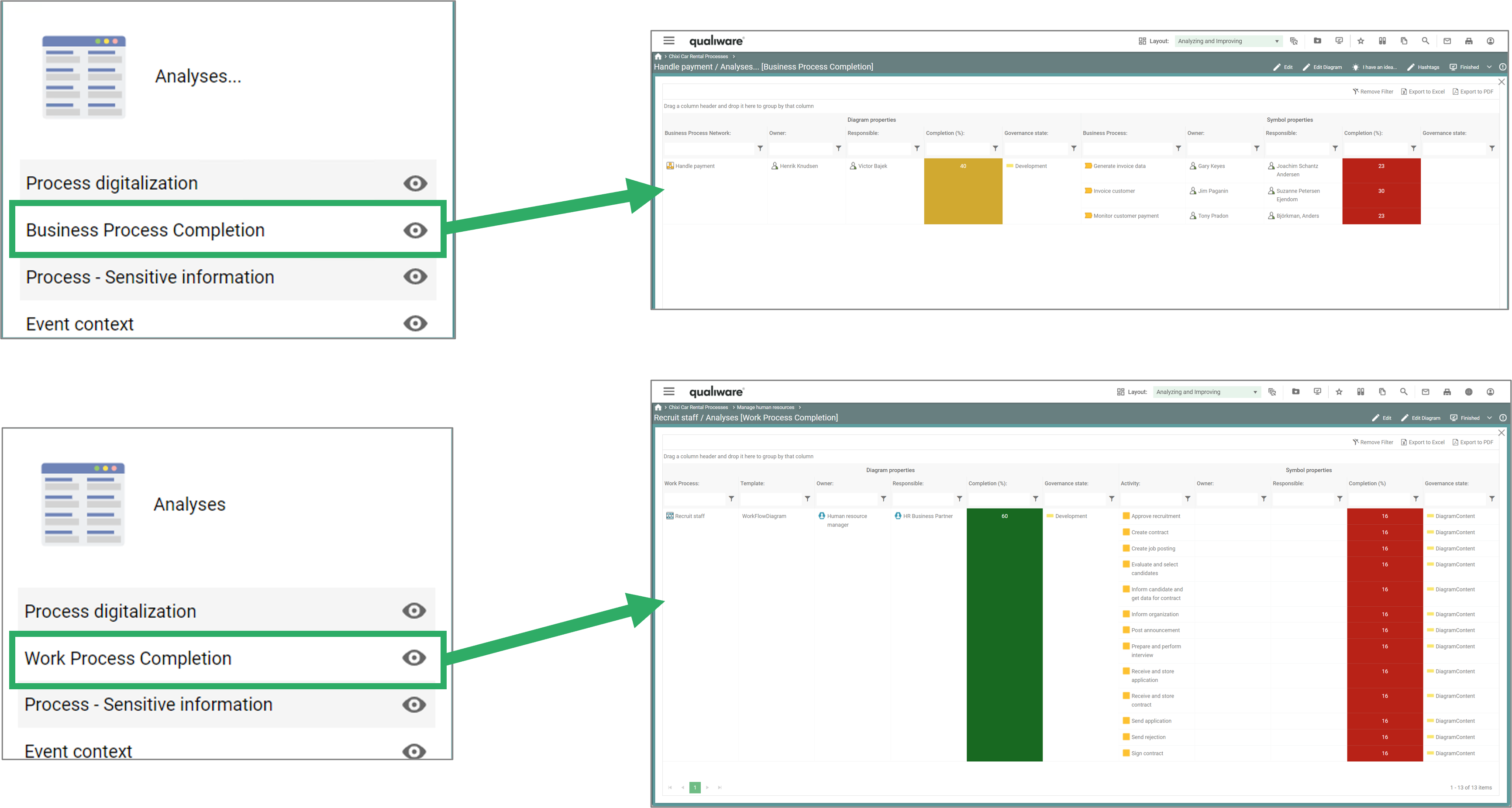





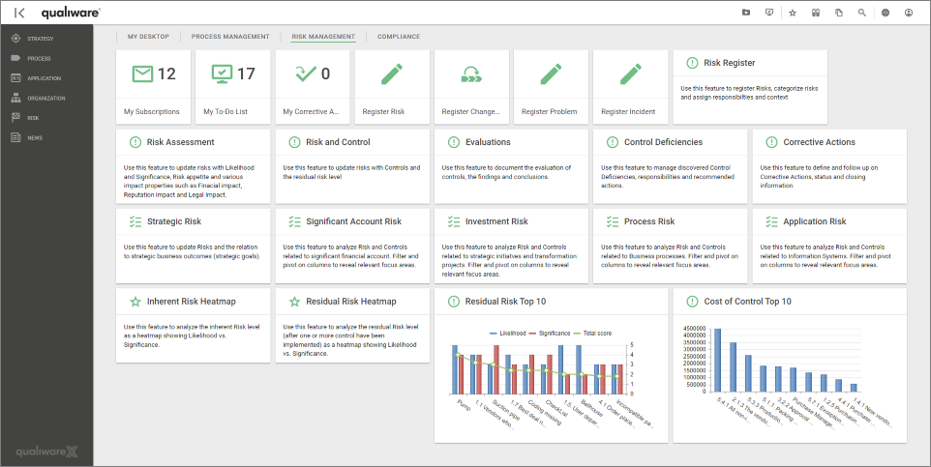

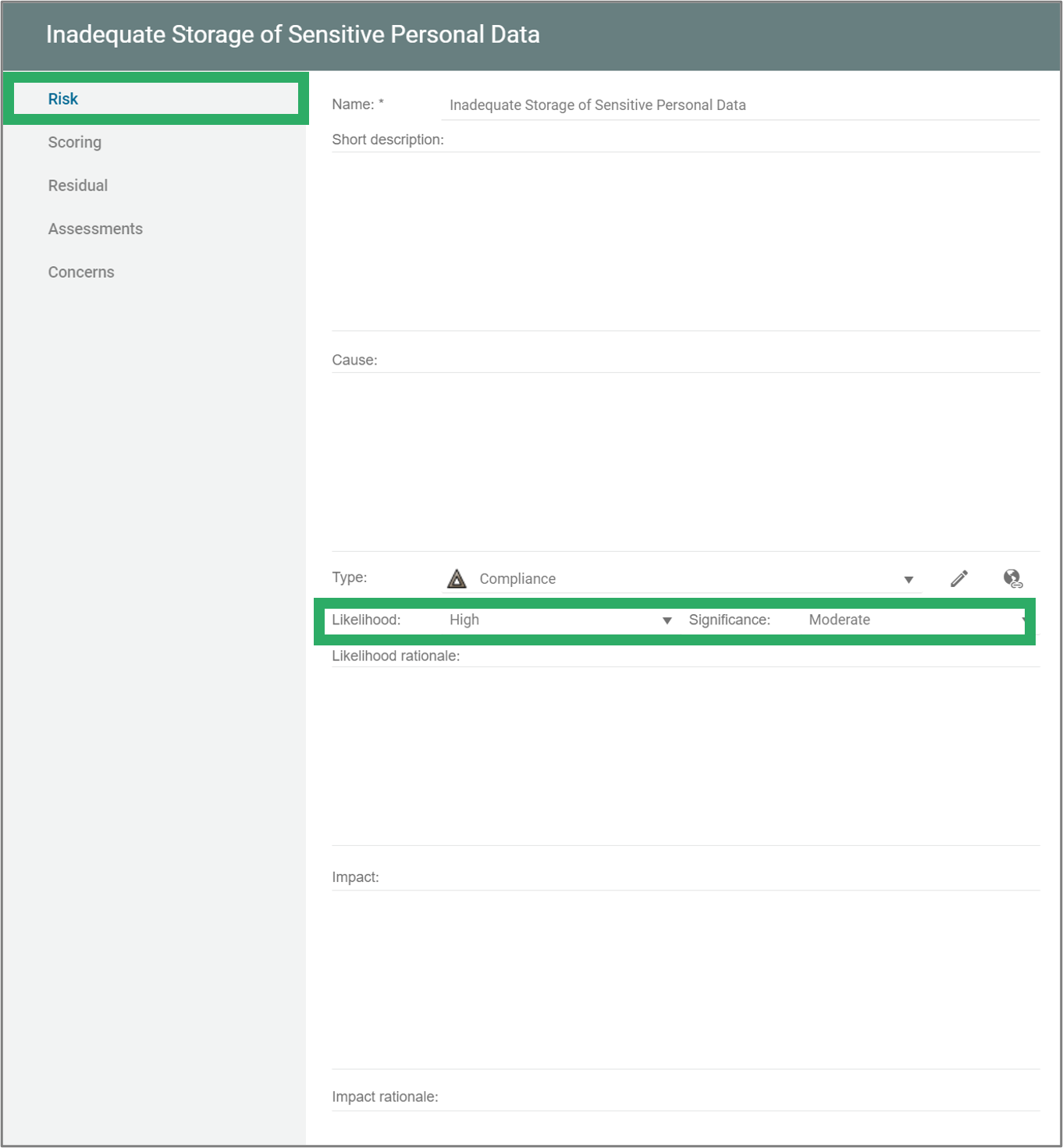
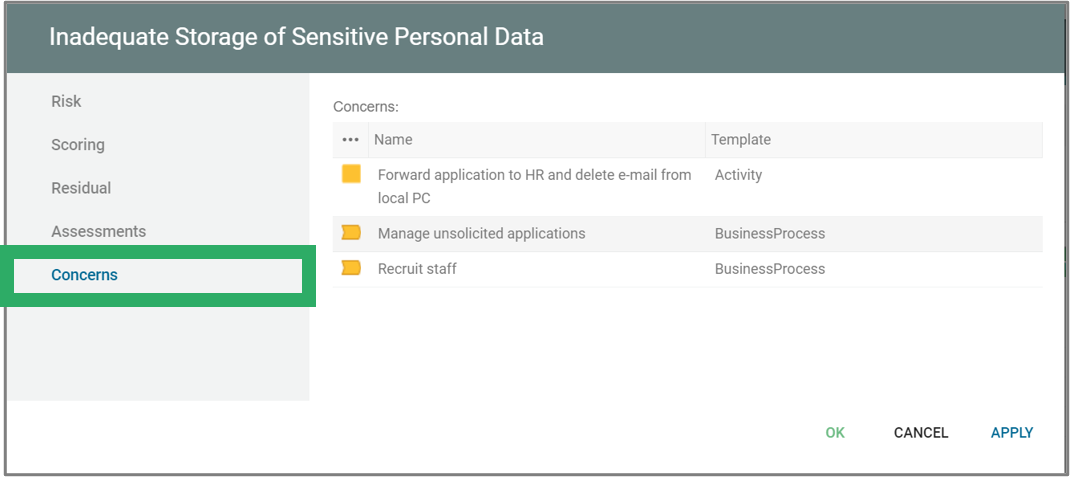
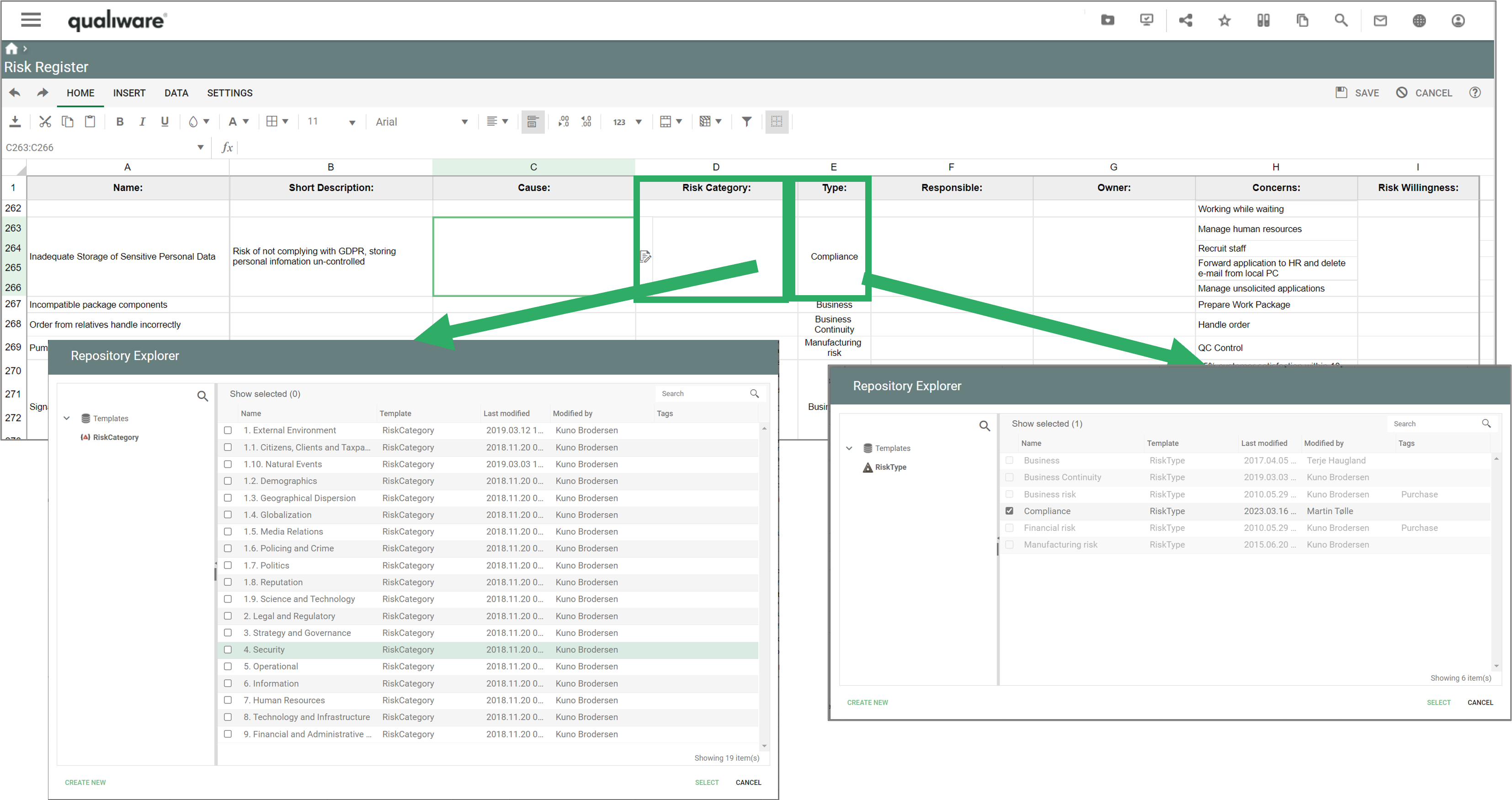

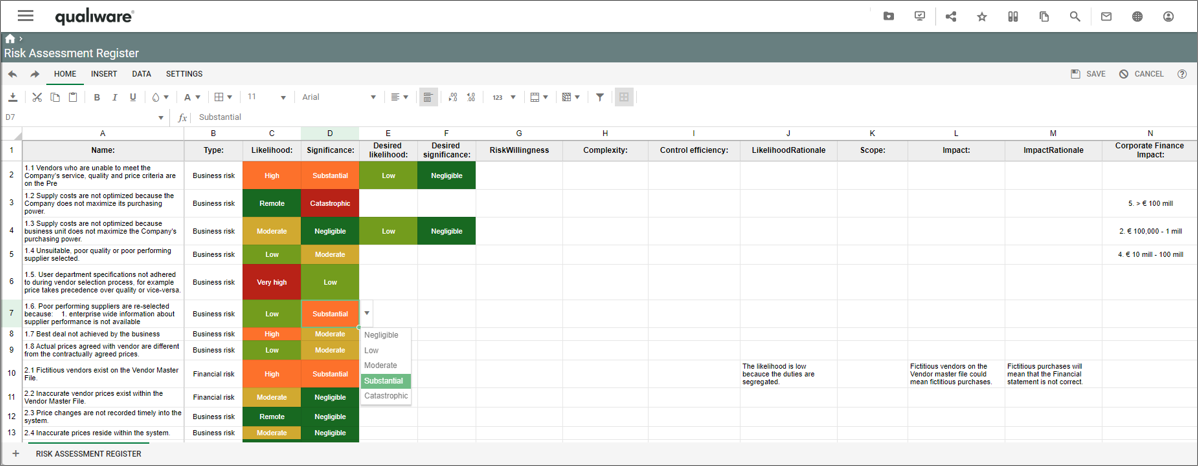

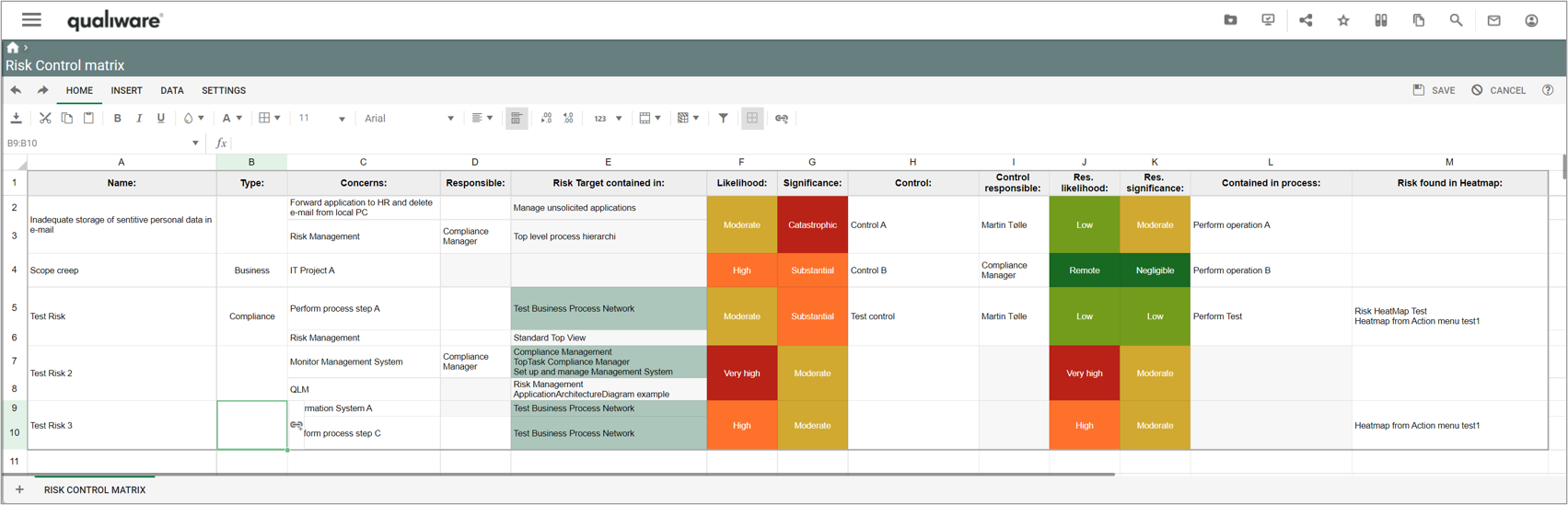









 Two lists of processes are available from the standard Process menu. The lists are structured in a similar way, but differs in the scope.
Two lists of processes are available from the standard Process menu. The lists are structured in a similar way, but differs in the scope.
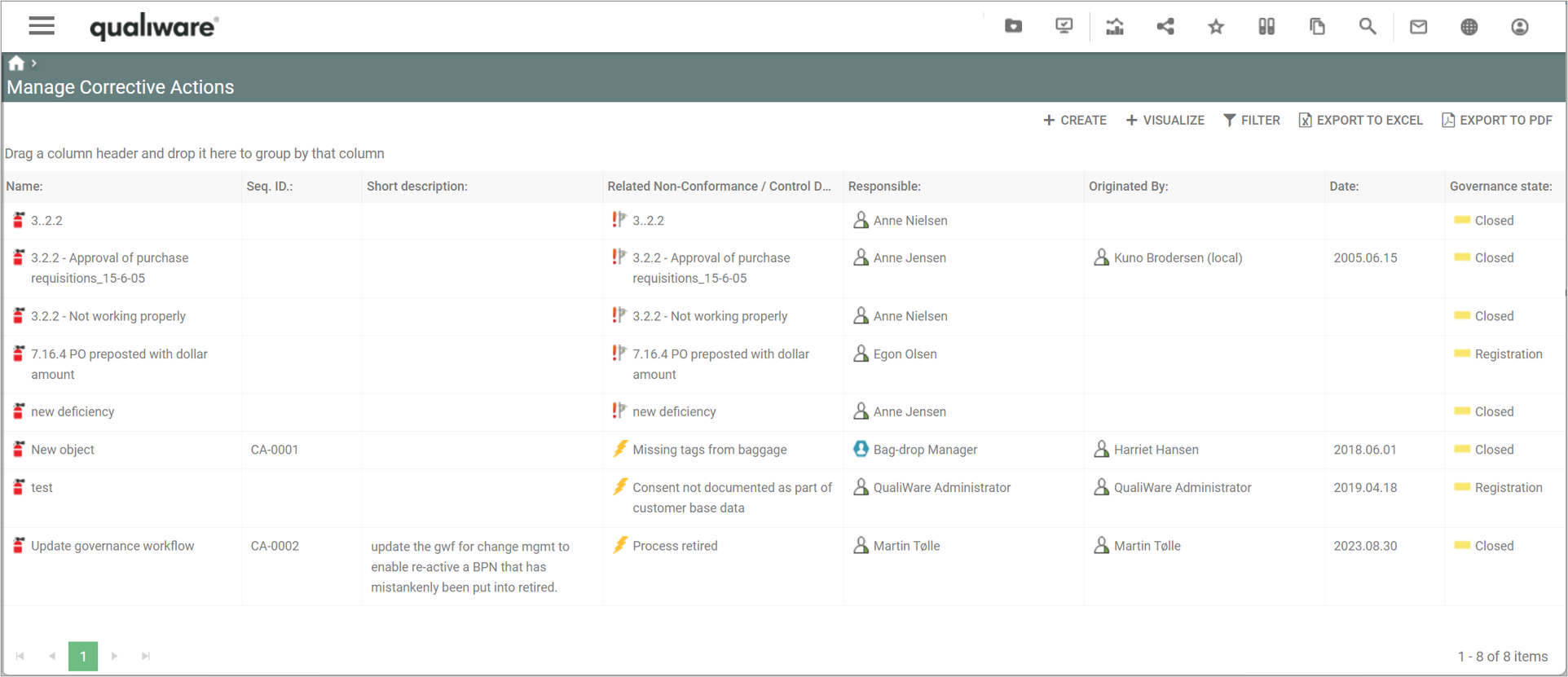
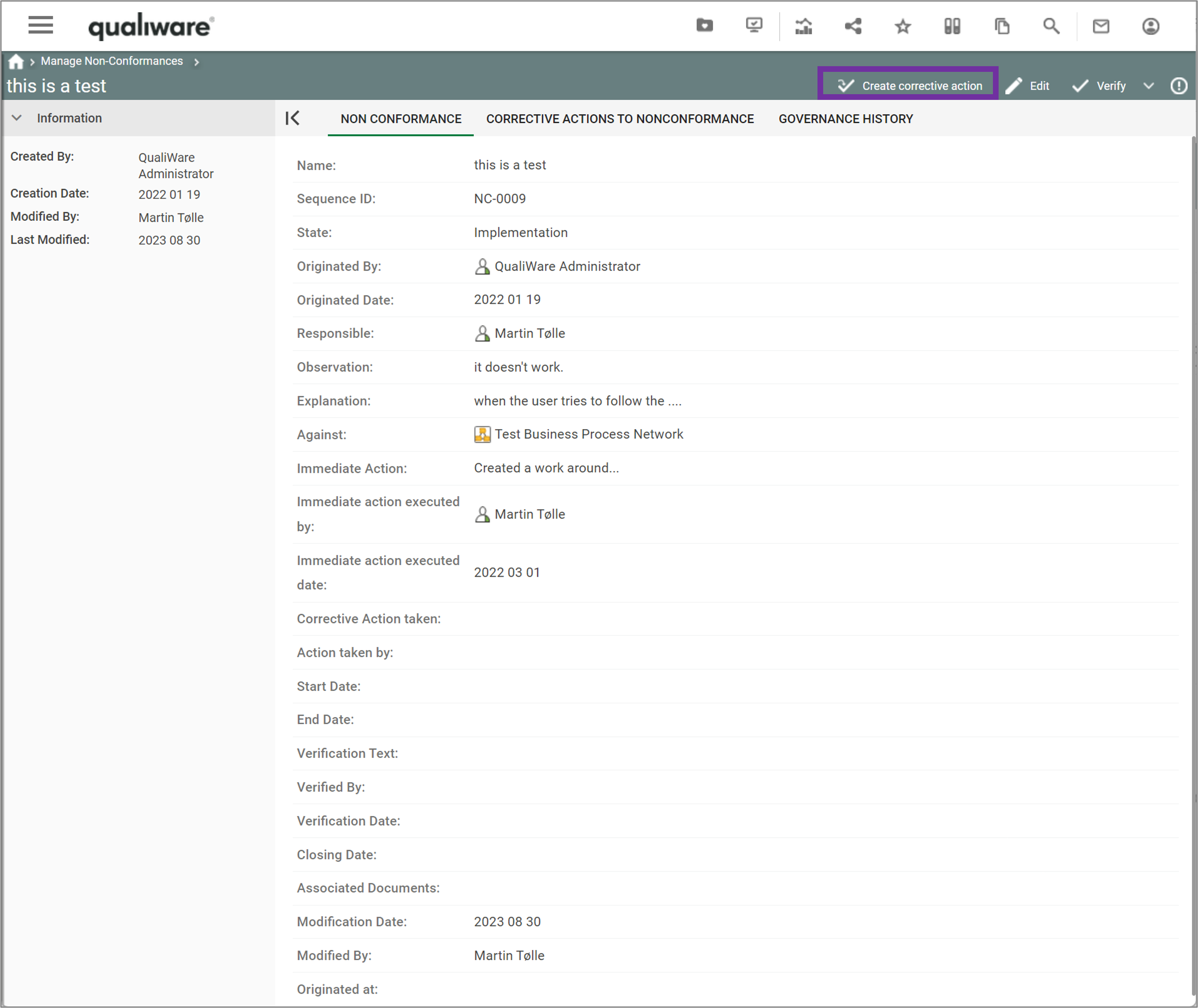
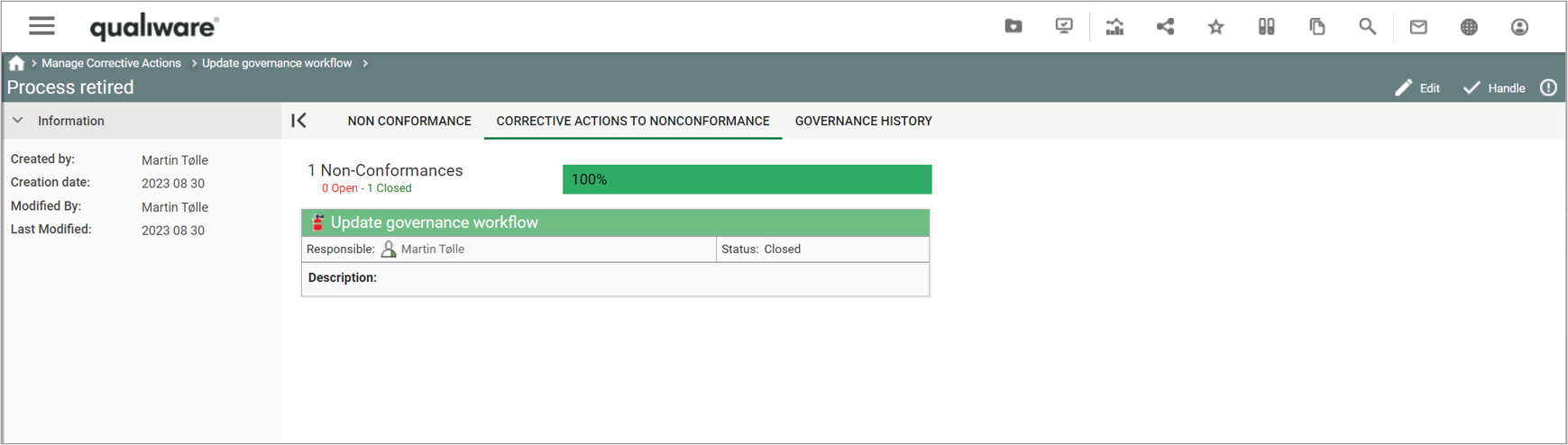


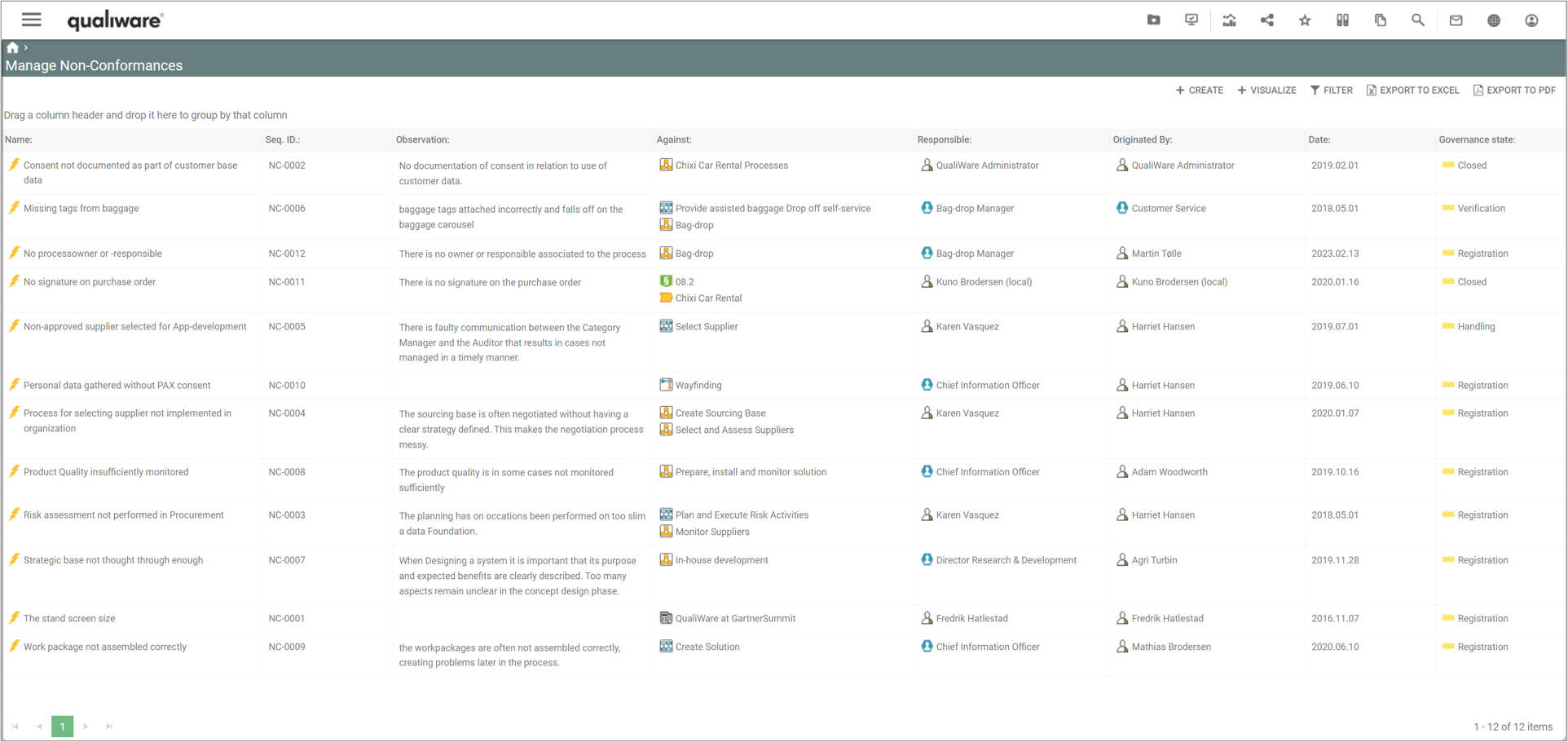
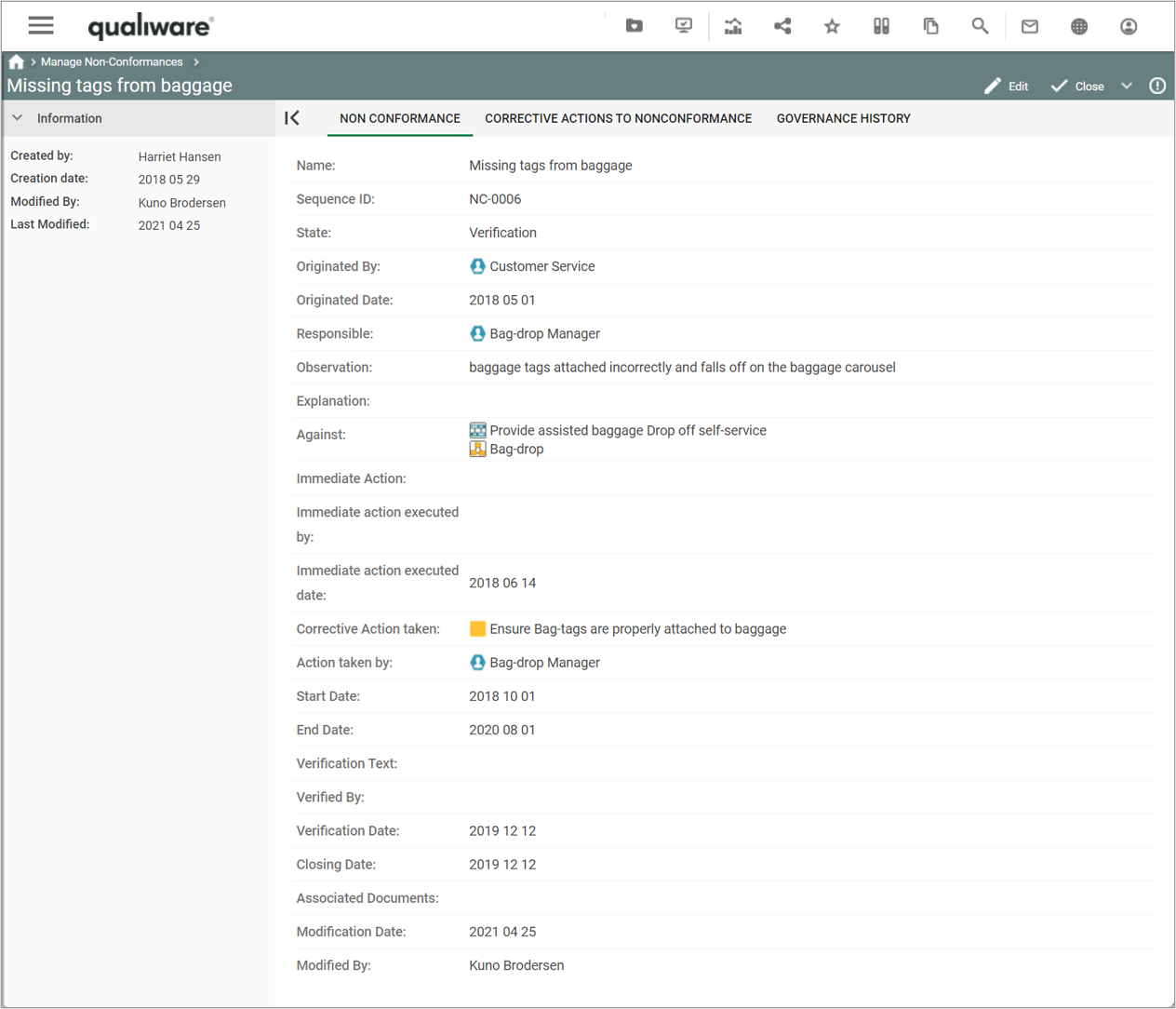
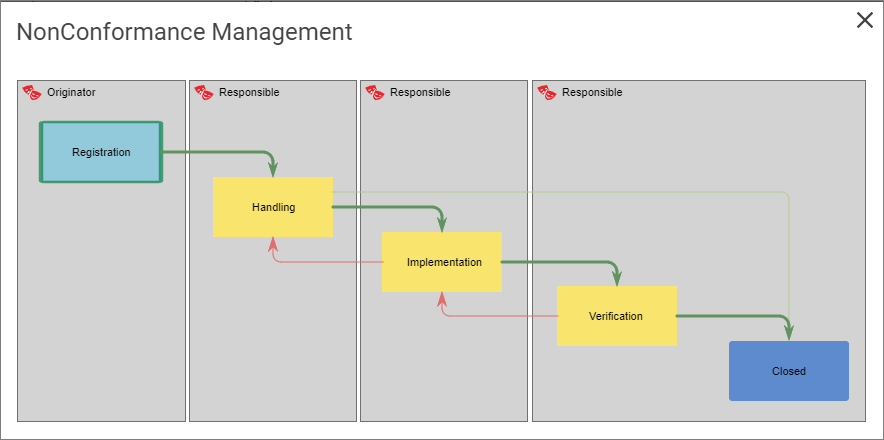
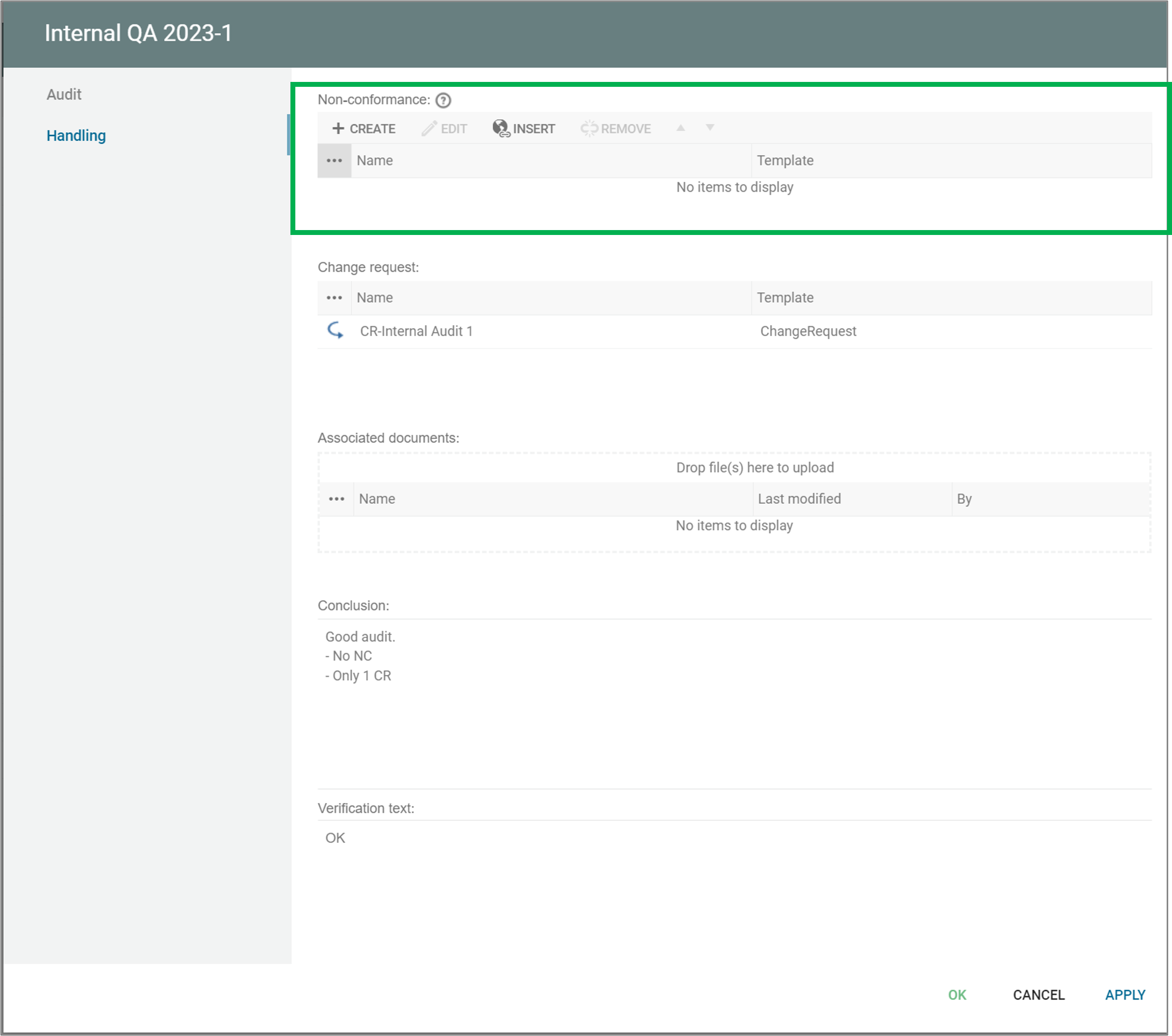
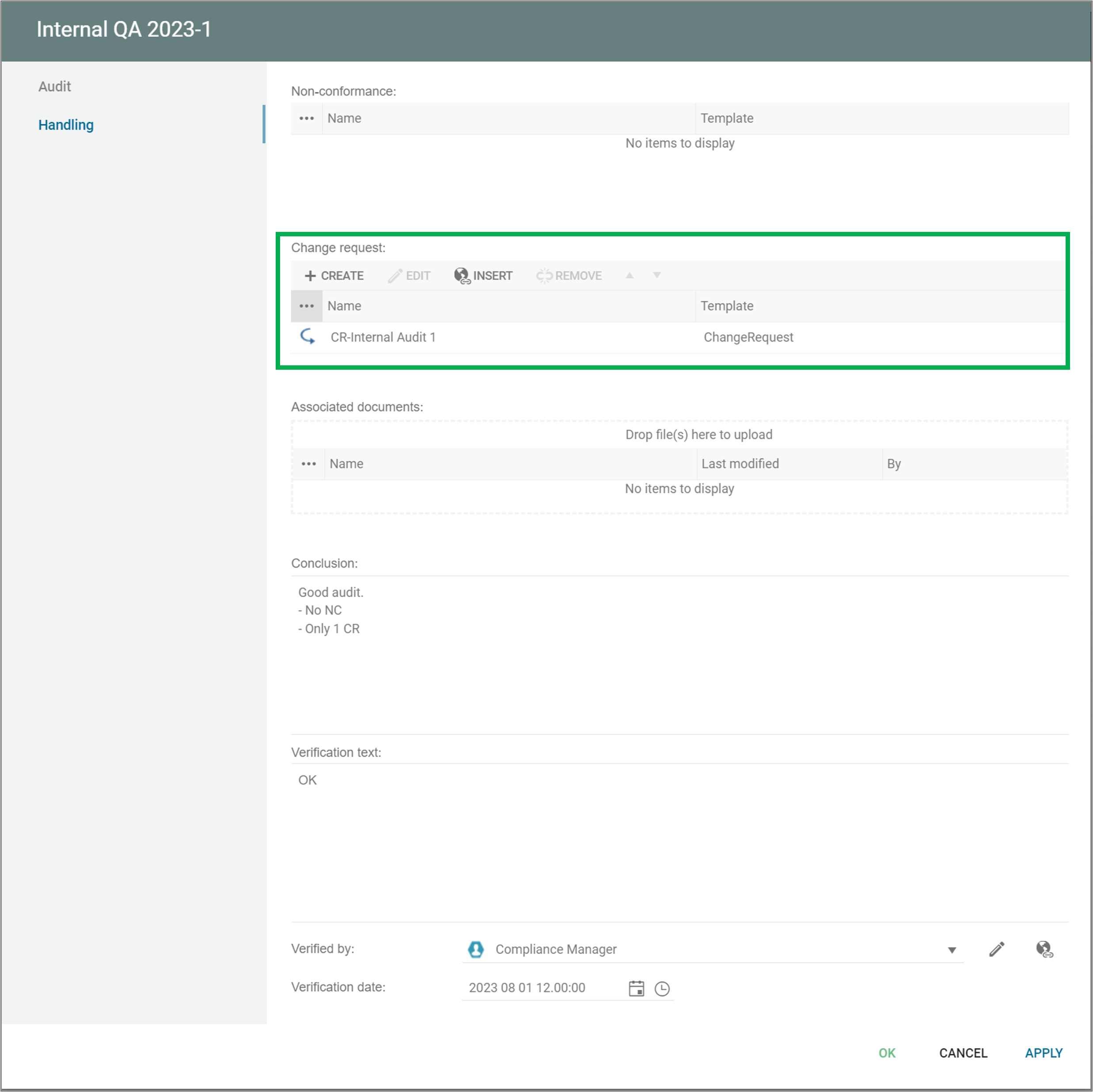
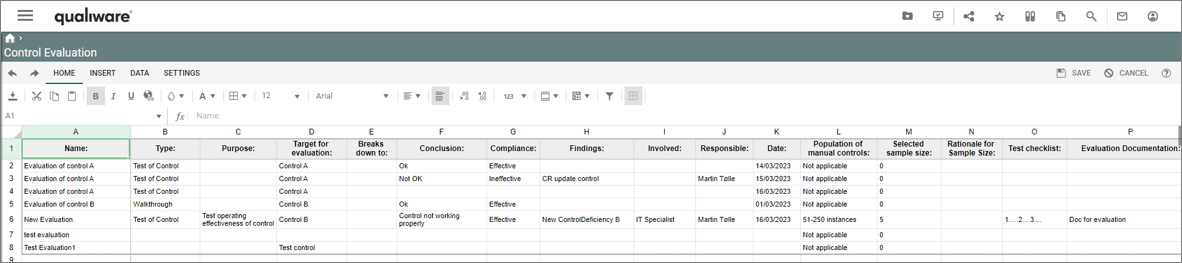
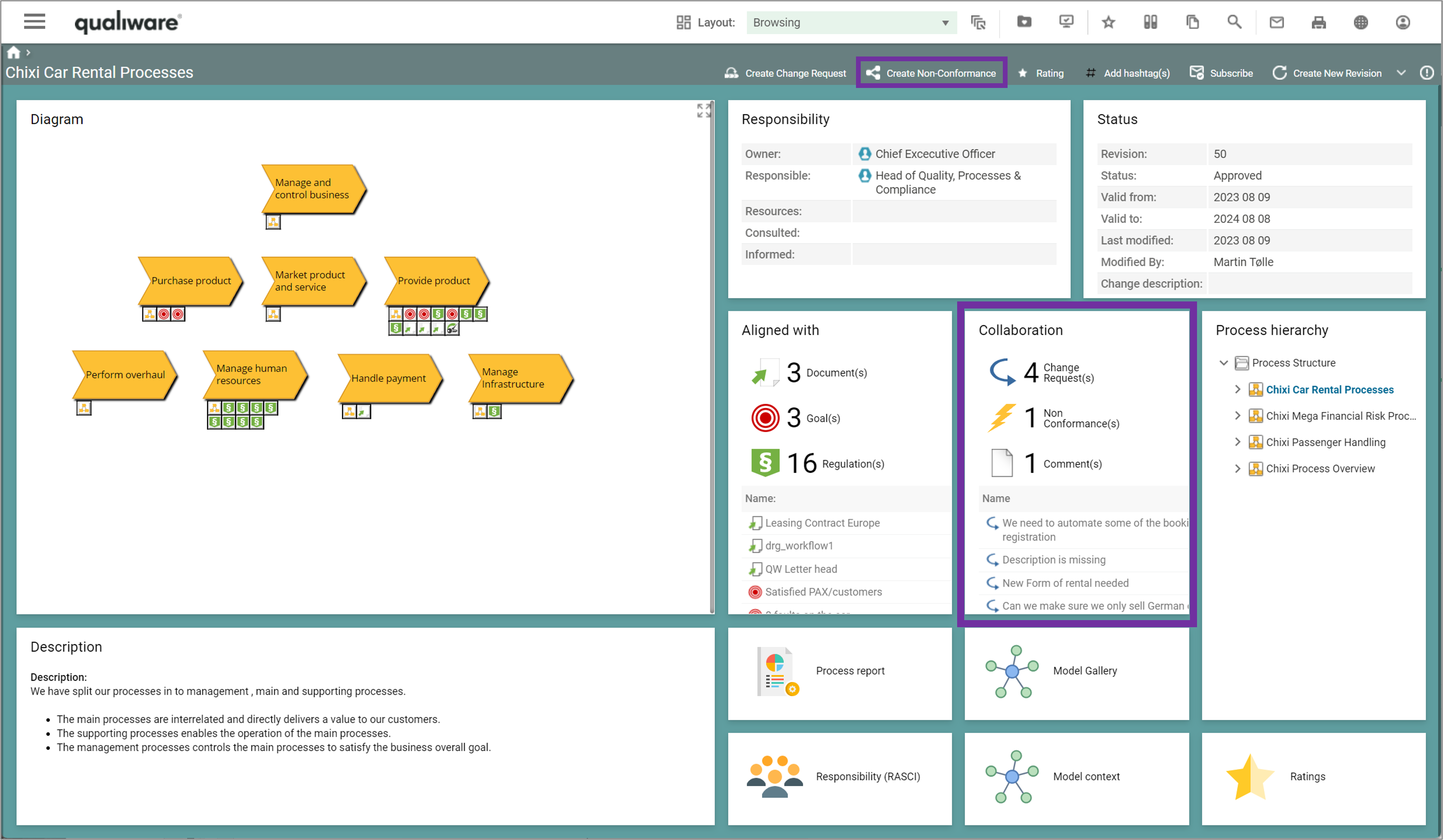 You can add/insert a non-conformance from an audit.
You can add/insert a non-conformance from an audit.